The Cardiovascular System: Blood
Which is NOT a major function of the blood?
- Transportation of nutrients
- Regulation of blood pH
- Protection against disease infection
- Transportation of heat
- Production of oxygen
E
The normal average temperature of blood is around
- 98.6oF
- 100.4oF
- 90.8oF
- 89.6oF
- 101.6oF
B
The normal pH range for blood is
- 7.35-8.5
- 7.35-9.45
- 6.35-7.35
- 6.35-9.35
- 7.35-7.45
E
Which of the following is not a component of blood?
- Blood plasma
- Formed elements
- Carbon dioxide
- Platelets
- White blood cells
C
The hematocrit is composed of
- WBC
- Platelets
- RBC
- plasma
- proteins
C
How much of blood plasma is water (approximately)?
- 95%
- 91%
- 88%
- 80%
- 50%
B
Which of the following plasma proteins plays a role in disease resistance?
- Albumins
- Globulins
- Fibrinogens
- Myoglobin
- Hemoglobin
B
Which of the following plasma proteins plays a role in blood clotting?
- Albumins
- Globulins
- Fibrinogens
- Prostaglandins
- None of the above
C
A hemocrit measures
- Percentage of RBC in packed blood
- Percentage of WBC in packed blood
- Percentage of platelets in packed blood
- Both A and B
- All of the above
A
The process by which formed elements of the blood develop is called:
- Hematocritation
- Hemopoiesis
- Albumin genesis
- Immunology
- None of the above
B
A megakaryoblast will develop into
- Red blood cell
- White blood cell
- Platelet
- Both B and C
- Any of the above
C
During hemopoiesis, some of the myeloid stem cells differentiate into
- Progenitor cells
- Enzymes
- Plasma proteins
- Heme molecules
- Nitric oxide
A
This hormone stimulates proliferation of red blood cells in red bone marrow
- EPO
- TPO
- Human growth hormone
- Calcitonin
- Follicle stimulating hormone
A
How many hemoglobin molecules are in each RBC?
- 50 million
- 100 million
- 280 million
- 320 million
- 430 million
C
Ferritin is used to
- Transport iron
- Store iron
- Convert iron
- Synthesize iron
- Digest iron
B
A red blood cell’s function is
- Nutrient transport
- Cytokine stimulation
- Blood cell proliferation
- Gas transport
- Disease resistance
D
A red blood cell without a nucleus is called a
- Proerythroblast
- Cytokine
- Precursor cell
- Interleukin
- Reticulocyte
E
Which of the following is a phagocyte?
- Monocytes
- Platelet
- Lymphocyte
- Basophil
- Eosinophil
A
Which of the following reduces blood loss?
- Erythrocyte
- Platelet
- Lymphocyte
- Basophil
- Neutrophil
B
Which of the following promotes inflammation?
- Eosinophil
- Monocyte
- Lymphocyte
- Basophil
- Neutrophil
D
Which of the following destroys antigen-antibody complexes?
- Eosinophil
- Monocyte
- Lymphocyte
- Basophil
- Neutrophil
A
Which of the following is not an agranular leukocyte?
- Monocytes
- Macrophage
- Lymphocyte
- Basophil
- All of the above
D
The process of a white blood cell squeezing between cells to exit the blood vessel is called
- Emigration
- Wandering
- Adhesion
- Hempoiesis
- Phagocytosis
A
Which of the following do mast cells not release?
- Heparin
- Histamine
- Nitric oxide
- Protease
- All of the above
C
This hormone causes the development of megakaryoblasts.
- Erythropoietin
- Thrombopoietin
- Nitric oxide
- Human growth hormone
- Heparin
B
Which methods provide hemostasis?
- vascular spasm, clotting, polycythemia
- hemolysis, vascular spasm, platelet plug formation
- emigration, clotting, hemolysis
- platelet plug formation, vascular spasm, clotting
- anemia, hemogenesis, platelet plug formation
D
Once this is formed, the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways are identical.
- Thromboplastin
- Prothrombinase
- Fibrinogen
- Fibrin
- Calcium
B
Which of the following clotting factors has the most to do with strengthening and stabilizing a blood clot?
- Factor V
- Factor VII
- Factor XI
- Factor XIII
- Factor XIV
D
Considering Rh blood types, which of the below situations would result in maternal antibodies attacking the fetus?
- Mom is Rh negative and fetus is Rh negative
- Mom is Rh negative and fetus is Rh positive
- Mom is Rh positive and fetus is Rh negative
- Mom is Rh positive and fetus is Rh positive.
D
Which of the following opposes the action of thromboxane A2?
- Heparin
- Fibrinogen
- Plasmin
- Antithrombin
- Prostacyclin
E
Which of the following is an anticoagulant?
- Heparin
- Fibrinogen
- Protease
- Prostacyclin
- Plasmin
A
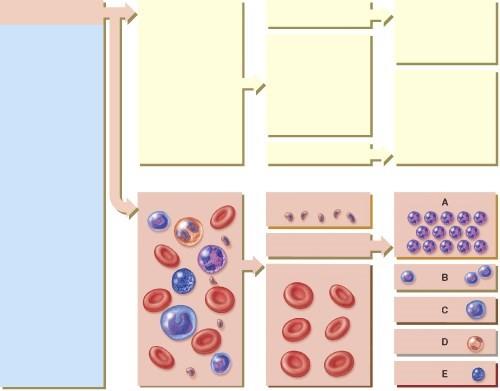
Which of the following cells will develop into macrophages?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
C

Which of the following cells will increase the number of nuclear lobes as they age?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
A

Which of the following cells is normally classified as small or large?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
B
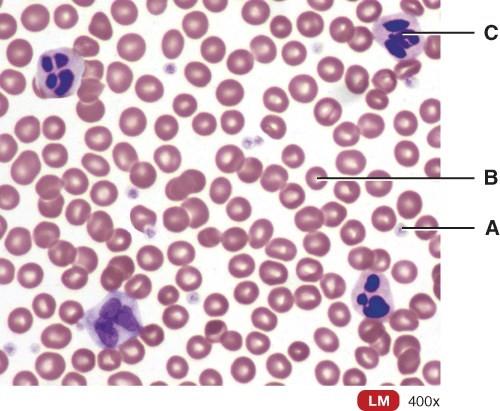
Which one is a WBC?
- A
- B
- C
- Both B and C
- All of the above
C
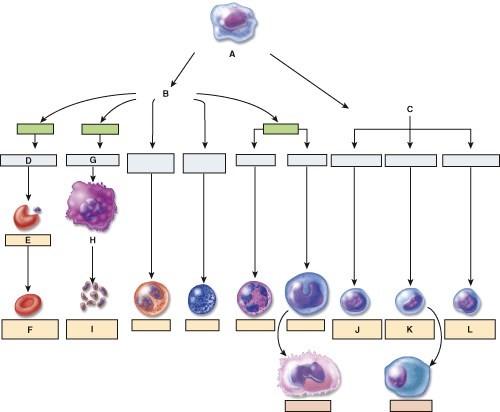
Which one is the pluripotent stem cell?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- G
A

Which cell is the myeloid stem cell?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- G
B

Which cell is the reticulocyte?
- D
- G
- E
- H
- F
C

Which cell is the T lymphocyte?
- C
- J
- K
- L
- A
B

Which cell is the natural killer cell?
- A
- C
- J
- K
- L
E
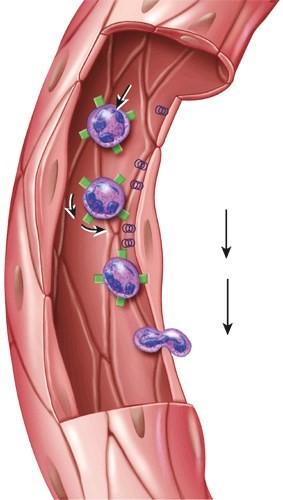
What is this figure demonstrating?
- Erythropoeisis
- RBC differentiation
- Emigration
- Clot formation
- Clot retraction
C
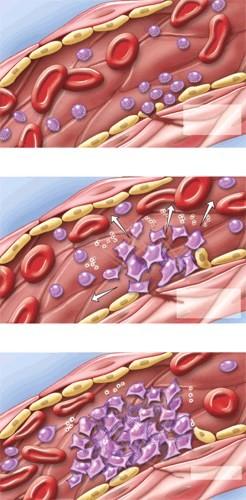
What does this figure represent?
- Erythropoeisis
- RBC differentiation
- Emigration
- Clot formation
- Clot retraction
D
What antibodies does a person with type O blood have in their plasma?
- A
- B
- A and B
- No antibodies
- Not enough information to answer
C
What antigens does a person have on their RBC if their plasma has antibody A?
- A
- B
- O
- A and B
- No antigens
B