Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
antimicrobial drugs
front 1 isoniazid is a particular value | back 1 for treating tuberculosis |
front 2 the two major drawbacks to the use of penicillin are | back 2 allergic reactions and development of drug-resistant bacteria |
front 3 a common feature of bacitracin and polymyxin B is that both antibiotics | back 3 are produced by bacillus species |
front 4 both the cephalosporin and penicillin antibiotic | back 4 act on the cell wall of bacteria |
front 5 chloroquine, primaquine, and quinine are of value for the treatment of | back 5 cases of malaria |
front 6 the tubercle bacillus is usually susceptible to | back 6 streptomycin but not penicillin |
front 7 the Kirby-Bauer test is useful for determining | back 7 which antibiotic may be employed to treat an infection |
front 8 cephalosporin antibiotics may be used | back 8 as alternatives to penicillin |
front 9 all aminoglycoside antibiotics function by | back 9 attaching irreversibility to bacterial ribosomes |
front 10 the range of activity of tetracycline antibiotics | back 10 includes viruses, protozoa, and fungi |
front 11 flucytosine, clotrimazole, and ketoconazole typify the | back 11 antifungal antibiotics |
front 12 pseudomembranous colitis is a condition of the intestine that may be related to | back 12 overuse of lincomycin and clindamycin |
front 13 carbenicillin and methicillin should not be used to treat disease if | back 13 a person has penicillin allergy |
front 14 In competitive inhibition, sulfanilamide is used by a bacterium in an aborted attempt to | back 14 form folic acid |
front 15 the beta lactam nucleus is the basic structure of the | back 15 penicillin |
front 16 first generationo cephalosporins must be injected because | back 16 they have variable absorption in the GI tract |
front 17 ampicillin is preferable to penicillin because it | back 17 is absorbed more easily from the intestine when taken orally |
front 18 cephalosporins act by | back 18 interfering with cell-wall biosynthesis |
front 19 a physician has determined that he must prescribe chloramphenicol to treat an infection. He should | back 19 monitor for development of aplastic anemia |
front 20 tetracycline antibiotics interfere with | back 20 protein synthesis |
front 21 penicillin is most effective against | back 21 log phase gram positive bacteria |
front 22 carbenicillin is best classified as a | back 22 semisynthetic antibiotic |
front 23 chloramphenicol | back 23 interferes with protein synthesis in microorganisms |
front 24 MRSA is resistant to | back 24 methicillin |
front 25 both vancomycin and rifampin interfere with aspects of folic acid metabolism in bacteria that cause urinary tract infections | back 25 false |
front 26 penicillinase-producing bacteria convert penicillin to penicilloic acid, which has no effect on the bacterial cell wall | back 26 true |
front 27 aplastic anemia, which is related to chloramphenicol therapy, arises from activity in the bone marrow that prevents hemoglobin incorporation into red blood cells | back 27 true |
front 28 pseudomembranous colitis, a side effect of clindamycin and linconmycin therapy, is accompanied by membranous lesions on the intestinal wall | back 28 true |
front 29 the antituberculosis drug isoniazid presumably interferes with cell wall synthesis in Mycobacterium by inhibiting production of sulfanic acid | back 29 false |
front 30 antibiotic abuse encourages the emergence of resistant species of microorganisms | back 30 true |
front 31 penicillin antibiotics are used primarily against gram-positive bacteria, but in high concentrations they are also inhibitory to gram-negative bacteria | back 31 true |
front 32 most of the available antimicrobial agents are effective against | back 32 bacteria |
front 33 in what way are semisynthetic penicillin and natural penicillin alike | back 33 both are based on lactam |
front 34 which of the following antimicrobial agents is recommended for use against systemic fungal infections | back 34 amphotericin B |
front 35 which of the following antibiotics does NOT interfere with cell wall synthesis | back 35 macrolides |
front 36 the antimicrobial drugs with the broadest spectrum of activity are | back 36 tetracyclines |
front 37 protozoan and helminthic diseases are difficult to treat because | back 37 their cells are structurally and functionally similar to human cells |
front 38 niclosamide prevents ATP generation in mitochondria. You would expect this drug to be effective against | back 38 helminths |
front 39 which of the following does NOT affect eukaryotic cells | back 39 semisynthetic penicillins |
front 40 a major side effect of chloramphenicol therapy is yellowish staining teeth | back 40 false |
front 41 antibiotic penicillin is used primarily against gram-negative bacteria | back 41 false |
front 42 two major side effects of the use of amoxicillin are the loss of hearing and nephrotoxicity | back 42 false |
front 43 chloroquine and quinine are the drugs of choices for the treatment of fungal disease | back 43 false |
front 44 isoniazid is of particular value for treating tuberculous bacterial infections | back 44 true |
front 45 the range of activity of tetracycline includes gram positive and negative bacteria, rickettsia, mycoplasma and chlamydial infections | back 45 true |
front 46 photosensitivity is one of the side effects of the tetracycline drug | back 46 true |
front 47 athlete foot can be treated with bacitracin | back 47 false |
front 48 Nalidixic acid is a type of fluoroquinolone which inhibits the DNA replications. The drug is effective against urinary tract infections | back 48 true |
front 49 clavulanic acid is a beta-lactamase inhibitor | back 49 true |
front 50 a drug such as clotrimazole, would be more effective against | back 50 fungal infections |
front 51 the antimicrobial drug with the broadest spectrum of activity is | back 51 tetracycline |
front 52 protozoan and helminthic diseases are difficult to treat because | back 52 their cells are structurally and functionally similar to human cells |
front 53 niclosamide drug is effective against | back 53 tapeworm infections |
front 54 the tubercle bacillus is usually effective against | back 54 mycobacteria |
front 55 the Kirby-Bauer test is useful for determining | back 55 the activity of antimicrobials |
front 56 mebendazole is effective against | back 56 parasites |
front 57 erythromycin antibiotics may be used when person is allergic to which antibiotic | back 57 penicillin |
front 58 miconazole and ketoconazole typify the | back 58 anti-fungal |
front 59 ciprofloxacin is a type of | back 59 fluoroquinolone |
front 60 in competitive inhibition, sulfanilamide is used by a bacterium in an aborted attempt to | back 60 form folic acid |
front 61 cephalosporins act by | back 61 interfering with cell wall biosynthesis |
front 62 MRSA is resistant to which group of antibiotic | back 62 methicillin |
front 63 carbenicillin is best classified as | back 63 semisynthetic antibiotic |
front 64 which antibiotics work by inhibiting the process of translation by interfering with 50s ribosomes and inhibiting formation of peptide bond | back 64 chloramphenicol |
front 65 which antibiotics inhibits the DNA replication and transcription processes | back 65 fluoroquinolones |
front 66 oral penicillin | back 66 penicillin V |
front 67 metronidazole | back 67 antiprotozoan drug interfere with anaerobic metabolism |
front 68 ribavirin | back 68 interferes with RNA metabolism |
front 69 cloxacillin | back 69 interferes with the last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis |
front 70 vancomycin | back 70 inhibits the second stage of cell wall synthesis |
front 71 penicillin V | back 71 acts against gram-positive bacteria |
front 72 fluconazole | back 72 inhibits fungal activity |
front 73 ethambutol | back 73 inhibits cell wall synthesis |
front 74 oxacillin | back 74 inhibits cell wall synthesis |
front 75 azithromycin | back 75 inhibits protein synthesis |
front 76 tetracycline | back 76 inhibits protein synthesis |
front 77 aminoglycoside | back 77 protein synthesis inhibitor |
front 78 doxycycline | back 78 protein synthesis inhibitor acne treatment |
front 79 neomycin | back 79 protein synthesis inhibitor |
front 80 acyclovir | back 80 inhibits DNA or RNA synthesis |
front 81 when the effect of two drugs together is greater than the effect of either alone, it is called | back 81 synergism |
front 82 which antibiotic is most likely to cause bone marrow suppression in children | back 82 chloramphenicol |
front 83 which antibiotic can be used for anaerobic clostridium prefringens infection | back 83 metronidazole |
front 84 narrow spectrum of microbial activity | back 84 range of different microbial types of affect |
front 85 broad spectrum antibiotics | back 85 antibiotics that affect a broad range of gram positive or gram negative bacteria |
front 86 bacillus subtills | back 86 bacitracin |
front 87 saccharopolispora erythraea | back 87 erythromycin |
front 88 streptomyces griseus | back 88 streptomycin |
front 89 superinfection | back 89 overgrowth of a target pathogen that has developed resistance to the antibiotic |
front 90 inhibition of cell wall synthesis | back 90 penicillin, cephalosporins, bacitracin vancomycin |
front 91 inhibition of protein synthesis | back 91 chloramphenicol, erythromycin, tetracyclines, streptomycin |
front 92 inhibition of nucleic acid replication and transcription | back 92 quinolones, rifampin |
front 93 injury to plasma membrane | back 93 polymyxin B |
front 94 inhibition of essential metabolite synthesis | back 94 sulfanilamide, trimethoprim |
front 95 what is the difference between bactericidal and bacteriostatic | back 95 bactericidal kills microbes while nacteriostatic prevent microbes from growing |
front 96 chloramphenicol | back 96 binds to 50s portion and inhibits formation of peptide bond |
front 97 tetracyclines | back 97 interfere with attachment of tRNA and mRNA broad spectrum drug causes rickettsia yellow staining teeth and photosensitivity |
front 98 streptomycin | back 98 changes shape of 30s portion, causing code on mRNA to be read incorrectly p |
front 99 penicillin G | back 99 requires injection against gram positive bacteria |
front 100 Beta lactam ring | back 100 all penicillins contain this portion |
front 101 methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) | back 101 bacteria resistant to methicillin |
front 102 penicillin plus Beta-Lactamase inhinitors | back 102 clavulanic acid |
front 103 amoxicillin + clavulanic acid | back 103 augmentin |
front 104 carbapenems | back 104 B-lactam antibiotics that substitute carbon atom for sulfur atom and added a bond to the penicillin nucleus. |
front 105 bacitracin | back 105 effective against gram positive bacteria such as staphyloccoci and streptococci |
front 106 vancomycin resistant staphyloccocus aureus | back 106 resistant to vancomycin |
front 107 isoniazid (INH) | back 107 antimycobacterial antibiotic very effective against tuberculosis primary effect is to inhibit synthesis of mycolic acid |
front 108 ethambutol | back 108 antimycobacterial antibiotic effective only against mycobacteria |
front 109 actions of the antibacterial synthetics trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole | back 109 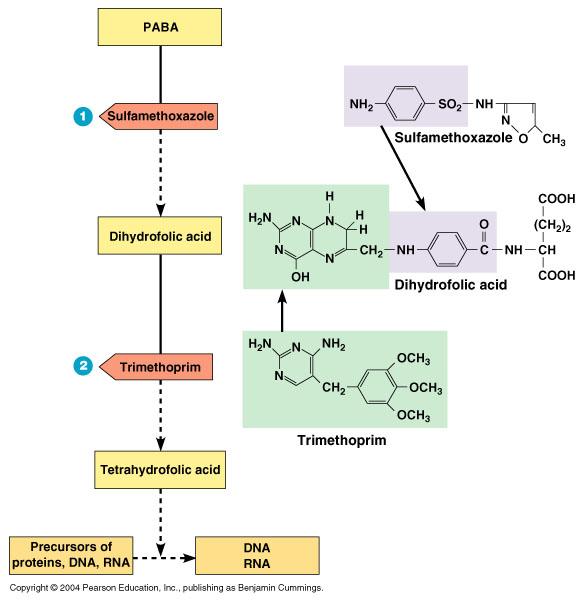 |
front 110 what were the first penicillins | back 110 aminopenicilllins such as ampicillin and amoxicillin |
front 111 streptomycin | back 111 ototoxic causes deafness |
front 112 gentamycin | back 112 nephrotoxic causes kidney failure |
front 113 macrolides | back 113 erythromycin (azithromycin, clarithromycin) |
front 114 steven johnson syndrome | back 114 disorder of the skin and mucous |
front 115 penicillinase-resistant penicilin | back 115 oxacillin cloxacillin azlocillin ticarcillin methicillin |
front 116 3 antibiotics in first aid ointment | back 116 neomycin bacitracin polymixin B s |
front 117 streptomycin gentacin tobramycin | back 117 anti TB drugs |
front 118 lincomycin | back 118 kills both harmful and friendly bacteria |
front 119 C. difficile | back 119 anaerobic infection metronidazole |
front 120 fluoroquinolones | back 120 UTI infection negram |
front 121 antifungal | back 121 have -ole suffixes tinidazole miconazole clotrimazole ketoconazole |
front 122 antiviral | back 122 -vir suffix famciclovir acyclovir ganciclovir |
front 123 antiprotozoal | back 123 metronidazole chloroquine primaquine quinine |
front 124 anithelminth | back 124 flatworms - platyhelminths - niclosamide round worms - nermathelminths albendazole mebendazole |
front 125 anti TB drugs | back 125 pyrazinamie (PZA) streptomycin isoniazid (INH) rifampicin ethambutol |