How long is the secondary oocyte viable and capable of being fertilized after it is ovulated?
- 36-72 hours
- 12-24 hours
- 24-36 hours
- a full week
12-24 hours
At what point is meiosis II completed for the female gamete?
- implantation
- fertilization
- ovulation
- puberty
fertilization
During which stage of labor is the fetus delivered?
- placental stage
- gastrula stage
- dilation stage
- expulsion stage
expulsion stage
The embryo is directly enclosed in and protected by the amnion.
- True
- False
True
Which hormone maintains the viability of the corpus luteum?
- human chorionic gonadotropin
- estrogen
- human placental lactogen
- progesterone
human chorionic gonadotropin
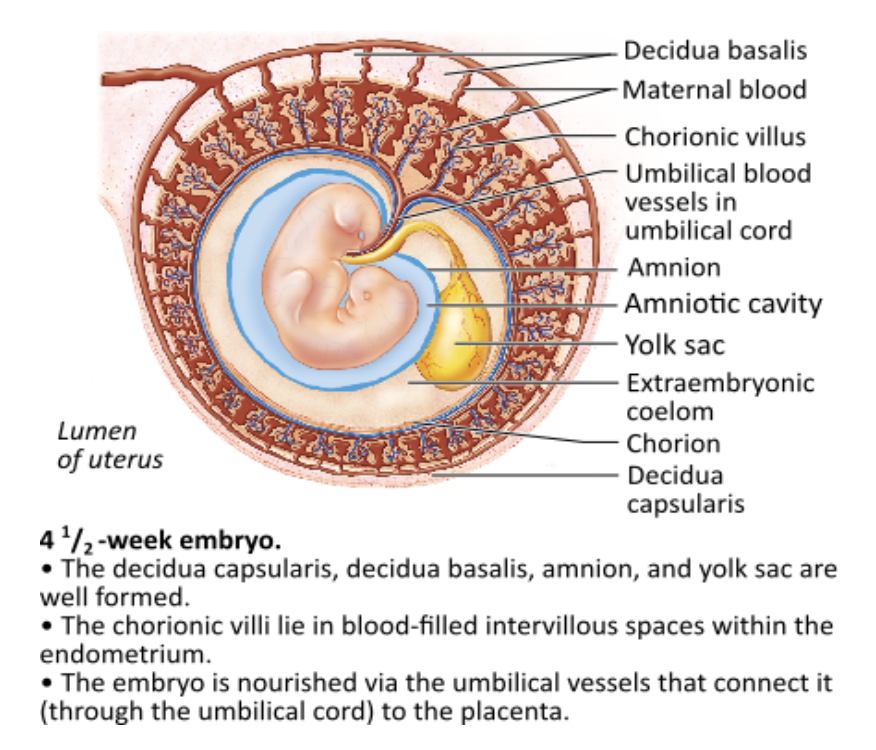
Which of these is the innermost (closest) structure that completely surrounds the embryo?
- yolk sac
- amnion
- chorion
- placenta
amnion
Ex.
The amniotic fluid, found in the amnion and intimate with the embryo, protects the embryo from physical trauma and maintains a constant homeostatic temperature.
The trophoblast is mostly responsible for forming the ________.
- allantois
- placental tissue
- lining of the endometrium
- archenteron
placental tissue
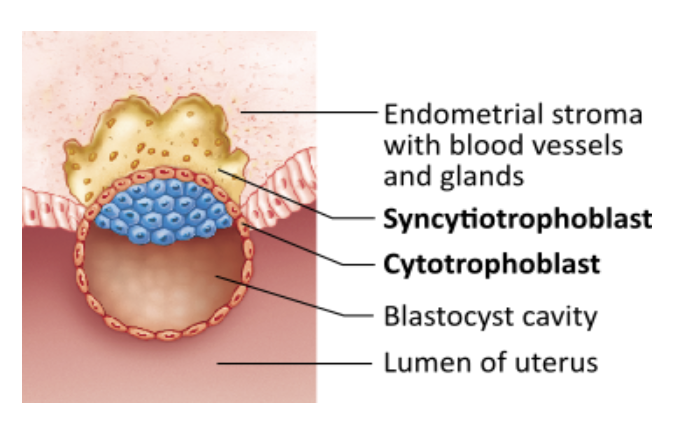
What cellular area shown in the figure secretes human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)?
- the entire blastocyst
- cytotrophoblast
- embryoblast
- syncytiotrophoblast
syncytiotrophoblast
Ex.
Syncytiotrophoblast cells begin to secrete human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) following implantation.
Thalidomide was once used to treat intense nausea and morning sickness in pregnant women. Unfortunately, if administered at certain points during gestation it resulted in limb malformation. This drug is an example of a(n) ________.
- teratogen
- carcinogen
- neurotoxin
- endocrine disruptor
teratogen
Which of the following is the longest stage of labor, lasting 6-12 hours or more?
- expulsion stage
- placental stage
- dilation stage
- delivery stage
dilation stage
Ex.
The dilation stage often lasts the longest, up to 12 hours or more.
The period from fertilization through week eight is called the embryonic period.
- True
- False
True
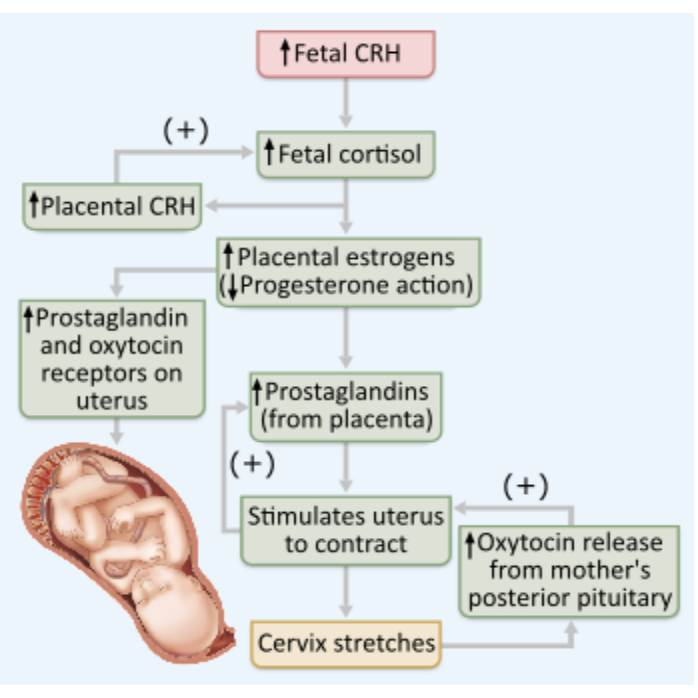
What role does oxytocin play in promoting labor?
- Oxytocin stimulates the uterus to contract.
- Oxytocin antagonizes progesterone’s quieting influence on uterine muscle.
- Oxytocin promotes the formation of gap junctions between the uterine smooth muscle cells.
- Oxytocin stimulates the myometrial cells of the uterus to form oxytocin receptors.
Oxytocin stimulates the uterus to contract.
Ex.
Oxytocin from fetal cells, and eventually the posterior pituitary, stimulates the uterus to contract both directly and through the release of prostaglandins.
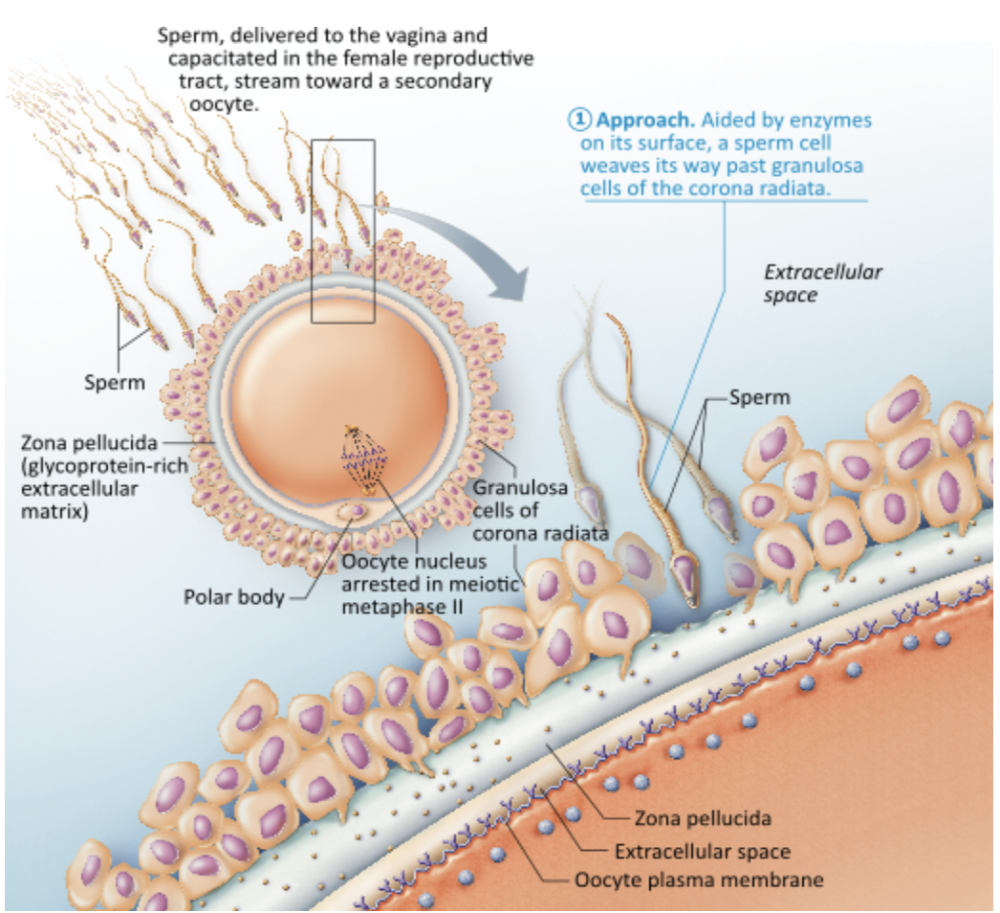
Once sperm are deposited into the vagina, the sperm's motility must be enhanced and they must be prepared to release hydrolytic enzymes from their acrosomes. What is this process called?
- cortical reaction
- acrosomal reaction
- capacitation
- fertilization
capacitation
Ex.
Sperm must undergo capacitation in order to gain the ability to penetrate and fertilize an oocyte.
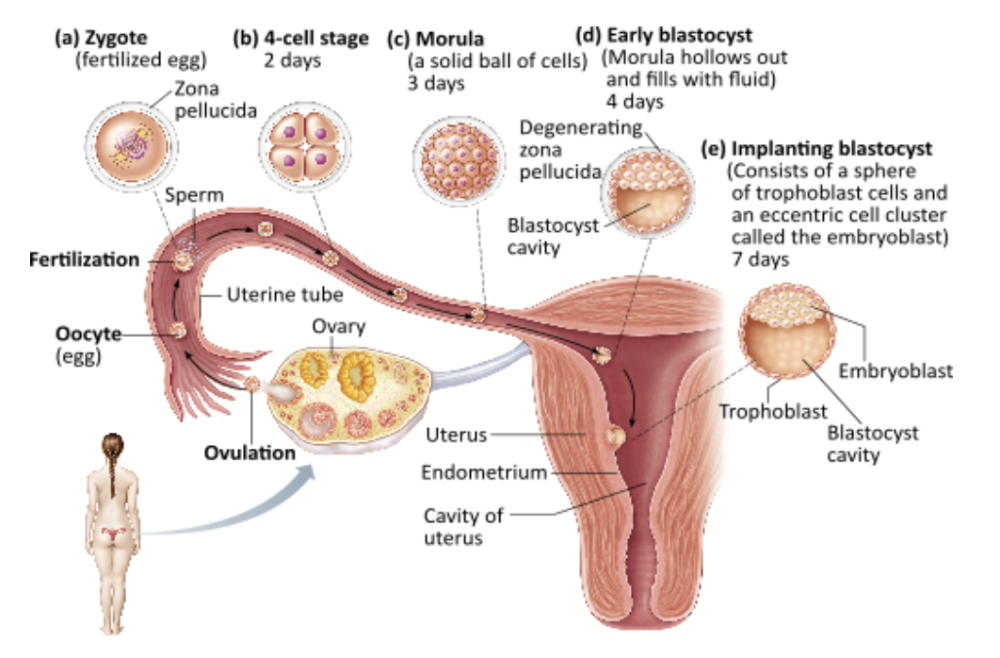
Which of the following implants in the mucosa of the endometrium?
- oocyte
- zygote
- blastocyst
- morula
blastocyst
Ex.
The blastocyst implants after about seven days. It consists of a hollow ball of cells with a smaller, inner cell mass pressed to the inside wall.