Dyads are visible in
both mitosis and meiosis
tetrads are visible in
meiosis only
product is 2 diploid daughter cells genetically identical to the mother cell
mitosis only
product is 4 haploid daughter cells quantitatively different from the mother cell
meiosis only
involves the phases prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase
both mitosis and meiosis
occurs throughout the body
mitosis only
occurs only in the ovaries and testes
meiosis only
provides cells for growth and repair
mitosis only
hologoues synapse: chiasmata are seen
meiosis only
chromosomes are replicated before the division process begins
both mitosis and meiosis
Provides cells for replication of the species
meiosis only
consists of 2 consecutive nuclear divisions, without chromosomal replication occurring before the second division.
meiosis only
Describe the process of synapsis
The pairing of homologous chromosomes (23 tetrads become attached to spindle fibers & begin to align on the equator.
How does crossover introduce variability in the daughter cells?
The homologues seperate from one another, breaking & exchanging parts- where crossovers occur
Define homologous chromosomes
Egg & sperm chromosomes that carry genes for the same traits (1 paternal, 1 maternal)
primative stem
spermatogonium
haploid
secondary spermatocyte, spermatid, sperm
Provides nutrients to developing sperm
sustentacular cells
products of meiosis II
spermatid
product of spermiogenesis
sperm
product of meiosis I
spermatocyte
Why are spermatids not considered functional gametes?
They are non-motile and have too much excess baggage to function well in a reproductive capacity.
Differentiate between spermatogenesis and spermiogenesis
Spermiogenesis is the final stage of spermatogenesis, which sees the maturatin of spermatids into mature, mobile spermatozoa. * formation of haploid gametes by Male sloughing off excess spermatid cytoplams to form a motle functioning sperm
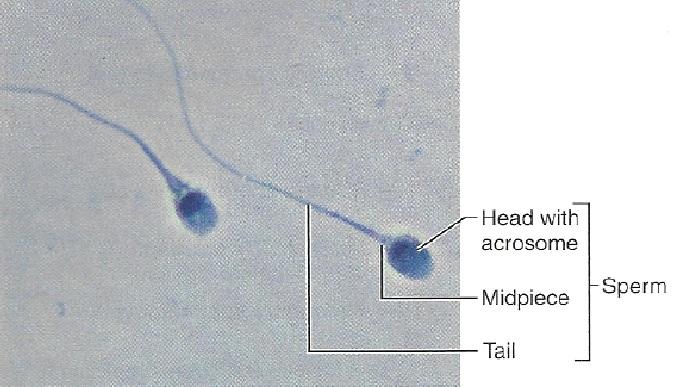
Draw a sperm, label: acrosome, head, midpiece and tail. Beside each label, note the composition, and function of each sperm structures.
acrosome:(composition & function) penetrating device containing digestive enzymes
head:(composition & function) genetic region, nucleus
midpiece:(composition & function) contains mitochondria which provide ATP
tail:(composition & function) contactile filaments (locomotor region)
The lifespan of a sperm is very short? What anatomical characterists might lead you to suspect this even if you don't know it's life span?
No cytoplasm in which to store nutrients.
The sequence of events leading to germ cell formation in the female begins during fetal development, by the time the child is born, all viable oogonia have been converted to
primary oocytes
How does the total germ cell potential of the female compare to that of the male?
much smaller, and the total number is predetermined
Female gametes develop n structures called follicles. What is a follicle?
A saclike structure containing follicle cells in one or more layers that enclose a developing gamete.
How are primary and vesicular follicles anatomically different?
Primary follice=primary oocyte; a single layer of cuboidal/columnar follicle cellsSecondary follice=several layers of cuboidal/columnar cells collectively called the membranous granulosa which secrete follicular fluid
What is a corpus luteum?
It is what's left of the follicle after a woman ovulates. Glandular ovarian structure that produces progesterone. The ruptured vescicular follicle is converted to corpus leuteum.
What is the major hormone produced by the vesicular follicle?
Estrogen
What is the major hormone produced by the corpus luteum?
Progesterone (and some estrogen)
The cell type you would find forming part of the primary follicle in the ovary
primary oocyte
The cell type you would find in the uterine tube before fertilization
secndary oocyte
The cell type you would find in the mature vesicular follicle of the ovary
secondary oocyte
The cell type you would find in teh uterine tube shortly afer sperm penetration
ovum
The cellular product of spermatogenesis is four _____________; the final product of oogenesis is one ________ and three ____________
spermatids, ovum, polar bodies.
What is the function of the unequal result of oogenesis in the female?
to provide the ovum or functional gamete w/adequate nutritional reserves so that it can survive it;s journey to the uterus.
What is the fate of the 3 tiny cells producted during oogenesis? Why?
They will deteriorate; they lack sustaining cytoplasm w/nutrient reserves.
The hormone produced by primary follicles in the ovaries
FSH
Ovulation occurs after it's burstlike release
LH
Exert negative feedback on the anterior pituitary relative to FSH secretion
Estrogen and progesterone
Stimulates LH release by the anterior pituitary
Estrogen
Stimulates the corpus leuteum to produce progesterone and estrogen
LH
Maintains the hormonal production of the corpus luteum in a non pregnant woman
LH
Why does the corpus luteum deteriorate toward the end of the ovarian cycle?
Because blood levels of the anterior pituitary hormone LH are very low
The amount of LH in the blood during meses is greater than or less than the amount of LH in the blood at ovulation?
less than
The amount of FSH iin the blood on day 6 of the cycle is greater than or less than the amount of FSH in the blood on day 20 of the cycle
greater than
The amount of estrogen in the blood during menses is greater or lesser than the amount of estrogen in the blood at ovulation?
less than
The amount of progesterone in the blood on day 14 is less than or greater than the amount of progesterone in the blood on day 23?
less than
The amount of estrogen in the blood on day 10 is greater than or less than the amount of progesterone in the blood on day 10?
greater than
What uterine tissue undergoes dramatic changes during the menstrual cycle?
endometrium
When during the female menstruaol cycle would fertilization be unlikely? Explain why?
Anytime but the three-day interval (days 14-16) around ovulation (28 day cycle assumed)
Assume that a woman could be an "on demand" ovulator like the rabbit, in which copulation stimulates the hypothalamic-anterior pituitary axis and causes LH release, and an oocyte was ovulated and fertilized on day 26 of her 28-day cycle. Why would a successful pregnancy be unlikely at this time?
The uterine lining goes through a cycle of building up every cycle to accept an embryo. By the time day 26 comes along, the lining is getting ready to slough off during the next period. Most likely the lining of the uterus would not be able to support the implantation and development of the embryo at this time.