Final Exam
When applying the process of science, which of these is tested?
Hypothesis
About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which 4 of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living matter?
carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen
Which of the following is not a common life property?
Inductive Reasoning
Why does ice float in liquid water?
Hydrogen bonds stabilize and keep the molecules of ice farther apart than the water molecules of liquid water.
The crystalline lattice of ice causes it to be denser than liquid water.
A water sample from a hot thermal vent contained a single-celled organism that had a cell wall but lacked a nucleus. What is its most likely classification?
Archaea
The first electron shell can be filled with a maximum of _________ electrons. All subsequent shells can be filled with a maximum of _________ electrons.
2,8
One liter of a solution of pH 2 has how many more hydrogen ions (H+) than 1 L of a solution of pH 6?
10,000 times more
What results from an unequal sharing of electrons between atoms?
A polar covalent bond
Knowing just the atomic mass of an element allows inferences about which of the following?
the number of protons plus neutrons in the element
Which of the following statements is true about buffer solutions?
They maintain a relatively constant pH when either acids or bases are added to them.
Which of the following is not a polymer?
Starch
Which of the following best summarizes the relationship between dehydration reactions and hydrolysis?
Dehydration reactions assemble polymers, and hydrolysis reactions break down polymers.
Which of the following is true of both starch and cellulose?
They are both polymers of glucose.
Testosterone and estradiol are male and female sex hormones, respectively, in many vertebrates. In what way(s) do these molecules differ from each other?
Testosterone and estradiol have different functional groups attached to the same carbon skeleton.
Which bonds are created during the formation of the primary structure of a protein?
Peptide bonds
Which level of protein structure do the α helix and the β pleated sheet represent?
secondary
Which of the following descriptions best fits the class of molecules known as nucleotides?
a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a pentose sugar
Denaturation of proteins can occur if there is a change in ____________.
pH
The Central Dogma:
0.0015
How does a raft spider manage to walk on water?
The spider is supported on the surface of the water due to the water’s strong surface tension that forms a tight, invisible film underneath the spider’s legs.
What color is a positive test for proteins?
Purple
You are working at the food lab when your boss gives you an unknown carbohydrate. You test the substance with biuret and Benedict’s reagents. The biuret test is blue as well as the Benedict’s test. What does this tell you about the sample?
negative for both reducing sugars and protein
Which form do potatoes predominantly store their carbohydrates as?
Starch
Give an example of form (structure) and function in biology. (I will accept examples used in lecture, or any example you may know from prior knowledge.)
Galapagos finches and their beaks. Hummingbird beaks. Gills on fish. Expansion of water molecules during freezing. Electronegativity of oxygen. Multiple examples can be used... structure and function are EVERYWHERE!
Organisms are classified using taxonomic hierarchy. What two least inclusive levels are used universally to identify living organisms?
Genus and Species.
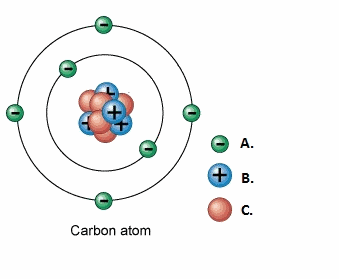
Label the following:
A.1.Electron
B.2.Proton
C.3.Neutron
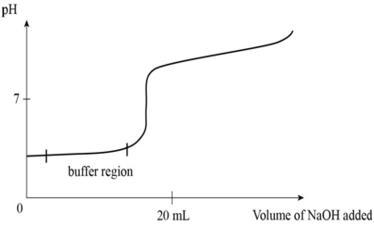
Is the following graph an example of a "good buffer"? Explain.
Yes. The pH is maintained at the buffer region, only with increased addition of NaOH does the buffer reach capacity and yield to change.
Describe the difference between cohesion and adhesion.
Cohesion= water's affinity for itself. Adhesion= water's affinity for others (polar).
________ cells lack a membrane-enclosed nucleus.
Prokaryotic
A bacterial cell's DNA is found in its
nucleoid region
The membranous compartmentalization of a cell
allows different chemical conditions to be maintained in different parts of the cell.
All of the following are part of a prokaryotic cell except
an endoplasmic reticulum
Large numbers of ribosomes are present in cells that specialize in producing which of the following molecules?
proteins
The liver is involved in detoxification of many poisons and drugs. Which of the following structures is primarily involved in this process and therefore abundant in liver cells?
smooth ER
Tay-Sachs disease is a human genetic abnormality that results in cells accumulating and becoming clogged with very large, complex, undigested lipids. Which cellular organelle must be involved in this condition?
the lysosome
In a plant cell, DNA may be found
in the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts.
Unlike animal cells, plant cells have ________ and ________. Unlike plant cells, animal cells have ________.
chloroplasts . . . cell walls . . . centrioles
Motor proteins provide for molecular motion in cells by interacting with what types of cellular structures?
cytoskeletal structures
The fluid mosaic model describes the plasma membrane as consisting of
diverse proteins embedded in a phospholipid bilayer.
In order for a protein to be an integral membrane protein it would have to be
amphipathic, with at least one hydrophobic region.
What kinds of molecules pass through a cell membrane most easily?
small and hydrophobic
Diffusion does not require the cell to expend ATP. Therefore, diffusion is considered a type of
passive transport
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of a carrier protein in a plasma membrane?
It exhibits a specificity for a particular type of molecule.
Which of the following statements correctly describes the normal tonicity conditions for typical plant and animal cells?
The animal cell is in an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypotonic solution
Some protozoans have special organelles called contractile vacuoles that continually eliminate excess water from the cell. The presence of these organelles tells you that the environment
is hypotonic to the protozoan.
You are adrift in the Atlantic Ocean, and, being thirsty, drink the surrounding seawater. As a result,
you dehydrate yourself.
Which of the following processes can move a solute against its concentration gradient?
active transport
The process of a white blood cell engulfing a bacterium is
phagocytosis.
According to ________, energy cannot be created or destroyed.
the first law of thermodynamics
Which of the following processes is endergonic?
the synthesis of glucose from carbon dioxide and water
When a cell uses chemical energy to perform work, it uses the energy released from a(n) ________ reaction to drive a(n) ________ reaction.
exergonic . . . endergonic
Which term most precisely describes the cellular process of breaking down large molecules into smaller ones?
catabolism
Which of the following is an example of potential rather than kinetic energy?
a molecule of glucose
When an enzyme catalyzes a reaction,
it lowers the activation energy of the reaction.
The active site of an enzyme is
the region of an enzyme that attaches to a substrate.
According to the induced fit hypothesis of enzyme catalysis, which of the following is correct?
The binding of the substrate changes the shape of the enzyme's active site.
How does a noncompetitive inhibitor decrease the rate of an enzyme reaction?
by changing the shape of the enzyme's active site
If an enzyme in solution is saturated with substrate, the most effective way to obtain a faster yield of products is to
add more of the enzyme.
What is the magnification of the oculars (eyepieces) of the compound light microscope you used in the lab?
10x
How does the field of view change as you move from the scanning to low power and then high power objectives?
The field of view decreases.
Every plant cell contains chloroplasts, even if it is not directly involved in the process of photosynthesis.
False
Samantha is working with a slide of bacteria and knows that she will need to use the high-power objective to see them clearly. She puts the slide on the microscope, centers it, rotates the high-power objective into place, and uses the coarse-adjustment knob to focus the image. What (if anything), has Samantha done wrong, and what could be the consequences of her actions?
Samantha should never use the coarse adjustment knob to focus with the high-power objective since the working distance is very small and this could damage both the lens and the slide.
What were the results of the diffusion and osmosis experiment?
The glucose diffused outward from the bag, and the iodine diffused into the bag reacting with starch.
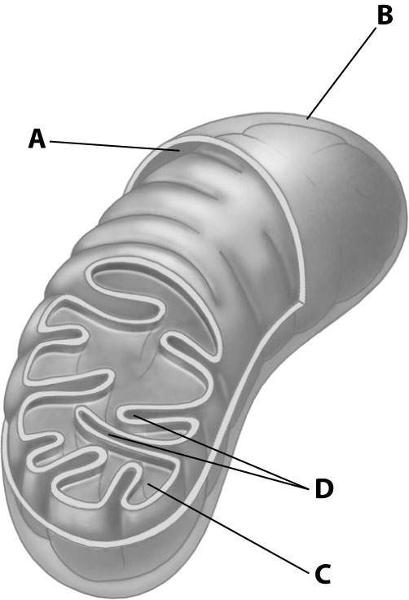
Which part of the mitochondrion shown enhances its ability to produce ATP by increasing the surface area of a mitochondrial membrane?
Structure D
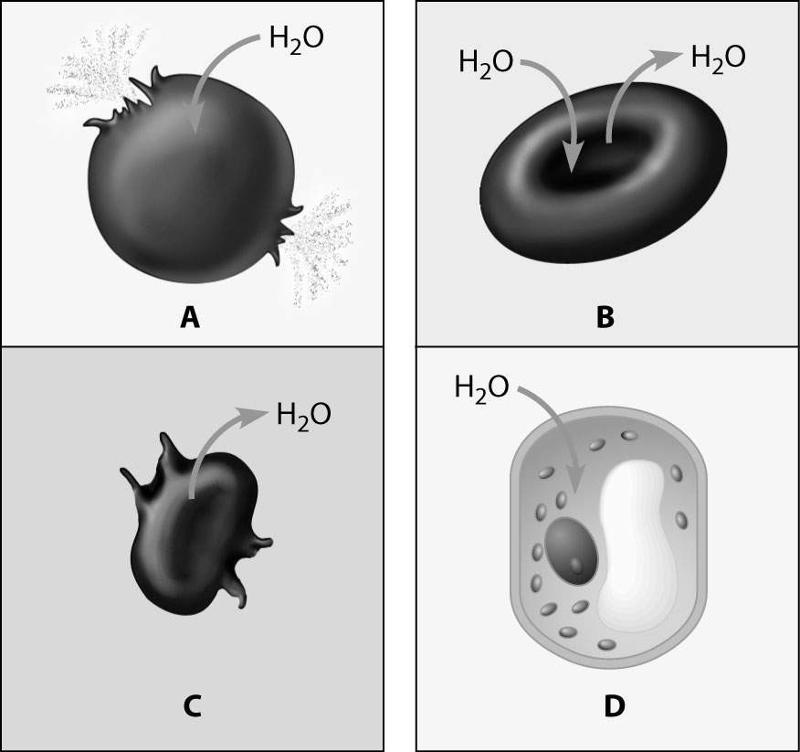
Which figure depicts an animal cell placed in a solution hypotonic to the cell?
Cell A
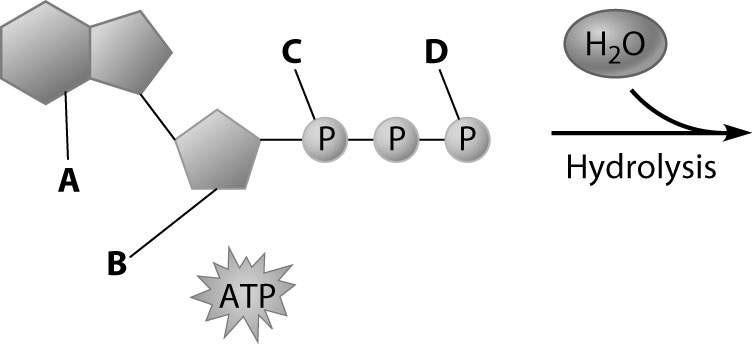
Which part of the ATP molecule breaks free of the rest when an ATP molecule is used for energy?
Part D
After reading the paragraph, answer the question(s) that
follow.
Americans spend up to $100 billion annually for bottled water (41 billion gallons). The only beverages with higher sales are carbonated soft drinks. Recent news stories have highlighted the fact that most bottled water comes from municipal water supplies (the same source as your tap water), although it may undergo an extra purification step called reverse osmosis.
Imagine two tanks that are separated by a membrane that's permeable to water, but not to the dissolved minerals present in the water. Tank A contains tap water and Tank B contains the purified water. Under normal conditions, the purified water would cross the membrane to dilute the more concentrated tap water solution. In the reverse osmosis process, pressure is applied to the tap water tank to force the water molecules across the membrane into the pure water tank.
After the reverse osmosis system has been operating for 30 minutes, the solution in Tank A would
be hypertonic to Tank B.
If you shut the system off and pressure was no longer applied to Tank A, you would expect
the water to reverse flow from Tank B to Tank A
Which of the following statements regarding photosynthesis and cellular respiration is true?
Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts, and cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria.
What is the term for metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules?
catabolic pathways
The molecule that functions as the reducing agent (electron donor) in a redox or oxidation-reduction reaction
loses electrons and loses potential energy.
How do cells capture the energy released by cellular respiration?
They produce ATP.
Respiration ________, and cellular respiration ________.
is gas exchange . . . produces ATP
Which of the following are products of cellular respiration?
energy to make ATP and carbon dioxide
The overall equation for the cellular respiration of glucose is
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + energy.
Oxidation is the ________, and reduction is the ________.
loss of electrons . . . gain of electrons
Which of the following options lists the stages in cellular respiration in the correct order?
glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation
Which of the following metabolic pathways is common in aerobic and anaerobic metabolism?
glycolysis
Where does glycolysis take place in eukaryotic cells?
cytosol
Why is glycolysis described as having an investment phase and a payoff phase?
It uses stored ATP and then forms a net increase in ATP.
Pyruvate
forms at the end of glycolysis.
After glycolysis but before the citric acid cycle,
pyruvate is oxidized.
In the absence of oxygen, yeast cells can obtain energy by fermentation, resulting in the production of
ATP, CO2, and ethanol (ethyl alcohol).
The molecule that functions as the reducing agent (electron donor) in a redox or oxidation-reduction reaction
loses electrons and loses potential energy.
What is the likely origin of chloroplasts?
photosynthetic prokaryotes that lived inside eukaryotic cells
In most green plants, chloroplasts are
concentrated in a zone of leaf tissue called the mesophyll.
CO2 enters and O2 escapes from a leaf via
stomata.
In the chloroplast, sugars are made in a compartment that is filled with a thick fluid called the
stroma.
Chloroplasts contain disklike membranous sacs arranged in stacks called
grana.
Where is chlorophyll found in a plant cell?
thylakoid membranes
The oxygen released into the air as a product of photosynthesis comes from
water.
What is the source of energy that provides the boost for electrons during photosynthesis?
light
The light reactions occur in the ________, while the Calvin cycle occurs in the ________.
thylakoid membranes . . . stroma
Carbon fixation
occurs when carbon atoms from CO2 are incorporated into an organic molecule.
Which of the following are produced during the light reactions of photosynthesis?
ATP, NADPH, O2
Which of the following are produced during the Calvin cycle?
glucose, ADP, NADP+
Which of the following colors contributes the least energy to photosynthesis?
green
A packet of light energy is called a
photon.
Briefly describe the relationship between cell respiration and photosynthesis.
The products of cellular respirations are the reactants of photosynthesis. Both are intrinsically linked within the life cycle of our ecosystem.
Your friend has completed a day of heavy weight lifting at the local gym that was interrupted by moments of muscle burning relieved by rest. They are curious as to what type of biological mechanism is at work. Please briefly explain what is occurring at the cellular level and how it relates to your friends "muscle burning".
Your friend is experiencing a build up of lactic acid. This occurs in muscle cells because they are facultative anaerobes. When oxygen is present, ATP is produced. When oxygen is not present, muscle cells with enter into fermentation producing lactic acid.
Which of the following statements regarding prokaryotes is false?
Prokaryotic chromosomes are more complex than those of eukaryotes.
Eukaryotic chromosomes differ from prokaryotic chromosomes in that they
are housed in a membrane-enclosed nucleus.
Prior to mitosis, each chromosome of a eukaryotic cell consists of a pair of identical structures called
sister chromatids.
Eukaryotic cells spend most of their cell cycle in which phase?
interphase
The genetic material is duplicated during
the S phase.
The process by which the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell divides to produce two cells is called
cytokinesis
The process by which the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell divides to produce two cells is called
metaphase
At the start of mitotic anaphas
the centromeres of each chromosome come apart.
During which phase of mitosis does the nuclear envelope re-form?
telophase
As a patch of scraped skin heals, the cells fill in the injured area but do not grow beyond that. This is an example of
density-dependent inhibition.
Mature human nerve cells and muscle cells
are permanently in a state of nondivision.
During which stage of meiosis do synapsis and crossing over occur?
prophase I
Independent orientation of chromosomes at metaphase I results in an increase in the number of
possible combinations of characteristics.
Karyotyping
can reveal alterations in chromosome number.
Nondisjunction occurs when
members of a chromosome pair fail to separate.
Mendel conducted his most memorable experiments on
peas
A monohybrid cross is
a breeding experiment in which the parental varieties differ in only one character.
All the offspring of a cross between a black-eyed mendelien and an orange-eyed mendelien have black eyes. This means that the allele for black eyes is ________ the allele for orange eyes.
dominant to
The alleles of a gene are found at ________ chromosomes.
the same locus on homologous
The phenotypic ratio resulting from a dihybrid cross showing independent assortment is expected to be
9:3:3:1.
A testcross is
a mating between an individual of unknown genotype and an individual homozygous recessive for the trait of interest.
All the offspring of a cross between a red-flowered plant and a white-flowered plant have pink flowers. This means that the allele for red flowers is ________ to the allele for white flowers.
incompletely dominant
What is the normal complement of sex chromosomes in a human male?
one X chromosome and one Y chromosome
Recessive X-linked traits are more likely to be expressed in a male fruit fly than a female fruit fly because
the male's phenotype results entirely from his single X-linked gene.
Which of the following variations of the sentence "Where is the cat" is most like a chromosomal deletion?
Where is cat?
If a chromosome fragment breaks off and then reattaches to the original chromosome, but in the reverse direction, the resulting chromosomal abnormality is called a(n)
inversion.
Asexual reproduction requires ________ individual(s).
1
Which of the following statements regarding genetic diversity is false?
Genetic diversity is enhanced by mitosis.
Cancer is not usually inherited because
Cancer is not usually inherited because
The individual features of all organisms are the result of
genetics and the environment.