Exam 2 Micro MW
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
a) Glycocalyx--
adherence
b) Pili-- reproduction
c) Cell wall--
toxin
d) Cell wall-- protection
e) Plasma membrane-- transport
e) Plasma membrane-- transport
Heredity material passes from parent to offspring during
______.
A. Reproduction
B. DNA
C. Chromosomes
D. Duplication of sperm
A. Reproduction
Who is considered the "Father of Genetics?"
A. Dimitri Mendeleev
B. Albert Einstein
C. Gregor Mendel
D. Alfred Wegener
C. Gregor Mendel
An organic nutrient essential to an organism’s metabolism that cannot be synthesized itself is termed a /an
A. Trace element
B. Micronutrient
C. Growth factor
D. Mineral
C. Growth factor
Which of the following statements about prokaryotic cells is
generally false?
A) They lack membrane-bound nuclei.
B) They
have a semirigid cell wall.
C) They reproduce by binary
fission.
D) They are motile by means of flagella.
E) They
possess 80S ribosomes.
E) They possess 80S ribosomes.
Which of the following statements about gram-negative cell walls is
false?
A) They have an extra outer layer composed of
lipoproteins, lipopolysaccharides, and phospholipids.
B) They are
sensitive to penicillin.
C) They are toxic to humans.
D)
Their Gram reaction is due to the outer membrane.
E) They protect
the cell in a hypotonic environment.
B) They are sensitive to penicillin.
Which of the following structures is NOT found in prokaryotic
cells?
A) Cilium
B) Axial filament
C) Flagellum
D)
Pilus
E) Peritrichous flagella
A) Cilium
Which of the following statements about the glycocalyx is
false?
A) It may be responsible for virulence.
B) It may be
composed of polysaccharide.
C) It is used to adhere to
surfaces.
D) It may be composed of polypeptide.
E) It
protects from osmotic lysis.
E) It protects from osmotic lysis.
Where are phospholipids most likely found in a prokaryotic
cell?
A) flagella
B) around organelles
C) the plasma
membrane
D) ribosomes
E) the plasma membrane and around organelles
C) the plasma membrane
_______ are tiny, naked pieces of RNA that are significant plant pathogens.
A)Viroids B)Prions C)Hepatitis viruses D)Virons E)none of the above
A)Viroids
Gram-negative bacteria have what advantage over gram-positive bacteria?
A)Gram-negative bacteria are better able to survive environmental changes than are gram-positive bacteria.
B)Gram-negative bacteria are able to survive longer without water than can gram-positive bacteria.
C)Gram-negative bacteria can metabolize a wider variety of nutritional materials than can gram-positive bacteria.
D)Gram-negative bacteria are able to resist antibiotics that attack the cell wall while gram-positive bacteria are susceptible to these drugs.
E)Gram-negative bacteria have longer life cycles than do gram-positive bacteria.
D)Gram-negative bacteria are able to resist antibiotics that attack the cell wall while gram-positive bacteria are susceptible to these drugs.
Endospores function to
A)help the organism survive periods of drought.
B)transmit genetic information from one bacterium to another.
C)help the organism survive exposure to high temperatures.
D)all of the above
E)both a and c
E)both a and c
The end result of the viral lytic cycle is
A)lysis of the infected cell.
B)immunity of the host cell to further viral infection.
C)the release of new viruses.
D)both a and b
E)both a and c
E)both a and c
An acid fast stain allows you to see Gram-positive microorganisms that are resistant to gram stain.
A) True B) False
A) True
Game to help identify bacteria shapes. https://www.purposegames.com/game/identifying-bacteria-by-shape-and-arrangement-quiz
Game to help identify bacteria shapes. https://www.purposegames.com/game/identifying-bacteria-by-shape-and-arrangement-quiz
Which of the following describes the fluid-mosaic model of the plasma membrane structure?
A)phospholipid monolayer with embedded proteins
B)phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins
C)phospholipid trilayer with embedded proteins
D)triglyceride bilayer with embedded proteins
E)triglyceride monolayer with embedded proteins
B)phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins
Cocci arranged in "grape-like" clusters are known as __ .
A. streptococci
B. staphylococci
C. sarcinae
D. micrococci
B. staphylococci
Rod shaped bacteria are called
A)bacilli
B)streptococci
C)cocci
D)staphylobacilli
E)spirilla
A)bacilli
Gram-positive bacteria have an outer membrane that stains purple.
A)True
B)False
A)True
Gram-negative bacteria have what advantage over gram-positive bacteria?
A)Gram-negative bacteria are better able to survive environmental changes than are gram-positive bacteria.
B)Gram-negative bacteria are able to survive longer without water than can gram-positive bacteria.
C)Gram-negative bacteria can metabolize a wider variety of nutritional materials than can gram-positive bacteria.
D)Gram-negative bacteria are able to resist antibiotics that attack the cell wall while gram-positive bacteria are susceptible to these drugs.
E)Gram-negative bacteria have longer life cycles than do gram-positive bacteria.
D)Gram-negative bacteria are able to resist antibiotics that attack the cell wall while gram-positive bacteria are susceptible to these drugs.
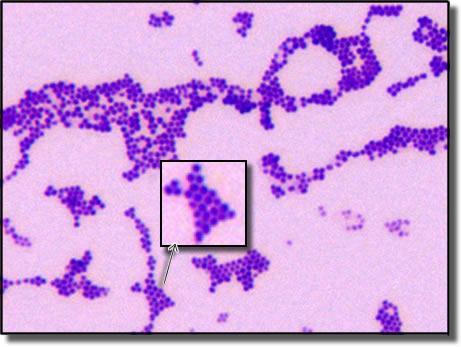
a. bacillus
b. coccus
c. spirillum
b. coccus
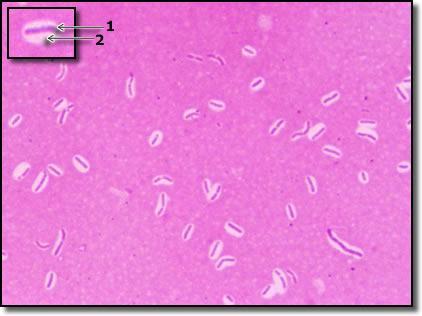
a. capsule
b. endospore
c. flagella
a. capsule
Which of the following describes the fluid-mosaic model of the plasma membrane structure?
A)phospholipid monolayer with embedded proteins
B)phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins
C)phospholipid trilayer with embedded proteins
D)triglyceride bilayer with embedded proteins
E)triglyceride monolayer with embedded proteins
B)phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins
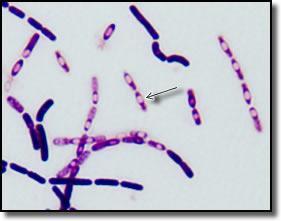
a. capsule
b. endospore
c. flagella
b. endospore
The two functions of bacterial appendages are
A. Attachment and
protection
B. Attachment and motility
C. Motility and slime
production
D. Energy reactions and synthesis
E. Protection
and motility
B. Attachment and motility
Spirochetes have a twisting and flexing locomotion due to appendages
called
A. Flagella
B. Cilia
C. Fimbriae
D.
Periplasmic flagella (axial filaments)
E. Sex pili
D. Periplasmic flagella (axial filaments)
The first prokaryotes appeared about ___ billion years ago.
A.
5
B. 4
C. 3
D. 2
E. 1
C. 3
Which of the following is not a characteristic of a
prokaryote?
A. It's DNA is not encased in a membrane
B. It
has a cell wall made of peptidoglycans or other distinct
chemicals
C. It does not have membrane-bound organelles
D.
Its DNA is wrapped around histones
E. All of these are
characteristics of prokaryotes
D. Its DNA is wrapped around his tones
The basal body of a flagellum is anchored into the
A.
Hook
B. Outer membrane
C. Cell wall
D. Peptidoglycan
layer
E. Cell membrane
E. Cell membrane
The term that refers to the presence of flagella all over the cell
surface is
A. Amphitrichous
B. Atrichous
C.
Lophotrichous
D. Monotrichous
E. Peritrichous
E. Peritrichous
The term that refers to the presence of a tuft of flagella emerging
from the same site is
A. Amphitrichous
B. Atrichous
C.
Lophotrichous
D. Monotrichous
E. Peritrichous
C. Lophotrichous
The term that refers to flagella at both poles is
A.
Amphitrichous
B. Atrichous
C. Lophotrichous
D.
Monotrichous
E. Peritrichous
A. Amphitrichous
Chemo taxis refers to the ability to
A. Move in response to
light
B. Move in response to a chemical
C. Not move in
response to a chemical
D. Transport desired molecules into
cell
E. None of the choices are correct
B. Move in response to a chemical
A nutrient binds to receptors near the basal body. This will result
in
A. Clockwise rotation of flagella
B. Counter clockwise
rotation of flagella
C. Inhibition of flagella rotation
D.
Numerous tumbles
E. None of the choices are correct
B. Counter clockwise rotation of flagella
The prokaryotic flagellum has three parts in the order from cytoplasm
to external environment
A. Filament, hook, basal body
B.
Filament, basal body, hook
C. Basal body, hook, filament
D.
Hook, basal body, filament
E. Basal body, filament, hook
C. Basal body, hook, filament
The short, numerous appendages used by some bacterial cells for
adhering to surfaces are called
A. Flagella
B. Cilia
C.
Fimbriae
D. Periplasmic flagella (axial filaments)
E. Sex pili
C. Fimbriae
Which of the following is mismatched?
A. Ribosomes - protein
synthesis
B. Inclusions - excess cell nutrients and
materials
C. Plasmids - genes essential for growth and
metabolism
D. Nucleoid - hereditary material
E. Cytoplasm -
dense, gelatinous solution
C. Plasmids - genes essential for growth and metabolism
All bacterial cells have
A. One or more chromosomes
B. One
or more fimbriae
C. The ability to produce endospores
D.
Capsules
E. Flagella
A. One or more chromosomes
The most commonly encountered bacteria are roughly spherical. The microbiological term describing this shape is
A) coccus
B) bacillus
C) pleomorphic
A) coccus
Gram positive cells
A)have a second, outer membrane that helps retain the crystal violet stain.
B)have multiple layers of peptidoglycan that help retain the crystal violet stain.
C)have a thick capsule that traps the crystal violet stain.
D)have a periplasmic space that traps the crystal violet.
B)have multiple layers of peptidoglycan that help retain the crystal violet stain.
The transfer of genes during bacterial conjugation involves rigid,
tubular appendages called
A. Flagella
B. Cilia
C.
Fimbriae
D. Periplasmic flagella (axial filaments)
E. Sex pili
E. Sex pili
Which structure protects bacteria from being phagocytized?
A.
Slime layer
B. Fimbriae
C. Cell membrane
D.
Capsule
E. All of the choices are correct
E. All of the choices are correct
Which order below reflects the correct procedure for Gram
staining?
A. Alcohol/acetone-Crystal
violet-Safranin-Iodine
B. Crystal
violet-Alcohol/acetone-Iodine-Safranin
C. Crystal
violet-Iodine-Alcohol/acetone-Safranin
D. Iodine-Safranin-Crystal
violet-Alcohol/acetone
E. Alcohol/acetone-Safranin-Crystal violet-Iodine
C. Crystal violet-Iodine-Alcohol/acetone-Safranin
The cell _____ can be composed of three layers: the membrane, the
cell wall and the outer
membrane.
A. Glycocalyx
B.
Envelope
C. Pathogenic package
D. Slime coat
E. None of
the choices are correct
B. Envelope
Peptidoglycan is a unique macromolecule found in bacterial
A.
Cell walls
B. Cell membranes
C. Capsules
D. Slime
layers
E. Inclusions
A. Cell walls
The function of bacterial endospores is
A. Convert gaseous
nitrogen to a usable form for plants
B. Reproduction and
growth
C. Protection of genetic material during harsh
conditions
D. Storage of excess cell materials
E. Sites for photosynthesis
C. Protection of genetic material during harsh conditions
Which is the hardiest of all life form and can withstand extreme heat , which is NOT a meant of reproductions?
A) sporulation
B) conversion
C) dimorphism
D) binary fission
A) sporulation
Gram-negative cells contain a thin peptidoglycan wall and cell envelope.
True or False
True
Peptidoglycan is unique to bacteria.
True or False
True
The periplasmic space is between the cell membrane and cell wall.
True or False
True
Porin proteins have which function?
A) Regulate molecules entering and leaving cell
B) Repel water
C) Absorb shock
D) Act as receptor for antigens
A) Regulate molecules entering and leaving cell
L-forms arise from mutations in what type of genes?
A) RNA
B) membrane forming genes
C) cell wall forming genes
D) cytoplasm forming genes
C) cell wall forming genes
True or False
Pleomorphic bacteria are those, which shows variable shape and size in a response to changing environmental conditions.
True or False
True
True or False
Archaea do not have the typical peptidoglycan structure found
in bacterial cell walls.
True False
True
True or False
The first cells on earth were probably archaea.
True
True or False
Prokaryotes include bacteria and viruses.
False
True or False
Flagella move in a whip-like motion.
False
True or False
True pili used for conjugation are only found on gram negative bacteria.
True
True or False
The slime layer gives bacteria a greater pathogenicity as compared to the capsule.
False
True or False
The cell envelope of gram positive bacteria has two layers: a thick cell wall and the cell membrane.
True
True or False
The internal structure of eukaryotic cilia and flagella are the same.
True
True or False
Gram negative bacteria do not have peptidoglycan in their cell walls.
False
True or False
Endospores of certain bacterial species can enter tissues in
the human body, germinate and cause an
infectious disease.
True
What is this the correct order of the eukaryotic cell layers?
1)Cell membrane
2)Glycocalyx
3)Cell wall
2
3
1
Which of the following is NOT a distinguishing characteristic of
prokaryotic cells?
a) They usually have a single, circular
chromosome
b) They lack membrane-enclosed organelles
c) They
have cell walls containing peptidoglycan
d) Their DNA is not
associated with histones
e) They lack a plasma membrane
e) They lack a plasma membrane
Which one of the following steps occurs during the multiplication of
animal viruses, but not during the multiplication of
bacteriophages?
a) assembly
b) biosynthesis
c)
penetration
d) uncoating
d) uncoating
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
a) Glycocalyx--
adherence
b) Pili-- reproduction
c) Cell wall--
toxin
d) Cell wall-- protection
e) Plasma membrane-- transport
e) Plasma membrane-- transport
You have isolated a motile, gram-positive cell with no visible
nucleus. You can assume this cell has...
a) Ribosomes
b)
Mitochondria
c) An endoplasmic reticulum
d) A golgi
complex
e) All of the above
a) Ribosomes
The antibiotic amphothericin B disrupts plasma membranes by combining
with sterols; it will affect all of the following cells except…
a) Animal cells
b) Gram (-) bacterial cells
c) Fungal
cells
d) Mycoplasma cells
e) Plant cells
b) Gram (-) bacterial cells
An example of an systemic mycosis is when…
a) Blastomyces
infects the lungs
b) Sporothrix creates ulcerative
lesions
c) Microsporum infects the fingernails
d)
Trichosporon infects the hair shafts
a) Blastomyces infects the lungs
By what means are helminthic parasites transmitted to humans?
a) Phagocytosis
b) Endocytosis
c) Ingestion
d)
Active transport
c) Ingestion
Which of the following eukaryotes has a thick, rigid cell
wall?
a) fungi and algae
b) Protozoa
c)
Helminths
d) Bacteria
a) fungi and algae
Which of the following are non-motile parasites with special
organelles for penetrating host tissue?
a) Apicomplexa
b)
Ciliates
c) Dinoflagellates
d) Microsporidia
a) Apicomplexa
Helminths refer to _______ and arthropods refer to animal vectors of
diseases
a) Animals
b) Insects
c) Snakes
d) Worms
d) Worms
Quiz Questions
What is the similarity between algae and protozoa?
both contain mitochondria
What are the characteristics of protozoa?
singled-celled, lack tissues and are animal-like because they are heterotrophic & motile eat by engulfing other microbes
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
A) nematodes —
complete digestive tract
B) cestodes — segmented body made of
proglottids
C) trematodes — flukes
D) nematodes — many are
free-living
E) cestodes — all are free-living
E) cestodes — all are free-living
Which of the following is NOT a distinguishing characteristic of
prokaryotic cells?
a) They usually have a single, circular
chromosome
b) They lack membrane-enclosed organelles
c) They
have cell walls containing peptidoglycan
d) Their DNA is not
associated with histones
e) They lack a plasma membrane
e) They lack a plasma membrane
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
a) Glycocalyx--
adherence
b) Pili-- reproduction
c) Cell wall--
toxin
d) Cell wall-- protection
e) Plasma membrane-- transport
b) Plasma membrane-- transport
Which of the following statements about algae is false?
A) They
produce oxygen from hydrolysis of water.
B) They use light as
their energy source.
C) They use CO2 as their carbon
source.
D) All are unicellular.
E) Some are capable of
sexual reproduction
D) All are unicellular.
Which of the following statements about protozoa is false?
A)
All are eukaryotic.
B) All have complex cells.
C) They are
classified by their method of locomotion.
D) All are
unicellular.
E) They have rigid cell walls.
E) They have rigid cell walls.
Which of the following statements about helminths is false?
A)
They are heterotrophic.
B) They are multicellular
animals.
C) Some have male and female reproductive organs in one
animal.
D) All are parasites.
E) They have eukaryotic cells.
D) All are parasites.
Which of the following statements about archaea is false?
A)
They are prokaryotes.
B) They lack peptidoglycan in their cell
walls.
C) Some are thermoacidophiles; others are extreme
halophiles.
D) They evolved before bacteria.
E) Some produce
methane from carbon dioxide and hydrogen.
D) They evolved before bacteria.
True or False
The prokaryotic cell membrane is a site for many enzymes and metabolic reactions.
True
True or False
The term diplococcus refers to an irregular cluster of spherical bacterial cells.
False
True or False
The prokaryote cell membrane is made of the same materials as the eukaryote cell membrane.
True
True or False
Boiling water (100°C) can normally destroy endospores.
False
True or False
Bacteria in the genus Mycoplasma and bacteria called L-forms lack cell walls.
True
Chapter 9
Chapter 9
1) What is the use of microbe cells, and cellular compounds to make a
product?
a) biotechnology
b) bioremediation
c)
biogenetics
d) bioengineering
a) Biotechnology
2) What is NOT a practical property of DNA?
a) intrinsic
properties of DNA hold true even in a test tube
b) Need to avoid
accidental release into the environment
c) DNA - heated from 90C
to 95C the two strands separate. The nucleotides can be identified,
replicated, or transcribed
d) Slowly cooling the DNA allows
complementary nucleotides to hydrogen bond and the DNA will regain
double-stranded form
b) Need to avoid accidental release into the environment
The size of the restriction fragments produced by a restriction endonuclease depends on what?
ANSWER: the frequency of the recognition sites and the distances between them, which are usually 4 to 6 bp and palindromes
DNA is denatured at
A. 37 C
B. 42 C
C. 60 C
D. 90
C
E. 100 C
D. 90 C
Restriction endonucleases recognize and clip at DNA base sequences
called
A. Codons
B. Palindromes
C. Introns
D.
Exons
E. Genes
B. Palindromes
DNA strands can be clipped crosswise at selected positions by using
enzymes called
A. palindromes.
B. reverse
transcriptases.
C. restriction endonucleases.
D.
ligases.
E. DNA polymerases.
C. restriction endonucleases.
Information
These enzymes are found in bacteria and archaea and provide a defense mechanism against invading viruses.
Analysis of DNA fragments in gel electrophoresis involves
A.
Larger fragments move slowly and remain closer to the wells
B.
DNA has an overall negative charge and moves to the positive
pole
C. DNA fragments are stained to see them
D. An electric
current through the gel causes DNA fragments to migrate
E. All of
the choices are correct
E. All of the choices are correct
In recombinant DNA technique, what enzyme is needed to seal the
sticky ends of genes into plasmids or
chromosomes?
A. DNA
polymerase I
B. DNA polymerase II
C. DNA helicase
D.
DNA ligase
E. Primase
D. DNA ligase
Geneticists can make complimentary DNA copies of messenger, transfer,
and ribosomal RNA by using
A. palindromes.
B. reverse
transcriptases.
C. restriction endonucleases.
D.
ligases.
E. DNA polymerases.
B. reverse transcriptases.
The enzyme ____ _____ is a preformed protein carried in by HIV responsible for converting its RNA genome DNA.
reverse transcriptase
6) Which of the following best describes reverse
transcriptase?
a) RNA > cDNA
b) DNA > cDNA
c)
cDNA > RNA
d) RNA > mRNA
a) RNA > cDNA
Analysis of DNA fragments in gel electrophoresis involves
A.
Larger fragments move slowly and remain closer to the wells
B.
DNA has an overall negative charge and moves to the positive
pole
C. DNA fragments are stained to see them
D. An electric
current through the gel causes DNA fragments to migrate
E. All of
the choices are correct
E. All of the choices are correct
7) cDNA can be made from ALL BUT WHICH?
a) mRNA
b)
tRNA
c) rRNA
d) RNA
e) All the above are correct.
f) None of the above is the correct answer
d) RNA
8) Gel electrophoresis separates DNA fragments according to
a)
Electricity
b) Light
c) Size
d) Chemical makeup
b) Light
9) A dye often used to visualize DNA fragments and compare for
genetic similarities after agarose gel electrophoresis is
a)
Safranin
b) Ethidium Bromide
c) Bromothymol blue
d) Iodine
c) Bromothymol blue
What is being compared during DNA hybridization studies of two bacteria?
A) rate of DNA replication
B) mechanism of RNA synthesis from DNA
C) ratio of nitrogenous base to all other bases
D) similarity of base sequences
E) nature of the 16S RNA component
D) similarity of base sequences
Two different nucleic acids can _____ by uniting at their
complementary sites.
A. Hybridize
B. Covalently bond
C.
Form a peptide bond
D. Ligate
E. None of the choices are correct
A. Hybridize
Which of the following is NOT based on nucleic-acid
hybridization?
A) DNA chip
B) FISH
C) PCR
D)
Southern blotting
E) Western blotting
D) Southern blotting
The Southern blot method analyzes
A. DNA to DNA
B. RNA to
DNA
C. RNA to RNA
D. DNA to RNA
E. mRNA to proteins
A. DNA to DNA
The technique that utilizes probes to detect specific DNA sequences is known as what?
A)Southern blot
B)Northern blot
C)Western blot
D)Eastern blot
E)Northwestern blot
A)Southern blot
The Southern Blot technique detects
A. DNA.
B. RNA.
C.
proteins.
D. recombinant DNA.
E. specific genetic marker
sequence on genes.
A. DNA
When determining the sequence of nucleotides in an unknown sample of
DNA, which method is used to
sequence the DNA?
A.
PCR
B. Cloning
C. The Sanger Method
D. Southern blot
hybridization
E. Microarray analysi
C. The Sanger Method
The function of the dideoxy (dd) nucleotides that are used in the
Sanger method of DNA sequencing is to
A. Denature DNA into single
strands
B. Serve as primers
C. Be a fluorescent tag
D.
Incorporate into newly replicated DNA strands and stop elongation
D. Incorporate into newly replicated
What is TRUE about Sanger Technique?
a) Most common sequencing
technique
b) Test strands are denatured to serve as a template to
synthesize complementary strands
c) A method to amplify
DNA
d) All are true
e) ONLY A and B are true
e) ONLY A and B are true
The size of DNA is often given in the number of _____ that it
contains.
A. Genes
B. Codons
C. Base pairs
D.
Proteins
E. Triplets
C. Base pairs
Amplification of DNA is accomplished by
A. Polymerase chain
reaction
B. DNA sequencing
C. Gene probes
D. Southern
blot
E. Western blot
A. Polymerase chain reaction
12) What is FALSE about Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)?
a)
Repetitively cycled through denaturation, priming, and
extension
b) Each subsequent cycle triples the number of copies
for analysis
c) Primers of known sequence are added, to indicate
where amplification will begin
d) Important in gene mapping, the
study of genetic defects and cancer, forensics, taxonomy, and
evolutionary studies
b) Each subsequent cycle triples the number of copies for analysis
DNA polymerases used in PCR( Polymerase Chain Reaction)
A. use
an RNA template to make complementary DNA.
B. must remain active
at very cold temperatures.
C. include Taq polymerases and Vent
polymerase.
D. are labeled with fluorescent dyes.
E. All of
the choices are correct.
c) include Taq polymerases and Vent polymerase.
What is FALSE about Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)?
a)
Repetitively cycled through denaturation, priming, and
extension
b) Each subsequent cycle triples the number of copies
for analysis
c) Primers of known sequence are added, to indicate
where amplification will begin
d) Important in gene mapping, the
study of genetic defects and cancer, forensics, taxonomy, and
evolutionary studies
b) Each subsequent cycle triples the number of copies for analysis
Which PCR step causes the denaturation of double-stranded
DNA?
A. add DNA polymerase and nucleotides at 72°C
B. cool
DNA to between 50°C and 65°C
C. add primers
D. heat target
DNA to 94°C
E. repeat the cycle of heating and cooling
D. heat target DNA to 94°C
Which PCR step synthesizes complementary DNA strands?
A. add DNA
polymerase and nucleotides at 72°C
B. cool DNA to between 50°C
and 65°C
C. add primers
D. heat target DNA to 94°C
E.
repeat the cycle of heating and cooling
A. add DNA polymerase and nucleotides at 72°C
Which of the following is a serious concern when performing
PCR?
A. high temperature needed may denature the DNA
B.
restriction enzymes are difficult to obtain in adequate
quantities
C. introduction and amplification of contaminating
DNA
D. exposure to radiation by the lab personnel
E. it is a
very time consuming process
C. introduction and amplification of contaminating DNA
The primers in PCR are
A. synthetic DNA
oligonucleotides.
B. bacterial enzymes.
C. short RNA
strands.
D. DNA polymerases.
E. reverse transcriptases.
A. synthetic DNA oligonucleotides.
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) has been used in all of the
following fields, except
A. forensics.
B. evolutionary
studies.
C. gene mapping.
D. medicine.
E. None of the
choices; it is useful for all these fields.
E. None of the choices; it is useful for all these fields.
The following steps are used to make DNA fingerprints. What is the
third step?
A) Collect DNA.
B) Digest with a restriction
enzyme.
C) Perform electrophoresis.
D) Lyse cells.
E)
Add stain.
D) Lyse cells.
Each of the following are features of a cloning host except
A.
Quick generation time
B. Minimal growth requirements
C.
Mapped genome
D. Pathogenic
E. Transformable
D. Pathogenic
Common vectors used to transfer a piece of DNA into a cloning host
are
A. Plasmids
B. Viruses
C. Bacteriophages
D.
Artificial chromosomes
E. All of the choices are correct
E. All of the choices are correct
The deliberate removal of genetic material from one organism and
combining it with the genetic material
of another organism is a
specific technique called
A. genetic engineering.
B.
biotechnology.
C. recombinant DNA technology.
D. gel
electrophoresis.
E. gene probes.
C. recombinant DNA technology.
Transformation is the transfer of DNA from a donor to a recipient
cell
A) By a bacteriophage.
B) By cell-to-cell
contact.
C) By crossing over.
D) As naked DNA in
solution.
E) By sexual reproduction.
D) As naked DNA in solution.
Which of the following methods of making rDNA could be described as
"hit or miss"?
A) Gene gun
B) Viral
transduction
C) Transformation
D) Cloning
E) Protoplast fusion
E) Protoplast fusion
In Figure 9.4, the bacteria transformed with the recombinant plasmid
and plated on media
containing ampicillin and X-gal will
A)
form blue, ampicillin-resistant colonies.
B) form blue,
ampicillin-sensitive colonies.
C) form white,
ampicillin-resistant colonies.
D) form white,
ampicillin-sensitive colonies.
E) not grow.
C) form white, ampicillin-resistant colonies.
Which of the following is not true of vectors?
A. An origin of
replication (ORI) is present
B. Must accept DNA of desired
size
C. Contain a gene for drug resistance
D. Must have a
promoter in front of the cloned gene
E. Can detect RNA in cells
E. Can detect RNA in cells
Which enzyme covalently links the DNA pieces together?
a) DNA
polymerase
b) RNA polymerase
c) DNA Ligase
d) Palindrome
c) DNA Ligase
How can DNA be inserted in the cell?
a) Transformation
b)
Electroporation
c) Protoplast fusion
d)
Microinjection
e) All of the above
e) All of the above
Which of the following CANNOT be made by using recombinant DNA
technology?
A) Pharmaceutical drugs
B) Vaccines
C)
Pest-resistant crops
D) Life
E) Human hormones
D) Life
An agent that reproduces in cells but is NOT composed of cells and
contains RNA as its genetic material is
a(n)
A) Bacterium.
B) Virus.
C) Fungus.
D) Helminth.
E) Alga.
B) Virus.
In the figure above, the enzyme in step 1 is
A) DNA
polymerase.
B) DNA ligase.
C) RNA polymerase.
D)
reverse transcriptase.
E) spliceosome.
C) RNA polymerase.
In the figure above, the enzyme in step 2 is
A) DNA
polymerase.
B) DNA ligase.
C) RNA polymerase.
D)
reverse transcriptase.
E) spliceosome.
A) DNA polymerase.
Which of the following is an advantage of using E. coli to make a
human gene product?
A) Endotoxin may be in the product.
B)
It can't process introns.
C) It doesn't secrete most
proteins.
D) Its genes are well known.
E) None of the above.
D) Its genes are well known.
When patient tissues are transfected with viruses carrying a needed,
normal human gene, the technique is
called
A.
cloning.
B. gene therapy.
C. antisense therapeutic.
D.
DNA
fingerprinting.
E. None of the choices are correct.
B. gene therapy.
The process whereby naked DNA is absorbed into a bacterial cell is
known as:
A) transcription.
B) transduction.
C)
transformation.
D) translation.
C) transformation.
TRUE OR FALSE:
Restriction endonucleases is recognizing specific sequences of DNA and break phosphodiester bonds between adjacent nucleotides
TRUE
Bacteria differ from viruses in that bacteria
A) Can live
without a host.
B) Have DNA and RNA.
C) Are composed of cells.
D) All of the above.
D) All of the above.
Which of the following processes is NOT involved in making
cDNA?
A) Translation
B) Transcription
C) Reverse transcription
D) RNA processing to remove introns
A) Translation
The value of cDNA in recombinant DNA is that
A) It contains
introns and exons.
B) It lacks exons.
C) It lacks introns.
D) It's really RNA.
C) It lacks introns.
Acquisition of new genetic material by the
uptake of naked
DNA.
A) True
B) False
False
True or False
After 3 replication cycles in PCR, there will be a total of 4 double-stranded DNA molecules.
False
True or False
Reverse transcriptase is used to make cDNA from an RNA template.
True
True or False
In recombinant DNA technology, a vector is a
self-replicating segment of DNA, such as a
plasmid or viral genome.
True
True or False
One of the first commercial successes of recombinant DNA
technology was the production of
human insulin using genetically
engineered E. coli.
TRUE
True or False
The Bt toxin derived from Bacillus thuringiensis has been introduced into some crop plants to make them resistant to insect destruction.
True
True or False
One of the first commercial successes of recombinant DNA
technology was the production of
human insulin using genetically
engineered E. coli.
True
TRUE OR FALSE
Raccoon roundworm in humans has been identified as an emerging disease.
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
Protozoa are unicellular.
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
Flagella are long, sheathed cylinder containing microtubules in a 9+2 arrangement.
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
The difference between cilia and flagella is that flagella are shorter and more numerous
FALSE
TRUE OR FALSE
The nuclear envelope is composed of one membrane that is perforated with pores.
FALSE
TRUE OR FALSE
On a cell image, the nucleolus is the dark area for rRNA synthesis and ribosome assembly.
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) extends in a continuous network of ribosomes through cytoplasm.
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
The Golgi apparatus consists of ribosomes.
FALSE
TRUE OR FALSE
Ribosomes are larger in prokaryotic cells than in eukaryotic cells.
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
Lysosomes are involved in intracellular digestion of food particles and in protection against invading microbes.
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
All fungi are autotrophic.
FALSE
TRUE OR FALSE
If a microscopic fungi has a round ovoid shape and reproduces asexually, then it is called A YEAST
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
The two types of hyphae are long and short.
FALSE
TRUE OR FALSE
Coenocytic hyphae lack the cross wall, known as the septa.
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
A mycosis is a fungal infection.
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
All animal cells lack chloroplasts.
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
When conditions are unfavorable for growth, protozoa become cysts, where they enter into a dormant stage.
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
Malaria, brain infections, amoebiasis (intestinal infections) are all examples of pathogenic protozoa.
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
Amoeba are your alternates between a large trophozoite and a smaller nonmotile cyst.
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
Pathogenic flagellate give rise to giardia lamblia agent, which causes diarrhea and abdominal pain.
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
Ciliophora members are pathogenic.
FALSE
TRUE OR FALSE
Arthropods that transmit infectious diseases are called vectors.
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
Parasitic helminths are multicellular eukaryotic plants.
FALSE
TRUE OR FALSE
Schistosomiasis is a prominent blood fluke disease.
TRUE
Chapter 13
Chapter 13
In which of the following ways do viruses differ from
bacteria?
A) Viruses don't reproduce.
B) Viruses are not
composed of cells.
C) Viruses are filterable.
D) Viruses
don't have any nucleic acid.
E) Viruses are obligate
intracellular parasites.
B) Viruses are not composed of cells.
Which of the following statements provides the most significant
support for the idea that viruses are
nonliving
chemicals?
A) They are chemically simple.
B) They cause
diseases similar to those caused by chemicals.
C) They are
filterable.
D) They cannot reproduce themselves outside a
host.
E) They are not composed of cells.
D) They cannot reproduce themselves outside a host.
Which of the following is NOT a distinguishing characteristic of
prokaryotic cells?
a) They usually have a single, circular
chromosome
b) They lack membrane-enclosed organelles
c) They
have cell walls containing peptidoglycan
d) Their DNA is not
associated with histones
e) They lack a plasma membrane
d) Their DNA is not associated with histones
Helical and icosahedral are terms used to describe the shapes of a
virus
A. Spike
B. Capsomere
C. Envelope
D.
Capsid
E. Core
D. Capsid
A viroid is
A) An infectious protein.
B) A nonenveloped,
infectious piece of RNA.
C) A provirus.
D) A capsid without
a nucleic acid.
E) A complete, infectious virus particle.
B) A nonenveloped, infectious piece of RNA.
Viruses always have at least _____.
A) an outer capsid
B)
a cell wall
C) an inner core of nucleic acid
D) both A and C
D) both A and C
Viral DNA and capsids are assembled to produce hundreds of viral
particles during the _____ stage of the lytic cycle.
A)
attachment
B) biosynthesis
C) maturation
D) release
C) maturation
The outer layer of flukes and tapeworms is the
A) tegument.
B) pellicle.
C) epidermis.
D) shell.
A) tegument.
A lytic virus has infected a patient. Which of the following would
best describe what is
happening inside the patient?
A) The
virus is causing the death of the infected cells in the
patient.
B) The virus is not killing any cells in the
host.
C) The virus is incorporating its nucleic acid with that of
the patient's cells.
D) The virus is slowly killing the patient's
cells.
E) The virus is infecting cells and then releasing only
small amounts of virus.
A) The virus is causing the death of the infected cells in the patient.
Some viruses, such as human herpesvirus 1, infect a cell without
causing symptoms. These
are called
A) latent
viruses.
B) lytic viruses.
C) phages.
D) slow
viruses.
E) unconventional viruses
A) latent viruses.
Which of the following statements is NOT true of lysogeny?
A) It
can give infected pathogens the genetic information for toxin
production.
B) Prophage is inserted into the host genome.
C)
Lytic cycle may follow lysogeny.
D) It is a "silent"
infection; the virus does not replicate.
E) It causes lysis of
host cells.
E) It causes lysis of host cells.
When a bacteriophage is integrated into a cellular genome it is called a
A) virulent virus
B) lytic virus
C) prophage
D) transducing virus
E) microphage
C) prophage
The infectious substance of prions is
A) protein
B) glycophosphate
C) RNA
D) DNA
E) glycoprotein
A) protein
Which of the following is NOT caused by prions?
A)
Rabies
B) Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
C) Kuru
D) Sheep
scrapie
E) Elk chronic wasting disease
A) Rabies
Diseases such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), or mad cow disease, are caused by ________.
A) oncogenes
B) phage
C) prions
D) viroids
E) bacteria
C) prions
Infectious protein particles are called
A. viroids.
B.
phages.
C. prions.
D. oncogenic viruses.
E. spikes.
C. prions.
The mechanism whereby an enveloped virus leaves a host cell is
called
A) transduction.
B) budding.
C)
abduction.
D) lysogeny.
E) penetration.
B) budding.
Viruses have an overall structure that is
A) spherical
B) isometric
C) icosahedron
D) helical
E) all of the above
E) all of the above
Hollow coil like arrangement of capsomeres that looks like a rod shaped is known as
a) Helical
b) Icosahedral
c) Spiral
d) Triangular
a) Helical
The only structural pattern that has been found among isometric viruses is
A) icosahedral
B) spherical
C) helical
D) tetrahedral
E) capsular
A) icosahedral
______ are viruses that reproduce inside bacteria.
A) Adenoviruses
B) Retroviruses
C) Oncoviruses
D) Bacteriophages
E) HIV
D) Bacteriophages
Some differences between animal viral reproduction and bacteriophages are _______.
A) animal viruses enter by endocytosis
B) the entire virus enters and the genome undergoes uncoating
C) viral release involves budding
D) the viral particle acquires a membranous envelope by budding
E) all of the above
E) all of the above
Once the bacterial cell has been digested, the amoeba will dispose of indigestible materials by which of the following processes?
A) facilitated diffusion
B) through gated channels in membrane proteins
C) exocytosis
D) active transport
E) by any of the above processes
C) exocytosis
_________ is the virus causing fever blisters
A) Herpes simplex
B) Chlamydia
C) Epstein-Barr virus
D) Human papillomavirus
E) Lyme disease
A) Herpes simplex
The following steps occur during multiplication of retroviruses.
Which is the fourth step?
A) synthesis of double-stranded
DNA
B) synthesis of +RNA
C) attachment
D)
penetration
E) uncoating
A) synthesis of double-stranded DNA
The general steps in a viral multiplication cycle are:
A) adsorption, penetration, replication, maturation, and release
B) endocytosis, uncoating, replication, assembly, budding
C) adsorption, uncoating, duplication, assembly, and lysis
D) endocytosis, penetration, replication, maturation, and exocytosis
A) adsorption, penetration, replication, maturation, and release
Learn more about the Hersey-Chase Experiment Noble prize winners
copy the link
http://highered.mheducation.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::535::535::/sites/dl/free/0072437316/120076/bio21.swf::Hershey+and+Chase+Experiment
Possible Essay question
Compare and contrast the lytic cycle of infection of a DNA virus and an RNA virus.
DNA transcribes itself into mRNA which is used to direct the cells ribosomes.
Retroviruses(RNA) use reverse transcriptase which transcribes RNA into DNA, which is transcribed again into the mRNA.
The mRNA instructs the cell to create more viral proteins.
Both end with the lysis of the host cell after enough viruses are produced.
How would you describe this virus?
A. Icosahedral and
Naked
B. Helical and Naked
C. Complex and Naked
D.
Icosahedral and Enveloped
E. Helical and Enveloped
F.
Complex and Enveloped
A. Icosahedral and Naked
Persistent infections=
cell harbors the virus and is not immediately lysed
Delta agent=
naked strand of RNA expressed only in the presence of hepatitis B virus
Adeno=
associated virus – replicates only in cells infected with adenovirus
On entering a bacterial cell, all bacteriophages
immediately
initiate the lytic cycle.
A) True
B) False
B) False
True or False
A viroid is a completely developed infectious agent composed of
nucleic acid and surrounded
by a capsid.
Answer: FALSE
True or False
The lytic cycle of bacteriophages has four stages.
A) True
B) False
B) False
True or False
The basic mechanism of viral multiplication is similar for all viruses.
Answer: TRUE
True or False
A viroid is a completely developed infectious agent composed of nucleic acid and surrounded by a capsid.
False
True or False
Viruses are more closely related to chemical matter than to a living organism.
A) True
B) False
A) True
True or False
Helical and icosahedral are terms used to describe the shapes of a virus envelope.
FALSE
True or False
Viruses are the only known infectious agents that are obligatory intracellular parasites.
FALSE
True or False
A tegument is the external covering of an animal.
A) True
HIV is a DNA virus.
A) True
B) False
B) False
End of Chapter Review Questions
End of Chapter Review Questions
What is the similarity between algae and protozoa?
both contain mitochondria; You cannot say both are unicellular because algae may be either unicellular or multicellular
What is the overall process of protein transport? List in order
= nucleus→ RER→ SER→ vesicles→ Golgi→ maturation→ secretion
What are the characteristics of protozoa?
singled-celled, lack tissues and are animal-like because they are heterotrophic & motile [eat by engulfing other microbes]
Which are the four representative eukaryotic microbes?
= fungi & algae & protozoa & parasitic worms
What are the most important organelles within the cell membrane?
=cytoplasmic matrix, nucleus, organelles, ribosomes and cytoskeleton
What is the main function of the golgi complex?
= digestive enzyme storage
What is the main function of the SER?
= biosynthesis of phospholipids and cholesterol & the synthesis of membranes
What structure converts the energy of sunlight into chemical energy through photosynthesis?
chloroplasts
What are examples of Macroscopic fungi?
=mushrooms, puffballs
What are the characteristics of asexual reproduction?
spores are formed through budding or mitosis; common examples of fungi that reproduce asexually are conidia or sporangiospores or protozoa
What beneficial roles can fungi have?
decomposers of dead plants & animals, sources of antibiotics and alcohol, and used in making food and in genetic studies
Why is classification of protozoa difficult?
= diversity. Simple grouping is based on method of motility, reproduction and life cycle
Amebiasis can affect which parts of your body?
intestines, brain
What is the dominant protozoan disease?
plasmodium
The primary vector is _________?
the female mosquito
What is the most abundant worm group?
roundworms
How can you develop elephantiasis?
from tissue nematodes