antimicrobial drugs
isoniazid is a particular value
for treating tuberculosis
the two major drawbacks to the use of penicillin are
allergic reactions and development of drug-resistant bacteria
a common feature of bacitracin and polymyxin B is that both antibiotics
are produced by bacillus species
both the cephalosporin and penicillin antibiotic
act on the cell wall of bacteria
chloroquine, primaquine, and quinine are of value for the treatment of
cases of malaria
the tubercle bacillus is usually susceptible to
streptomycin but not penicillin
the Kirby-Bauer test is useful for determining
which antibiotic may be employed to treat an infection
cephalosporin antibiotics may be used
as alternatives to penicillin
all aminoglycoside antibiotics function by
attaching irreversibility to bacterial ribosomes
the range of activity of tetracycline antibiotics
includes viruses, protozoa, and fungi
flucytosine, clotrimazole, and ketoconazole typify the
antifungal antibiotics
pseudomembranous colitis is a condition of the intestine that may be related to
overuse of lincomycin and clindamycin
carbenicillin and methicillin should not be used to treat disease if
a person has penicillin allergy
In competitive inhibition, sulfanilamide is used by a bacterium in an aborted attempt to
form folic acid
the beta lactam nucleus is the basic structure of the
penicillin
first generationo cephalosporins must be injected because
they have variable absorption in the GI tract
ampicillin is preferable to penicillin because it
is absorbed more easily from the intestine when taken orally
cephalosporins act by
interfering with cell-wall biosynthesis
a physician has determined that he must prescribe chloramphenicol to treat an infection. He should
monitor for development of aplastic anemia
tetracycline antibiotics interfere with
protein synthesis
penicillin is most effective against
log phase gram positive bacteria
carbenicillin is best classified as a
semisynthetic antibiotic
chloramphenicol
interferes with protein synthesis in microorganisms
MRSA is resistant to
methicillin
both vancomycin and rifampin interfere with aspects of folic acid metabolism in bacteria that cause urinary tract infections
false
penicillinase-producing bacteria convert penicillin to penicilloic acid, which has no effect on the bacterial cell wall
true
aplastic anemia, which is related to chloramphenicol therapy, arises from activity in the bone marrow that prevents hemoglobin incorporation into red blood cells
true
pseudomembranous colitis, a side effect of clindamycin and linconmycin therapy, is accompanied by membranous lesions on the intestinal wall
true
the antituberculosis drug isoniazid presumably interferes with cell wall synthesis in Mycobacterium by inhibiting production of sulfanic acid
false
antibiotic abuse encourages the emergence of resistant species of microorganisms
true
penicillin antibiotics are used primarily against gram-positive bacteria, but in high concentrations they are also inhibitory to gram-negative bacteria
true
most of the available antimicrobial agents are effective against
bacteria
in what way are semisynthetic penicillin and natural penicillin alike
both are based on lactam
which of the following antimicrobial agents is recommended for use against systemic fungal infections
amphotericin B
which of the following antibiotics does NOT interfere with cell wall synthesis
macrolides
the antimicrobial drugs with the broadest spectrum of activity are
tetracyclines
protozoan and helminthic diseases are difficult to treat because
their cells are structurally and functionally similar to human cells
niclosamide prevents ATP generation in mitochondria. You would expect this drug to be effective against
helminths
which of the following does NOT affect eukaryotic cells
semisynthetic penicillins
a major side effect of chloramphenicol therapy is yellowish staining teeth
false
antibiotic penicillin is used primarily against gram-negative bacteria
false
two major side effects of the use of amoxicillin are the loss of hearing and nephrotoxicity
false
chloroquine and quinine are the drugs of choices for the treatment of fungal disease
false
isoniazid is of particular value for treating tuberculous bacterial infections
true
the range of activity of tetracycline includes gram positive and negative bacteria, rickettsia, mycoplasma and chlamydial infections
true
photosensitivity is one of the side effects of the tetracycline drug
true
athlete foot can be treated with bacitracin
false
Nalidixic acid is a type of fluoroquinolone which inhibits the DNA replications. The drug is effective against urinary tract infections
true
clavulanic acid is a beta-lactamase inhibitor
true
a drug such as clotrimazole, would be more effective against
fungal infections
the antimicrobial drug with the broadest spectrum of activity is
tetracycline
protozoan and helminthic diseases are difficult to treat because
their cells are structurally and functionally similar to human cells
niclosamide drug is effective against
tapeworm infections
the tubercle bacillus is usually effective against
mycobacteria
the Kirby-Bauer test is useful for determining
the activity of antimicrobials
mebendazole is effective against
parasites
erythromycin antibiotics may be used when person is allergic to which antibiotic
penicillin
miconazole and ketoconazole typify the
anti-fungal
ciprofloxacin is a type of
fluoroquinolone
in competitive inhibition, sulfanilamide is used by a bacterium in an aborted attempt to
form folic acid
cephalosporins act by
interfering with cell wall biosynthesis
MRSA is resistant to which group of antibiotic
methicillin
carbenicillin is best classified as
semisynthetic antibiotic
which antibiotics work by inhibiting the process of translation by interfering with 50s ribosomes and inhibiting formation of peptide bond
chloramphenicol
which antibiotics inhibits the DNA replication and transcription processes
fluoroquinolones
oral penicillin
penicillin V
metronidazole
antiprotozoan drug
interfere with anaerobic metabolism
ribavirin
interferes with RNA metabolism
cloxacillin
interferes with the last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis
vancomycin
inhibits the second stage of cell wall synthesis
penicillin V
acts against gram-positive bacteria
fluconazole
inhibits fungal activity
ethambutol
inhibits cell wall synthesis
oxacillin
inhibits cell wall synthesis
azithromycin
inhibits protein synthesis
tetracycline
inhibits protein synthesis
aminoglycoside
protein synthesis inhibitor
doxycycline
protein synthesis inhibitor
acne treatment
neomycin
protein synthesis inhibitor
acyclovir
inhibits DNA or RNA synthesis
when the effect of two drugs together is greater than the effect of either alone, it is called
synergism
which antibiotic is most likely to cause bone marrow suppression in children
chloramphenicol
which antibiotic can be used for anaerobic clostridium prefringens infection
metronidazole
narrow spectrum of microbial activity
range of different microbial types of affect
broad spectrum antibiotics
antibiotics that affect a broad range of gram positive or gram negative bacteria
bacillus subtills
bacitracin
saccharopolispora erythraea
erythromycin
streptomyces griseus
streptomycin
superinfection
overgrowth of a target pathogen that has developed resistance to the antibiotic
inhibition of cell wall synthesis
penicillin, cephalosporins, bacitracin vancomycin
inhibition of protein synthesis
chloramphenicol, erythromycin, tetracyclines, streptomycin
inhibition of nucleic acid replication and transcription
quinolones, rifampin
injury to plasma membrane
polymyxin B
inhibition of essential metabolite synthesis
sulfanilamide, trimethoprim
what is the difference between bactericidal and bacteriostatic
bactericidal kills microbes while nacteriostatic prevent microbes from growing
chloramphenicol
binds to 50s portion and inhibits formation of peptide bond
tetracyclines
interfere with attachment of tRNA and mRNA
broad spectrum drug
causes rickettsia
yellow staining teeth and photosensitivity
streptomycin
changes shape of 30s portion, causing code on mRNA to be read incorrectly p
penicillin G
requires injection
against gram positive bacteria
Beta lactam ring
all penicillins contain this portion
methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
bacteria resistant to methicillin
penicillin plus Beta-Lactamase inhinitors
clavulanic acid
amoxicillin + clavulanic acid
augmentin
carbapenems
B-lactam antibiotics that substitute carbon atom for sulfur atom and added a bond to the penicillin nucleus.
bacitracin
effective against gram positive bacteria such as staphyloccoci and streptococci
vancomycin resistant staphyloccocus aureus
resistant to vancomycin
isoniazid (INH)
antimycobacterial antibiotic
very effective against tuberculosis
primary effect is to inhibit synthesis of mycolic acid
ethambutol
antimycobacterial antibiotic
effective only against mycobacteria
actions of the antibacterial synthetics trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole
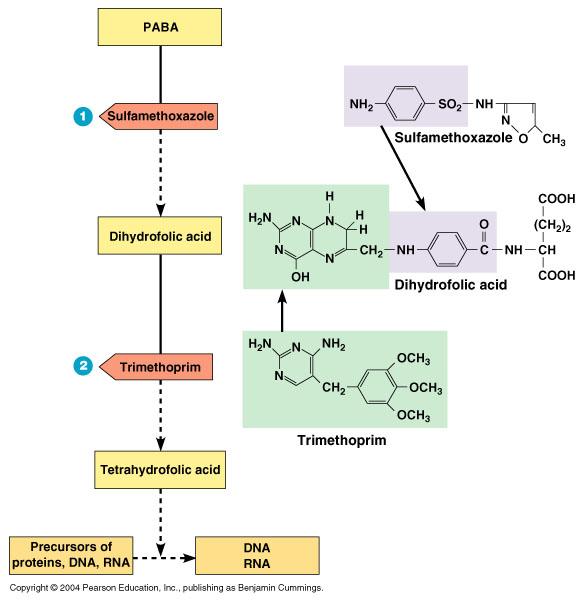
what were the first penicillins
aminopenicilllins such as ampicillin and amoxicillin
streptomycin
ototoxic
causes deafness
gentamycin
nephrotoxic
causes kidney failure
macrolides
erythromycin (azithromycin, clarithromycin)
steven johnson syndrome
disorder of the skin and mucous
penicillinase-resistant penicilin
oxacillin
cloxacillin
azlocillin
ticarcillin
methicillin
3 antibiotics in first aid ointment
neomycin
bacitracin
polymixin B s
streptomycin
gentacin
tobramycin
anti TB drugs
lincomycin
kills both harmful and friendly bacteria
C. difficile
anaerobic infection metronidazole
fluoroquinolones
UTI infection
negram
antifungal
have -ole suffixes
tinidazole
miconazole
clotrimazole
ketoconazole
antiviral
-vir suffix
famciclovir
acyclovir
ganciclovir
antiprotozoal
metronidazole
chloroquine
primaquine
quinine
anithelminth
flatworms - platyhelminths - niclosamide
round worms - nermathelminths
albendazole
mebendazole
anti TB drugs
pyrazinamie (PZA)
streptomycin
isoniazid (INH)
rifampicin
ethambutol