Muscular endurance:
capacity to perform repeated muscle contractions
power:
rate of performing work (explosive)
strength:
max force a muscle can generate
Describe how genetics may affect performance
differential DNA methylation patterns ⇒ mRNA lvl change, protein expression, functional measures
What is the principle of specificity?
- adaptations to mode+intensity (stress most relevant physiological systems)
- weight lifting to increase size+strength
What is the principle of reversibility?
- You’ll lose gains if stop working out
What specific enzymes might decline when we cease aerobic training?
- aerobic enzyme activity declines // performance and muscle mitochondrial enzyme activity
What is the principle of progressive overload? Provide an example
- muscle improves if push/loaded beyond normal load
- Decrease rest time
What is the principle of periodization?
- reordering+emphasizing different parts of your fitness (change variables)
Why is periodization in exercise training important for performance?
keep training challenging + improve
Describe the fitness-fatigue paradigm
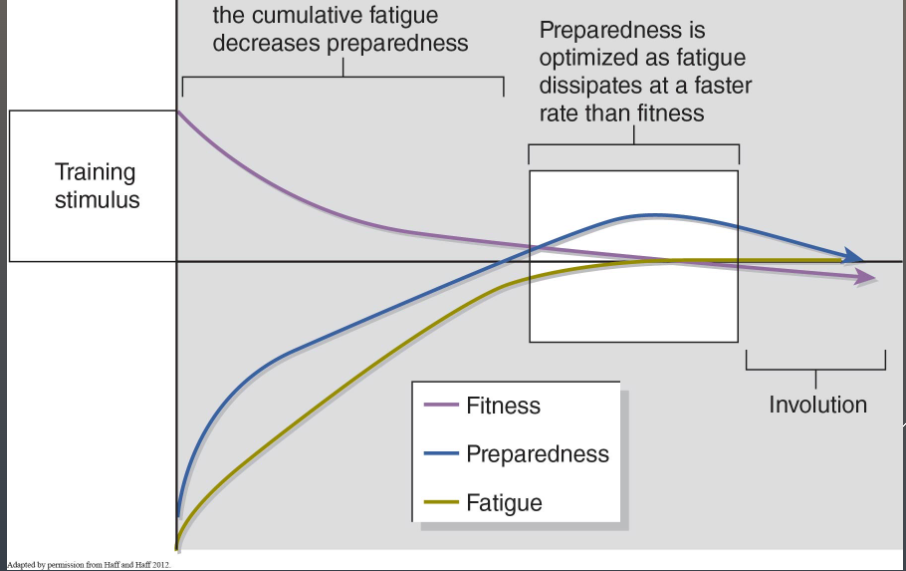
- Optimized prepare when ⬇ fitness + ⬇ ⬇fatigue
- Start: ⬆fitness + fatigue // ⬆fatigue = ⬇prepareness
When training, how should we order our resistance training exercises?
- large muscle groups ⇒ smaller
- multi-joint ⇒ single joint
High ⇒ low intensity
Describe isometric resistance training and its benefits.
post surgery rehab/less stress on joints/stabilization
Describe the advantages to using free weights.
recruit muscles (support+stabilize)||
Describe the disadvantages to using free weights.
can be dangerous, difficult to use,
Explain the following statement: the maximum weight one can lift is limited by the weakest portion in the range of motion
- there are points in a joint's range of motion at which the
muscle is stronger, and points at which it is weaker
- Free weights aims at weaker muscles
The core musculature is mostly what fiber type?
Type 1 fibers
- Describe high-intensity interval training.
- How would it be performed?
- 8x30” all-out with 4’ recovery (high reps, low rest/recovery), time-efficient exercises
How does it HIIT benefit aerobic performance? (explain its impact on mitochondrial growth and glycogen storage)
- regulates mitochondrial quality (increase ATP synthesis), reduce muscle glycogen stores (⬆ rate of glycolysis)
Where do we cross over from anaerobic to aerobic energy systems being the primary contributor to exercise?
- cardiovascular system
- energy is released by oxygen-dependent metabolic processes
- after 2 mins of anaerobic energy system (short)
- What are the gains in strength primarily due to early in one’s resistance training program (4 to 6 weeks?)
neural adaptation (nervous system builds stronger links to muscles cells)
What about the later gains in strength?
muscle cross-sectional area changes (size+shape)
What is hypertrophy a result of?
repaired myofibrils increase in thickness and number
Describe transient hypertrophy
- short term
- Fluid accumulation in the
interstitial and intracellular space (from the plasma)
- Disappears within hours
Describe chronic hypertrophy
- long-term increase in muscle size // Uncontrolled high blood pressure (heart)
- Reflects actual structural change in muscle
- Hypertrophy + Hyperplasia
3 neuromuscular adaptations to resistance training
- 1) motor unit recruitment + neural drive
increase nerve activity + same time recruitment
3 neuromuscular adaptations to resistance training
2) Rate coding
increase stim. frequency
3 neuromuscular adaptations to resistance training
3) Autogenic inhibition
GTO is silenced
Which type of muscle fiber is recruited first? What does this allow for?
- Type I < Type IIa < Type IIx
- allows for cross-innervation (motor neuron takeover)
What is hyperplasia?
an increase in the number of muscle fibers
Do you believe hyperplasia occurs in humans? Why of why not.
No, because of a lack of evidence, fibers tend to switch over and not be produced more. Unclear how to trigger the process
Describe how immobilization may lead to muscle atrophy.
- ⬇protein synthesis rate
- strength
- cross-sectional fiber area(size)
- neuromuscular activity (affects type 1 fibers more)
- muscle breakdown>synthesis
Training Phases
Macrocycle
longest phase, long-term view centered around goal
Training Phases
Mesocycle
Second longest phase, focus on developing a certain skill
Training Phases
Microcycle
Shortest phase, several-day period of vigorous training followed by
a
short period of lighter training or rest
PHYSIOLOGY OF PLYOMETRICS –
MECHANICAL MODEL
- Elastic energy is created in the muscles and tendons and stored
as a result of a rapid stretch
- stored energy is released
when the stretch is followed by a concentric muscle action
- Similar to a stretching spring
- stored energy is released
when the stretch is followed by a concentric muscle action
DELAYED-ONSET MUSCLE SORENESS (DOMS)
- Soreness is 12 to 48 hours after
- From eccentric muscle activity
- Related to structural damage, impaired calcium homeostasis, accumulation of by-products and irritants, increased macrophage activity
How does resistance exercise increase protein synthesis at the cellular level?
increases in rates of myofibrillar MPS (translational efficiency +capacity)
How might consume protein aid in protein synthesis? (Hint: think about the mTOR response).
activated: muscle protein synthesis + mTOR signalling pathway
What are the benefits that elderly individuals might gain by performing resistance training?
helps with loss of muscle mass (sarcopenia), helps prevent falls
- Do older adults have the same response to resistance training as young adults? Why or why not?
- no, because the older population has a decreased amt of GH and testosterone
- older has decreased mTOR signaling responses
- younger: higher response to bone adaptations
BONE ADAPTATIONS TO
RESISTANCE TRAINING
- Positive correlation between BMD and muscle strength/mass
- Changes in BMD: > 6 months
Osteoporosis
- Critically low BMD: leads to fractures
- Hip, spine, distal radius
Osteocytes (bone cells)
- can detect and respond to mechanical loading
- Transmit information to the osteoblasts and osteoclasts to maintain skeletal homeostasis
Osteogenesis
requires mechanical loading, sufficient magnitude, rate, and frequency of loading