ACSM 2017 Definition
range of motion (ROM) of a joint of group of joints, as per the skeletal muscles and not any external forces
CDC definition
a joint’s ability to move through its full range of motion
Body Tissues
- ligaments
CT between bones, thereby protecting the joint from excessive mvt
Body Tissues
- articular cartilage
= covers the ends of articular/joint surfaces of bones
Body Tissues
- collagen
- = the principal protein of in the body accounting for around 30% of all proteins
- type I
- type II
Body Tissues
- collagen // TYPE 1
consists of thick fibers that elongate very little when placed under tension, relatively stiff and strong
Body Tissues
- collagen // TYPE 2
fibers that are much thinner than type I and possess slightly less tensile strength → framework to maintain general shape and consistency
Body Tissues
tendons
- = non-contractile fibrous CT connecting ends of muscle to one or more bones
- cord-like (tendon) OR sheet-like (aponeurosis)
Stress-Strain Curve
- elastic strain
high stresses, but tissue can return to the original framework
Stress-Strain Curve
- plastic strain
veryhigh stresses you have tissue deformation
Stress-Strain Curve
- Failure
tissues fail under stresses and strain
Tissues Strength & resilience
plantar fascia & IT band need 2K of force to deform it 1%
Extrafusal Fibers
- innervated by alpha motor N to produce force
Intrafusal Fibers
- → GTOs = do measurements by sensing the static length of
extra-fibers and rate of change of length of the muscle
- sensory component → transmit info
- motor component → keeps spindle tight to be sensitive to changes in length
Range of Motion definitions
- passive ROM (PROM)
- = the degree to which a joint can be moved through available ROM completely dependent on assistance
Range of Motion definitions
- active assisted ROM (AAROM)
- = the degree to which a joint can be moved through available ROM with external assistance and muscle contraction
Range of Motion definitions
- active ROM (AROM)
- the degree to which a joint can be moved through available ROM under the participant’s own power
Range of Motion definitions
- resisted ROM (RROM)
- the degree to which a joint can be moved while engaging the musculature of the joint with resistive forces
Types of Stretching
- static
= isolating and moving a muscle to its end ROM, gradually, and holding for a certain time
Types of Stretching
- dynamic
= involves a progressive increase in reach and ROM as the movt is repeated
Types of Stretching
- progressive
= static stretching starting slow allowing the tissue to relax into stretch before pushing more
Types of Stretching
- ballistic
= continuous bouncing mvt at end ROM to try to get MAXlength out of muscle, usually athletes
Variables Can Manipulate
- INTENSITY
→ light to moderate discomfort
Variables Can Manipulate
- DURATION
→ around a min. total each
Variables Can Manipulate
- SPEED
→ depends on type of stretch
Variables Can Manipulate
- FREQUENCY
→ how many sets/day per week
Variables Can Manipulate
- MODE
→ what type
Variables Can Manipulate
- POSITION
→ seated, standing, side-lying, supine, prone
Variables Can Manipulate
- ALIGNMENT
→ are joints & limbs/body position is correct for desired stretch
Stress Strain Curve
Elastic strain
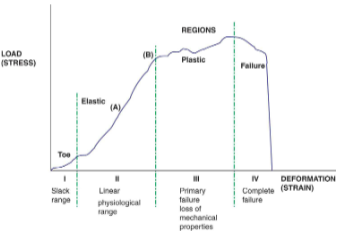
high stresses, but tissue can return to original framework
Stress Strain Curve
Plastic strain

such high stresses you have tissue deformation
Stress Strain Curve
Failure

tissue fails under stresses and strain
Stress Strain Curve
A

stiffness (modulus)
Stress Strain Curve
B

Yield point