Homeostasis
The goal of physiological regulation and the key to survival in a changing environment
Surface anatomy:
exterior features
Regional anatomy:
body areas
Systemic anatomy:
organ systems
Clinical anatomy:
medical specialties
Developmental anatomy:
from conception to death
Cell physiology:
processes within and between cells
Organ physiology:
functions of specific organs
Systemic physiology:
functions of an organ system
Pathological physiology:
effects of diseases
Anatomical position:
hands at sides, palms forward
Supine:
lying down, face up
Prone:
lying down, face down
Abdominopelvic quadrants

Popliteal
back of knee
Otic
or ear
Cephalic
or head
Mental
or chin
Axillary
or armpit
Brachial
or arm
Antecubital
or front of elbow
Buccal
or cheek
Cervical
or neck
Antebrachial
or forearm
Pollex
or thumb
Patellar
or kneecap
Crural
or leg
Tarsal
or ankle
Hallux
or great toe
Pedal
or foot
Inguinal
or groin
Femoral
or thigh
Acromial
or shoulder
Olecranal
or back of elbow
Lumbar
or loin
Popliteal
or back of knee
Sural
or calf
Calcaneal
or heal of foot
Plantar
or sole of foot
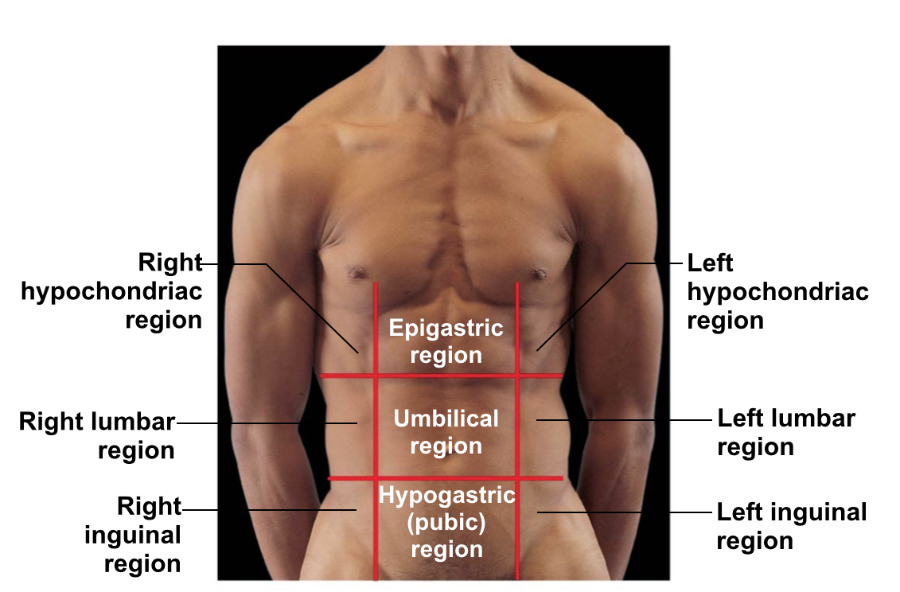
Abdominopelvic regions.
A _______________, section separates anterior and posterior portions of the body.
frontal, or coronal
____________ usually refers to sections passing through the skull.
Coronal
Frontal or coronal plane
Midsagittal plane
A _______________ separates right and left portions.
sagittal section
A ___________________
misses the midline. It
separates the body into
unequal right and left sides.
parasagittal section
Transverse plane
A _____________________ section separates superior and inferior
portions of the body.
transverse, or cross,
Essential Functions of ________________:
- Protect organs from accidental shocks
- Permit changes in size and shape of internal organs
Body Cavities
Toward the midline
Medial
_____________________: lines the internal body wall
Parietal peritoneum
_____________________: covers the organs
Visceral peritoneum
The _____________ receives the stimulus
Receptor
The _____________ processes the signal and sends instructions
Control Center
The _____________ carries out instructions
Effector
____________ Is the study of tissues and their structures.
Histology
Humans have ____ organ systems.
11
Skin, hair, sweat glands, & nails belong to the ________________ organ system.
Integumentary
Protects against environmental hazards, helps regulate body temperature, and provides sensory information are functions to _________________ organ systems.
Integumentary
Bone, cartilages, associated ligaments, and bone marrow belong to the _____________ organ system.
Skeletal
Provides support and protection for other tissues, stores calcium and other minerals, and forms blood cells are functions to the _________________ organ system.
Skeletal
Skeletal muscles and associated tendons belong to the _______________ organ system.
Muscular
Provides movement, provides protection and support for other tissues, generates heat that maintains body temperature are functions to the ___________________ organ system.
Muscular
Brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, sense organs belong to the _______________ organ system.
Nervous
Directs immediate responses to stimuli, coordinates or moderates activities of other organ systems, and provides and interprets sensory information about external conditions are functions of the __________________.
Nervous system
Pituitary gland, thyroid, pancreas, adrenal glands, gonads belong to the _______________ system.
Endocrine
Directs long-term changes in the activities of other organ systems, adjusts metabolic activity and energy use by the body, controls many structural and functional changes during development are functions of the ____________________.
Endocrine system
Heart, blood, and blood vessels belong to the _____________________ system.
Cardiovascular
Distributes blood cells, water, and dissolved materials; Didtributes heat and assists in control of body temperature are functions of the ___________________ .
Cardiovascular system
Spleen, Thymus, Lymphatic vessels, Lymph nodes, Tonsils are apart of the __________________ system.
Lymphatic
Defends against infection and disease, and Returns tissue fluids to the bloodstream are functions to the _______________.
Lymphatic system
Nasal cavities, Sinuses, Larynx, Trachea, Bronchi, Lungs, and Alveoli belong to the ___________________ system.
Respiratory
Delivers air to alveoli (sites in lungs where gas exchange occurs), Provides oxygen to bloodstream, Removes carbon dioxide from bloodstream, Produces sounds for communication are functions of the ________________________.
Respiratory System
Teeth, Tongue, Pharynx, Esophagus, Stomach, Small intestine, Large intestine, Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas are part of the _________________ system
Digestive
Processes and digests food, Absorbs and conserves water, Absorbs nutrients, and Stores energy reserves are functions of the ______________________.
Digestive system
Kidneys, Ureters, Urinary bladder, Urethra belong to the _________________ system.
Urinary
Excretes waste products from the blood, Controls water balance by regulating volume of urine produced, Stores urine prior to voluntary elimination, and Regulates blood ion concentrations and pH are functions of the _________________.
Urinary system
_____________ is the automatic response in a cell, tissue, or organ to some environmental change.
Autoregulation (intrinsic)
_______ is the responses controlled by nervous and endocrine systems
Extrinsic regulation
Below; at a lower level; toward the feet
Inferior
Above; at a higher level (in the human body, toward the head)
Superior
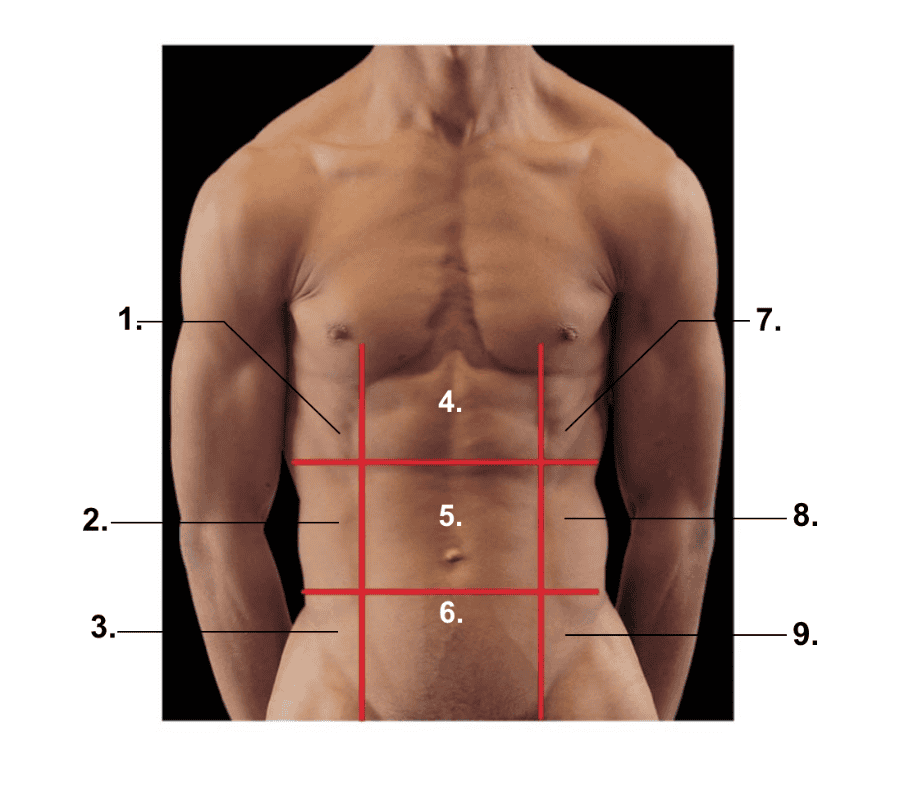
What is 1?
Right hypochondriac region

What is 2?
Right lumbar region

What is 3?
Right inguinal region

What is 4?
Epigastric region

What is 5?
Umbilical region

What is 6?
Hypogastric (pubic) region
Frontal
or forehead
The ________________ moves the body away from homeostasis and is used to speed up the processes.
Positive Feedback
Below=
Inferior
Below=
Caudal
Front view or ________________.
Ventral
Superficial is....
anything close to the skin
Deep or _______________.
Visceral
Bilateral means _______________________.
Both sides of the body
Dorsal
or back
Gluteal
or buttock
Ipsilateral
two on the same side
The right arm and the right leg are ______________________.
Ipsilateral
Contralateral
on the opposite side
If you have a clot in the right side of the brain the left side will be paralyzed. This is an example of ___________________.
Contralateral
Fingers are _____________ to the wrist.
Distal
The shoulder is ________________ to the wrist.
Proximal
The Scapula is located ______________ to the rib cage.
Posterior
The umbilicus is on the ____________ surface of the trunk.
Anterior
_______________ is used to visualize internal organization and structure.
Sectional Anatomy
Thoracic, mammary, abdominal, and umbilical are all apart of the ______________.
Trunk
The _____________ is in the Left Hypochondriac region
Speen
The ______________ & ______________ are in the Epigastric region
Liver, stomach
The ______________ is in the Hypogastric region.
Urinary Bladder
Ventral Body Cavity (Coelom) is divided by the diaphragm into the ______________ & _______________
Thoracic cavity & Abdominopelvic cavity
______________________ line body cavities and cover organs
Serous Membranes
Right and left ____________________ contain right and left lungs.
pleural cavities
Upper portion filled with blood vessels, trachea, esophagus, and thymus in the Thoracic Cavity is the __________________.
Mediastinum
The ____________ is located within the pericardial cavity.
heart
The muscular diaphragm subdivides the body cavities into a superior ________________ and an inferior _______________________.
thoracic cavity; abdominopelvic cavity
Peritoneal cavity is within the _________________ cavity
abdominopelvic
Parietal peritoneum (lines the internal body wall) and Visceral peritoneum (covers the organs) in the ______________________.
Peritoneal cavity
_________________ space contain organs that are not completely covered by cavity.
Retroperitoneal
Kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters, pancreas, duodenum (2nd part), aorta, Inferior vena cava, ascending and descending colon, lower part of the rectum are ______________________.
Retroperitoneal organs
The _______________ is the superior portion from diaphragm to top of pelvic bones and contains digestive organs.
Abdominal cavity
The _______________ is the inferior portion within pelvic bones and contains reproductive organs, rectum, and bladder
Pelvic cavity
The internal organs that are enclosed by cavities are known as _____________.
Viscera
A large tissue mass:
mediastinum
A delicate ____________ membrane lines the walls of these internal cavities and covers the surfaces of the enclosed viscera.
serous
The portion of a serous membrane that directly covers a visceral organ is called the ________________.
visceral serosa
The opposing layer that lines the inner surface of the body wall or chamber is called the _______________.
parietal serosa
The ___________ and ______________ membranes are one membrane
Parietal, Visceral
The Parietal serosa folds back onto itself, forming the _________________.
visceral serosa
Because the moist parietal and visceral sersae are usually in close contact, the body cavities are called _________________.
potentail spaces
The serous membrane lining a pleural cavity is called a __________.
pleura
The ______________ covers the outer surface of the lung, and the ________________ covers the mediastinal surface and the inner body wall.
visceral pleura, parietal pleura
The _____________ would enclose the heart organ.
Pericardial Cavity
The _____________ would enclose the small and large intestine
peritoneal cavity
The _______________ would enclose the lungs.
pleural cavity
The ____________ would enclose the kidneys.
abdominal (or abdominopelvic) cavity
The mediastinum is the region between the ___________.
two pleural cavities
The two major cavities of the trunk are the _______________ and ___________________.
Thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity
Which sectional plane could divide the body so that the face remains intact?
Frontal (coronal) plane
______________ Is the study of body structures
Anatomy
The _____________________:
- Atoms are the smallest chemical units
- Molecules are a group of atoms working together
Chemical (or Molecular) Level
The __________________:
- Cells are a group of atoms, molecules, and organelles working together
Cellular Level
A ____________ is a group of similar cells working together
tissue
An ___________ is a group of different tissues working together
organ
An ________________ is a group of organs working together
organ system