Many mammals control their body temperature by sweating. Which property of water is most directly responsible for the ability of sweat to lower body temperature?
- Water's change in density when it condenses.
- Water's ability to dissolve molecules in the air.
- Water's high surface tension.
- The release of heat by the formation of hydrogen bonds.
- The absorption of heat by the breaking of hydrogen bonds.
The absorption of heat by the breaking of hydrogen bonds.
Ex.
The property of water that is most directly responsible for the ability to sweat to lower temperatures by mammals is the absorption of heat by the breaking of hydrogen bonds.
This is explained by the definition of the "heat of vaporization" which is the quantity of heat a liquid must absorb for 1 g of it to be converted from the liquid to the gaseous state. As a liquid evaporates, the surface of the liquid that remains behind cools down. This evaporative cooling occurs because the "hottest" molecules, those with the greatest kinetic energy, are the most likely to leave as gas. Evaporation of sweat from human skin dissipates body heat and helps prevent overheating on a hot day or when excess heat is generated by strenuous activity. High humidity on a hot day increases discomfort because the high concentration of water vapor in the air inhibits the evaporation of sweat from the body. In order to convert liquid water to a gas hydrogen bonds must be broken a process that requires the absorption of heat. Therefore the process that allows mammals to sweat to lower temperatures requires the absorption of heat so that the liquid water can vaporize.
"Water's change in density when it condenses" is not correct because it does not break hydrogen bonds but remains a liquid until it becomes a solid when it freezes.
"Water's ability to dissolve molecules in the air" is not correct because the definition of a solution requires that a there is a liquid that is a completely homogeneous mixture of two or more substances is called a solution. The dissolving agent of a solution is the solvent, and the substance that is dissolved is the solute. In this case, water is the solvent and sugar is the solute. An aqueous solution is one in which water is the solvent.
"The release of heat by the formation of hydrogen bonds" is not correct. Hydrogen bonds form when molecules of any liquid stay close together because they are attracted to one another. Molecules moving fast enough to overcome these attractions can depart the liquid and enter the air as a gas. This transformation from a liquid to a gas is called vaporization, or evaporation. Therefore the release of heat is the opposite of evaporative cooling.
"Water's high surface tension" is not correct because surface tension is related to cohesion, which is a measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid.
The absorption of human-generated CO2 by the oceans __________.
- reduces the carbonate ion concentration in the oceans and threatens calcifying organisms in marine ecosystems
- All of the listed responses are correct.
- increases the oceans' acidity and lowers pH
- increases the hydrogen ion concentration in the oceans but decreases the carbonate ion concentration and threatens the livability of the oceans for calcifying organisms
- increases the oceanic concentration of carbonic acid
All of the listed responses are correct.
Ex.
All of the listed responses are correct.
The absorption of human-generated CO2 by the oceans increases the oceanic concentration of carbonic acid because it reacts with water to form carbonic acid, it increases the oceans' acidity and lowers the pH of seawater, reduces the carbonate ion concentration in the oceans and threatens calcifying organisms in marine ecosystems because the absorption of CO2 by the oceans leads to a decrease in the carbonate ion concentration, which is required for calcification, the production of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) by many marine organisms, and increases the hydrogen ion concentration in the oceans but decreases the carbonate ion concentration and threatens the livability of the oceans for calcifying organisms. The absorption of CO2 by the oceans causes an increase in the carbonic acid, and hydrogen ion concentration (lower pH). The extra hydrogen ions bind with the carbonate ion to form bicarbonate. This reduces the amount of carbonate ions available for calcification, the production of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) by many marine organisms, including reef-building corals and animals that build shells. The absorption of CO2 by the oceans causes an increase in the carbonic acid, and hydrogen ion concentration (lower pH). The extra hydrogen ions bind with the carbonate ion to form bicarbonate. This reduces the amount of carbonate ions available for calcification, the production of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) by many marine organisms, including reef-building corals and animals that build shells
You can fill a glass of water to just slightly above the rim without it spilling over the glass. What property of water best explains this phenomenon?
- Adhesion
- Its polarity
- None of the listed responses is correct.
- Evaporative cooling
- Surface tension
Surface tension
Ex.
You can fill a glass of water to just slightly above the rim without it spilling over the glass. The property of water best explains this phenomenon is surface tension.
Surface tension is a measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid. Water has a greater surface tension than most other liquids. At the interface between water and air is an ordered arrangement of water molecules, hydrogen-bonded to one another and to the water below. This makes the water behave as though coated with an invisible film. You can observe the surface tension of water by slightly overfilling a drinking glass; the water will stand above the rim. In a more biological example, some animals can stand, walk, or run on water without breaking the surface. This is the correct answer.
"Adhesion" is incorrect because this is the attraction of unlike substances.
"Its polarity" is incorrect because although the property that is responsible for this phenomenon is a result of the polarity of water molecules, is a better answer.
“Evaporative cooling" is not correct because evaporative cooling is the cooling of a liquid's surface as some of the liquid evaporates.
A mole of methanol (CH3OH) weighs 32 g. The number of grams of methanol that are needed to produce 1 L of a 1 millimolar solution is __________.
- 64 g
- 3.2 g
- 0.0032 g
- 0.032 g
- 0.32 g
0.032 g
Ex.
A mole of methanol (CH3OH) weighs 32 g. The number of grams of methanol that are needed to produce 1 L of a 1 millimolar solution is 0.032 g.
In order to solve this problem, convert 1 millimolar to molar units. A millimolar unit is a unit of 1/1,000 molar units. Since we have 1/1,000 molar units, this gives us the decimal 0.001. To calculate the amount of grams needed for this solution, multiply 46 g × 0.001 = 0.032 g.
“64 g” is not the correct answer because this would give us a 2 M or (2,000 mM) solution, not a 0.002 M or (2 mM) solution.
“3.2 g” is not the correct answer because this would give us a 0.2 M or (200 mM) solution, not a 0.002 M or (2 mM) solution.
“0.32 g” is not the correct answer because this would give us a 0.02 M or (20 mM) solution, not a 0.002 M or (2 mM) solution.
“0.0032 g” is not the correct answer because this would give us a 0.0002 M or (0.2 mM) solution, not a 0.002 M or (2 mM) solution.
Nonpolar molecules that cluster away from water molecules are called __________ molecules.
- saponified
- hydrophobic
- hydrophilic
- ionic
- None of the listed responses is correct.
hydrophobic
Ex.
Nonpolar molecules that cluster away from water molecules are called hydrophobic molecules.
Substances that are nonionic and nonpolar repel water. There are, of course, substances that do not have an affinity for water. Substances that are nonionic and nonpolar (or otherwise cannot form hydrogen bonds) actually seem to repel water; these substances are said to be hydrophobic (from the Greek phobos, fearing). An example from the kitchen is vegetable oil, which, as you know, does not mix stably with water-based substances such as vinegar. The hydrophobic behavior of the oil molecules results from a prevalence of relatively nonpolar covalent bonds, in this case bonds between carbon and hydrogen, which share electrons almost equally. Hydrophobic molecules related to oils are major ingredients of cell membranes.
"Ionic" is not the correct because ions are attracted to water.
"Hydrophilic" is not the correct because the suffix "-philic" means "loving." Hydrophilic substances have an affinity for water.
"Saponified" is not the correct because when something is saponified, it is converted into soap.
The amount of heat required to convert 1 g of any substance from the liquid to the gaseous state is defined as __________.
- the specific heat of that substance
- molecular cohesion
- the heat of fusion of that substance
- 1 calorie
- the heat of vaporization of that substance
the heat of vaporization of that substance
Ex.
The amount of heat required to convert 1 g of any substance from the liquid to the gaseous state is defined as the heat of vaporization of that substance.
Heat of vaporization is the quantity of heat a liquid must absorb for 1 g of it to be converted from the liquid to the gaseous state.
“The specific heat of that substance" is not the correct because the specific heat of a substance is defined as the amount of heat required to change the temperature of 1 g of that substance by 1°C.
"1 calorie" is not the correct because this applies specifically to water and is the amount of energy it takes to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1°C.
"The heat of fusion of that substance" is not the correct because the heat of fusion is the heat required to convert a solid into a liquid with no temperature change.
"Molecular cohesion" is not the correct because this refers to the tendency of like substances to stick together, not to an amount of energy.
An acid is __________.
- a material that resists changes in the pH of a solution
- any compound that accepts hydrogen ions
- a compound that donates hydrogen ions to a solution
- any compound with a pH
- a solution with a pH between 7 and 14
a compound that donates hydrogen ions to a solution
Ex.
An acid is a compound that donates hydrogen ions to a solution.
When acids dissolve in water, they donate additional H+ to the solution. An acid is a substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution. For example, when hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to water, hydrogen ions dissociate from chloride ions: HCl → H+ + Cl-. This source of H+ (dissociation of water is the other source) results in an acidic solution—one having more H+ than OH-.
"Any compound with a pH" is incorrect because pH can be measured in all liquids.
"Any compound that accepts hydrogen ions" is incorrect because a base accepts hydrogen ions. Some bases reduce the H+ concentration directly by accepting hydrogen ions.
"A material that resists changes in the pH of a solution" is incorrect because a buffer resists pH changes.
"A solution with a pH between 7 and 14" is incorrect because acid solutions have a pH between 0 and 7.
Hydrophilic molecules __________.
- are uncharged, nonionic substances that repel water
- are nonionic molecules that are attracted to the nonpolar portion of the water molecule
- are polar molecules that are attracted to the nonpolar portion of the water molecule
- never have a partial charge at one end of the molecule
- are charged molecules that are attracted to the partial charge of the water molecule
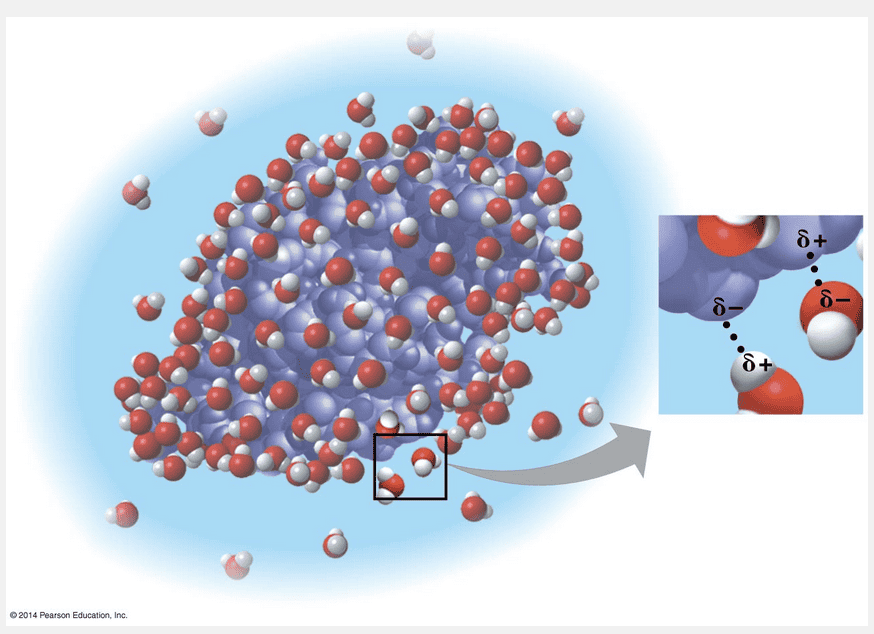
are charged molecules that are attracted to the partial charge of the water molecule
Ex.
Hydrophilic molecules are charged molecules that are attracted to the partial charge of the water molecule.
Any substance that has an affinity for water is said to be hydrophilic (from the Greek hydro, water, and philos, loving). In some cases, substances can be hydrophilic without actually dissolving. For example, some molecules in cells are so large that they do not dissolve. Another example of a hydrophilic substance that does not dissolve is cotton, a plant product. Cotton consists of giant molecules of cellulose, a compound with numerous regions of partial positive and partial negative charges that can form hydrogen bonds with water. Water adheres to the cellulose fibers. Thus, a cotton towel does a great job of drying the body, yet it does not dissolve in the washing machine. Cellulose is also present in the walls of water-conducting cells in a plant; the adhesion of water to these hydrophilic walls helps water move up the plant against gravity.
“Are polar molecules that are attracted to the nonpolar portion of the water molecule” is incorrect because the water molecule is polar and charged.
“Are uncharged, nonionic substances that repel water” is incorrect because this describes hydrophobic molecules.
“Are nonionic molecules that are attracted to the nonpolar portion of the water molecule” is incorrect because hydrophilic molecules are charged and interact with the polar water molecule.
“Never have a partial charge at one end of the molecule” is incorrect because in order for a hydrophilic molecule to interact with water, it must have a charge.
Adding a base tends to __________ of a solution.
- increase the hydrogen ion concentration and increase the pH
- lower the hydrogen ion concentration and lower the pH
- lower the hydrogen ion concentration and increase the pH
- increase the hydrogen ion concentration and lower the pH
- lower the hydroxide ion concentration and lower the pH
lower the hydrogen ion concentration and increase the pH
Ex.
Adding a base tends to lower the hydrogen ion concentration and increase the pH of a solution.
A substance that reduces the hydrogen ion concentration is a base. Reducing the hydrogen ion concentration increases the pH. Some bases reduce the H+ concentration directly by accepting hydrogen ions. Ammonia (NH3), for instance, acts as a base when the unshared electron pair in nitrogen’s valence shell attracts a hydrogen ion from the solution, resulting in an ammonium ion (NH4 +): NH3 + + H+ NH4+.
"Lower the hydrogen ion concentration and lower the pH" is incorrect because a lower pH means a higher hydrogen ion concentration.
"Increase the hydrogen ion concentration and lower the pH" is incorrect because this describes the result of adding an acid.
"Increase the hydrogen ion concentration and increase the pH" is incorrect because a higher pH means a lower hydrogen ion concentration.
"Lower the hydroxide ion concentration and lower the pH" is incorrect because an acid would lower the pH of a solution.
A substance that reduces the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution is __________.
- None of the listed responses is correct.
- a buffer
- an acid
- neutral
- a base
a base
Ex.
A substance that reduces the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution is called a base.
When bases dissolve in water, they donate additional OH+ to the solution, thereby increasing the hydroxyl ion concentration of a solution. For example, when sodium (NaOH) is added to water, hydroxyl ions dissociate from sodium ions: NaOH Na+ + OH– . This source of OH– (dissociation of water is the other source) results in an alkaline or basic solution—one having more OH– than H+.
“An acid” is incorrect because these are substances that increase the concentration of H+ in a solution.
“A buffer” is incorrect because buffers are substances that minimize changes in the concentration of H+ and OH– in a solution.
“Neutral” is incorrect because neutral substances have an equal concentration of H+ and OH– in a solution.
The specific heat of a substance is __________.
- the amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1 g of that substance to change its temperature by 1°C
- always the same as the mass of the liquid
- 1 calorie
- equivalent to the heat of vaporization
- 1 kilocalorie
the amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1 g of that substance to change its temperature by 1°C
Ex.
The specific heat of a substance is defined as the amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1 g of that substance to change its temperature by 1°C . The ability of water to stabilize temperature stems from its relatively high specific heat.
“1 calorie” is not the correct answer because this answer applies specifically to water and is the amount of energy it takes to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1°C.
“1 kilocalorie” is not the correct answer because this answer applies specifically to water and is the amount of energy it takes to raise the temperature of 1,000 g of water by 1°C.
“Always the same as the mass of the liquid” and “equivalent to the heat of vaporization” are incorrect because the specific heat is the amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1 g of that substance to change its temperature by 1°C.
Water moves up a plant because of hydrogen bonds by a process called __________.
- covalent interactions
- adhesion
- surface tension
- cohesion
- cohesion and adhesion
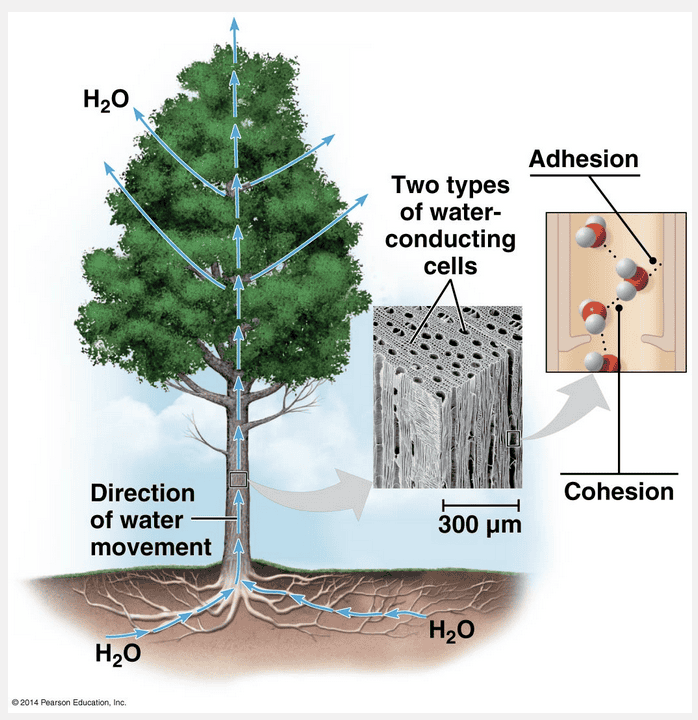
cohesion and adhesion
Ex.
Water moves up a plant because of hydrogen bonds by a process called cohesion and adhesion.
The hydrogen bonds hold the substance together, a phenomenon called cohesion. Cohesion due to hydrogen bonding contributes to the transport of water and dissolved nutrients against gravity in plants. Water from the roots reaches the leaves through a network of water-conducting cells. As water evaporates from a leaf, hydrogen bonds cause water molecules leaving the veins to tug on molecules farther down, and the upward pull is transmitted through the water-conducting cells all the way to the roots. Adhesion, the clinging of one substance to another, also plays a role. Adhesion of water by hydrogen bonds to the molecules of cell walls helps counter the downward pull of gravity.
“Adhesion” and “cohesion” are incorrect because both processes are involved in moving water up a tree.
“Surface tension” is incorrect because it is a measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid.
“Covalent interactions” is incorrect because they are shared interactions between valence electrons of two atoms.
The phenomenon responsible for maintaining the upward movement of water through a vessel is __________.
- evaporation
- heat of vaporization
- cohesion
- surface tension
- adhesion
cohesion
Ex.
The phenomenon responsible for maintaining the upward movement of water through a vessel is cohesion.
Water molecules stay close to each other as a result of hydrogen bonding. Although the arrangement of molecules in a sample of liquid water is constantly changing, at any given moment many of the molecules are linked by multiple hydrogen bonds. These linkages make water more structured than most other liquids. Collectively, the hydrogen bonds hold the substance together, a phenomenon called cohesion. This is the correct answer.
"Adhesion" is not correct because adhesion describes the attraction of different types of molecules to one another.
"Surface tension" is not correct because even though surface tension is related to the correct phenomenon. Surface tension is a measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid.
“Evaporation" is not correct because evaporation is the transformation from a liquid to a gas.
“Heat of vaporization" is not correct because heat of vaporization is the quantity of heat a liquid must absorb for 1 g of it to be converted from the liquid to the gaseous state.
When the pH of a solution shifts from 3 to 7, the hydrogen ion concentration has changed, and __________.
- it has increased by 10,000 times
- it has decreased by 4 times
- it has decreased by 10,000 times
- It has not changed.
- it has increased by 4 times
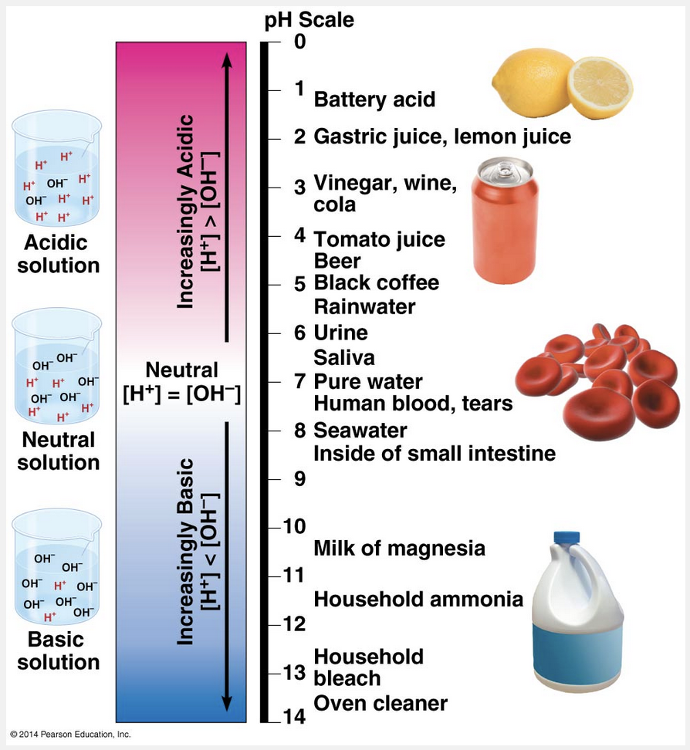
it has decreased by 10,000 times
Ex.
When the pH of a solution shifts from 3 to 7, the hydrogen ion concentration has changed, and it has decreased by 10,000 times. The pH scale compresses the range of H+ and OH– concentrations by employing logarithms.
The pH of a solution is defined as the negative logarithm (base 10) of the hydrogen ion concentration: pH log [H+]. For a neutral aqueous solution, [H+] is 10–7 M, giving us log 10–7 = –(–7) = 7. Notice that pH declines as H+ concentration increases. Remember that each pH unit represents a tenfold difference in H+ and OH– concentrations. It is this mathematical feature that makes the pH scale so compact. A solution of pH 3 is not twice as acidic as a solution of pH 6, but a thousand times (10 × 10 × 10) more acidic. Because the pH number is the negative log of the hydrogen ion concentration, a change from a pH of 7 to a pH of 3 increases the hydrogen ion concentration by 10,000 times (7 – 3 = 4; [10 × 10 × 10 × 10] 104 = 10,000).
“It has increased by 4 times” is incorrect because the pH scale is a base-10 logarithmic scale. Each unit represents a tenfold increase or decrease in the hydrogen ion concentration.
“It has decreased by 4 times” is incorrect because the pH scale is a base-10 logarithmic scale. Each unit represents a tenfold increase or decrease in the hydrogen ion concentration.
“It has increased by 10,000 times” is incorrect because the pH is shifting to the basic range, and therefore the H+ is decreasing.
“It has not changed” is incorrect because the pH changes with changes in hydrogen ion concentration.
Glucose has a molecular mass of 180 daltons. To make a 2-molar (2 M) solution of glucose, __________.
- stir 360 g of glucose in water to dissolve the sugar, and then add enough water to bring the total volume of the solution up to 2 L
- stir 360 g of glucose in water to dissolve the sugar, and then add enough water to bring the total volume of the solution up to 0.5 L
- stir 360 g of glucose in water to dissolve the sugar, and then add enough water to bring the total volume of the solution up to 1 L
- stir 180 g of glucose in water to dissolve the sugar, and then add enough water to bring the total volume of the solution up to 1 L
- stir 90 g of glucose in water to dissolve the sugar, and then add enough water to bring the total volume of the solution up to 2 L
stir 360 g of glucose in water to dissolve the sugar, and then add enough water to bring the total volume of the solution up to 1 L
Ex.
Glucose has a molecular mass of 180 daltons. To make a 2-molar (2 M) solution of glucose, stir 360 g of glucose in water to dissolve the sugar, and then add enough water to bring the total volume of the solution up to 1 L.
If we wanted to make a liter (L) of solution consisting of 1 mol of glucose dissolved in water, we would measure out 180 g of glucose and then gradually add water, while stirring, until the sugar was completely dissolved. We would then add enough water to bring the total volume of the solution up to 1 L. At that point, we would have a 1-molar (1 M) solution of glucose. In this problem we want a 2 M solution. That means that we must double the amount of grams that we weigh out and measure out 360 g of glucose and then gradually bring the total volume of the solution up to 1 L.
“Stir 180 g of glucose in water to dissolve the sugar, and then add enough water to bring the total volume of the solution to 1 L” is incorrect because this is a 1 M solution and we want a 2 M solution.
“Stir 360 g of glucose in water to dissolve the sugar, and then add enough water to bring the total volume of the solution up to 2 L” is incorrect because this is a 1 M solution and we want a 2 M solution.
“Stir 360 g of glucose in water to dissolve the sugar, and then add enough water to bring the total volume of the solution up to 0.5 L” is incorrect because this is a 4 M solution and we want a 2 M solution.
“Stir 90 g of glucose in water to dissolve the sugar, and then add enough water to bring the total volume of the solution up to 2 L” is incorrect because this is a 0.5 M solution and we want a 2 M solution.
When ice forms, the __________ are farther apart than in liquid water, allowing the ice to form an organized crystal structure and float.
- adhesive interactions
- ionic bonds
- All of the listed responses are correct.
- partial charges on the oxygen and hydrogen
- hydrogen bonds
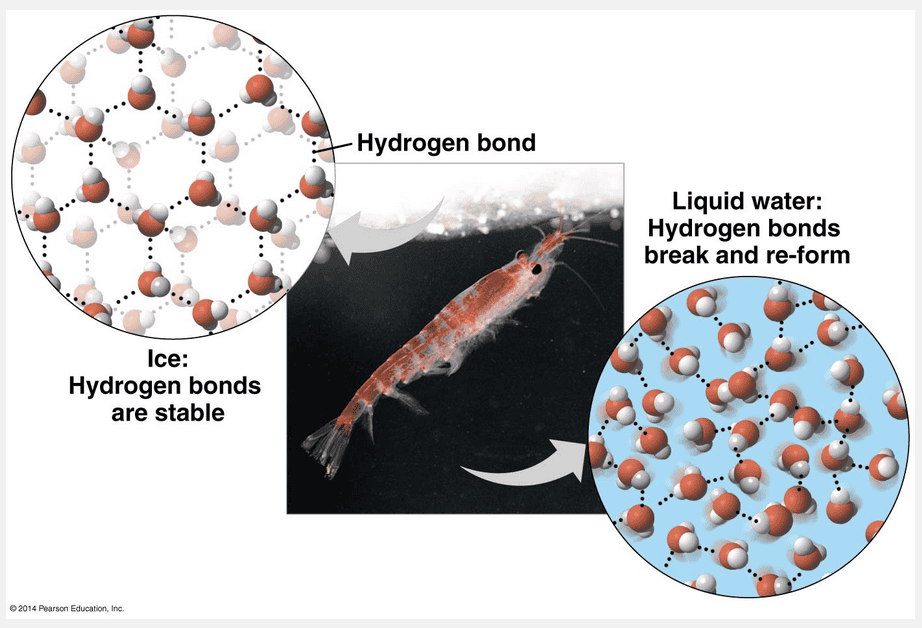
hydrogen bonds
Ex.
When ice forms, the hydrogen bonds are farther apart than in liquid water, allowing the ice to form an organized crystal structure and float.
At 0°C, the molecules become locked into a crystalline lattice, each water molecule hydrogen-bonded to four partners. The hydrogen bonds keep the molecules at “arm’s length,” far enough apart to make ice about 10% less dense (10% fewer molecules for the same volume) than liquid water at 4°C. When ice absorbs enough heat for its temperature to rise above 0°C, hydrogen bonds between molecules are disrupted. The ability of ice to float due to its lower density is an important factor in the suitability of the environment for life. If ice sank, then eventually all ponds, lakes, and even oceans would freeze solid, making life as we know it impossible on Earth.
“Ionic bonds” is incorrect because these are chemical bonds that result from the attraction between oppositely charged ions.
“Adhesive interactions” is incorrect because this is the clinging of one substance to another, such as water to plant cell walls by means of hydrogen bonds.
“Partial charges on the oxygen and hydrogen” is incorrect because the partial charges on the oxygen and hydrogen of the water molecule make the molecule polar.
Adhesion is best described as __________.
- None of the listed responses is correct.
- a property of water that helps moderate Earth's temperature
- the clinging of one substance to another substance
- the process by which a crystalline lattice forms
- the process that contributes to the transport of water and dissolved nutrients in plants by causing water molecules to tug on other water molecules
the clinging of one substance to another substance
Ex.
Adhesion is best described as the clinging of one substance to another substance.
Adhesion is the attraction of one substance to another. Water transport in plants is aided by the adhesion of the water to cell walls by hydrogen bonds. This helps resist the downward pull of gravity. This is the correct answer.
"A property of water that helps moderate Earth's temperature" is not the correct answer because this describes water's high heat of vaporization.
"The process by which a crystalline lattice forms" is not the correct answer because a crystalline lattice forms when temperatures 0°C and water freezes.
"The process that contributes to the transport of water and dissolved nutrients in plants by causing water molecules to tug on other water molecules" is not correct because this answer refers to cohesion.
The ability of water molecules to form hydrogen bonds with other water molecules and water's ability to dissolve substances that have charges or partial charges are __________.
- both caused by water's partial charges
- both due to water's low molecular mass
- due to water's partial charges and low molecular mass, respectively
- both caused by water's two electron shells
- both caused by water's ability to form covalent bonds with hydrophobic substances
both caused by water's partial charges
Ex.
The ability of water molecules to form hydrogen bonds with other water molecules and water's ability to dissolve substances that have charges or partial charges are both caused by water's partial charges.
Two molecules of water are held together by a hydrogen bond formed between the slight positive charge of the hydrogen and the slight negative charge of the oxygen. Water is a very versatile solvent, a quality traced to the polarity of the water molecule. This is the correct answer.
The statement "both caused by water's ability to form covalent bonds with hydrophobic substances" is incorrect because water does not form covalent bonds with hydrophobic substances.
"Due to water's partial charges and low molecular mass, respectively" is incorrect because although water's partial charges is correct, have a low molecular mass is incorrect. Both parts of the answer must be correct when choosing an answer that has multiple parts.
The statement "both caused by water's two electron shells" is incorrect because electrons shells are properties of atoms and not properties of molecules.
Finally, "both due to water's low molecular mass" is incorrect because neither property of water can be attributed to its molecular mass.
__________ is an emergent property of water that allows insects like the raft spider to walk on water.
- The heat of vaporization
- Adhesion
- All of the listed responses are correct.
- Surface tension
- Kinetic energy
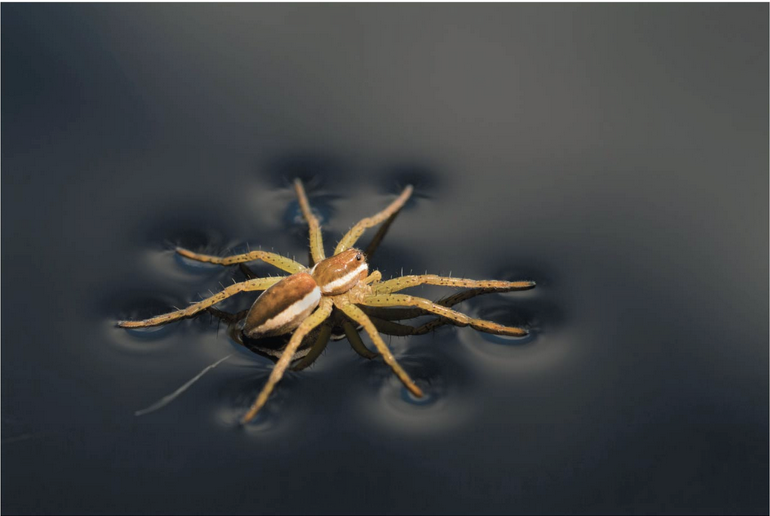

Surface tension
Ex.
Surface tension is an emergent property of water that allows insects like the raft spider to walk on water.
Surface tension is related to cohesion, a measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid. At the interface between water and air is an ordered arrangement of water molecules, hydrogen-bonded to one another and to the water below. This gives water an unusually high surface tension, making it behave as though it were coated with an invisible film. You can observe the surface tension of water by slightly overfilling a drinking glass; the water will stand above the rim. The spider pictured here takes advantage of the surface tension of water to walk across a pond without breaking the surface.
“Kinetic energy” is incorrect because it is energy of motion.
“Adhesion” is incorrect because it is the clinging of one substance to another.
“Heat of vaporization” is incorrect because it is the quantity of heat a liquid must absorb for 1 g (gram) of it to be converted from the liquid to the gaseous state.
Hydrophobic molecules __________.
- are polar molecules that are attracted to the nonpolar portion of the water molecule
- always have a partial charge at one end of the molecule
- are uncharged, nonionic substances that seem to repel water
- are nonionic molecules that are attracted to the nonpolar portion of the water molecule
- are ionic molecules that are attracted to the polar portion of the water molecule
are uncharged, nonionic substances that seem to repel water
Ex.
Hydrophobic molecules are uncharged, nonionic substances that seem to repel water.
Hydrophobic substances do not have an affinity for water. Substances that are nonionic and nonpolar (or otherwise cannot form hydrogen bonds) actually seem to repel water; these substances are said to be hydrophobic (from the Greek phobos, fearing). An example from the kitchen is vegetable oil, which, as you know, does not mix stably with water-based substances such as vinegar. The hydrophobic behavior of the oil molecules results from a prevalence of relatively nonpolar covalent bonds, in this case bonds between carbon and hydrogen, which share electrons almost equally. Hydrophobic molecules related to oils are major ingredients of cell membranes.
“Are polar molecules that are attracted to the nonpolar portion of the water molecule” is incorrect because hydrophobic molecules are nonionic, uncharged molecules, and water is a polar molecule.
“Are nonionic molecules that are attracted to the nonpolar portion of the water molecule” is incorrect because water molecules do not have nonpolar regions.
“Are ionic molecules that are attracted to the polar portion of the water molecule” is incorrect because hydrophobic molecules are not ionic and do not have a charge.
“Always have a partial charge at one end of the molecule” is incorrect because hydrophobic molecules are uncharged.
A compound that donates hydrogen ions to a solution is __________.
- an acid
- None of the listed responses is correct.
- neutral
- a base
- a buffer
an acid
Ex.
A compound that donates hydrogen ions to a solution is an acid.
When acids dissolve in water, they donate additional H+ to the solution. An acid is a substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution. For example, when hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to water, hydrogen ions dissociate from chloride ions: HCl → H+ + Cl–. This source of H+ (dissociation of water is the other source) results in an acidic solution—one having more H+ than OH–.
“A base” is incorrect because a base is a substance that reduces the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution.
“A buffer” is incorrect because it is a substance that minimizes changes in the concentrations of H+ and OH– in a solution.
“Neutral” is incorrect because a neutral solution has an equal number of H+ and OH– ions.
The amount of heat required to change the temperature of 1 g of any substance by one °C is defined as __________.
- 1 calorie
- the heat of vaporization of that substance
- molecular cohesion
- the specific heat of that substance
- 1 kilocalorie
the specific heat of that substance
Ex.
The amount of heat required to change the temperature of 1 g of any substance by one °C is defined as the specific heat of that substance.
The specific heat of a substance is defined as the amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1 g of that substance to change its temperature by 1°C. This is the correct answer.
"1 calorie" is not the correct answer because this answer applies specifically to water and is the amount of energy it takes to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1°C.
"The heat of vaporization of that substance" is not the correct because this is the amount of energy required to convert 1 g of a liquid to the gaseous state.
"1 kilocalorie" is not the correct because this answer applies specifically to water and is the amount of energy it takes to raise the temperature of 1,000 g of water by 1°C.
"Molecular cohesion" is not the correct because this refers to the tendency of like substances to stick together, not to an amount of energy.
Buffers are __________.
- substances that increase the concentration of H+ in a solution
- substances that increase the concentration of OH– in a solution
- substances that minimize changes in the concentration of H+ and OH– in a solution
- substances that decrease the concentration of H+ in a solution
- substances that decrease the concentration of OH– in a solution
substances that minimize changes in the concentration of H+ and OH– in a solution
Ex.
Buffers are substances that minimize changes in the concentration of H+ and OH– in a solution.
The presence of substances called buffers allows biological fluids to maintain a relatively constant pH despite the addition of acids or bases. Buffers do so by accepting hydrogen ions from the solution when they are in excess and donating hydrogen ions to the solution when they have been depleted. Most buffer solutions contain a weak acid and its corresponding base, which combine reversibly with hydrogen ions.
“Substances that increase the concentration of H+ in a solution,” “substances that decrease the concentration of H+ in a solution,” “substances that increase the concentration of OH– in a solution,” and “substances that decrease the concentration of OH– in a solution” are incorrect because buffers are substances that minimize changes in the concentration of H+ and OH– in a solution.
All of the following are hydrogen bonding properties except __________.
- partial charges on the oxygen and hydrogen
- nonpolar covalent bonding
- adhesion
- surface tension
- cohesion
nonpolar covalent bonding
Ex.
All of the following are hydrogen bonding properties except nonpolar covalent bonding.
Surface tension, adhesion, partial changes on the oxygen and hydrogen, and cohesion are hydrogen bonding properties, but nonpolar covalent bonding is not. Water’s polar nature is responsible for these properties. The extraordinary qualities of water are emergent properties resulting from hydrogen bonding.
The properties in question refer to the electrical attraction between something and a water molecule or between water molecules.
Urine, at pH 6, contains __________ H+ as household bleach, at pH 13.
- 10,000,000 times as much
- 1/7 times as much
- half as much
- 7 times as much
- 1/10,000,000 times as much
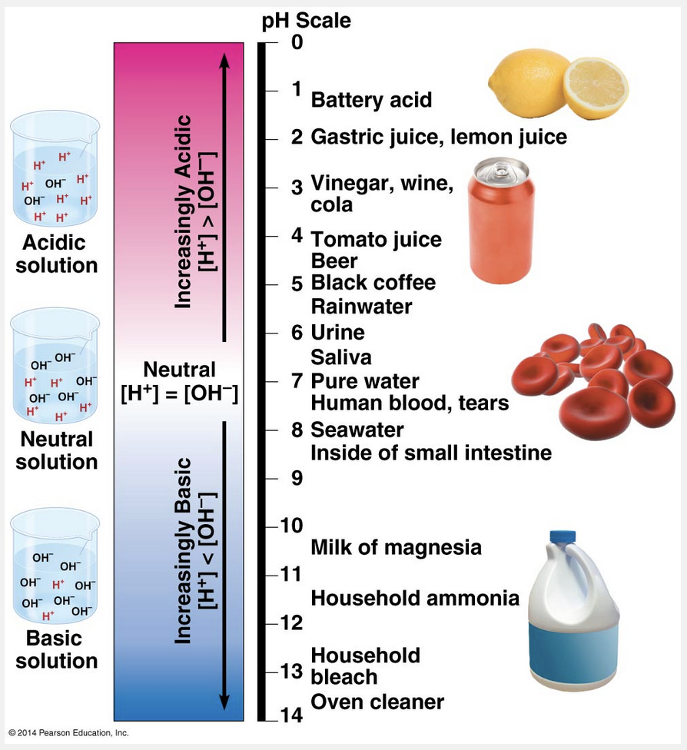
10,000,000 times as much
Ex.
Urine, at pH 6, contains 10,000,000 times as much H+ as household bleach, at pH 13.
The pH scale compresses the range of H+ and OH– concentrations by employing logarithms. The pH of a solution is defined as the negative logarithm (base 10) of the hydrogen ion concentration: pH log [H+]. For a neutral aqueous solution, [H+] is 10–7 M, giving us log 10–7 = –(–7) = 7. Notice that pH declines as H+ concentration increases. Remember that each pH unit represents a tenfold difference in H+ and OH– concentrations. It is this mathematical feature that makes the pH scale so compact. A solution of pH 3 is not twice as acidic as a solution of pH 6, but a thousand times (10 × 10 × 10) more acidic. When the pH of a solution changes slightly, the actual concentrations of H+ and OH– in the solution change substantially. Since the difference between pH 6 and pH 13 is “107,” urine is 10,000,000 times more acidic than household bleach.
“1/10,000,000 times as much” is incorrect because we are looking at the pH of urine (pH 6) compared to that of household bleach (pH 13) and not the pH of household bleach compared to that of urine.
“Half as much” is incorrect because the pH scale is a base-10 logarithmic scale. Each unit represents a tenfold increase or decrease in the hydrogen ion concentration.
“7 times as much” is incorrect because the pH scale is a base-10 logarithmic scale. Each unit represents a tenfold increase or decrease in the hydrogen ion concentration.
“1/7 times as much” is incorrect because the pH scale is a base-10 logarithmic scale. Each unit represents a tenfold increase or decrease in the hydrogen ion concentration.
Water is a polar molecule. This means that __________.
- All of the listed responses are correct.
- the opposite ends of the molecule have opposite electrical charges
- the atoms in water have equal electronegativities
- water is one of the many hydrophobic molecules
- water molecules are linear, like a pole
the opposite ends of the molecule have opposite electrical charges
Ex.
Water is a polar molecule. This means that the opposite ends of the molecule have opposite electrical charges.
Atoms in a molecule attract shared electrons to varying degrees, depending on the element. The attraction of a particular atom for the electrons of a covalent bond is called its electronegativity. The more electronegative an atom is, the more strongly it pulls shared electrons toward itself. Oxygen is one of the most electronegative of all the elements, attracting shared electrons much more strongly than hydrogen does. In a covalent bond between oxygen and hydrogen, the electrons spend more time near the oxygen nucleus than they do near the hydrogen nucleus. Because electrons have a negative charge and are pulled toward oxygen in a water molecule, the oxygen atom has a partial negative charge (indicated by the Greek letter δ with a minus sign, δ–, or “delta minus”), and each hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge (δ+, or “delta plus”). Because the oxygen atom in the water molecule is more electronegative than the hydrogen atoms the oxygen, the electrons of the bond are not shared equally. This type of bond is called a polar covalent bond.
"Water molecules are linear, like a pole" is not correct because the molecule is bent as shown in the Lewis dot structure.
"Water is one of the many hydrophobic molecules" is not correct. Hydrophobic molecules are substances that are nonionic and nonpolar (or otherwise cannot form hydrogen bonds) actually seem to repel water; these substances are said to be hydrophobic (from the Greek phobos, fearing). An example from the kitchen is vegetable oil.
"The atoms in water have equal electronegativites" is incorrect because oxygen is one of the most electronegative of all of the elements.
Sweating has a cooling effect because of water's high __________.
- density
- heat of vaporization
- buffering capacity
- surface tension
- specific heat
heat of vaporization
Ex.
Sweating has a cooling effect because of water's high heat of vaporization.
Water's high heat of vaporization results in evaporative cooling because when water evaporates, the surface of the water cools down. As a liquid evaporates, the surface of the liquid that remains behind cools down. This evaporative cooling occurs because the “hottest” molecules, those with the greatest kinetic energy, are the most likely to leave as gas. Evaporation of sweat from human skin dissipates body heat and helps prevent overheating on a hot day or when excess heat is generated by strenuous activity.
"Buffering capacity" is not the correct because buffers resist changes in pH but do not have an effect on water's cooling capacity.
"Surface tension" is not the correct because this relates to water's cohesion.
"Specific heat” is not the correct because the specific heat of a substance is defined as the amount of heat required to change the temperature of 1 g of that substance by 1°C.
"Density" is not the correct because water's density is not related to this property of water.
A solution at pH 10 contains __________ than the same amount of solution at pH 8.
- 2 times more H+
- 100 times more H+
- 4 times less H+
- 100 times less H+
- 2 times less H+

100 times less H+
Ex.
A solution at pH 10 contains 100 times less H+ than the same amount of solution at pH 8.
The pH scale compresses the range of H+ and OH– concentrations by employing logarithms. The pH of a solution is defined as the negative logarithm (base 10) of the hydrogen ion concentration: pH log [H+]. For a neutral aqueous solution, [H+] is 10–7 M, giving us log 10–7 = –(–7) = 7. Notice that pH declines as H+ concentration increases. Remember that each pH unit represents a tenfold difference in H+ and OH–concentrations. It is this mathematical feature that makes the pH scale so compact. A solution of pH 3 is not twice as acidic as a solution of pH 6, but a thousand times (10 × 10 × 10) more acidic. When the pH of a solution changes slightly, the actual concentrations of H+ and OH– in the solution change substantially. Since the difference between pH 10 and pH 8 is “10 × 10,” this pH 10 solution is 100 times more alkaline than the pH 8 solution.
“2 times more H+” is incorrect because the pH scale is a base-10 logarithmic scale. Each unit represents a tenfold increase or decrease in the hydrogen ion concentration.
“2 times less H+” is incorrect because the pH scale is a base-10 logarithmic scale. Each unit represents a tenfold increase or decrease in the hydrogen ion concentration.
“4 times less H+” is incorrect because the pH scale is a base-10 logarithmic scale. Each unit represents a tenfold increase or decrease in the hydrogen ion concentration.
“100 times more H+” is incorrect because the pH value is inversely related to the hydrogen ion concentration.
Water molecules have __________ than molecules of similar size, such as ammonia and methane, reflecting its capacity to absorb large amounts of heat.
- lower specific heat
- a lower capacity for forming hydrogen bonds
- less surface tension
- a higher boiling point
- a lower melting point
a higher boiling point
Ex.
Water molecules have a higher boiling point than molecules of similar size, such as ammonia and methane, reflecting its capacity to absorb large amounts of heat.
This is because more heat is needed to vaporize 1 g of water than most other liquids. Heat of vaporization is the quantity of heat a liquid must absorb for 1 g of it to be converted from the liquid to the gaseous state. To evaporate 1 g of water at 25°C, about 580 cal of heat is needed—nearly double the amount needed to vaporize a gram of alcohol or ammonia.
"Lower specific heat" is not the correct because to evaporate 1 g of water at 25°C, about 580 cal of heat is needed—nearly double the amount needed to vaporize a gram of alcohol or ammonia. Water’s high heat of vaporization is another emergent property resulting from the strength of its hydrogen bonds, which must be broken before the molecules can make their exodus from the liquid.
"A lower melting point" is not the correct because this is not an emergent property of water.
"A lower capacity for forming hydrogen bonds" is not the correct because water is a polar molecule and thus has a high capacity for forming hydrogen bonds.
"Less surface tension" is not the correct because water molecules are very cohesive.
The partial charges on a water molecule occur because of __________.
- widespread ionization
- covalent bonding
- the achievement of a stable configuration by one atom of a bond but not by the other partner
- the high electronegativity of hydrogen
- the unequal sharing of electrons between the hydrogen and the oxygen atoms of a water molecule
the unequal sharing of electrons between the hydrogen and the oxygen atoms of a water molecule
Ex.
The partial changes on a water molecule occur because of the unequal sharing of electrons between the hydrogen and oxygen atoms of the water molecule.
Atoms in a molecule attract shared electrons to varying degrees, depending on the element. The attraction of a particular atom for the electrons of a covalent bond is called its electronegativity. The more electronegative an atom is, the more strongly it pulls shared electrons toward itself. Oxygen is one of the most electronegative of all the elements, attracting shared electrons much more strongly than hydrogen does. In a covalent bond between oxygen and hydrogen, the electrons spend more time near the oxygen nucleus than they do near the hydrogen nucleus. Because electrons have a negative charge and are pulled toward oxygen in a water molecule, the oxygen atom has a partial negative charge (indicated by the Greek letter δ with a minus sign, δ–, or “delta minus”), and each hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge (δ+, or “delta plus”). Because the oxygen atom in the water molecule is more electronegative than the hydrogen atoms the oxygen, the electrons of the bond are not shared equally. This type of bond is called a polar covalent bond.
"The achievement of a stable configuration by one atom of a bond but not by the other partner" is not correct because the entire water molecule is stabilized by covalent bonds joining the oxygen to the two hydrogen atoms, but because oxygen is highly electronegative a polar molecule is formed.
"Covalent bonding" is not correct because oxygen is highly electronegative forming a polar molecule.
"Widespread ionization" is not correct because the molecule is stabilized by polar covalent interactions. However, the partial charges on a water molecule contribute to its ability to dissociate.
"The high electronegativity of hydrogen" is not correct because hydrogen is not a highly electronegative element.