What is the:
Hard, calcified, and matrix containing many collagen fibers
Osseous connective tissue
aka bone
Osteocytes lie in
Lacunae
Bones are very well ____________
vascularized
The framework of the body is
skeleton
The skeleton is constructed of 2 of the most supportive tissues in the human body
cartilage and bone
The skeleton is predominately composed of
___________ : in embryo
___________ : in adults
hyaline cartilage
rigid bones
Cartilage persists only in __________ areas.
Isolated.
(external ears, bridge of nose, larynx, trachea, joints, and parts of the rib cage)
Bones are connected at the __________ or _________.
joints or articulation
skeleton is subdivided into 2 groups
axial and appendicular
How many bones are found in an adult body?
206 (WOAHHH!)
Skeletons are composed of 2 basic tissues that differ in texture:
Compact and Spongy
texture of compact bone
Smooth and homogeneous
What are spongy bones composed of?
small trabeculae (bars) of bones
and lots of open space
4 groups of bones:
long
short
irregular
flat
General characterstics of Long bone:
- much _________ than they are wide.
- consists of _______ with heads at either ____.
- composed predominantly of _________ bone.
- much LONGER than they are WIDE.
- consists of SHAFTS with HEADS at either ENDS.
- composed predominantly of COMPACT bone.
Short bones are typically _______ shaped.
Contain more _____ bone than compact bone.
- cube
- spongy
Flat bones are generally thin.
They have 2 wafer-like layers which is composed of:
2 layers of compact bones with a layer of spongy bone in between.
Although flat bone implies a flat surface, many bones are ________.
curved
Bones that do not fall into the long, short or flat category, fit into _________
irregular bones
special types of short bones formed in tendons are called ___________
sesamoid bone
tiny bones found between cranial bones are called ________ or wormian
sutural bones or wormian
the markings on the bone reveal:
- where the bones form ______ with other bones,
- where muscles, tendons, and ligaments were ______,
- where __________ and __________ passed
- where the bones form joints with other bones,
- where muscles, tendons, and ligaments were attached,
- where blood vessels and nerves passed
Anatomy of a long bone:
- Shaft is called - ___________
- diaphysis
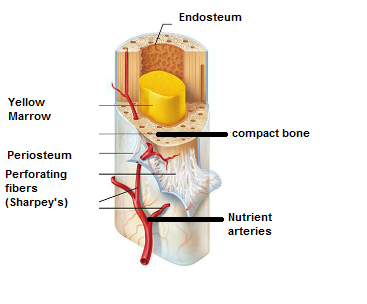
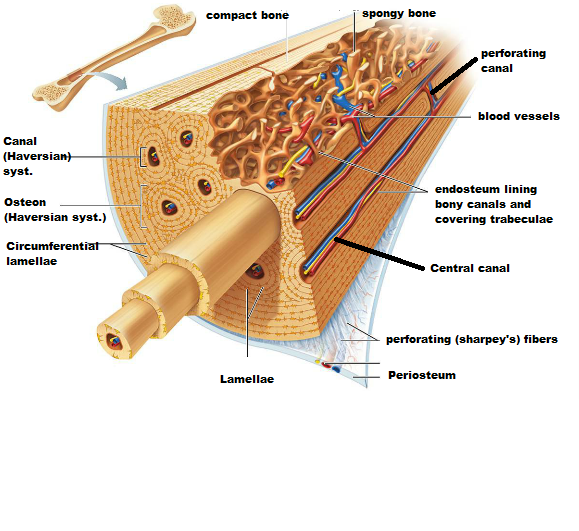
- A fibrous membrane covering the bone surface -________
periosteum
- Fibers of the periosteum penetrating into the bone- ___________________________
Perforating (Sharpey's) fibers
Blood vessel and nerves travel through the ___________ and invade the bone
periosteum
- end of the long bone - _____________________
epiphysis
- A glassy hyaline cartilage that covers the epiphyseal surface in place of the periosteum - _________________
articular cartilage
Articular cartilage prevents _________ at joint surfaces.
friction
A thin area of hyaline cartilage that provides for longitudal growth of the bone during youth.
Epiphyseal plate
Once the bone has stopped growing, the plates are replaced with bone and appear as thin and barely discernible remnants-
Epiphyseal line
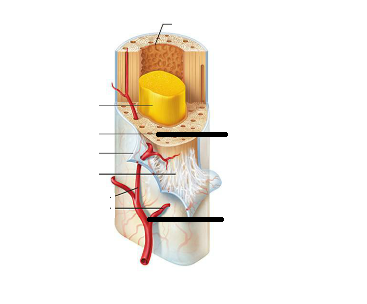
In adults, The central cavity or the medullary cavity of the shaft is a storage region for adipose tissue or _____________ marrow
yellow marrow
In infants, the central cavity or the medullary cavity of the shaft is involved in forming blood cells, so __________ marrow is found.
red marrow
In adults the red marrow is confined to the interior of ___________.
Epiphyses (occupies the spaces b/w the trabeculae of spongy bone)
Endosteum covers the -
__________ of spongy bones
lines the canals of _________ bone
trabeculae
canals of compact bone
Periosteum and Endosteum both contains ___________ and ____________.
Osteoblasts and Osteoclasts
An abnormally thin epiphyseal plate indicates growth ________
retardation
The hardness of the bone is due to the inorganic ___________ salts deposited in its ground substances
Inorganic calcium salts
Bones flexibity comes from the _________ elements f the matrix
organic elements of the matrix.
(collagen fibers)
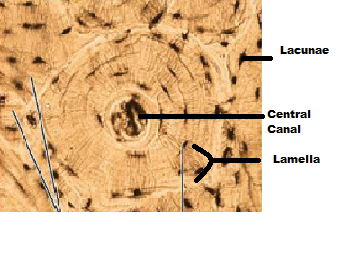
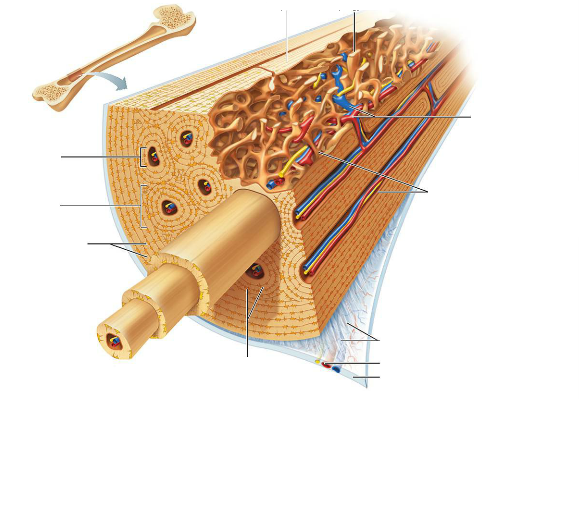
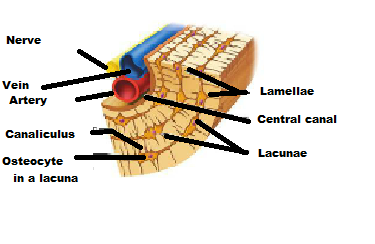
Identify the microscopic structures of compact bone:
A canal that runs parallel to the long axis of the bone and carries blood vessels, nerves, and lymph vessels through the bony matrix
Central (Harversian) Canal
Identify the microscopic structures of compact bone:
- mature bone cells: ___________
- the mature bone cells are located in chambers called: ____________
osteocytes
lacunae
Identify the microscopic structures of compact bone:
Lacunae are arranged in concentric circles around the central canal
circumferential lamellae
Identify the microscopic structures of compact bone:
A central canal and all the concentric lamellae surrounding it are referred to as ______ or _________ system
Osteon or Haversian system
Identify the microscopic structures of compact bone:
Tiny canals radiating outward from a central canal to the lacunae of the first lamella and then from lamella to lamella.
Canalicli
Identify the microscopic structures of compact bone:
Canals that run into the compact bone and marrow cavity from the periosteum at right angle to the shaft
Perforating (Volkmann's) Canal
Location of Articular cartilage
covers the bone ends at movable joints
Location of Costal cartilage
found connecting the ribs to the sternum (breastbone)
Location of Laryngeal cartilage
largely constructs the larynx (voice box)
Location of Tracheal and Bronchial cartilages
reinforces other passageway of the respiratory system
Location of Nasal cartilages
supports the external nose
Location of Invertebral discs
seperates and cushions the vertebrae
Cartilage tissues contain NO ____________ or __________
nerves or blood vessels
Cartilage is surrounded by a covering of dense connective tissue called a _____________
perichondrium
Perichondrium resists __________________ and also plays a role in _______ and __________.
distortion (under pressure)
growth and development
3 types of Cartilage tissues
Hyaline
Elastic
Fibrocartilage
Cartilage tissue that looks like frosted glass.
Most abundant.
Provides sturdy support.
Hyaline cartilage
Cartilage tissue that is known as "hyaline cartilage with more elastic fibers."
More flexible than hyaline cartilage.
Cartilages of external ears and epiglottis.
Elastic cartilage
Fibrocartilage consists of rows of __________ alternating with rows of thick _________ ________.
rows of CHONDROCYTES and rows of thick COLLAGEN FIBERS
Fibrocartilage tissue looks like a hybrid of 2 types of tissues...
CARTILAGE and DENSE REGULAR CONN. TISSUE
Why are fibrocartilages used to contruct the invertebral discs and cartilages within the knee joints?
they have great tensile strength and withstand heavy compression

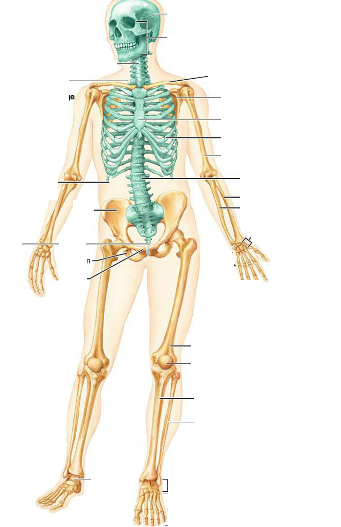
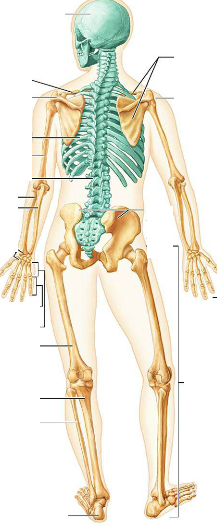
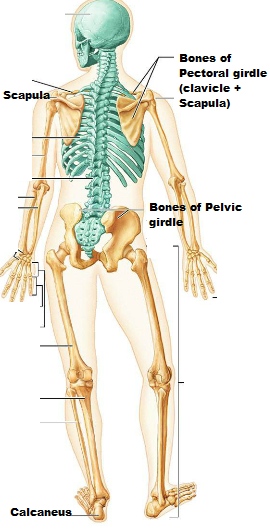
What color are the Axial bones represented in this picture?
What about Appendicular bones?
Axial- Green
Appendicular- Tan
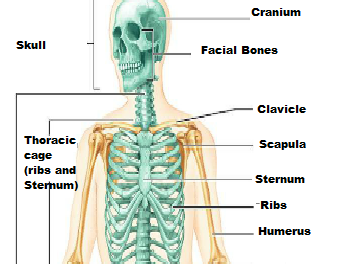
Identify the parts.
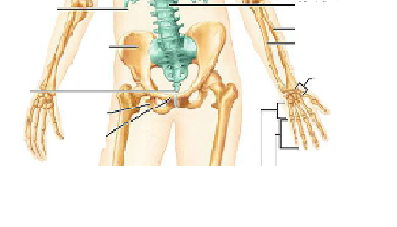
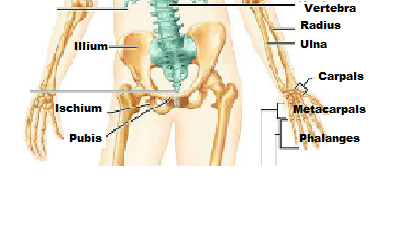
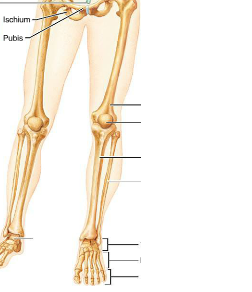
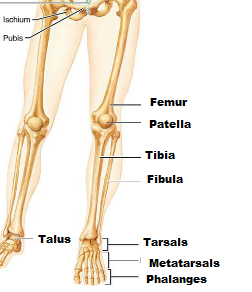
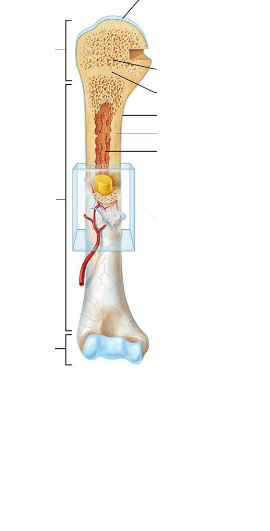
Identify the parts of the long bone
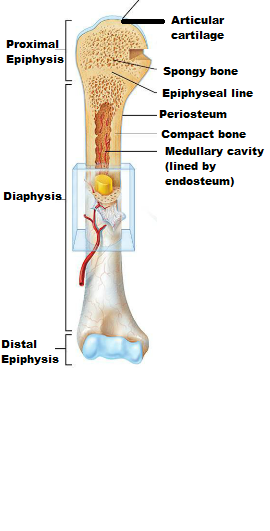
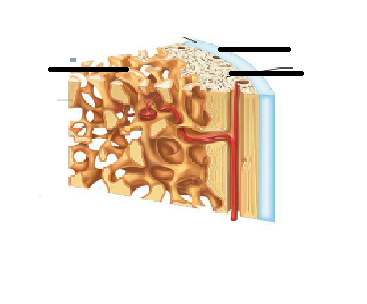
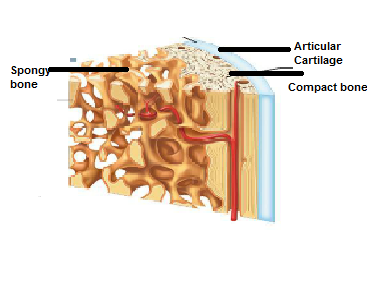
A 3-D view of spongy bone and compact bone of the Epiphysis
Projections that are sites of muscle and ligament attachments.
tuberosity
crest
trochanter
line
tubercle
epicondyle
spine
process
Large rounded projection; may be roughened.
Tuberosity
Narrow ridge of bone; usually prominent
Crest
Very large, blunt, irregularly shaped process
Trochanter
Narrow ridge of bone; less prominent than crest
Line
Small rounded projection or process
Tubercle
Raised area, on or above a condyle
Epicondyle
Sharp, slender, often pointed projection
Spine
Projections that help to form joints
Head
Facet
Condyle
Ramus
Bony expansion carried on a narrow neck
Head
Smooth, nearly flat articular surface
Facet
Rounded articular projection
Condyle
Armlike bar of bone
Ramus
space within a bone, filled with air and lined with mucous membrane
Sinus
Depressions and openings allowing blood vessels and nerves to pass
Meatus
Fossa
Groove
Fissure
Foramen
canal- like passageway
Meatus
Shallow, basin- like depression in a bone, often serving as an articular surface
fossa
furrow
groove
narrow, slitlike opening
Fissure
Round or oval opening through a bone
foramen
The 4 major anatomical classifications of bones are long, short, flat, and irregular.
Which category has the least amount of spongy bone relative to its total volume?
Long bone
Femur, Humerus, Tibia, Fibula,Radius, Ulna, Metacarpals, Metatarsals, and Phalanges are examples of ________ bone.
Long bone
carpals and tarsals are ____ bones.
Short
Scapula, Sternum, Cranium, Coxal, Pelvis, and Ribs are ________ bones
Flat
Vertebrae, sacrum, and mandible are ______ bones
Irregular
Periosteum is the attachement point of what.
tendons and ligaments thru tendons and ligaments
Route taken by nutrients through a bone starting with periosteum and ending with osteocytes
Periosteum -> Perforating canals -> central canals -> canaliculi -> Lancunae -> Osteocytes
organic matrix in bone gives bone...
flexibility and strength
inorganic material in bone gives bone...
hardness and compressional strength