Skeletal system lecture exam
This is a structure of a long bone that stores energy.
Marrow
This is the region of a long bone that articulates with other bones.
Epiphysis
This is the shaft of a long bone.
Diaphysis
This is a layer of hyaline cartilage that reduces friction between bones involved in the joint.
Articular cartilage
This is a layer of hyaline cartilage that allows the Diaphysis to grow in length.
Epiphyseal plate
This is a lining found in bone that promotes bone growth in width.
Periosteum
These are considered bone-dissolving cells.
Osteoclast
Which of the following structures contains osteocytes?
Lacunae
These are considered bone-building cells.
Osteoblasts
These are extensions of the lacunae and are filled with extracellular fluid.
Canaliculi
Osteons in compact bone tissue are aligned along
Lines of stress
The correct sequence of processes that occur during bone elongation at the epiphyseal plate are: RPHCO
Resting, proliferation, hypertophication, calciifcation, ossification
During adulthood, what contributes to bone remodeling and growth?
Calcium, Vitamin D, sex hormones, human growth hormone
This type of fracture is considered a partial fracture and is usually seen in children.
Greenstick

1. Where in the diagram is the distal epiphysis?
2. Where in the diagram can you find the medullary cavity?
3. Where in the diagram can you find red bone marrow in an adult?
4. Where in the diagram is the metaphysis?
5. Where in the diagram is the only place not to have a periosteum?

1. D
2. C
3. A and B
4. B
5. E

1. In the diagram, where is the Haversian canal?
2. In the diagram, where is the Volkman's canal?
3. In the diagram, where is the osteon?
4. In the diagram, where is the trabeculae?

1. E
2. F
3. C.
4. B
The branch of medicine that deals with correction of disorders of the musculoskeletal system is called
Orthopedics
How many bones are found in the adult human skeleton?
206
What is axial skeleton?
This includes the skull bones, the ossicles of the middle ear, the hyoid bone, the rib cage, sternum and the vertebral column.
Which type of bone is the femur
A long bone
Which type of bone is the occipital?
A flat bone
This is a bone located within ankles or wrists
A short bone
Bones in the following area protect the brain.
The cranium
These projections on either side of the foramen magnum articulate with depressions on the first cervical vertebrae.
Occipital condyles
Joe was found dead. His hyoid bone was broken. What was most likely cause of death?
Strangulation
Know the facial bones
- Inferior nasal concha (2)
- Lacrimal bones (2)
- Mandible.
- Maxilla (2)
- Nasal bones (2)
- Palatine bones (2)
- Vomer.
- Zygomatic bones (2)
Which of the following bones is not visible from the anterior view of the skull?
Occipital
This facial bone articulates with teeth
Maxillae and Mandible
What is the junction between the manubrium and the body of the sternum called?
Sternal angle
What is the purpose of the nucleus pulposus
To absorb vertical shock
The curves of the vertebrae include
Thoracic curve, sacral curve, lumbar curve, cervical curve
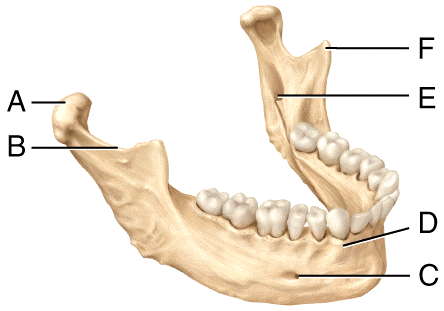
1. Where is the mental foramen in the diagram?
2. Where is the mandibular notch in the diagram?
3. Where is the coronoid process in the diagram?
1. C
2. B
3. F
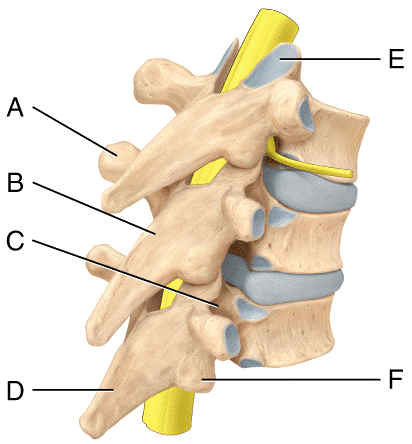
1. Where is the inferior articular process in the diagram?
2. In the diagram, where is lamina of the vertebral arch?
3. Where is the spinous process in the diagram?
1. F
2. B
3. D
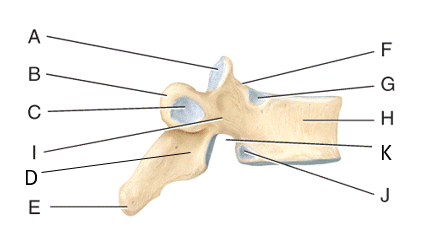
1. Where is the superior vertebral notch?
2. Where is the facet for articular part of the tubercle of the rib?
3. Where is the pedicle?
4. Where is the superior demifacet?
5. Where is the lamina?
1. F
2. C
3. I
4. G
5.
The lateral malleolus is found on the distal end of what bone?
Fibula
Which is not found in the foot?
Pollex
Which is not a tarsal bone?
Capitate
This is a bone that develops in the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle.
Patella
This is the largest foramen in the skeleton
Obturator foramen
Which is found in the elbow?
Olecranon, Coranoid process, radial head, capitulum, trochlea, olecranon process,
What is found in the glenoid cavity?
Head of the humerus
The female pelvis is
Wider, shallower, larger in the pelvic inlet, and larger in the pelvic outlet
This is the anterior bone that articulates with the manubrium of the sternum at the sternoclavicular joint.
Clavicle
This bone's shape comes from the medial half of the bone being convex anteriorly and the lateral half is concave anteriorly.
Clavicle