Which structure helps regulate the temperature of the testes?
Cremaster muscles
Which structure is the site of sperm production?
Seminiferous tubules
How many seminiferous tubules are found in each lobule?
1-3
Which of the following cells may eventually become spermatoza?
Spermatogonia
Which cells secrete testosterone?
Leydig cells
Which hormone stimulates Leydig cells to secrete testosterone?
LH
The straight tubules in the testis lead into the
rete testis
The function of the epididymis is
sperm maturation
Which structure is formed by the union of the duct from the seminal vesicle and the ampulla of the vas deferens?
ejaculatory duct
Which structure lies posteriorly to the bladder and anterior to the rectum and secretes an alkaline, fructose filled fluid?
seminal vesicles
Which of the following structures are located inferior to the prostate on either side of the membranous urethra within the deep muscles of the perineum?
bulbourethral glands
Which structure is composed of three cylindrical masses of erectile tissue each surrounded by a fibrous tissue?
penis
Which ligament arises from the pubic symphysis in males?
suspensory ligament
Which of the following are produced in and released from the ovaries?
secondary ooctyes, estrogen and progesterone
Which structure attaches the ovaries and the uterus to the pelvic wall?
suspensory ligament
Which of the following is the site of fertilization?
uterine tubes
Which part of the uterus opens into the vagina?
cervix
Anterior to the vagina and urethral openings is the
mons pubis
Paraurethral (Skene's) glands secrete
mucus
Which hormone promotes the final step of spermatogensis?
Testoterone
Which hormone triggers ovulation?
LH
Which hormone is secreted by the corpus luteum after ovulation?
progesterone
The uterine phase where the thickness of the endometrium doubles is the
proliferative phase
The ovarian phase between the end of menstruation and beginning of ovulation is the
preovulatory phase
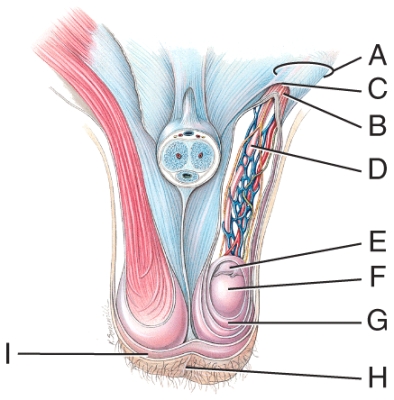
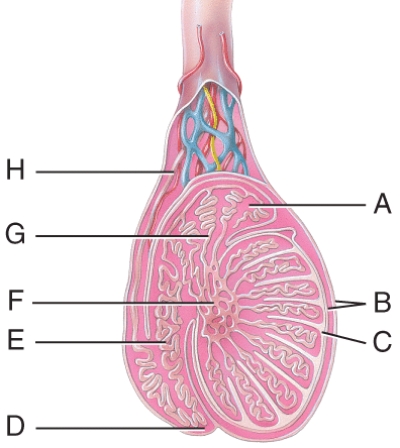
The septum of the scrotum is made up of a cutaneous layer and which muscle tissue in this figure?
E) I

What does line "A" point to in this figure?
spermatic cord

Which structure in this figure has a portion removed in a vasectomy?
B) D

What does the line "G" point to in this figure?
tunica vaginalis
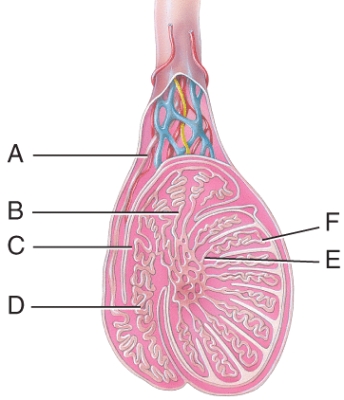
What does the line "C" point to in this figure?
body of epididmysis

Where are the straight tubules in this figure?
E) E

What is the line "F" pointing to in this figure?
seminiferous tubules
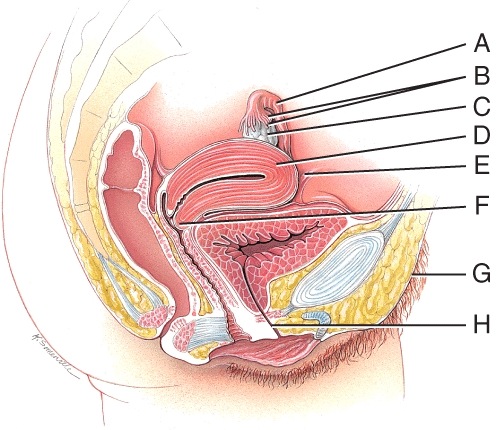
Which structure in this figure is part of the connective tissue structures that anchor the uterus within the pelvic cavity?
C) E

What is the line "C" pointing to in this figure?
ovary

In this figure, where is the site for implantation of a fertilized ovum?
D) D

In this figure, which line represents the part of the uterus that opens into the vagina?
B) F
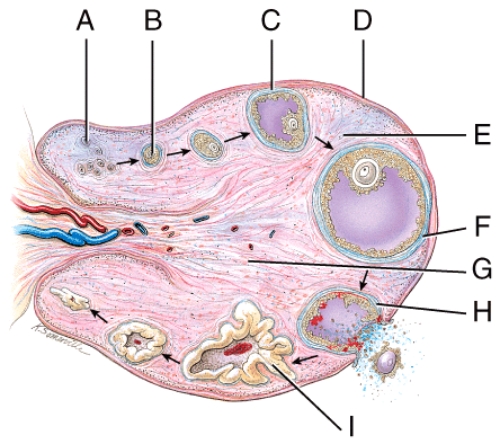
Which letter in this figure represents a primary oocyte that is surrounded by several layers of cuboidal granulosa cells?
B) B

Where in this figure is the mature ovarian follicle?
D) F

Where in this figure is the corpus albicans?
none of these choices

Which structure in the figure will produce progesterone, estrogens, relaxin and inhibin?
D) I
A forty year old woman experiences breast tenderness, slight swelling and some lumpiness each month during the third week of the menstrual cycle. She is most likely suffering from-
fibrocystic breast disease
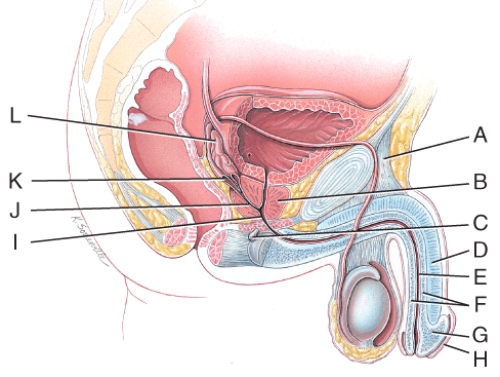
At which location in the figure do sperm and seminal vesicle secretions first join together in their path to the exterior?
B) J

Which structure in the figure secretes seminal plasmin, proteolytic enzymes like pepsin, lysozyme and citric acid?
C) B

Which structure in the figure secretes an alkaline fluid that protects sperm by neutralizing acids in the urethra?
A) C

Which structure in the figure together secrete liquid components of semen?
D) B, C, L

Which structure in the figure is the corpus spongiosum penis?
A) F
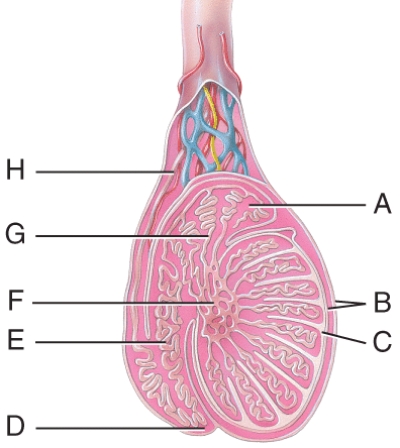
Which structure in the figure is a serous membrane derived from the peritoneum during descent of the testes?
A) B

Which structure in the figure is made of dense irregular connective tissue that forms septa dividing the testes into lobules?
B) C

Mature sperm arrive at the efferent ducts in the epididymis immediately from which structure in this figure?
C) F
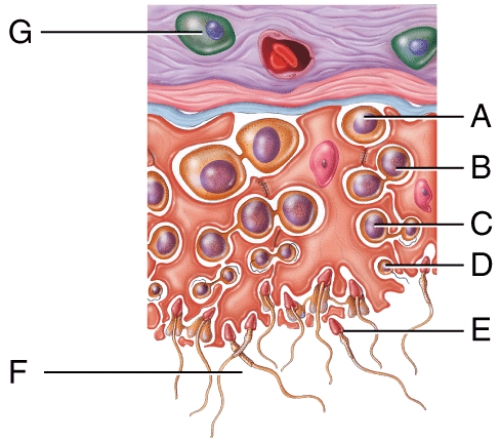
Which cell in the figure contains a diploid nucleus?
A) A
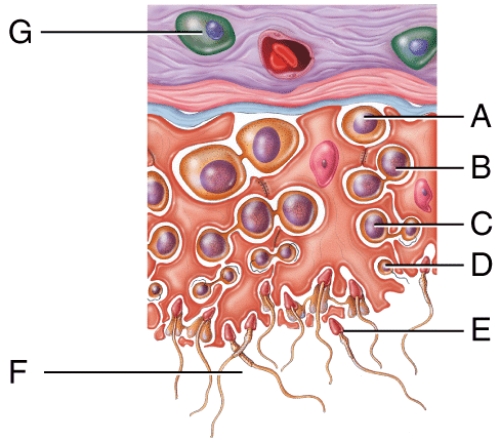
Where in this figure will you find mature sperm?
B) E

Which cell in the figure is actively secreting testosterone?
A) G
Where in the figure is the tail of the epididymis?
E) D

Which list below lists cells in the figure that all contain haploid nuclei?
C) C, E, F

The cell labelled H in the figure secretes which of the following hormones?
E) Testosterone
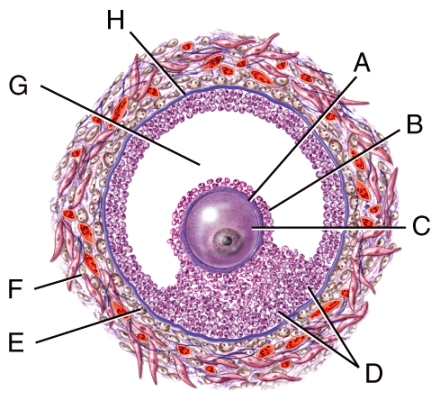
Which structure in the figure is filled with follicular fluid?
B) G
Postmenopausal woman tend to experience a degree of vaginal dryness. Which part of the reproductive system is most directly linked to this condition?
C) Bartholin's glands

Which structure in the figure is the theca INterna?
C) E

Which structure in the figure is the theca EXterna?
E) F

Which structure in the figure is the zona pellucida?
A) A

Which structure in the figure is the basement membrane?
E) H
Menarche is
the first menses
The male reproductive system arises from
mesonephric (Wolffian) ducts
The female reproductive system arises from
paramesonephric (Mullerian) ducts
During fetal development, which cells give rise to primary oocytes?
oogonia
The major hormone secreted from granulosa cells is
estrogen
A zygote is
a diploid fertilized ovum
Which hormone inhibits the release of FSH from the pituitary gland?
Inhibin
In male embryos, which hormone is responsible for the development of the urethra, prostate, and external genitals?
dihydrotesterone
Which of the following is a fungal disease of the reproductive system?
candidiasis
Which of the following is NOT a sexually transmitted disease?
all of these are sexually transmitted diseases
Which of the following is NOT a contribution of the reproductive system to the body?
Lowering blood cholesterol levels in males under the age of 50
Which of the following is the male pattern of development "master switch" gene?
SRY
In the female embryo, the absence of dihydrotesterone leads to the development of what structures?
A, B, C (clitoris, labia minora, labia majora)
The onset of puberty is marked by pulses of what hormones?
C, D, E (LH, FSH, GnRH)
In the female embryo, the absence of ___ gene causes the gonadal ridges to develop into ovaries.
SRY
The leading cause of death in cancer in men in the United States is
prostate cancer
The most common cancer in males between the ages of 20 and 35 is
testicular cancer
Breast cancer in women in the United States is the second-leading cause of death after which type of cancer?
lung
The most effective technique for detecting breast tumors less than 1 cm in diameter is
mammography
In the male embryo, dihydrotesterone stimulates the development of what structures?
B, C, D, E (urethra, prostate gland, scrotum, penis)