autonomic nervous system
daw a flowchart of the organization of the nervous system
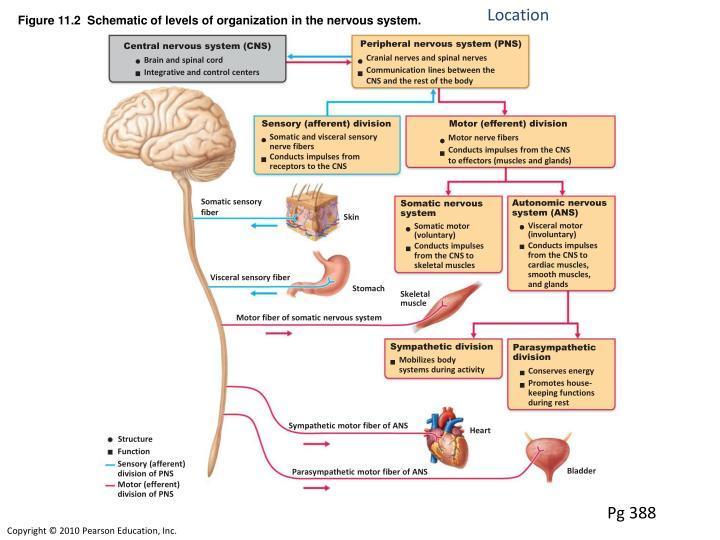
Effector of somatic ns
Effector of autonomic ns
SNS: skeletal muscles
ANS: smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands
Efferent pathway of SNS
Efferent pathway of ANS
one neuron system
two neuron system (pre- and post- synaptic)
neurotransmitter and response of target organ of somatic nervous system
acetylcholine - excitatory
neurotransmitter and response of target organ of autonomic nervous system
presynaptic neuron - acetylcholine - excitatory;
postsynaptic neuron - sympathetic - norepinephrine and epinephrine
postsynaptic neuron - parasympathetic - acetylcholine
where are motor neuron cell bodies located? sensory neuron cell bodies?
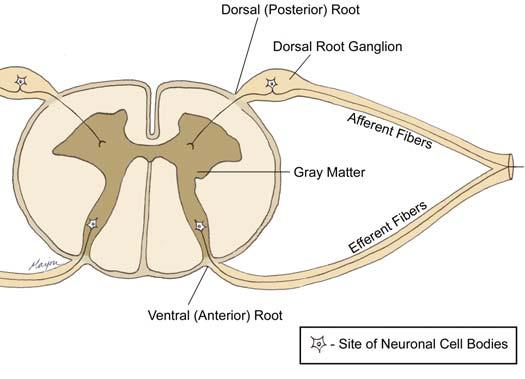
ventral horn of spinal cord; dorsal root ganglia
parasympathetic cranial nerves?
3,7,9,10
spinal cord levels of sympathetic nervous system?
T1-L2
spinal cord levels of parasympathetic nervous system?
S2-s4
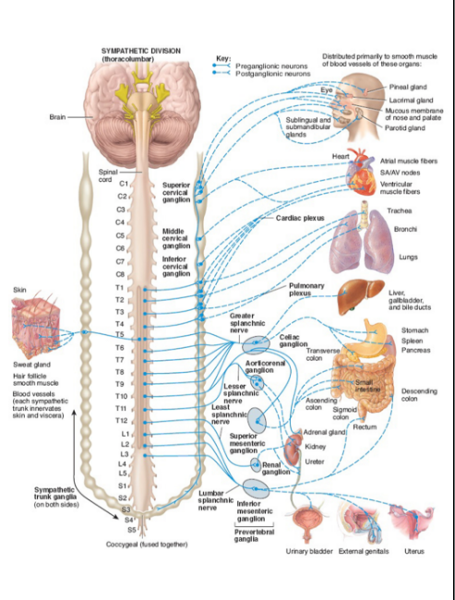
origin of presynpatic neuron cell body in SNS
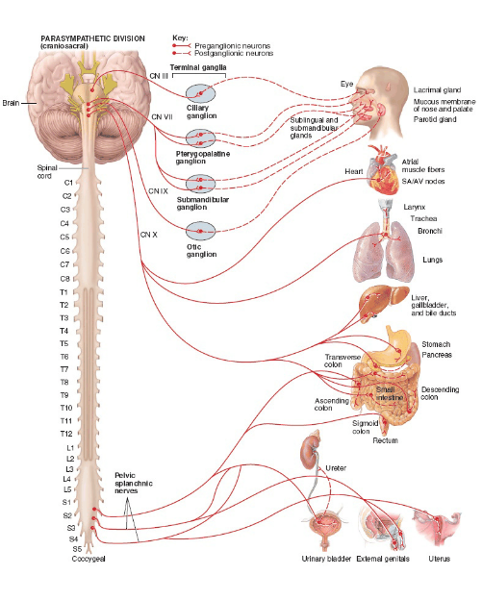
origin of presynaptic neuron cell body in PNS
(think not super specific)
thoracolumbar region of the spinal cord (called thoracolumbar region)
brain and sacral spinal cord (called craniosacral division)
pre and post synaptic fiber lengths of SNS and PNS
SNS - presynaptic is short and postsynaptic is long
PNS presynaptic is long and postsynaptic is short
Why is the presynaptic fiber length short and postsynaptic long in the SNS?
b/c presynpatic goes to the sympathetic chain of white rami communicnte - ganglia is close to spinal cord. and then postsynaptic has to travel all the way to effector organ
Why is the presynaptic fiber length long and postsynaptic fiber short in the PNS?
ganglia is located in the effector organ
what is the only major body function not inhibited by PNS?
digestion
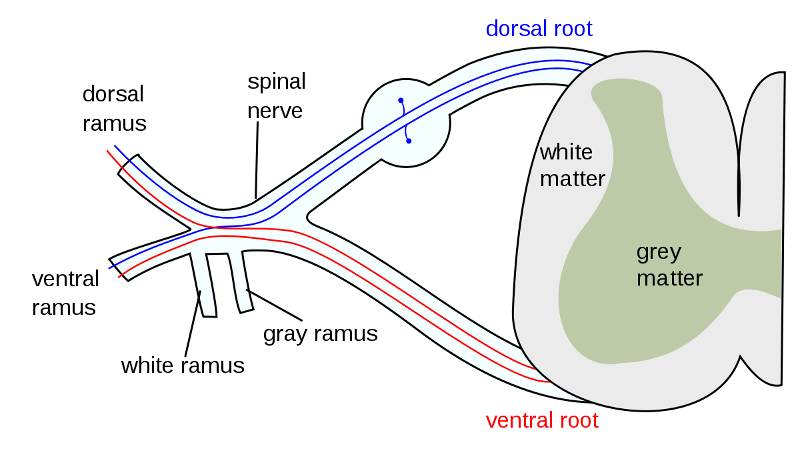
what are the three options when presynaptic fiber joins sympathetic chain via white rami?
synapse at same level of chain entrance
ascend or descend to different level
pass through chain without synapsing - splanchnic nerve
which are the only splanchnic nerves that carry parasympthetic fibers?
pelvic splanchnic nerves
presynaptic fibers enter sympathetic chain via _______ and exit via ____
white rami; grey rami
Where are presynaptic neuron cell bodies located in parasympathetic nervous system?
nuclei for cranial nerves III, VII, IX, X
and S2-S4 spinal cord levels
where is the synapse located between neurons in parasympathetic nervous system?
terminal ganglia
-named ganglia like ciliary, pterygopalatine, submandibular, and otic
-unnamed intramural gnaglia (in or near the wall of effector organ)
Presynaptic fibers running via the oculomotor nerve (III) innervates what?
facial nerve?
glossopharangyeal?
vagus?
smooth muscle in eye
lacrimal, submandibular and sublingual glands
parotid gland
almost every organ in the thoracic and abdominal cavity
which organs receive parasympathetic communication via the vagus nerve?
heart, lungs, liver, gallbladder, stomach, small intestine, pancreas, and proximal half of large intestine
what is the pathway of cranial outflow of PNS?
sacral outflow?
presynaptic fibers run via the four parasympathetic cranial nerves
presynaptic fibers run through the ventral root --> spinal nerve --> ventral rami --> exit ventral rami as pelvic splanchnic nerves
what innervates distal portion of large intestine? proximal?
pelvic splanchnic nerves; vagus nerve
where do pelvic splanchnic nerves synapse and what do they innervate?
synapse in intramural ganglia and innervate distal half of large intestine and pelvic viscera (urinary bladder, uterus, and reproductive organs)
where are presynaptic neuron cell bodies located in the SNS?
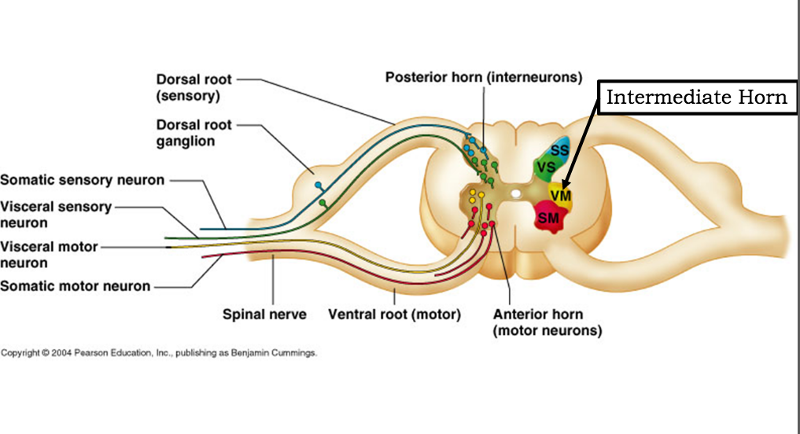
thoracolumbar region of spinal cord (T1-L2) and the intermediate horn
where is the synapse between the two neurons in the SNS?
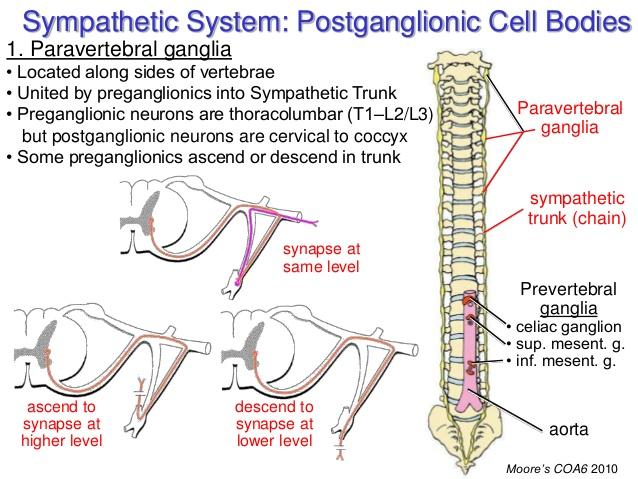
paravertebral ganglia on the sympathetic chain
or
prevertebral/collateral ganglia on the abdominal aorta
the sympathetic chain extends from _____ to _____
cranial base; coccyx
how are the paravertebral ganglia joined to the spinal nerve?
by white and grey rami communicantes
what is the pattern of thoracolumbar outflow in the SNS?
presynaptic fibers exit through ventral root --> spinal nerve--> white ramus--> paravertebral ganglia on the sympathetic chain
if preganglionic fibers do not synapse on the sympathetic chain in SNS, how do they exit the chain?
as splanchnic nerves