The basis of the VSEPR model of molecular bonding is
________.
A) regions of electron density on an atom will organize
themselves so as to maximize s-character
B) regions of electron
density in the valence shell of an atom will arrange themselves so as
to maximize overlap
C) atomic orbitals of the bonding atoms must
overlap for a bond to form
D) electron domains in the valence
shell of an atom will arrange themselves so as to minimize
repulsions
E) hybrid orbitals will form as necessary to, as
closely as possible, achieve spherical symmetry
D
In counting the electron domains around the central atom in VSEPR
theory, a ________ is not included.
A) nonbonding pair of
electrons
B) single covalent bond
C) core level electron
pair
D) double covalent bond
E) triple covalent bond
C
The electron-domain geometry of ________ is tetrahedral.
A)
CBr4
B) PH3
C) CCl2Br2
D) XeF4
E) all of the above
except XeF4
E
Of the following species, ________ will have bond angles of
120°.
A) PH3
B) ClF3
C) NCl3
D) BCl3
E) All
of these will have bond angles of 120°.
D
The molecular geometry of the BrO3- ion is ________.
A)
trigonal pyramidal
B) trigonal planar
C) bent
D)
tetrahedral
E) T-shaped
A
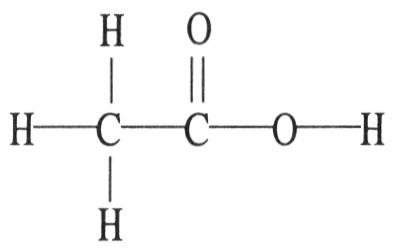
The molecular geometry of the left-most carbon atom in the molecule below is ________.
A) trigonal planar
B) trigonal bipyramidal
C)
tetrahedral
D) octahedral
E) T-shaped
C
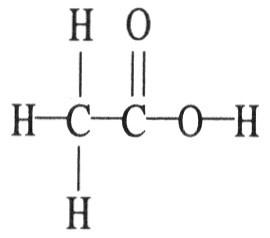
The molecular geometry of the right-most carbon in the molecule below is ________.
A) trigonal planar
B) trigonal bipyramidal
C)
tetrahedral
D) octahedral
E) T-shaped
A
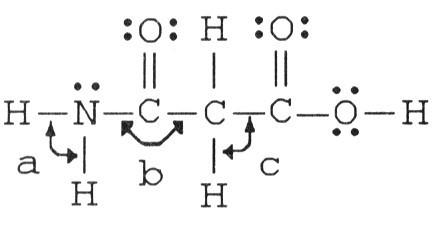
The bond angles marked a, b, and c in the molecule below are about ________, ________, and ________, respectively.
A) 90°, 90°, 90°
B) 120°, 120°, 90°
C) 120°, 120°,
109.5°
D) 109.5°, 120°, 109.5°
E) 109.5°, 90°, 120°
D
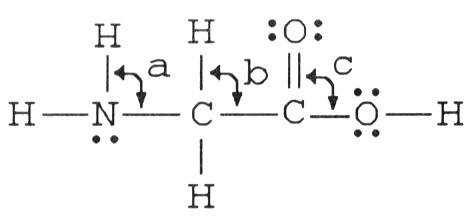
The bond angles marked a, b, and c in the molecule below are about ________, ________, and ________, respectively.
A) 109.5°, 109.5°, 109.5°
B) 120°, 109.5°, 120°
C) 109.5°,
109.5°, 120°
D) 90°, 180°, 90°
E) 109.5°, 109.5°, 90°
C
The central Xe atom in the XeF4 molecule has ________ unbonded
electron pair(s) and ________ bonded electron pair(s) in its valence
shell.
A) 1, 4
B) 2, 4
C) 4, 0
D) 4, 1
E) 4, 2
B
An electron domain consists of ________.
a) a nonbonding pair of electrons
b) a single bond
c) a
multiple bond
A) a only
B) b only
C) c only
D) a, b, and c
E)
b and c
D
The molecular geometry consists of ________.
a) a nonbonding pair of electrons
b) a single bond
c) a
multiple bond
A) a only
B) b only
C) c only
D) a, b, and c
E)
b and c
E
The electron-domain geometry and the molecular geometry of a molecule
of the general formula ABn are ________.
A) never the
same
B) always the same
C) sometimes the same
D) not
related
E) mirror images of one another
C
The electron-domain geometry and the molecular geometry of a molecule
of the general formula ABn will always be the same if
________.
A) there are no lone pairs on the central atom
B)
there is more than one central atom
C) n is greater than
four
D) n is less than four
E) the octet rule is obeyed
A
What is the molecular shape of H2O?
A) T-shaped
B)
tetrahedral
C) linear
D) trigonal pyramidal
E) bent
E
PCl5 has ________ electron domains and a ________ molecular
arrangement.
A) 6, trigonal bipyramidal
B) 6,
tetrahedral
C) 5, square pyramidal
D) 5, trigonal
bipyramidal
E) 6, seesaw
D
For molecules of the general formula ABn, n can be greater than four
________.
A) for any element A
B) only when A is an element
from the third period or below the third period
C) only when A
is boron or beryllium
D) only when A is carbon
E) only when
A is Xe
B
For which of the molecules is the molecular geometry (shape) the same as the VSEPR electron domain arrangement (electron domain geometry)?
(i) BCl3 (ii) CCl4 (iii) TeCl4 (iv) XeF4 (v) SF6
A) (i) and (ii)
B) (i) and (iii)
C) (ii) and (v)
D)
(iv) and (v)
E) (v) only
C
Of the molecules below, only ________ is polar.
(i) BCl3 (ii) CCl4 (iii) TeCl4 (iv) XeF4 (v) SF6
A) CCl4
B) CH4
C) SeF4
D) SiCl4
C
Of the molecules below, only ________ is nonpolar.
(i) BCl3 (ii) CCl4 (iii) TeCl4 (iv) XeF4 (v) SF6
A) BF3
B) NF3
C) IF3
D) PBr3
E) BrCl3
A
Three monosulfur fluorides are observed: SF2, SF4, and SF6. Of these,
________ is/are polar.
A) SF2 only
B) SF2 and SF4
only
C) SF4 only
D) SF6 only
E) SF2, SF4, and SF6
B
The molecular geometry of the PF3 molecule is ________, and this
molecule is ________.
A) trigonal planar, polar
B) trigonal
planar, nonpolar
C) trigonal pyramidal, polar
D) trigonal
pyramidal, nonpolar
E) tetrahedral, unipolar
C
Of the following molecules, only ________ is polar.
A)
BeCl2
B) BF3
C) C
D) SiH2Cl2
E) Cl2
D
Of the following molecules, only ________ is polar.
A)
CCl4
B) BCl3
C) NCl3
D) BeCl2
E) Cl2
C
For molecules with only one central atom, how many lone pairs on the
central atom guarantees molecular polarity?
A) 1
B)
2
C) 1 or 2
D) 3
E) 1 or 3
A
The molecular geometry of the CHF3 molecule is ________, and the
molecule is ________.
A) trigonal pyramidal, polar
B)
tetrahedral, nonpolar
C) seesaw, nonpolar
D) tetrahedral,
polar
E) seesaw, polar
D
The molecular geometry of the BCl3 molecule is ________, and this
molecule is ________.
A) trigonal pyramidal, polar
B)
trigonal pyramidal, nonpolar
C) trigonal planar, polar
D)
trigonal planar, nonpolar
E) trigonal bipyramidal, polar
D
Which of the molecules has a see-saw shape?
(i) BCl3 (ii) CCl4 (iii) TeCl4 (iv) XeF4 (v) SF6
A) (i)
B) (ii)
C) (iii)
D) (iv)
E) (v)
C
Which of the molecules has a square planar shape?
(i) BCl3 (ii) CCl4 (iii) TeCl4 (iv) XeF4 (v) SF6
A) (i) and (ii)
B) (i) and (v)
C) (iii) only
D) (ii)
and (iv)
E) (iv) only
E
The combination of two atomic orbitals results in the formation of
________ molecular orbitals.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D)
4
E) 0
B
Of the following, the central atom is sp3d2 hybridized only in
________.
A) PCl5
B) XeF4
C) PH3
D) Br3-
E) BeF2
B
The sp3d2 atomic hybrid orbital set accommodates ________ electron
domains.
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6
E
The sp2 atomic hybrid orbital set accommodates ________ electron
domains.
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
E) 6
B
The hybridizations of nitrogen in NF3 and NH3 are ________ and
________, respectively.
A) sp2, sp2
B) sp, sp3
C) sp3,
sp
D) sp3, sp3
E) sp2, sp3
D
The hybridizations of iodine in IF3 and IF5 are ________ and
________, respectively.
A) sp3, sp3d
B) sp3d, sp3d2
C)
sp3d, sp3
D) sp3d2, sp3d
E) sp3d2, sp3d2
B
The hybridizations of bromine in BrF5 and of arsenic in AsF5 are
________ and ________, respectively.
A) sp3, sp3d
B) sp3d,
sp3d2
C) sp3d, sp3
D) sp3d2, sp3d
E) sp3d2, sp3d2
D
The hybrid orbitals used for bonding by the sulfur atom in the SF4
molecule are ________ orbitals.
A) sp
B) sp2
C)
sp3
D) sp3d
E) sp3d2
D
What are the hybrid orbitals used for bonding by Xe in a XeCl4
molecule?
A) sp2
B) sp3d2
C) sp3
D) sp3d
E) sp
B
The hybridization scheme for BeF2 is ________.
A) sp
B)
sp2
C) sp3
D) sp3d
E) sp3d2
A
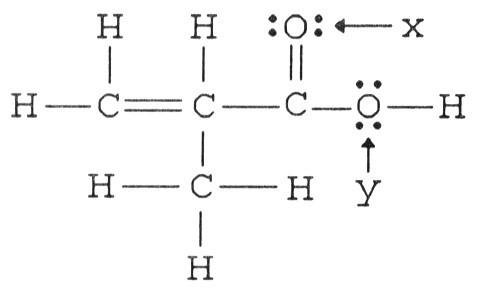
What is the hybridization of the carbon atom attached to the two oxygen atoms in the structure below?
A) sp3
B) sp
C) sp3d2
D) sp2
E) sp3d
D
What is the hybridization of the I atom in a IF5 molecule?
A)
sp2d2
B) sp3d
C) sp3
D) sp3d2
E) sp2
D
________ hybrid orbitals are used for bonding by Xe in the XeF4
molecule.
A) sp2
B) sp3
C) sp3d
D) sp3d2
E) sp
D
In which of the molecules is the central atom sp2 hybridized?
(i) BCl3 (ii) CCl4 (iii) TeCl4 (iv) XeF4 (v) SF6
A) (i) only
B) (i) and (ii)
C) (iii) and (iv)
D)
(iii) only
E) (iv) and (v)
A
When four atomic orbitals are mixed to form hybrid orbitals, how many
hybrid orbitals are formed?
A) one
B) six
C)
three
D) four
E) five
D
A triatomic molecule cannot be linear if the hybridization of the
central atoms is ________.
A) sp
B) sp2
C) sp3
D)
sp2 or sp3
E) sp2d or sp3d2
D
Valence bond theory addresses all of the following except
________.
A) molecular shape
B) covalent bonding
C)
excited states of molecules
D) hybridization
E) multiple bonds
C
A typical double bond ________.
A) is stronger and shorter than
a single bond
B) consists of one σ bond and one π bond
C)
imparts rigidity to a molecule
D) consists of two shared electron
pairs
E) All of the above answers are correct.
E
A typical triple bond ________.
A) consists of one σ bond and
two π bonds
B) consists of three shared electrons
C)
consists of two σ bonds and one π bond
D) consists of six shared
electron pairs
E) is longer than a single bond
A
In a SO42- ion, "localized" bonding electrons
are associated with ________ particular atoms.
A) zero
B)
one
C) two
D) three
E) four
C
There are ________ σ bonds and ________ π bonds in H3C-CH2-CH
CH-CH2-C CH.
A) 14, 2
B) 10, 3
C) 12, 2
D) 13,
2
E) 16, 3
E
Which of the following molecules or ions have various resonance
structures?
CO2 O3 CO32-
A) CO2, O3, and CO32-
B) CO2 and O3
C) O3 and
CO32-
D) CO32- only
E) None of the
above will exhibit delocalized bonding.
C
Which of the following molecules or ions will exhibit delocalized
bonding?
NO2- NH4+ N3-
A) NH4+ and N3-
B) NO2- only
C) NO2-, NH4+, and
N3-
D) N3- only
E) NO2- and N3-
B
A molecule must have at least two resonance structures in order to
display ________.
A) delocalized σ bonding
B) trigonal
planar electron group geometry
C) localized π bonding
D)
delocalized π bonding
E) localized σ bonding
D
In a C=C bond, the σ bond results from overlap of ________ orbitals
and the π bond(s) result from overlap of ________ orbitals.
A)
sp2-hybrid, p-atomic
B) sp2-atomic, p-hybrid
C) sp3-hybrid,
p-atomic
D) sp-hybrid, p-atomic
E) σ-atomic, π-hybrid
A
The carbon-hydrogen σ bond in ethylene, H2C CH2, results from the
overlap of ________.
A) sp2-hybrid and s-atomic orbitals
B)
sp hybrid orbitals
C) sp3 hybrid orbitals
D) s-hybrid and
sp2-atomic orbitals
E) s atomic orbitals
A
The π bond in ethylene, H2C CH2, results from the overlap of
________.
A) sp3 hybrid orbitals
B) s atomic
orbitals
C) sp hybrid orbitals
D) sp2 hybrid
orbitals
E) p atomic orbitals
E
A typical double bond consists of ________.
A) three sigma
bonds
B) three pi bonds
C) one sigma and two pi
bonds
D) one sigma and one pi bond
E) three ionic bonds
D
The N-H bond in ammonia consists of ________.
A) one σ bond and
one π bond
B) one σ bond and no π bonds
C) one σ bond and
two π bonds
D) two σ bonds and one π bond
E) two σ bonds and
two π bonds
B
The hybridization of the terminal carbons in the H2C C CH2 molecule
is ________.
A) sp
B) sp2
C) sp3
D) sp3d
E) sp3d2
B
The hybridization of nitrogen in the H—C N: molecule is
________.
A) sp
B) s2p
C) s3p
D) sp2
E) sp3
A
The hybridization of carbon in the H-C C-H molecule is
________.
A) sp2
B) sp
C) s2p
D) s3p
E) sp3
B
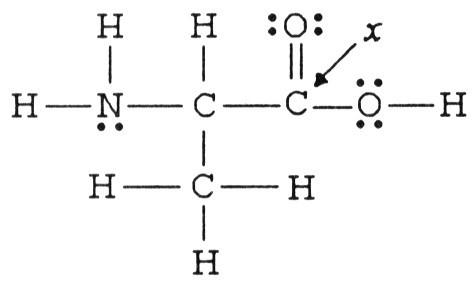
The hybridization of the carbon atom labeled x in the molecule below is ________.
A) sp
B) sp2
C) sp3
D) sp3d
E) sp3d2
B
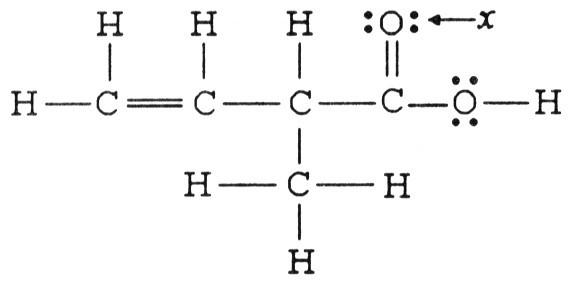
The hybridization of the oxygen atom labeled x in the structure below is ________.
A) sp
B) sp2
C) sp3
D) sp3d
E) sp3d2
B
The hybridization and molecular shape of the carbon atom in carbon
dioxide is ________.
A) sp and linear
B) sp3 and
bent
C) sp2 and linear
D) sp2d and bent
E) sp2d2 and linear
A
Electrons in ________ bonds remain localized between two atoms.
Electrons in ________ bonds can become delocalized between more than
two atoms.
A) pi, sigma
B) sigma, pi
C) pi, pi
D)
sigma, sigma
E) ionic, sigma
B
Structural changes around a ________ bond in the retinal portion of
the rhodopsin molecule trigger the chemical reactions that result in
vision.
A) C=C
B) C-C
C) C≡C
D) C-H
E) C=N
A
The bond order of any molecule containing equal numbers of bonding
and antibonding electrons is ________.
A) 0
B) 1
C)
2
D) 3
E) 1/2
A
In comparing the same two atoms bonded together, the ________ the
bond order, the ________ the bond length, and the ________ the bond
energy.
A) greater, shorter, greater
B) greater, greater,
greater
C) greater, longer, greater
D) smaller, longer,
smaller
E) smaller, greater, greater
D
In comparing the same two atoms bonded together, the ________ the
bond order, the ________ the bond length, and the ________ the bond
energy.
A) greater, shorter, greater
B) greater, greater,
greater
C) greater, longer, greater
D) greater, greater,
smaller
E) smaller, greater, greater
A
Based on molecular orbital theory, the bond orders of the H—H bonds
in H2, H2+, and H2- are ________, respectively
A) 1, 0, and
0
B) 1, 1/2, and 0
C) 1, 0, and 1/2
D) 1, 1/2, and
1/2
E) 1, 2, and 0
D
Based on molecular orbital theory, the bond order of the H—H bond in
the H2+ ion is ________.
A) 0
B) 1/2
C) 1
D)
3/2
E) 2
B
An antibonding π orbital contains a maximum of ________
electrons.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6
E) 8
B
According to MO theory, overlap of two s atomic orbitals produces
________.
A) one bonding molecular orbital and one hybrid
orbital
B) two bonding molecular orbitals
C) two bonding
molecular orbitals and two antibonding molecular orbitals
D) two
bonding molecular orbitals and one antibonding molecular
orbital
E) one bonding molecular orbital and one antibonding
molecular orbital
E
A molecular orbital can accommodate a maximum of ________
electron(s).
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6
E) 12
B
Molecular Orbital theory correctly predicts paramagnetism of oxygen
gas, O2. This is because ________.
A) the bond order in O2 can be
shown to be equal to 2
B) there are more electrons in the bonding
orbitals than in the antibonding orbitals
C) the energy of the
π2p MOs is higher than that of the σ2p MO
D) there are two
unpaired electrons in the MO electron configuration of O2
E) the
O—O bond distance is relatively short
D
Molecular Orbital theory correctly predicts diamagnetism of fluorine
gas, F2. This is because ________.
A) the bond order in F2 can be
shown to be equal to 1
B) there are more electrons in the bonding
orbitals than in the antibonding orbitals
C) all electrons in the
MO electron configuration of F2 are paired
D) the energy of the
π2pMOs is higher than that of the σ2p MO
E) the F—F bond enthalpy
is very low
C`
Based on molecular orbital theory, the only molecule in the list
below that has unpaired electrons is ________.
A) C2
B)
N2
C) F2
D) O2
E) Li2
D
According to molecular orbital theory, how many unpaired electrons
are in a peroxide ion, O22-?
A) 0
B) 1/2
C) 1
D)
2
E) 3
A
According to molecular orbital theory, the bond order of N-N in
nitrogen gas is ________.
A) 0
B) 1/2
C) 1
D)
2
E) 3
E
According to molecular orbital theory, the bond order of He-He in the
He2 molecule is ________.
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D)
3
E) 4
A
Which of the following is expected to be paramagnetic?
A)
F2
B) O2
C) N2
D) H2
E) He
B
Which of the following molecules would be expected to be attracted to a magnetic field?
F2 N2 O2
A) F2 and N2
B) F2 and O2
C) O2 only
D) N2
only
E) N2 and O2
C
According to MO theory, overlap of two p atomic orbitals produces
________.
A) two bonding molecular orbitals
B) one bonding
molecular orbital and one antibonding molecular orbital
C) two
bonding molecular orbitals and two antibonding molecular
orbitals
D) two bonding molecular orbitals and one antibonding
molecular orbital
E) three bonding molecular orbitals and three
antibonding molecular orbitals
B
According to MO theory, overlap of two p atomic orbitals produces
________.
A) one π MO and one σ* MO
B) one π MO and one σ
MO
C) one π MO and one π* MO or one σ MO and one σ* MO
D)
one π+ MO and one σ* MO
E) two π MOs, two π+ MOs, one σ MO, and
one σ* MO
C
An antibonding MO ________ the corresponding bonding MO.
A) is
always lower in energy than
B) can accommodate more electrons
than
C) can accommodate fewer electrons than
D) is always
higher in energy than
E) is always degenerate with
D
The more effectively two atomic orbitals overlap, ________.
A)
the more bonding MOs will be produced by the combination
B) the
higher will be the energy of the resulting bonding MO and the lower
will be the energy of the resulting antibonding MO
C) the higher
will be the energies of both bonding and antibonding MOs that
result
D) the fewer antibonding MOs will be produced by the
combination
E) the lower will be the energy of the resulting
bonding MO and the higher will be the energy of the resulting
antibonding MO
E
The bond order of a homonuclear diatomic molecule can be decreased by
________.
A) removing electrons from a bonding MO or adding
electrons to an antibonding MO
B) adding electrons to a bonding
MO or removing electrons from an antibonding MO
C) adding
electrons to any MO
D) removing electrons from any MO
E) The
bond order of a homonuclear diatomic molecule cannot be decreased by
any means.
A
The order of MO energies in B2, C2, and N2 (σ2p > π2p), is different from the order in O2, F2, and Ne2(σ2P<π2P). This is due to ________.
A) less effective overlap of p orbitals in O2, F2, and Ne2
B)
the more metallic character of boron, carbon and nitrogen as compared
to oxygen, fluorine, and neon
C) greater 2s-2p interaction in O2,
F2, and Ne2
D) greater 2s-2p interaction in B2, C2, and
N2
E) less effective overlap of p orbitals in B2, C2, and N2
D
For a molecule with the formula AB2, the molecular shape is
________.
A) linear or bent
B) linear or trigonal
planar
C) linear or T-shaped
D) T-shaped
E) trigonal planar
A
For a molecule with the formula AB3, the molecular shape is
________.
A) linear, octahedral, or bent
B) linear, bent, or
trigonal planar
C) linear, bent, or T-shaped
D)
tetrahedral
E) trigonal planar, trigonal pyramidal, or T-shaped
E
The molecular geometry of ________ is square planar.
A) CCl4
B) XeF4
C) PH3
D) XeF2
E) ICl3
B
The molecular geometry of the CS2 molecule is ________.
A)
linear
B) bent
C) tetrahedral
D) trigonal
planar
E) T-shaped
A
The molecular geometry of the SiH2Cl2 molecule is ________.
A)
trigonal planar
B) tetrahedral
C) trigonal pyramidal
D)
octahedral
E) T-shaped
B
The molecular geometry of the PHCl2 molecule is ________.
A)
bent
B) trigonal planar
C) trigonal pyramidal
D)
tetrahedral
E) T-shaped
C
The molecular geometry of the CHCl3 molecule is ________.
A)
bent
B) trigonal planar
C) trigonal pyramidal
D)
tetrahedral
E) T-shaped
D
The molecular geometry of the SF2 molecule is ________.
A)
linear
B) bent
C) trigonal planar
D)
tetrahedral
E) octahedral
B
The molecular geometry of the PF4+ ion is ________.
A)
octahedral
B) tetrahedral
C) trigonal pyramidal
D)
trigonal planar
E) trigonal bipyramidal
B
The F-B-F bond angle in the BF2- ion is approximately ________.
A) 90°
B) 109.5°
C) 120°
D) 180°
E) 60°
C
The Cl-Si-Cl bond angle in the SiCl2F2 molecule is approximately
________.
A) 90°
B) 109.5°
C) 120°
D) 180°
E) 60°
B
The F-B-F bond angle in the BF3 molecule is ________.
A)
90°
B) 109.5°
C) 120°
D) 180°
E) 60°
C
The H-B-H bond angle in BH3 is ________.
A) 180°
B)
90°
C) 109.5°
D) 60°
E) 120°
E
The F-N-F bond angle in the NF3 molecule is slightly less than
________.
A) 90°
B) 109.5°
C) 120°
D) 180°
E) 60°
B
The molecular geometry of the H3O+ ion is ________.
A)
linear
B) tetrahedral
C) bent
D) trigonal
pyramidal
E) octahedral
D
The electron-domain geometry of a sulfur-centered compound is
trigonal bipyramidal. The hybridization of the central sulfur atom is
________.
A) sp
B) sp2
C) sp3
D) sp3d
E) sp3d2
D
The hybridization of orbitals on the central atom in a molecule is
sp. The electron-domain geometry around this central atom is
________.
A) octahedral
B) linear
C) trigonal
planar
D) trigonal bipyramidal
E) tetrahedral
B
The hybridization of orbitals on the central atom in a molecule is
sp2. The electron-domain geometry about this central atom is
________.
A) octahedral
B) linear
C) trigonal
planar
D) trigonal bipyramidal
E) tetrahedral
C
The hybridization of the carbon atom in carbon dioxide is
________.
A) sp
B) sp2
C) sp3
D) sp3d
E) sp3d2
A
The hybridization of the central atom in the XeF4 molecule is
________.
A) sp
B) sp2
C) sp3
D) sp3d
E) sp3d2
E
The electron-domain geometry of the AsF6- ion is
octahedral. The hybrid orbitals used by the As atom for bonding are
________ orbitals.
A) sp2d2
B) sp3
C) sp3d
D)
sp3d2
E) sp2
D
In order to produce sp3 hybrid orbitals, ________ s atomic orbital(s)
and ________ p atomic orbital(s) must be mixed.
A) one,
two
B) one, three
C) one, one
D) two, two
E) two, three
B
In order to produce sp2 hybrid orbitals, ________ s atomic orbital(s)
and ________ p atomic orbital(s) must be mixed.
A) one,
two
B) one, three
C) one, one
D) two, two
E) two, three
A
The angles between sp2 orbitals are ________.
A) 45°
B)
180°
C) 90°
D) 109.5°
E) 120°
E
There are ________ σ and ________ π bonds in the H—C≡C—H
molecule.
A) 3, 2
B) 3, 4
C) 4, 3
D) 2, 3
E)
5, 0
A
There are ________ σ and ________ π bond(s) in the H2C=CH2
molecule.
A) 3, 2
B) 3, 4
C) 4, 3
D) 2, 3
E)
5, 1
E
There are ________ σ and ________ π bonds in the H2C=C=CH2
molecule.
A) 4, 2
B) 6, 4
C) 2, 2
D) 2, 6
E)
6, 2
E
The total number of π bonds in the H—C≡C—C≡C—C≡N molecule is
________.
A) 3
B) 4
C) 6
D) 9
E) 12
C
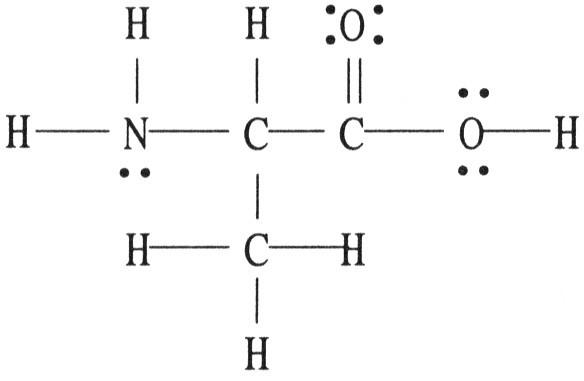
There is/are ________ σ bond(s) in the molecule below.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 12
D) 13
E) 18
C
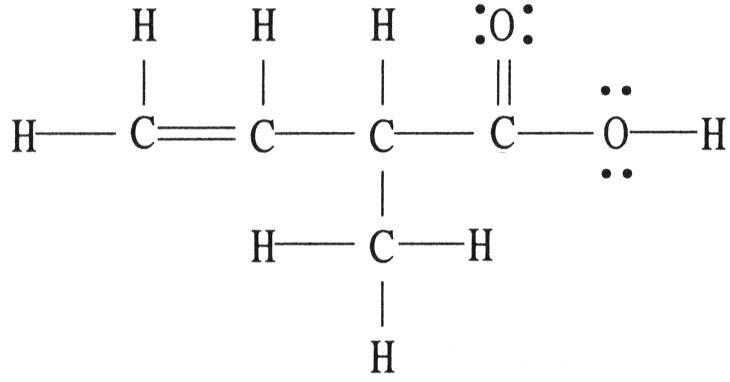
There is/are ________ π bond(s) in the molecule below.
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 4
E) 16
C
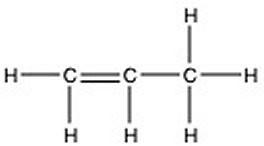
There is/are ________ π bond(s) in the molecule below.
A) 7
B) 6
C) 2
D) 1
E) 0
D
The Lewis structure of carbon monoxide is given below. The hybridizations of the carbon and oxygen atoms in carbon monoxide are ________ and ________, respectively.
- :C ≡ O: +
A) sp, sp3
B) sp2, sp3
C) sp3, sp2
D) sp, sp
E)
sp2, sp2
D
How may lone pair electrons are found on the central atom in a ClF3
molecule which has a "T-shaped" geometry?
A) 2
B)
3
C) 1
D) 4
E) 0
A
The electron domain and molecular geometry of SO3 are
________.
A) trigonal bipyramidal, trigonal planar
B)
trigonal planar, bent
C) trigonal bipyramidal, T-shaped
D)
trigonal planar, trigonal planar
E) octahedral, seesaw
D
The H-C-H bond angle in the CH4 ion is approximately ________.
A) 180
B) 120
C) 109.5
D) 60
E) 90
C
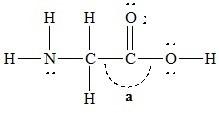
The bond angle marked a in the following molecule is about ________.
A) 109.5
B) 60
C) 180
D) 120
E) 90
D
The central atom in the ICl4- ion has ________ nonbonded
electron pair(s) and ________ bonded electron pair(s) in its valence
shell.
A) 4, 2
B) 0, 4
C) 2, 4
D) 2, 2
E) 6, 0
C
The central atom in a certain molecule has 1 nonbonded electron pairs
and 2 bonded electron pairs in its valence shell. The molecular
geometry of this molecule is ________.
A) tetrahedral
B)
bent
C) seesaw
D) trigonal bipyrimidal
E) trigonal pyramidal
B
The central atom in a certain molecule has 4 nonbonded electron pairs
and 2 bonded electron pairs in its valence shell. The molecular
geometry of this molecule is ________.
A) seesaw
B) square
planar
C) linear
D) trigonal bipyramidal
E) T-shaped
B
The central atom in the O3 molecule has ________ nonbonded electron
pair(s) and ________ bonded electron pair(s) in its valence
shell.
A) 6, 2
B) 1, 3
C) 2, 2
D) 3, 1
E) 3, 2
B
According to VSEPR theory, if there are three electron domains in the
valence shell of an atom, they will be arranged in a(n) ________
geometry.
A) tetrahedral
B) octahedral
C)
linear
D) square planar
E) trigonal planar
E
The electron-domain geometry and molecular geometry of iodine
trichloride are ________ and ________, respectively.
A) trigonal
bipyramidal, trigonal planar
B) tetrahedral, trigonal
pyramidal
C) trigonal bipyramidal, T-shaped
D) octahedral,
trigonal planar
E) T-shaped, trigonal planar
C
The electron-domain geometry and molecular geometry of the nitrite
ion are ________ and ________, respectively.
A) trigonal
bipyramidal, trigonal planar
B) tetrahedral, trigonal
pyramidal
C) trigonal bipyramidal,T-shaped
D) trigonal
planar, bent
E) T-shaped, trigonal planar
D
Using the VSEPR model, the electron-domain geometry of the central
atom in O3 is ________.
A) linear
B) trigonal planar
C)
tetrahedral
D) trigonal bipyramidal
E) octahedral
B
Using the VSEPR model, the electron-domain geometry of the central
atom in ClO3- is ________.
A) linear
B) trigonal
planar
C) tetrahedral
D) trigonal bipyramidal
E) octahedral
C
Using the VSEPR model, the electron-domain geometry of the central
atom in ClF3 is ________.
A) linear
B) trigonal
planar
C) tetrahedral
D) trigonal bipyramidal
E) octahedral
D
Using the VSEPR model, the electron-domain geometry of the central
atom in XeF4 is ________.
A) linear
B) trigonal
planar
C) tetrahedral
D) trigonal bipyramidal
E) octahedral
E
Using the VSEPR model, the molecular geometry of the central atom in
KrF2 is ________.
A) linear
B) trigonal planar
C)
tetrahedral
D) bent
E) trigonal pyramidal
A
Using the VSEPR model, the molecular geometry of the central atom in
SO3 is ________.
A) linear
B) trigonal planar
C)
tetrahedral
D) bent
E) trigonal pyramidal
B
Using the VSEPR model, the molecular geometry of the central atom in
CH4 is ________.
A) linear
B) trigonal planar
C)
tetrahedral
D) bent
E) trigonal pyramidal
C
Using the VSEPR model, the molecular geometry of the central atom in
ClO2- is ________.
A) linear
B) trigonal planar
C)
tetrahedral
D) bent
E) trigonal pyramidal
D
Using the VSEPR model, the molecular geometry of the central atom in
PCl3 is ________.
A) linear
B) trigonal planar
C)
tetrahedral
D) bent
E) trigonal pyramidal
E
Using the VSEPR model, the molecular geometry of the central atom in
IF5 is ________.
A) tetrahedral
B) square planar
C)
square pyramidal
D) seesaw
E) trigonal bipyramidal
C
The bond angles in a tetrahedral molecule are ________
degrees.
A) 109.5
B) 120
C) 90
D) 45
E) <45
A
Of the molecules below, only ________ is polar.
A) CO2
B)
CH4
C) PF5
D) SnF3
E) H2
D
Which of the following molecules would be considered
nonpolar?
A) PF3
B) Br2S
C) BeH2
D) TeCl2
E) HCl
C
The molecular geometry of the BeCl2 molecule is ________, and this
molecule is ________.
A) bent, nonpolar
B) linear,
polar
C) bent, polar
D) seesaw, polar
E) linear, nonpolar
E
The molecular geometry of the IF5 molecule is ________, and this
molecule is ________.
A) trigonal bipyramidal, polar
B)
trigonal bipyramidal, nonpolar
C) trigonal planar, polar
D)
square pyramidal, polar
E) square pyramidal, nonpolar
D
According to valence bond theory, which orbitals overlap in the
formation of the bond in HCl?
A) 1s on H and 2p on Cl
B) 2s
on H and 3p on Cl
C) 1s on H and 3s on Cl
D) 1s on H and 3p
on Cl
E) 1s on H and 4p on Cl
D
According to valence bond theory, which orbitals overlap in the
formation of the bond in Cl2?
A) 4p on Cl and 4p on Cl
B) 3p
on Cl and 3p on Cl
C) sp on Cl and sp on Cl
D) 3s on Cl and
3s on Cl
E) 2p on Cl and 2p on Cl
B
According to valence bond theory, which orbitals overlap in the
formation of the bond in ?
A) 3s
B) 3p
C) 4s
D)
4p
E) 3d
D
The hybrid orbital set used by the central atom in SO3 is
________.
A) sp
B) sp2
C) sp3
D) sp3d
E) sp3d2
B
The hybrid orbital set used by the central atom in ClO2- is
________.
A) sp
B) sp2
C) sp3
D) sp3d
E) sp3d2
C
The hybrid orbital set used by the central atom in PCl5 is
________.
A) sp
B) sp2
C) sp3
D) sp3d
E) sp3d2
D
The electron-domain geometry of a boron-centered compound BH3 is
trigonal planar. The hybridization of the central boron atom is
________.
A) sp2
B) sp3d2
C) sp3
D) sp3d
E) sp
A
Of the following, only ________ has sp2 hybridization of the central
atom.
A) NF3
B) HCN
C) BF3
D) ICl3
E) CH4
C
How many unhybridized p atomic orbital(s) are found in an
sp-hybridized carbon atom?
A) 4
B) 2
C) 0
D)
1
E) 3
B
How many hybridized s atomic orbital(s) are found in an
sp2-hybridized carbon atom?
A) 0
B) 3
C) 2
D)
1
E) 4
D
How many hybrid orbitals are formed upon the mixing of three atomic
orbitals?
A) three
B) six
C) four
D) one
E) five
A
Mixing one s atomic orbital and one p atomic orbital gives rise to
________.
A) three sp2 hybrid orbitals
B) two sp2 hybrid
orbitals
C) two sp3 hybrid orbitals
D) three sp hybrid
orbitals
E) two sp hybrid orbitals
E
A typical triple bond consists of ________ sigma bond(s) and ________
pi bond(s).
A) 1, 2
B) 2, 2
C) 1, 3
D) 0,
3
E) 1, 4
A
Construct a molecular orbital diagram for a Li2 molecule. According
to molecular orbital theory, the σ1s orbital is ________
and the σ1s* orbital is ________.
A) filled,
filled
B) half-filled, filled
C) empty, filled
D)
filled, empty
E) filled, half-filled
A
Based on molecular orbital theory, the bond order of the N—N bond in
the N2 molecule is ________.
A) 0
B) 1/2
C) 3
D)
2
E) 1
C
According to molecular orbital theory, the bond order in a Be2
molecule is ________.
A) 3
B) 1/2
C) 1
D)
2
E) 0
E
In molecular orbital theory, the bond order of the He—He bond in He2
is ________.
A) 0
B) 2
C) He—He
D) 1
E) 1/2
C
The highest energy occupied molecular orbital in the F—F bond of the
F2 molecule is ________.
A) π*2s
B) π2s
C)
σ*1p
D) π*2p
E) π2p
D
The highest energy occupied molecular orbital in the C—C bond of the
C2 molecule is ________.
A) σ2p
B) σ*1p
C) π2p
D) π2s
E) π*2p
C
What is the molecular geometry of ICl5?
trigonal bipyramidal
In the valence shell of an atom there are six electron domains. They will be arranged in a(n) ________ geometry.
octahedral
What are the three bond angles in the trigonal bipyramidal structure?
90°, 120°, 180°
Three molecules have similar electron domains, but different molecular shapes. Why?
different numbers of non-bonding domains
The ________ hydrogen orbital overlaps with the ________ bromide orbital in HBr.
1s, 4p
A covalent bond in which overlap regions lie above and below an internuclear axis is called a(n) ________.
π bond
The ________ hydrogen orbital overlaps with the ________ fluoride orbital in HF.
1s, 2p
According to molecular orbital theory, the greater the ________ ,the shorter the bond length.
bond order
According to the Pauli exclusion principle, no more than ________ electrons with their spins paired can occupy a molecular orbital.
2
A ________ compound would display unpaired electrons in the molecular orbital diagram.
paramagnetic
Possible shapes of AB3 molecules are linear, trigonal planar, and T-shaped.
false
Boron trifluoride has three bonding domains, and its electron domain geometry is trigonal planar.
true
Electron domains for single bonds exert greater force on adjacent domains than the electron domains for multiple bonds.
false
The quantitative amount of charge separation in a diatomic molecule contributes to the dipole moment of that molecule.
true
XeF4 is a polar molecule.
false
Hybridization is the process of mixing atomic orbitals as atoms approach each other to form a bond.
true
Electrons in core orbitals contribute to atom bonding.
false
Nitrogen is colorless because the minimum energy to excite an electron is in the ultraviolet section of the spectrum.
true