Exam II
What includes all of the pyrimidines found in RNA and DNA?
cytosine, uracil, thymine
Lactose, a sugar in milk, is composed of one glucose molecule joined by a glycosidic linkage to one galactose molecule. How is lactose classified?
as a disaccharide
Which class of biological molecules does NOT include polymers?
lipids
You disrupt all hydrogen bonds in a protein. What level of structure will be preserved?
primary structure
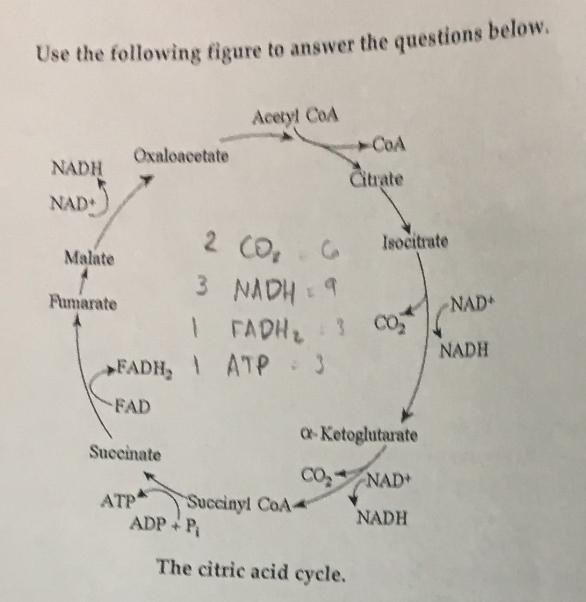
A fat (or triaclygycerol) would be formed as a result of a dehydration reaction between...
three molecules of 9 and one molecule of 10
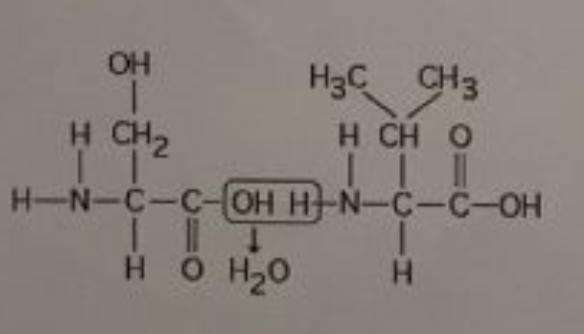
The chemical reaction illustrated in the accompanying figure___.
results in a peptide bond
If one strand of a DNA molecule has the sequence of bases 5'ATTGCA3', the other complementary strand would have the sequence___.
5'TGCAAT3'
What description best fits the class of molecules known as nucleosides?
a nitrogenous base and a sugar
Which statement summarizes the relationship between dehydration reactions and hydrolysis?
Dehydration reactions assemble polymers; hydrolysis reactions break polymers apart
Proteorhodopsin consists of a single polypeptide chain. What is the highest level of structure found in this protein?
tertiary
The R-group, or side chain, of the amino acid serine is -CH2-OH. The R-group, or side chain, of the amino acid leucine is -CH2-CH-(CH3)2. Where would you expect to find these amino acids in a globular protein in aqueous solution?
Leucine would be in the interior, and serine would be on the exterior of the globular protein
Why is glycogen extensively branched?
to be digested faster
Which macromolecule leaves the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell thorugh pores in the nuclear membrane?
mRNA
Which organelle is the primary state of ATP synthesis in eukaryotic cells?
Mitochondrion
What is the most likely pathway taken by a newly synthesized protein that will be secreted by a cell?
ER --> Golgi --> vesicles that fuse with plasma membrane
Which structure is common to plant and animal cells?
mitochondrion
The advantage of light microscopy over electron microscopy is that___.
light microscopy allows one to view dynamic processes in living cells
All of the following are part of a prokaryotic cell EXCEPT___.
an endoplasmic reticulum
What produces and modifies polysaccharides that will be secreted?
Golgi apparatus
A cell with a predominance of free ribosomes is most likely...
primarily producing proteins in the cytosol
Where would you expect to find tight junctions?
in the plasma membrane of prokaryotes
Ions can travel directly from the cytoplasm of one animal cell to the cytoplasm of an adjacent cell through...
gap junctions
Which statement correctly describes a prokaryotic cell's length?
10,000 nano-meter.
A sperm would be unable to swim if it does not have___.
Ribosome, actin, and centrosome.
Why are lipids and proteins free to move laterally in membranes?
There are only weak hydrophobic interactions in the interior of the membrane
The membranes of winter wheat are able to remain fluid when it is extremely cold by ___.
increasing the percentage of unsaturated phospholipids in the membrane
What will happen to a red blood cell (RBC), which has an internal ion concentration of about 0.9 percent, if it is placed into a beaker of pure water?
the cell would swell because the water in the beaker is hyoptonic relative to the cytoplasm of the RBC.
In some cells, there are many ion electrochemical gradients across the plasma membrane even though there are usually only one or two proton pumps present in the membrane. The gradients of the other ions are most likely accounted for by ___.
passive diffusion across the plasma membrane
What is NOT amphipathic?
the surface of peripheral proteins
What kinds of molecules pass through a cell membrane most easily?
small and hydrophobic
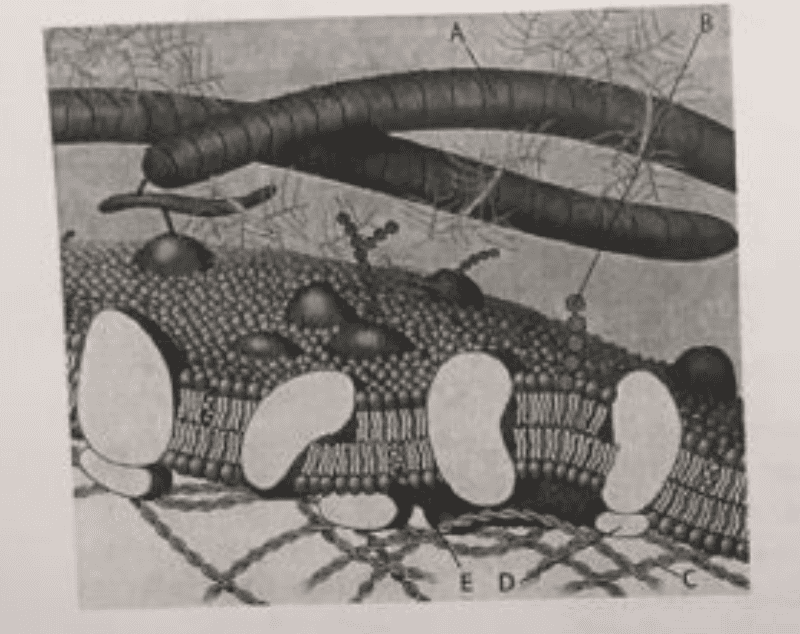

Which component is a peripheral protein?
D
White blood cells engulf bacteria using___.
Phagocytosis
Which term most precisely describes the cellular process of breaking down large molecules into smaller ones?
Catabolism (catabolic pathways)
A chemical reaction that has a positive ΔG is best desribed as...
endergonic
What is an example of potential rather than kinetic energy?
a molecule of glucose
Which of the following is true of enzymes?
enzymes increase the rate of chemical reaction by lowering energy barriers.
Which of the following involves a decrease in entropy?
condensation reactions
A noncompetitive inhibitor decreases the rate of enzyme reaction by...
changing the shape of the enzyme's active site
The mathematical expression for the change in free energy of a system is ΔG= ΔH-TΔS. Which of the following is correct?
ΔG is the change in free energy.
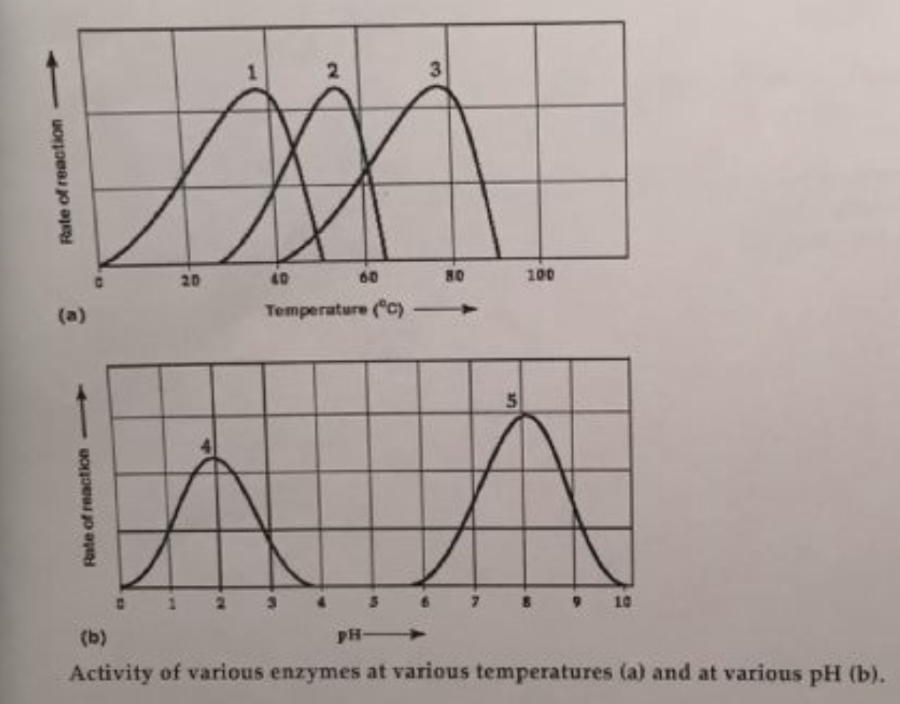
Which temperature and pH profile curves on the graphs were most likely generated from analysis of an enzyme from a human stomach where conditions are strongly acid?
curves 3 and 4
Which of the following statements is a logical consequence of the second law of thermodynamics?
every chemical reaction must increase the total entropy of the universe