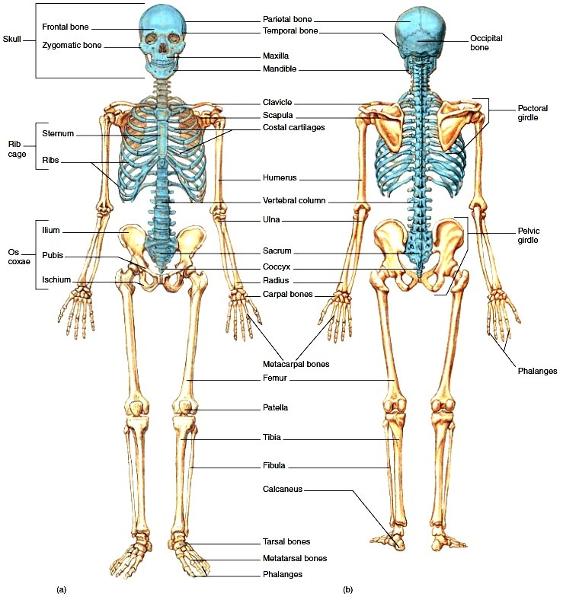
Skeleton, the body's framework, is constructed of two of the most supportive tissue found in the human body~cartilage and ~bone.
This is where the bones connect
Joints, or articulations
The Skeleton is subdivided into divsions:
1. axial
2. appendicular
Cartilages in the adult skeleton
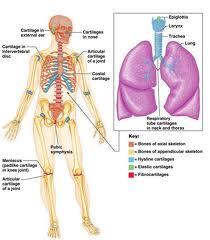
Most important cartilages (7) are
1.articular cover the bones ends at movable joints
2.costal found connecting ribs to the sternum
3.laryngeal largely construct the larynx (voicebox)
4.trahcial and bronchial reinforce passages of the respiratory system
5.nasal support the external nose
6.intervertebral discs
7.supports the ears, epiglottis
Cartilage tissue is primarily composed of
water and is fairly resilient.
The dense connective tissue that covers catillage is called
perichondrium
Role of the perichondrium
acts to resist distortion of the cartilage when it is subjected to pressure and plays a role in cartilage growth and repair
Describe each
~Hyaline Cartilage
~Elastic Cartilage
~Fibrocartilage
~Hyaline, provides steady support with some resilience or give.
~Elastic, much more flexible than hyaline and resists repeated bending
~consists of rows of chondrocytes alternating with rows of thick collagen fibers.
Classification of Bones
Texture: Compact or Spongy
Shape: Long, Short, Flat and Irregular
Two subcatergories of Irregular bones:
1. sesamoid
2. wormian or sutural bones
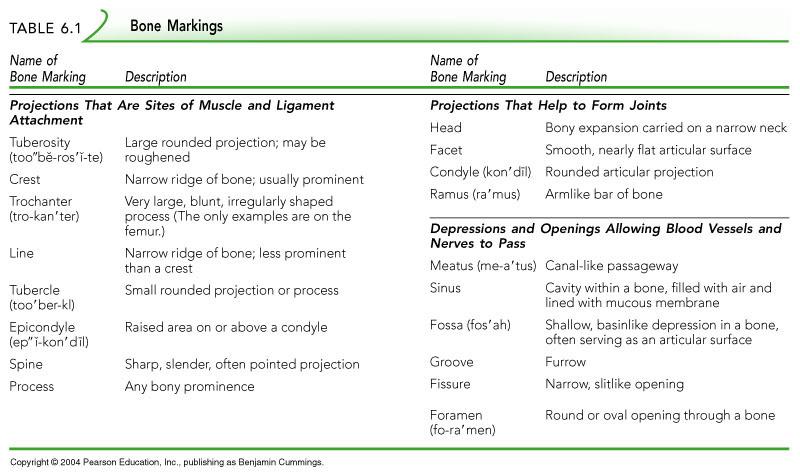
Bone Markings
Parts of the Long Bone
Proximal epiphysis, diapiphysis, Distal epiphysis, epiphyseal plate or line, endosteum, medullary cavity,
Microscopic Structure of the Bone
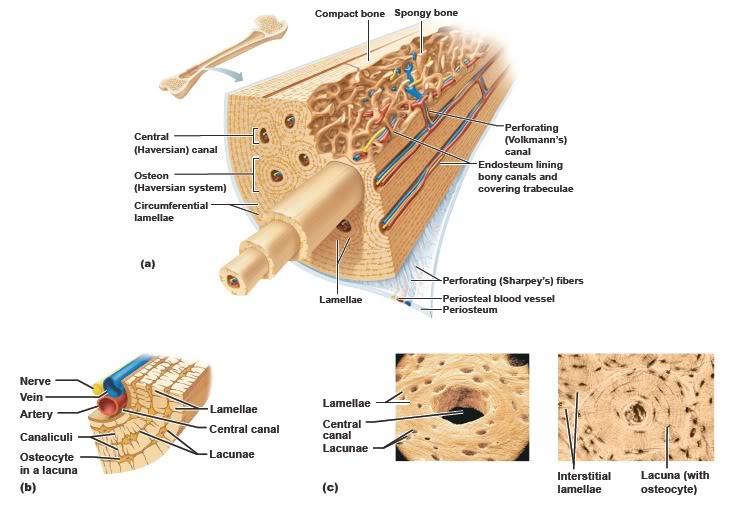
The difference between Compact bone and Spongy bone
Spongy bone has a spiky, open-network appearance and compact bone is dense and homogeneous.
Describe the Central (Haversian) Canal
Runs parallel to the long axis of the bone and carries blood vessels, nerves and lymph vessels through the bony matrix.
Osteocytes
mature bone cells
lacunae (chambers)
arranged in concentric circles (concentric lamellae)around the central canal.
Osteon
A central canal and all the concentric lamellae surrounding it
canaliculi
tiny canals radiating outward from a central canal to the lacunae of the first lamellae and then from lamella to lamella; forming a dense transportation network through the hard bone matrix.
endochondral ossification and the major events of this process
uses hyaline cartilage"bones"as patterns for bone formation.
~The fibrous membrane covering the hyaline cartilage model is vascularized and coverted to a periosteum.
~Osteoblasts at the inner surface of the periosteum
secrete bone matrix around the hyaline cartilage model, forming a bone collar.
~Cartilage in the shaft center calcifies and then hollows out, forming an internal cavity.
periosteal bud
(blood vessels, nerves, red marrow, elements, osteoblasts, and osteoclasts) invades the cavity, which becomes the medullary cavity.
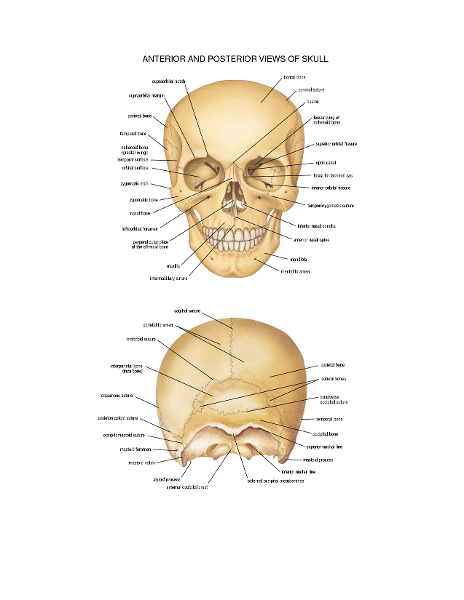
Which two sets of bone compose the skull?
1.Cranial
2.Facial
Forming the superior, lateral, and posterior walls of the skull
cranial vault or calcaria
Name the three distinct concavities
1.Anterior cranial fossa
2.Middle cranial fossa
3.Psoterior cranial fossa
Anterior portion of the cranium; forms the forehead, superior part of the orbit, and the floor of the anterior cranial fossa
Frontal Bone
What is the name of the opening above each orbit allowing blood vessels and nerves to pass?
Supraorbital foramen (notch)
What is the Glabella?
Smooth area between the eyes
Midline articulation point of the two parietal bones
Saggital suture
The Parietal bone is
postlateral to the frontal bone, forming sides of the cranium
Point of articulation point of parietals and frontal bones
Coronal Suture
Inferior to parietal bone on later skull
Temporal Bone
The frontal bone can be divided into four major parts:
squamous region, tympanic region, mastoid region, petrous region
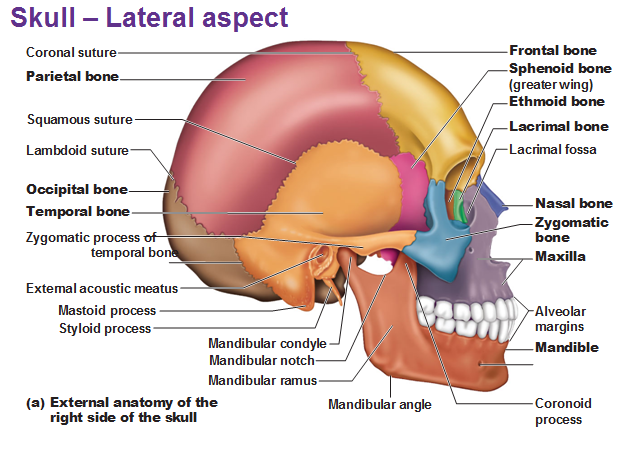
External Anatomy of the lateral aspect of the skull
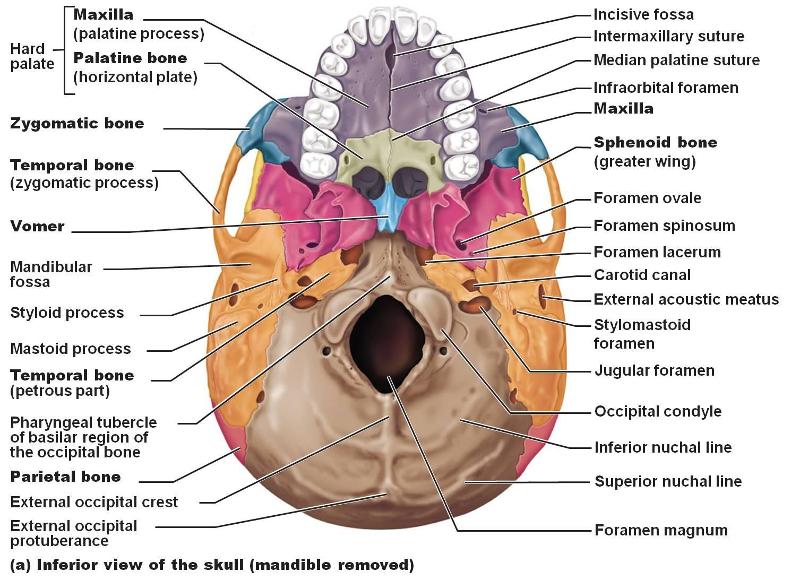
Inferior Region of the skull
Point of articulation of the temporal bone with the parietal bone.
Squamous Suture
A bridgelike projection joining the zygomatic bone (cheekbone) anteriorly. Together these two bones form the zygomatic arch.
Zygomatic Process
Rounded depression on the inferior surface of the zygomatic process; forms the socket for the mandibular condyle, the point where the mandible joins the cranium.
mandibular fossa
External Acoustic Meatus
canal leading to ear drum and middle ear
Needle like projection inferirior to external acoustic meatus; attachment point for muscles and ligaments of the neck. This process is often broken off demonstration skulls.
Styloid Process
Rough projection inferior and posterior to external acoustic meatus; attachment site for muscles. Full of air cavities and close to the middle ear---- a trouble spot for infections---- often becomes infected too a condition called__________.
Mastoid Process and Mastoiditis
What is meningitis?
Inflammation of brain coverings
Styloid foramen
Tiny opening between the mastoid and the styloid processes through which Cranial Nerve VII leaves the cranium.
Opening medial to the styloid process through which the internal jugular vein and cranial nerves IX, X, and XI pass.
Jugular Formamen
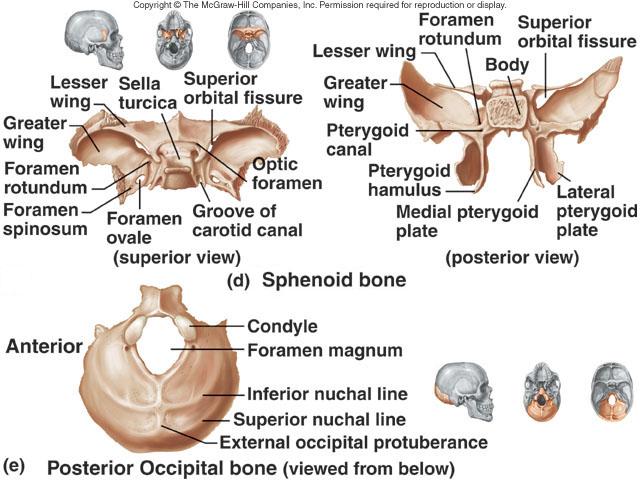
Most posterior bone of the cranium
Occipital Bone
Opening medial to the styloid process through which the internal carotid artery passes into the cranial cavity.
Carotid Canal
Opening on posterior aspect (petrous region) of temporal bone allowing passage of cranial nerves VII and VIII.
Internal Acoustic Meatus
A jagged opening between the petrous temporal bone and the sphenoid providing passage for a number of small nerves and for the internal carotid artery to enter the middle cranial fossa(after it passes through part of the temporal bone).
Foramen Lacerum
Internal anatomy of the inferior portion of the skull
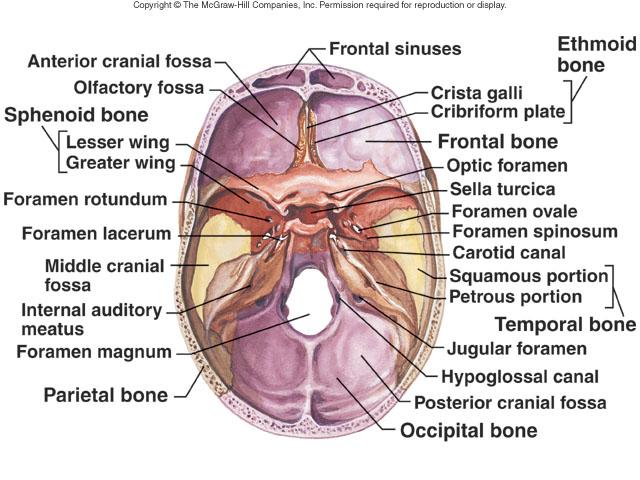
Large opening in base of occipital, which allows magnum that articulate with the spinal chord to join the brain.
Foramen Magnum
Opening medial and superior to the occipital condyle through which the hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve XII) passes.
Hypoglossal Canal
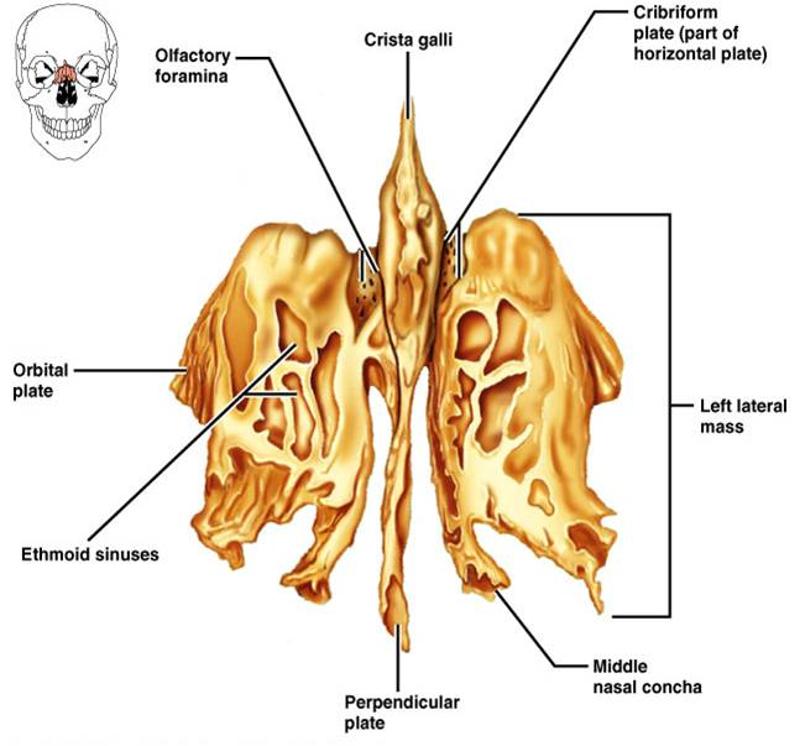
The Ethmoid Bone
Spenoid Bone
Anatomy of posterior and anterior skull
What froms the horizontal plates of the ethmoid bone?
The cribiform plates and the midline crista galli
Bones tha form the orbit
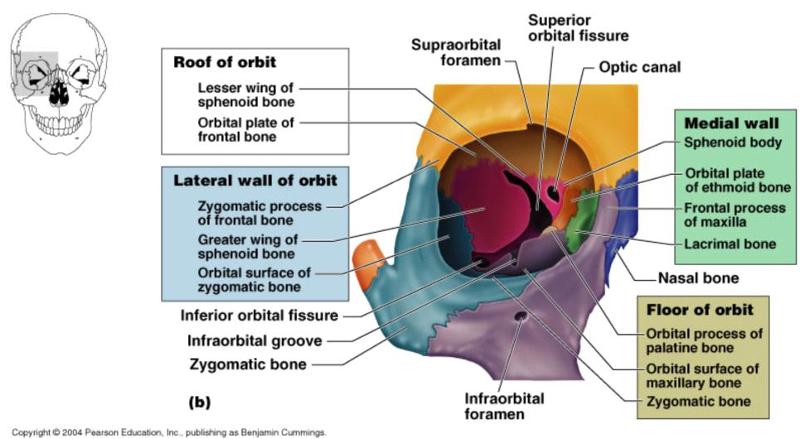
12 Pair of Facial Bones
Maxillae bone, Palatine bone, Zygomatic bone, Nasal bone, Temporal bone, Lacrimal bone
2 unused Facial bones
Mandible and Vomer
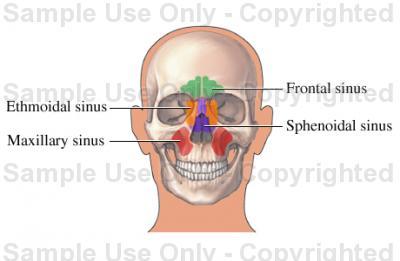
Paranasal Sinuses
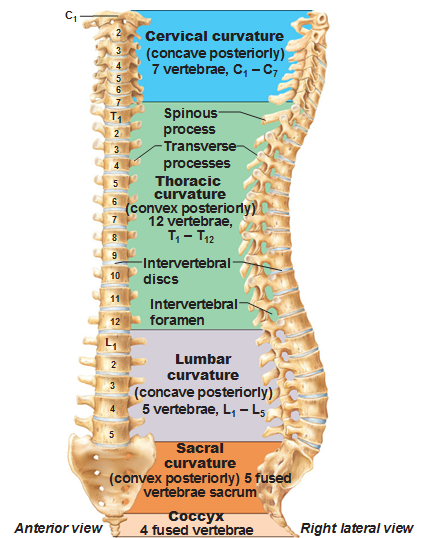
The Vertebral Column
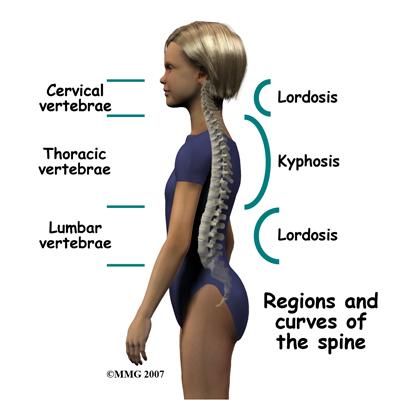
Abnormal Spinal Curvatures
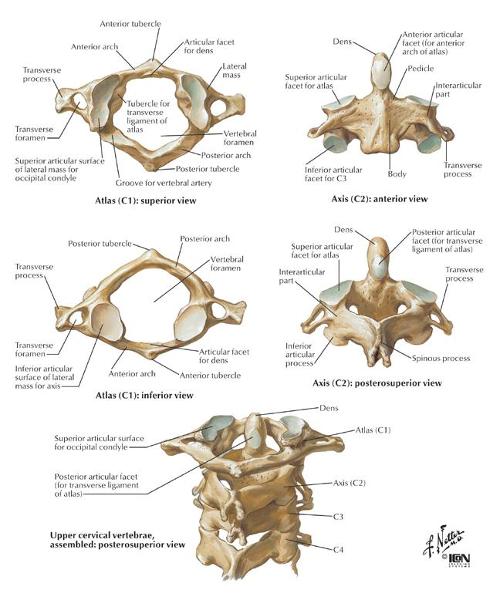
Cervical Vertebrae
Thoracic Vertebrae
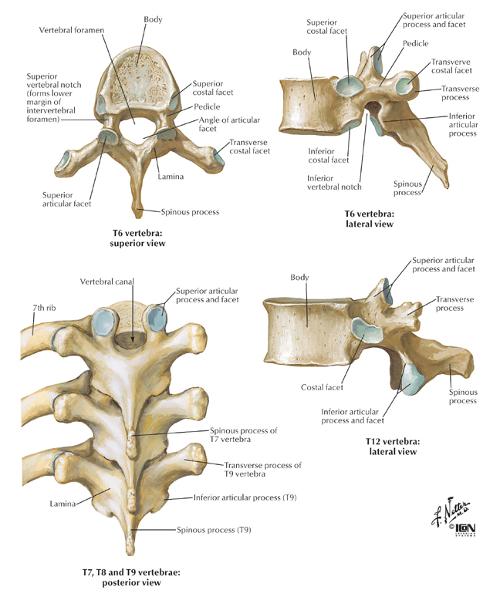
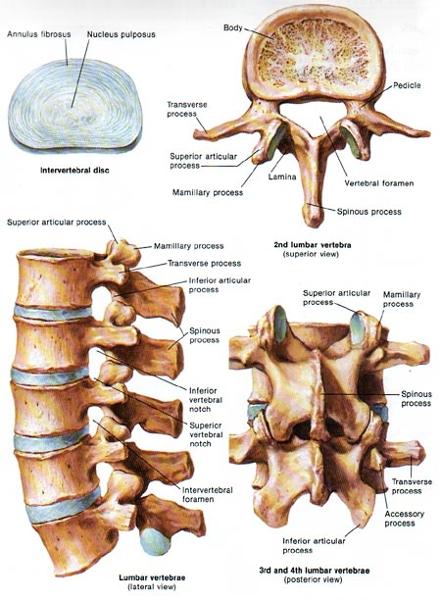
Lumbar Vertebrae
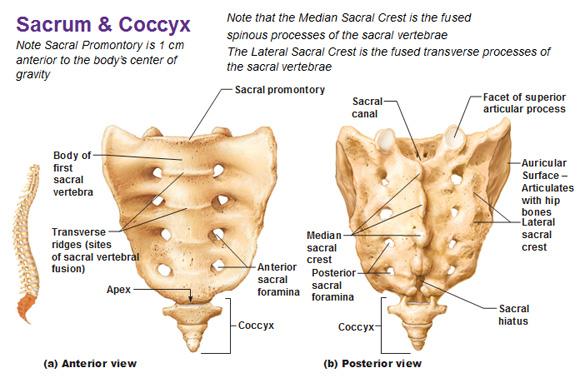
Sacrum and Coccyx
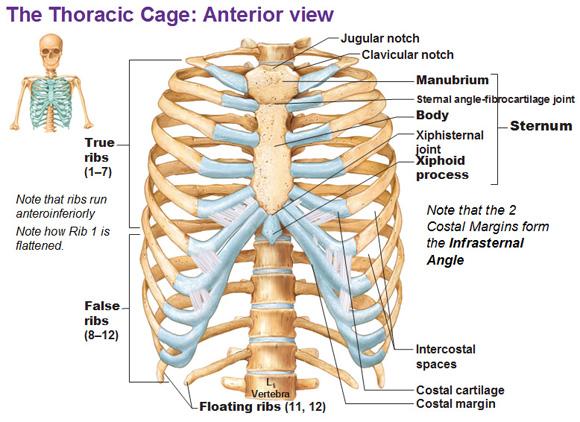
The Thoracic Cage
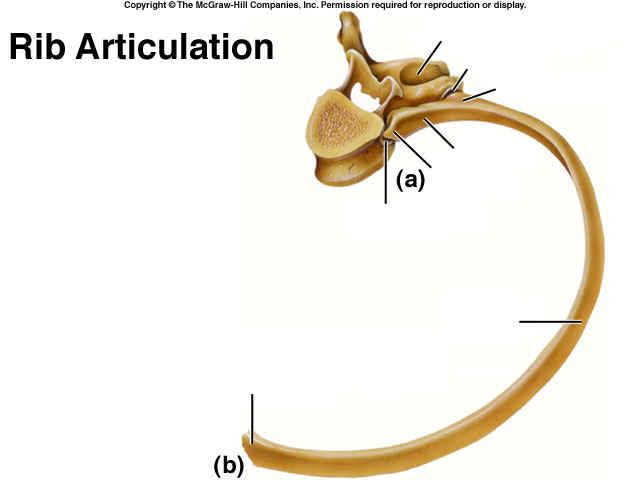
The Rib and it's articulation
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
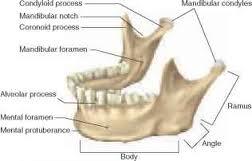
Anatomy of Mandible
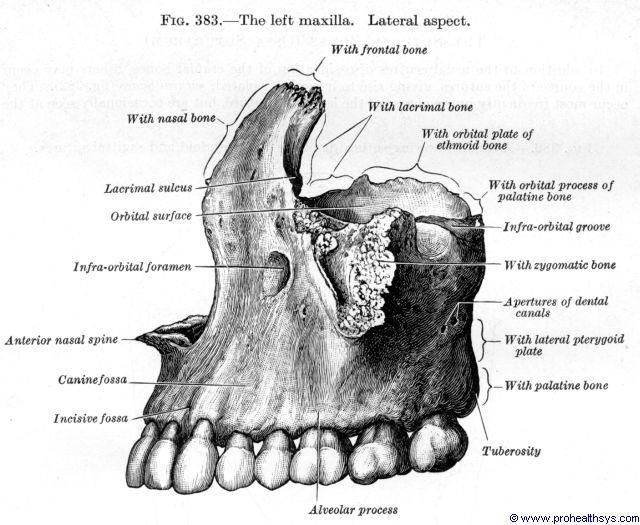
Anatomy of Maxilla