Human A&P Exam 3
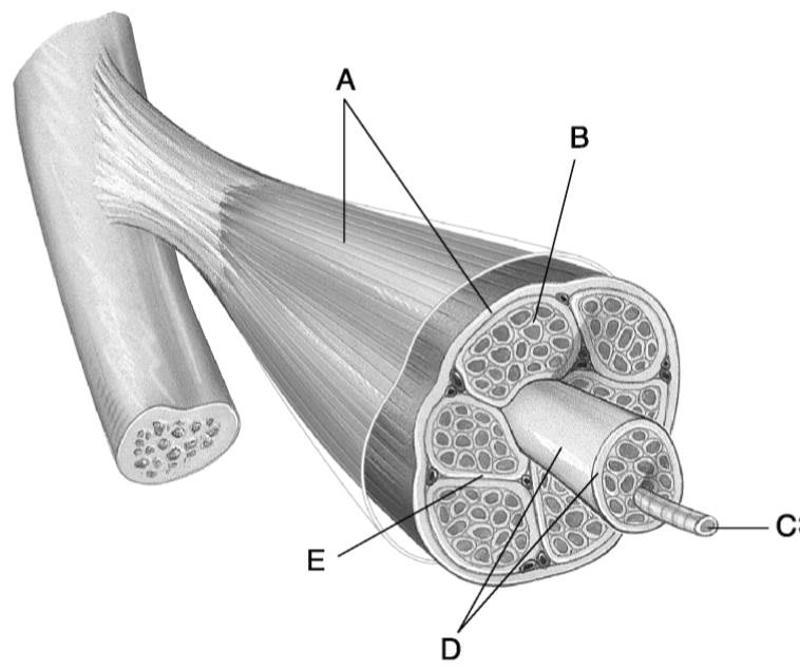
Using Figure 9.1, match the following:
1) Endomysium.
2) Fascicle.
3) The tissue that binds
muscles into functional groups.
4) Perimysium.
5) Muscle fiber.
1) B
2) D
3) A
4) E
5) C
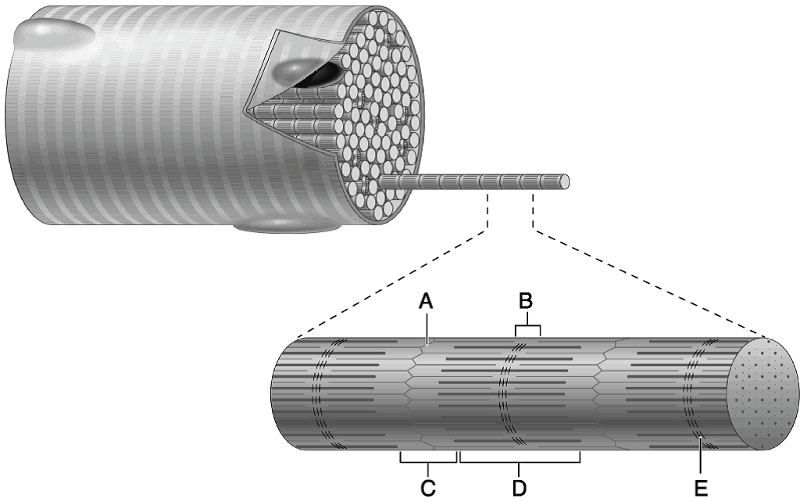
Using Figure 9.2, match the following:
6) I band.
7) H zone.
8) A band.
9) Z
disc.
10) M line
6) C
7) B
8) D
9) A
10) E
Match the following:
A) Slow (oxidative), fatigue-resistant fibers
B) Fast (oxidative or glycolytic), fatigable fibers
11) Depends on oxygen delivery and aerobic mechanisms.
12) Have very fast-acting myosin ATPases and depend upon
anaerobic metabolism during contraction.
13) Red fibers,
the smallest of the fiber types.
14) Contain abundant
amounts of glycogen.
15) Abundant in muscles used to
maintain posture.
16) A relatively high percentage are
found in successful marathon runners.
11) A
12) B
13) A
14) B
15) A
16) A
Once a motor neuron has fired, all the muscle fibers in a muscle contract.
False
The thin filaments (actin) contain a polypeptide subunit G actin that bear active sites for myosin attachment.
True
A contraction in which the muscle does not shorten but its tension increases is called isometric contraction.
True
During isotonic contraction, the heavier the load, the faster the velocity of contraction
False
During isometric contraction, the energy used appears as movement
False
What is the role of tropomyosin in skeletal muscles?
A)
Tropomyosin serves as a contraction inhibitor by blocking the actin
binding sites on the myosin molecules.
B) Tropomyosin is the
chemical that activates the myosin heads.
C) Tropomyosin serves
as a contraction inhibitor by blocking the myosin binding sites on the
actin molecules.
D)Tropomyosin is the receptor for the motor
neuron neurotransmitter.
C) Tropomyosin serves as a contraction inhibitor by blocking the myosin binding sites on the actin molecules.
Fatigued muscle cells that recover rapidly are the products of ________.
intense exercise of short duration
excitation-contraction coupling requires which of the following substances
Ca2+ and ATP
what structure in skeletal muscle cells functions in calcium storage?
sacroplasmic reticulum
Articular (hyaline) cartilage
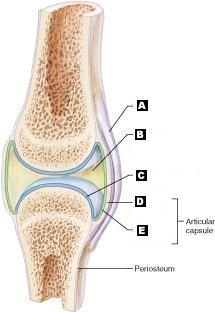
C
Fibrous capsule
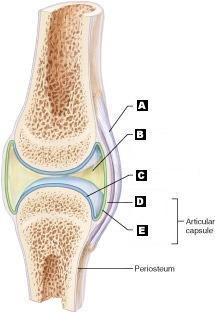
D
Ligament
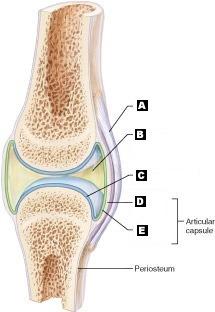
A
Joint cavity (contains synovial fluid)
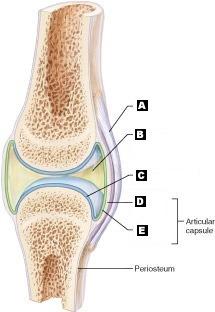
B
Synovial Membrane
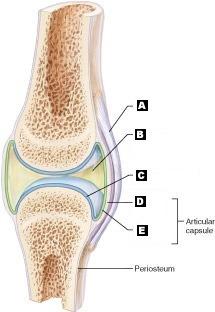
E
Label the types of movements allowed by synovial joints
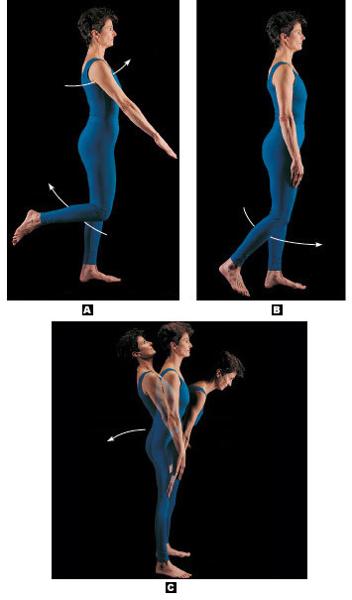
A=flexion
B=extension
C=Hyperextension
Label the types of movement allowed by synovial joints
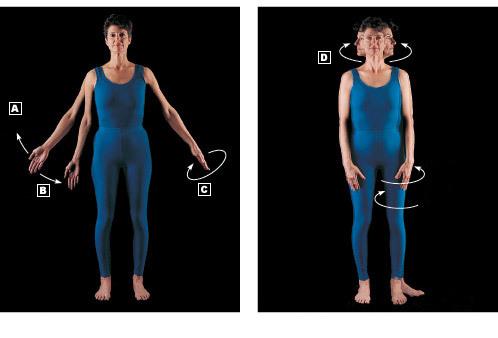
A=abduction
B=adduction
C=circumduction
D=rotation
Label the types of synovial joints
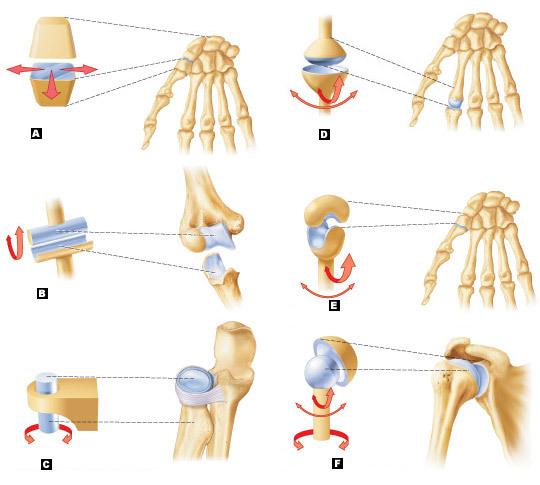
A=plane joint
B=hinge joint
C=pivot joint
D=condylar joint
E=saddle joint
F=ball-and-socket joint
abduction and adduction always refer to movements of the appendicular skeleton
True
a twisting motion of the foot that turns the sole inward is called eversion
False (inversion)
amphiarthroses are joints typically found at the end of long bones
False
only rotation is possible in pivot joints
True
a suture is an example of synarthroses
True
which of the following is NOT a function of synovial fluid
a. lubrication
b. protects articular cartilages
c. increases osmotic pressure within joint
d. shock absorption
c. increases osmotic pressure within joint
the epiphyseal growth plate is an example of a(n)
a. amphiarthrosis
b. symphysis
c. gomphosis
d. synchondrosis
d. synchondrosis