Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Human A&P Exam 3
front 1 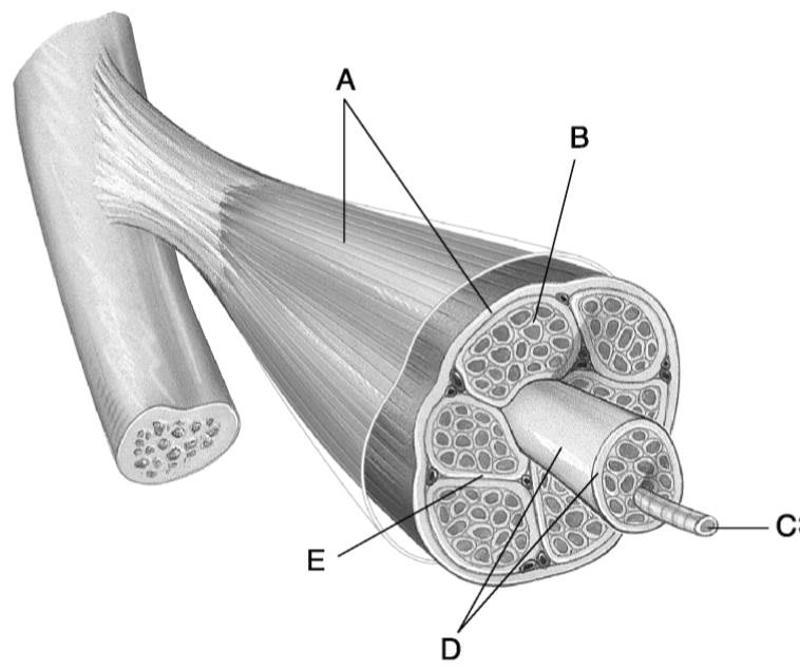 Using Figure 9.1, match the following: | back 1 1) B |
front 2 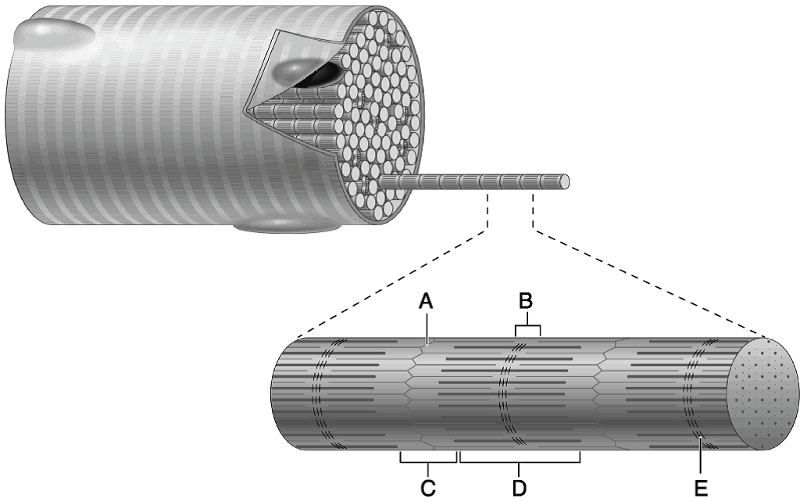 Using Figure 9.2, match the following: | back 2 6) C |
front 3 Match the following: A) Slow (oxidative), fatigue-resistant fibers 11) Depends on oxygen delivery and aerobic mechanisms. | back 3 11) A |
front 4 Once a motor neuron has fired, all the muscle fibers in a muscle contract. | back 4 False |
front 5 The thin filaments (actin) contain a polypeptide subunit G actin that bear active sites for myosin attachment. | back 5 True |
front 6 A contraction in which the muscle does not shorten but its tension increases is called isometric contraction. | back 6 True |
front 7 During isotonic contraction, the heavier the load, the faster the velocity of contraction | back 7 False |
front 8 During isometric contraction, the energy used appears as movement | back 8 False |
front 9 What is the role of tropomyosin in skeletal muscles? | back 9 C) Tropomyosin serves as a contraction inhibitor by blocking the myosin binding sites on the actin molecules. |
front 10 Fatigued muscle cells that recover rapidly are the products of ________. | back 10 intense exercise of short duration |
front 11 excitation-contraction coupling requires which of the following substances | back 11 Ca2+ and ATP |
front 12 what structure in skeletal muscle cells functions in calcium storage? | back 12 sacroplasmic reticulum |
front 13 Articular (hyaline) cartilage | back 13 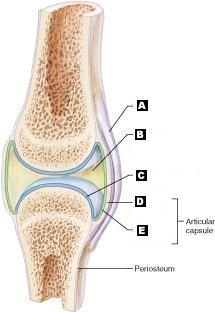 C |
front 14 Fibrous capsule | back 14 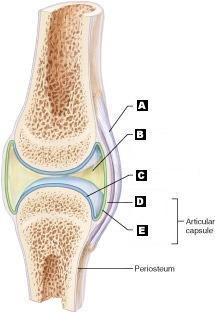 D |
front 15 Ligament | back 15 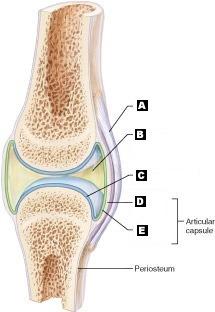 A |
front 16 Joint cavity (contains synovial fluid) | back 16 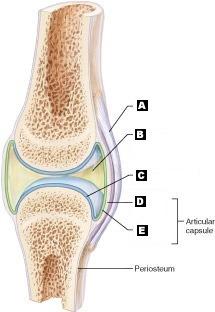 B |
front 17 Synovial Membrane | back 17 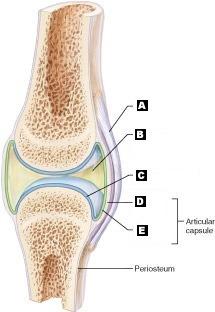 E |
front 18 Label the types of movements allowed by synovial joints | back 18 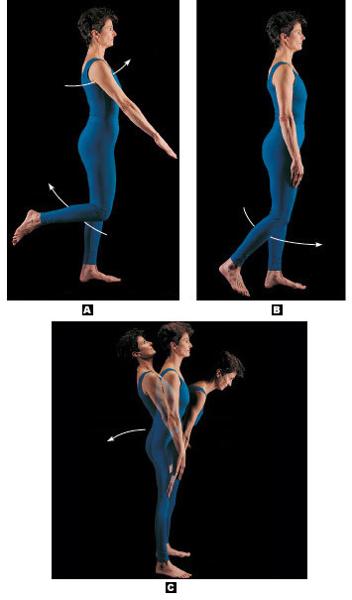 A=flexion B=extension C=Hyperextension |
front 19 Label the types of movement allowed by synovial joints | back 19 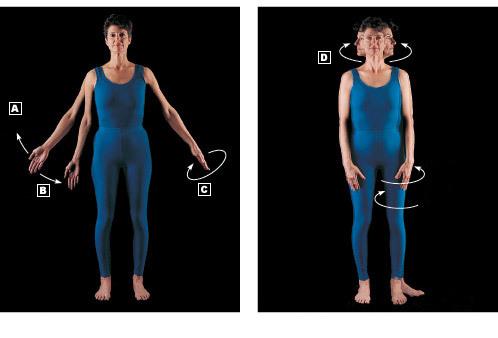 A=abduction B=adduction C=circumduction D=rotation |
front 20 Label the types of synovial joints | back 20 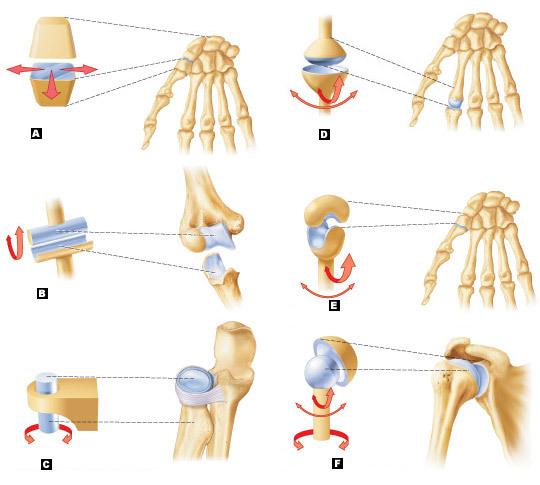 A=plane joint B=hinge joint C=pivot joint D=condylar joint E=saddle joint F=ball-and-socket joint |
front 21 abduction and adduction always refer to movements of the appendicular skeleton | back 21 True |
front 22 a twisting motion of the foot that turns the sole inward is called eversion | back 22 False (inversion) |
front 23 amphiarthroses are joints typically found at the end of long bones | back 23 False |
front 24 only rotation is possible in pivot joints | back 24 True |
front 25 a suture is an example of synarthroses | back 25 True |
front 26 which of the following is NOT a function of synovial fluid a. lubrication b. protects articular cartilages c. increases osmotic pressure within joint d. shock absorption | back 26 c. increases osmotic pressure within joint |
front 27 the epiphyseal growth plate is an example of a(n) a. amphiarthrosis b. symphysis c. gomphosis d. synchondrosis | back 27 d. synchondrosis |