Why did the researchers perform immediate duplicate sequences on some patients?
Immediate duplicate sequences were experimental controls (technical replicates) designed to verify the accuracy of the sequ
Why did the researchers perform sequencing at multiple time points on some patients?
Sequences taken at multiple time points enabled scientists to assess how the virus was evolving within a patient over time.
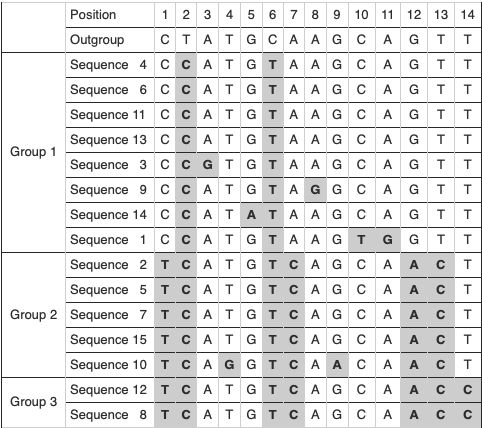
Identify the positions of the shared mutations that enabled scientists to organize the sequences into three groups.
Positions 1, 7, 12, 13, and 14

Using the sequence similarities and differences among the 4 groups, can you identify the tree that accurately represents the ancestor-descendant relationships among the four groups?
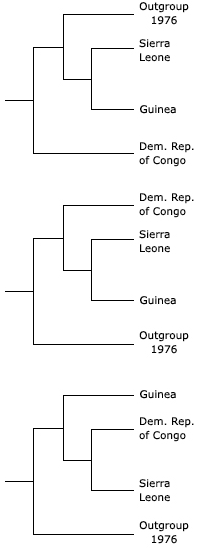
- second tree option
What did researchers conclude about the mode of transmission?
An outbreak started in Guinea, then spread to Sierra Leone through human-to-human transmission.
viruses only
host cell only

both

lytic cycle

lysogenic cycle

both cycles

Which statements about viruses are true?
- A retrovirus contains RNA.
- The capsid enters the host cell if the virus is enveloped.
- Enveloped viruses bud from the host cell.
- HIV contains reverse transcriptase.
Which of the three types of viruses shown in the figure would you expect to include a capsid(s)?

Emerging viruses arise by
- mutation of existing viruses
- the spread of existing viruses more widely within their host species
- the spread of existing viruses to new host species.
Which of the following descriptions correctly identifies a main structural difference between viruses with envelopes and viruses without envelopes?
Only viruses with envelopes have their contents enclosed by a layer containing lipids
How does a virus differ from a bacterium?
Viruses, unlike bacteria, lack metabolic enzymes
All of the statements below are true. Select the statement that best supports the view of most biologists that viruses are nonliving.
An isolated virus is unable to replicate its genes or regenerate ATP.
In the lysogenic cycle _____.
viral DNA is replicated along with host DNA
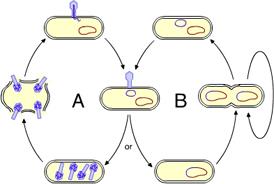
Cycle A is the _____ cycle and cycle B is the _____ cycle.
lytic ... lysogenic
The lytic cycle of bacteriophage infection ends with the _____.
rupture of the bacterium
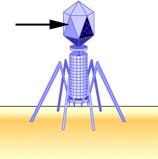
The pointer is indicating the _____.
viral protein coat
As a result of the lytic cycle, _____.
the host cell's DNA is destroyed
The genetic material of HIV consists of _____.
single-stranded RNA
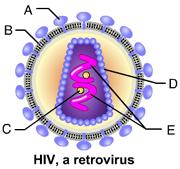
Which of these binds to receptor molecules on the host cell membrane?
A
What is the function of reverse transcriptase?
It catalyzes the formation of DNA from an RNA template.
What is the source of a viral envelope?
host cell membrane

Which of these is reverse transcriptase?
C

Which of these is the viral genome?
E
What enzyme allows a retrovirus to make DNA from an RNA template?
reverse transcriptase
Double-stranded viral DNA is incorporated into a host cell as a _____.
provirus
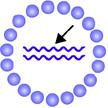
The pointer is indicating the virus's _____.
genome
Viral DNA makes mRNA by the process of _____
transcription
How does HIV cause disease?
HIV kills cells that defend the body against disease.
How do enveloped viruses differ from nonenveloped viruses?
They have a membrane-like outer covering.
Which replicative cycle describes a virus that can integrate its genome into the host cell's genome?
Lysogenic
Which enzyme inserts viral DNA into the host's chromosomal DNA?
Integrase
How does HIV bind to a host cell?
The viral envelope proteins interact with CD4 and a co-receptor on the cell membrane.
Which of the following events stimulates the production of viral particles in a host cell?
Activation of the host cell by cytokines, growth factors, or antigens.
True or false? The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) uses reverse transcriptase to make double-stranded RNA copies of its DNA genome.
False
Which of the following events or characteristics is the most likely explanation for why an individual experiences regular herpesvirus-mediated cold sore or genital sore flare-ups?
Copies of the herpesvirus genome permanently maintained in host nuclei are periodically "activated."
The host range of a virus is determined by whether ________.
the proteins on virus surface can bind with proteins on the host surface
Which of the following characteristics is typical of the lytic cycle of a bacteriophage?
The host membrane ruptures, releasing many phages.
Which of the following correctly describes the viral assembly process?
New viral components self-assemble without help from cellular components.
A newly identified virus has a single-stranded RNA genome that is used as mRNA after infection. Its capsid is 25-30 nm in diameter and contains 180 identical capsomeres. Which of the following processes would be the best to follow to analyze the reproduction of this virus in a host cell?
translation rate
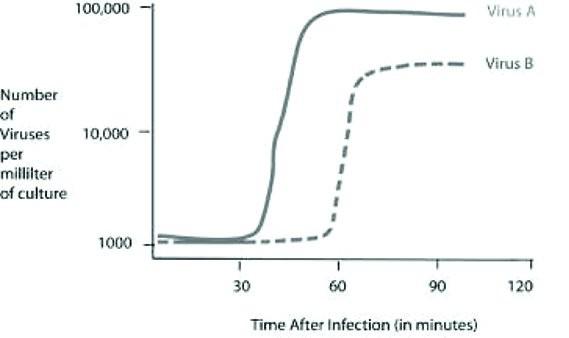
Cells were infected with approximately 1,000 copies of either virus A
or virus B at the 0 time point. At five-minute intervals, a sample of
the virus and cell mixture was removed. All intact cells were removed
from the sample, and the number of viruses per milliliter of culture
was determined.
Based on the data provided, the lytic cycle of
virus B is closest to ________.
60 minutes
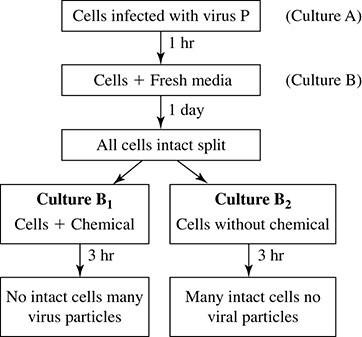
Which of the following best explains the results?
Virus P is capable of both lysogenic and lytic cycles.
Viruses require host cell's machinery to make copies of themselves. However, some viruses that infect humans require mechanisms that do not normally occur in human cells. Which of the following describes how the viruses can replicate in human cells?
The viral genome codes for specialized enzymes not found in the host cells.
Oseltamivir (Tamiflu), an antiviral drug prescribed for the flu, inhibits the enzyme neuraminidase. How could this drug prevent infection in someone exposed to the flu or shorten the course of flu in an infected patient (the reasons for which it is prescribed)?
Inhibiting neuraminidase blocks the release of new viruses from infected cells.
Which of the following statements correctly describes vaccines and how they help prevent viral infection?
Vaccines are inactive versions of a virus that stimulate an immune reaction in a person.
A researcher is studying a single plant infected with tobacco mosaic virus (TMV). She crushes three of the plant's leaves in a small amount of water and stores the sample in the refrigerator overnight. The next day she sprays the mixture onto a new set of tobacco plants she had recently trimmed and repotted. Which of the following results will most likely occur?
The plants would develop the typical symptoms of TMV infection and would be able to transmit the disease.
A person is most likely to recover from a cold due to viral infection if the infected cells are able to perform which of the following processes?
normal cell division
Which of the following statements best reflects what we know about how influenza virus moves between species?
An animal, such as a pig, is infected with more than one strain of the influenza virus and the genomes reassort into new combinations that can facilitate spread to other species.
An infectious substance capable of causing disease in plants is isolated and researchers want to determine whether the substance is a bacterium or a virus. Which of the following methods will best allow them to determine the type of infectious agent they have isolated?
Culture the substance on nutritive medium, away from any plant cells.