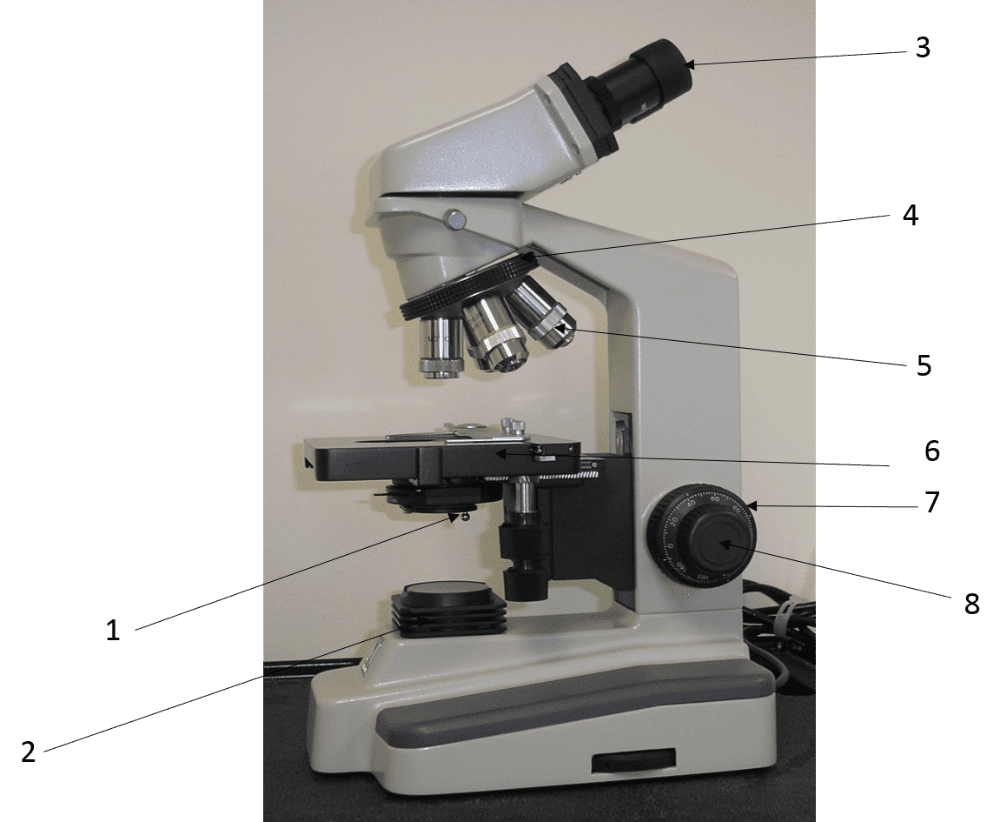
1.
Condenser

2.
Substage Light

3.
Ocular Lens

4.
Rotating Nosepiece

5.
Objective Lens

6.
Mechanical Stage

7.
Coarse Adjustment Knob

8.
Fine Adjustment Knob
Focuses the light to the slide
Condenser
It always has a 10x magnification
Ocular Lens
It has the slide holder on it
Mechanical Stage
Helps find the slide through the ocular lens
Coarse Adjustment Knob
Parfocal microscope
Stays in focus
Magnification of the lens
Enlargement
Resolution power of the lens
Clarity
Field of view
What you can see through the ocular lens
What is the total magnification if your objective lens has 40x maginifcation?
4
40
400
4000
400
What is the total magnification if your objective lens has 100x maginifcation?
1000
100
10
1
1000
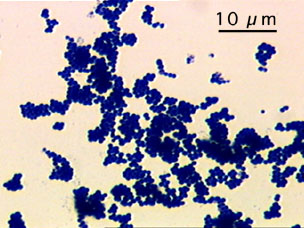
Name the bacteria based on the shape you can see on the picture.
Coccus
Bacillus
Spirillum
Streptococcus
Staphylococcus
Coccobacillus
Staphylococcus

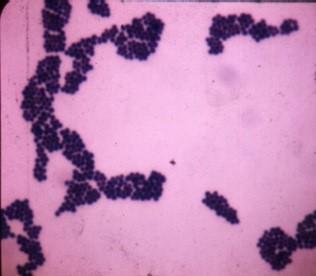
Name the bacteria based on the shape you can see on the picture.
Coccus
Bacillus
Spirillum
Streptococcus
Staphylococcus
Coccobacillus
Streptobacillus
Bacillus
When I see only 1 color on the slide (methylene blue or crystal violet), it is a differential staining.
True/False
False
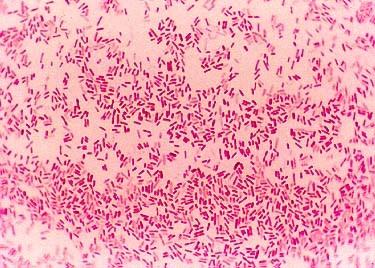
The color is purple, this is a Gram + staining.
True/False
True
The color is pink, this is a Gram + staining.
True/False
False
What is the basis of Gram staining?
Capsule
Cell membrane
Outer membrane
Cell wall
Cell Wall
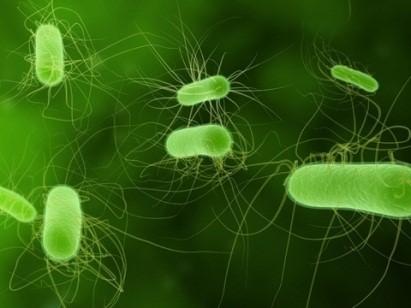
This is an electron microscopic picture. What kind of structure this bacteria have?
Pili
Flagella
Cilia
Pseudopod
Flagella

What is the function of this structure?
feeding
catching prey
attaching to surfaces
movement
movement
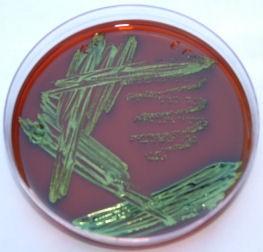
Which media would you use to grow G- fecal microbes?
Mannitol salt
Phenyl ethyl alcohol
EMB
Blood agar
EMB
Which bacteria did grow on this media if you see metallic shine green, blue or black color?
E. coli
Enterobacter
Non fermenter enteric
Staphylococcus aureus
E. coli
Approximately what percentage of DNA codes for genes?
1-2%
Which enzyme fills in the spaces between the Okazaki fragments with the correct nucleotides?
DNA ligases
Where do you find the OKAZAKI segment?
On the lagging strand
How do prokaryotic cell differs from eukaryotic cells with regard to transcription and translation?
They happen in the cytoplasm one after another
Which organ is responsible for metabolizing and detoxifying foreign chemicals in the blood, including drugs?
Liver
Physical agents for controlling microbial growth include all of the following, except:
hydrogen peroxide
Which of the following microbial forms have the highest resistance to physical and chemical controls?
bacterial endospores
The process that destroys or removes all microorganisms and microbial forms including bacterial endospores is:
sterilization
The use of a physical or chemical process to destroy vegetative pathogens is:
disinfection
Which is correct regarding the rate of microbial death?
A. cells die at increasingly greater rates
B. only older cells die in a culture
C. cells in a culture die at a constant rate
D. upon contact with the control agent, all cells die at one time
E. cells become metabolically inactive but are never killed
C. cells in a culture die at a constant rate
Sterilization is achieved by:
A. flash pasteurization.
B. hot water.
C. boiling water.
D. steam autoclave.
E. All of the choices are correct.
D. steam autoclave.
Dry heat:
A. is less efficient than moist heat.
B. cannot sterilize.
C. includes tyndallization.
D. is used in devices called autoclaves.
E. will sterilize at 121° C for 15 minutes.
A. is less efficient than moist heat.
The shortest time required to kill all the microbes in a sample at a specified temperature is called the:
A. thermal death point (TDP).
B. thermal death time (TDT).
C. sporicidal time.
D. death phase point.
E. None of the choices are correct.
B. thermal death time (TDT).
Which of the following chemicals is a disinfectant for soft contact lenses?
A. hydrogen peroxide
B. alcohol
C. hexachlorophene
D. glutaraldehyde
E. hypochorites
A. hydrogen peroxide
Substances that are naturally produced by certain microorganisms that can inhibit or destroy other microorganisms are called
A. antibiotics.
B. narrow-spectrum drugs.
C. semisynthetic drugs.
D. synthetic drugs.
E. broad-spectrum drugs
A. antibiotics.
Antimicrobics effective against a wide variety of microbial types are termed
A. antibiotics.
B. narrow-spectrum drugs.
C. semisynthetic drugs.
D. synthetic drugs.
E. broad-spectrum drugs.
E. broad-spectrum drugs.
Antibiotics are derived from all the following except
A. Penicillium.
B. Bacillus.
C. Staphylococcus.
D. Streptomyces.
E. Cephalosporium.
C. Staphylococcus.
Penicillins and cephalosporins
A. interfere with DNA synthesis.
B. are metabolic analogs of PABA and block folic acid synthesis.
C. attach to the 30S ribosomal subunit and disrupt protein synthesis.
D. damage cell membranes.
E. block the peptidases that cross-link glycan molecules.
E. block the peptidases that cross-link glycan molecules.
Sulfonamides
A. interfere with elongation of peptidoglycan.
B. are metabolic analogs of PABA and block folic acid synthesis.
C. attach to the 30S ribosomal subunit and disrupt protein synthesis.
D. damage cell membranes.
E. block peptidases that cross-link glycan molecules.
B. are metabolic analogs of PABA and block folic acid synthesis.
Aminoglycosides
A. interfere with elongation of peptidoglycan.
B. are metabolic analogs of PABA and block folic acid synthesis.
C. attach to the 30S ribosomal subunit and disrupt protein synthesis.
D. damage cell membranes.
E. block peptidases that cross-link glycan molecules.
C. attach to the 30S ribosomal subunit and disrupt protein synthesis.
Ampicillin, amoxicillin, mezlocillin, and penicillin G all have
A. a beta-lactam ring.
B. resistance to the action of penicillinase.
C. a semisynthetic nature. D. an expanded spectrum of activity.
E. All of the choices are correct.
A. a beta-lactam ring.
Which of the following is being used to replace hypochlorites in treating water because of the possibility of cancer-causing substances being produced?
A. hydrogen peroxide
B. chloramines
C. fluorine
D. quaternary ammonium compounds
E. sodium iodide
B. chloramines
An antiviral that is a guanine analog would have an antiviral mode of action that
A. blocks penetration.
B. blocks DNA replication.
C. inhibits peptidoglycan cross linking.
D. blocks maturation.
E. bonds to ergosterol in the cell membrane.
B. blocks DNA replication.
Acyclovir is used to treat
A. influenza A virus.
B. HIV.
C. shingles, chickenpox, and genital herpes.
D. respiratory syncytial virus.
E. hepatitis C virus.
C. shingles, chickenpox, and genital herpes.
The most versatile and useful antifungal drug that is used to treat serious systemic fungal infections is
A. nystatin.
B. griseofulvin.
C. amphotericin B.
D. sulfa drugs.
E. metronidazole.
C. amphotericin B.
The duplication of a cell's DNA is called
Replication
Which enzyme fills in the spaces between the Okazaki fragments with the correct nucleotides?
DNA ligases
The site where the old DNA strands separate and new DNA strands will be synthesized is called the
replication fork
Eukaryotic chromosomes differ from prokaryotic chromosomes because only eukaryotes have
histone proteins.
chromosomes in a nucleus.
several to many chromosomes.
elongated, not circular, chromosomes.
All of the choices are correct.
Semiconservative replication refers to
an original parent DNA strand and one newly synthesized DNA strand comprising a new DNA molecule.
A sequence of bases on a gene that does not code for protein is called a/an
intron
The nontranscribed region of DNA to which RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription is called the
promoter
The RNA molecules that carry amino acids to the ribosomes during protein synthesis are called
transfer RNA
All of the following pertain to transcription except it
occurs on a ribosome in the cytoplasm
This molecule is transcribed from the DNA template strand and later translated
messengerRNA
The use of a physical or chemical process to destroy vegetative pathogens is
disinfection.
sterilization.
antisepsis.
sanitization.
degermation.
disinfection.
Sterilization is achieved by
flash pasteurization.
hot water.
boiling water.
steam autoclave.
All of the choices are correct.
steam autoclave.
Which is correct regarding the rate of microbial death?
cells die at increasingly greater rates
only older cells die in a culture
cells in a culture die at a constant rate
upon contact with the control agent, all cells die at one time
cells become metabolically inactive but are never killed
cells in a culture die at a constant rate
Which of the following types of control agents would be used to achieve sterility?
virucide
bactericide
germicide
sporicide
fungicide
sporicide
The process of using a cleansing technique to mechanically remove and reduce microorganisms and debris to safe levels is
disinfection.
sterilization.
antisepsis.
sanitization.
degermation.
sanitization.
Alcohols denature proteins when
in a 50 - 95% alcohol-water solution.
disinfect items soaked in alcohol.
are skin degerming agents.
at 50% or higher concentrations dissolve cell membrane lipids.
All of the choices are correct.
All of the choices are correct.
Which of the following is not used as an antiseptic?
iodophor
chlorhexidine
3% hydrogen peroxide
Merthiolate
aqueous glutaraldehyde
aqueous glutaraldehyde
All of the following are benefits of food irradiation except
it can kill bacterial pathogens on the food.
it can kill insects on the food.
it can inhibit the sprouting of white potatoes.
it can reduce the number of food-borne deaths each year.
it makes the food less nutritious.
it makes the food less nutritious.
Which of the following is being used to replace hypochlorites in treating water because of the possibility of cancer-causing substances being produced?
hydrogen peroxide
chloramines
fluorine
quaternary
ammonium compounds
sodium iodide
chloramines
All of the following are correct about food irradiation except
food is not made radioactive by the process.
the World Health Organization does not endorse this process.
it is approved in the U.S. for beef, chicken and pork.
it can lead to a longer shelf life for the irradiated food.
no irradiated food can be sold without clear labeling.
the World Health Organization does not endorse this process.
Ampicillin, amoxicillin, mezlocillin, and penicillin G all have
a beta-lactam ring.
resistance to the action of penicillinase.
a semisynthetic nature.
an expanded spectrum of activity.
All of the choices are correct.
a beta-lactam ring.
Antibiotics are derived from all the following except
Penicillium.
Bacillus.
Staphylococcus.
Streptomyces.
Cephalosporium.
Staphylococcus.
Sulfonamides interfere with
elongation of peptidoglycan.
are metabolic analogs of PABA and block folic acid synthesis.
attach to the 30S ribosomal subunit and disrupt protein synthesis.
damage cell membranes.
block peptidases that cross-link glycan molecules.
are metabolic analogs of PABA and block folic acid synthesis.
Penicillins and cephalosporins
interfere with DNA synthesis.
are metabolic analogs of PABA and block folic acid synthesis.
attach to the 30S ribosomal subunit and disrupt protein synthesis.
damage cell membranes.
block the peptidases that cross-link glycan molecules.
block the peptidases that cross-link glycan molecules.
A chemical that inhibits beta-lactamase enzymes is
synercid.
penicillinase.
aztreonam.
clavulanic acid.
imipenem.
clavulanic acid.
Which antimicrobic does not inhibit cell wall synthesis?
gentamicin
vancomycin
cephalosporins
penicillins
clavamox
gentamicin
Which of these drugs is useful in treating infections by methicillin-resistant S. aureus and vancomycin-resistant
Enterococcus?
tetracycline
isoniazid
linezolid
aminoglycosides
cephalosporins
linezolid
The drug that can cause aplastic anemic, and is used to treat typhoid fever and brain abscesses is
chloramphenicol.
clindamycin.
ciprofloxacin.
bacitracin.
gentamicin.
chloramphenicol.
This drug is used to treat cases of tuberculosis
penicillin G.
vancomycin.
aminoglycosides.
synercid.
isoniazid.
isoniazid.
Drug susceptibility testing
determines the patient's response to various antimicrobics.
determines the pathogen's response to various antimicrobics.
determines if normal flora will be affected by antimicrobics.
determines if the drug is increasing to toxic levels in a patient.
determines the pathogen's identity.
determines the pathogen's response to various antimicrobics.
There are fewer antifungal, antiprotozoan, and antihelminth drugs compared to antibacterial drugs because
these organisms do not cause many human infections.
are not affected by antimicrobics.
are so similar to human cells that drug selective toxicity is difficult.
are parasites found inside human cells.
have fewer target sites compared to bacteria.
are so similar to human cells that drug selective toxicity is difficult.
An antiviral that is a guanine analog would have an antiviral mode of action that
blocks penetration.
blocks DNA replication.
inhibits peptidoglycan cross linking.
blocks maturation.
bonds to ergosterol in the cell membrane.
blocks DNA replication.
Which antimicrobic does not interfere with protein synthesis?
aminoglycosides
tetracyclines
erythromycin
trimethroprim
chloramphenicol
trimethroprim
The most versatile and useful antifungal drug that is used to treat serious systemic fungal infections is
nystatin.
griseofulvin.
amphotericin B.
sulfa drugs.
metronidazole.
amphotericin B.
Side effects that occur in patient tissues while they are on antimicrobic drugs include all the following except
development of resistance to the drug.
hepatotoxicity.
nephrotoxicity.
diarrhea.
deafness.
development of resistance to the drug.
The cellular basis for bacterial resistance to antimicrobics include
bacterial chromosomal mutations.
synthesis of enzymes that alter drug structure.
prevention of drug entry into the cell.
alteration of drug receptors on cell targets.
All of the choices are correct.
All of the choices are correct.
A "shotgun" approach to antimicrobial therapy involves giving a narrow spectrum drug.
culturing the pathogen and identifying it.
performing the disk diffusion assay.
using a broad spectrum drug so that the chance of killing the pathogen is greater.
using antiviral and antibiotic drugs in combination.
using a broad spectrum drug so that the chance of killing the pathogen is greater.
Which of the following is not a mode of action of antivirals?
block penetration
block transcription and translation
inhibit DNA synthesis
block maturation
bond to ergosterol in the cell membrane
bond to ergosterol in the cell membrane
All of the following could be reasons why antimicrobic treatment fails except the inability of the drug to diffuse into the infected body compartment.
a mixed infection where some of the pathogens are drug resistant.
not completing the full course of treatment.
a disk diffusion test showing pathogen sensitivity to the antimicrobic.
diminished gastrointestinal absorption due to an underlying condition or age.
a disk diffusion test showing pathogen sensitivity to the antimicrobic.
Antivirals that target reverse transcriptase would be used to treat influenza A virus.
HIV.
herpes zoster virus.
respiratory syncytial virus.
hepatitis C virus.
HIV.