Microbial growth
Figure 6.1, which line best depicts a facultative anaerobe in the absence of O2?
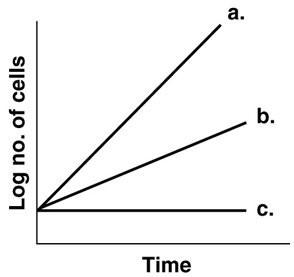
B
In figure 6.1, which line best depicts an obligate anaerobe in the presence of O2?
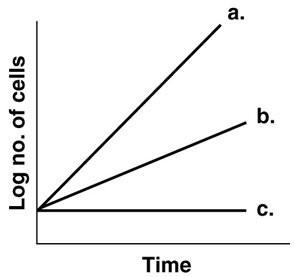
C
In figure 6.1, which line shows the growth of an obligate aerobe incubated anaerobically
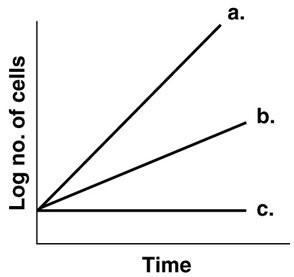
C
In figure 6.1, which line best illustrates the growth of a facultative anaerobe incubated aerobically
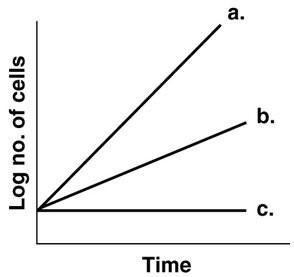
A
In figure 6.1, which line best depicts a psychrotroph incubated at 0 degree Celsius
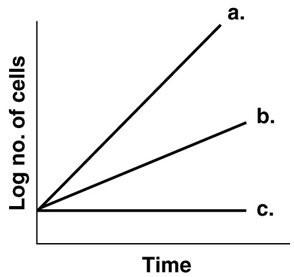
B
If cells are grown in media containing amino acids labeled with radioactive nitrogen, most of the radioactivity will be found in the cells'
DNA and proteins
Which of the following elements is NOT correctly matched with its cellular function
phosphorous - Used for production of carbohydrates
Pathogenic bacteria isolated from the respiratory or intestinal tracts of humans are
Capnophiles that grow best in carbon dioxide incubators
A sample of milk tested for its bacterial content in a plate count assay. a one-milliliter sample of the milk is diluted in a 1:10 dilution series. One milliliter of the third dilution tube is plated in a pour plate. After incubation, the plate has 54 colonies, indicating that the original milk sample contained
54,000 cells per milliliter
The addition of which of the following to a culture medium will neutralize acides
buffers
salts and sugars work to preserve foods by creating a
hypertonic environment
the term aerotolerant anaerobe refers to an organism that
does not use oxygen but tolerates it
Which of the following is an advantage of the standard plate count
determines the number of viable cells
Which of the following is an advantage of the direct microscopic count
requires no incubation time
quorum sensing
cell-to-cell chemical communication
allows bacteria to coordinate their activity and group together
thirty-six colonies grew in nutrient agar from 1.0ml of undiluted sample in a standard plate count. How many cells were in the original sample
36 per milliliter
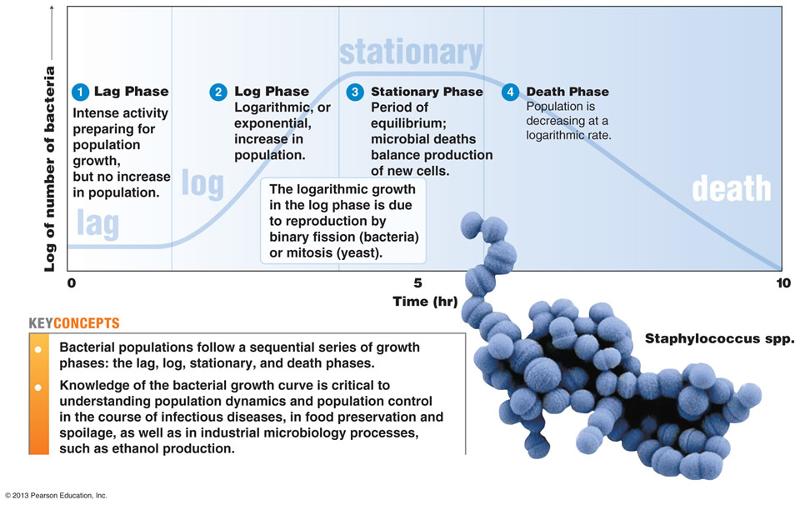
figure 6.2 shows a typical bacterial growth curve with the y-axis indicating the lof of the number of bacteria and the x-axis indicating time in culture. In the figure, which section shows a growth phase where the number of cells dying equals the number of cells dividing
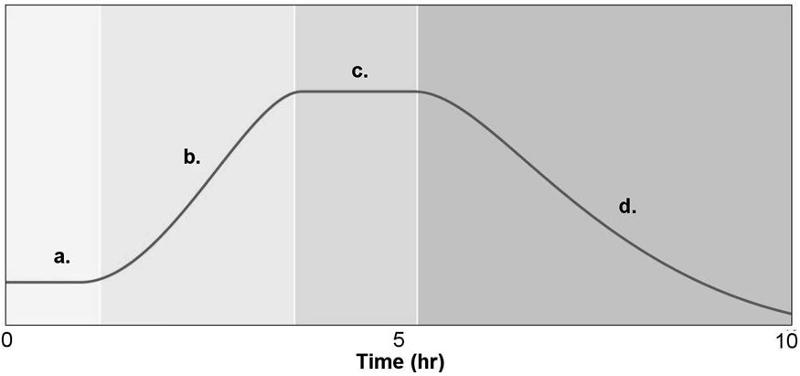
C
figure 6.2 shows a typical bacterial growth curve with the y-axis indicating the log of the number of bacteria and x-axis indicating time in culture. IN the figure, which sections of the graph illustrate a logarithmic change in cell numbers
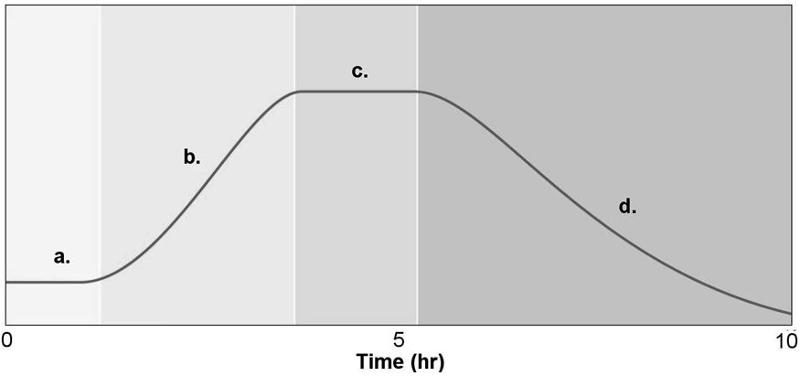
B
Most bacteria grow best at pH
7
Most fungi grow best at pH
5
consider a culture medium on which only gram-positive organism such at Staphylococcus aureus colonies can grow due to an elevated NaCl level. A yellow halo surrounds the growth, indicating the bacterium fermented a sugar in the medium, decreasing the pH as a result and changing the color of a pH indicator chemical. This type of medium would be referred to as an
selective and differential medium
a culture medium consisting of agar, peptone, and beef heart, is a
complex medium
Which of the following pairs of microbe classification terms and optimal growth temperatures is mismatched
thermophile - growth at 37 degrees celsius
during which growth phase will gram-positive bacteria be most susceptible to penicillin
log phase
which of the following is the best definition of generation time
the length of time needed for a cell to divide
which of the following is not a direct method to measure microbial growth
metabolic activity
which group of microorganisms is most likely to spoil a freshwater trout preserved with salt
facultative halophiles
which of the following is an organic growth factor
vitamin B1
which of the following is an example of metabolic activity that could be used to measure microbial growth
glucose consumption
an experiment began with 4 cells and ended with 128 cells. How many generations did the cells go through
5
three cells with generation times of 60 minutes are inoculated into a culture medium. How many cell are there after 5 hours
96
In figure 6.3 which tube shows the expected growth pattern for a microaerophile

E
in figure 6.3 which tube shows the expected growth pattern for facultative anaerobe

B
In one hospital, Pseudomonas aeruginosa seroptype 10 infected the biliary tract of 10% of 1300 patients, who underwent gastrointestinal endoscopic procedures. After each use, endoscopes were washed with an automatic reprocessor that flushed detergent and glutaraldehyde through the endoscopes, followd by a tap water rinse. P. aeruginosa serotype 10 was not isolated from the detergent, gluataraldehyde, or tap water. What was the source of the infections
a biofilm in the reprocessor
for the three types of media, which medium (or media) is/are chemically defined
Medium A
in which medium (or media) would an autotroph grow
Medium A
Assume you inoculated 100 cells, with a generation time of 20 minutes, into 100ml of nutrient broth. You then inoculated 100 cells of the same species into 200ml of nutrient broth. After incubation for 4 hours, you can reasonably expect to have
the same number of cells in both
The source of nutrients in nutrient agar is
peptone and beef extract
which enzyme catalyzes the reaction O2- + O2- + 2H+ → H2O2 + O2?
superoxide dismutase (SOD)
Which enzyme catalyzes the reaction: 2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2?
catalase
Which enzyme catalyzes the reaction: H2O2 + 2H+ → 2H2O?
peroxidase
the data in table 6.2 indicate that S. aureus is a(n)
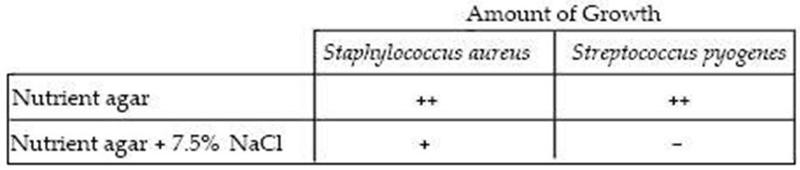
facultative halophile
Patients with indwelling catheters are susceptible to infections because
biofilms develop on catheters
an isolated colony on a streak plate contains millions (or even billions) of identical cells all arising from one initial cell
true
bacterial growth refers to an increase in the numbers of cells in a bacterial culture
true
pure cultures can easily be obtained on streak plates, even if the desired bacteria are present in very low concentrations in the initial culture broth
false
agar is used as a solidifying agent in microbiological media since few bacteria can degrade it
true
laboratory cultivation of obligate anaerobes requires reducing media or special growth chambers filled with inert gases
true
most pathogenic bacteria are thermophiles
false
in performing a ten-fold dilutions series from a sample containing 10,000 bacteria per milliliter, the fourth tube in the dilution series will have 10 cells per milliliter
false
What are the physical requirements for growth?
temperature
pH
osmotic pressure
What are the chemical requirements for growth
Carbon
nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus
trace elements
oxygen
organic growth factors
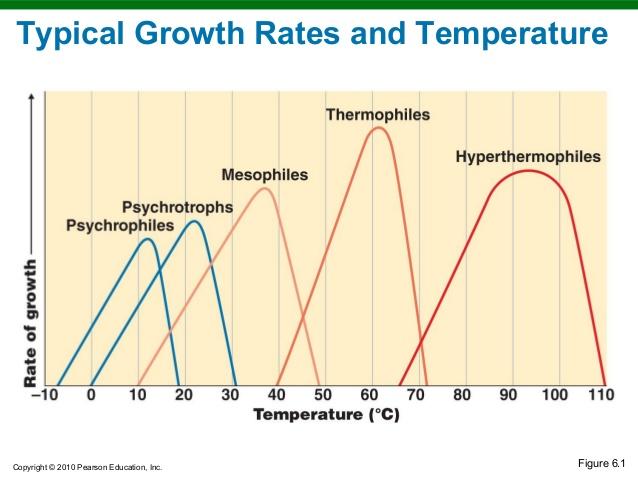
what are the 3 groups based on range of temperature
psychrophiles
mesophiles
thermophiles
psychrophiles
cold-loving microbes
-10 - 20oC
mesophiles
moderate-temperature loving
10 - 30oC
Thermophiles
heat-loving
50-60oC
minimum growth temperature
lowest temperature at which species will grow
optimum growth temperature
temperature at which species grow best
maximum growth temperature
highest temperature at which growth is possible
psychrotrophs
can grow at 20 - 30oC temperatur. Found in low temperature food spoilage
hyperthermophiles
optimum growth temperature of 80 oC or higher.
sulfur is important in metabolic activity
pH
acidity or alkalinity of a solution
bacteria grow best between pH 6.5 and 7.5
osmotic pressure
plasmolysis - shrinkage of cell's cytoplasm
high salt or sugar concentrations draw water out of microbial cells and prevents their growth
microorganism require water for growth. their composition is 80-90% water
extreme halophiles
high salt concentrations. organisms require 30% salt
falcultative halophiles
do not require high salt concentrations
carbon
needed for all organic compounds that make up a living cell.
one of the most important requirements for microbial growth
nitrogen, sulfur and phosphorus
nitrogen is used to form amino group
sulfur is used to synthesize sulfur-containing amino acids and vitamins
phosphorus is used for the synthesis of nucleic acids and phospholipids of cell membranes
nitrogen fixation
using gaseous nitrogen directly from the atmosphere
obligate aerobes
organisms that require oxygen to live
facultative anaerobes
ability to grow in the absence of oxygen
obligate anaerobes
bacteria that are unable to use molecular oxygen for energy-yielding reactions
how microorganisms can be harmed by O2
singlet oxygen
superoxide radicals
peroxide anion
hydroxyl radical
organic growth factors
essential organic compounds an organism is unable to synthesize
must be directly obtained from the environment b
biofilms
thin, slimy layer encasing bacteria that adheres to a surface
can be considered a hydrogel
quorum sensing
cell-to-sell chemical communication
allows bacteria to coordinate their activity and group together
growth rates of different types of microorganisms in response to temperature
culture media
nutrients prepared for microbial growth
inoculum
microbes that are introduced into a culture medium to initiate growth
culture
microbes that grow and multiply in or on a culture medium
criteria for culture medium
must contain the right nutrients for the specific microorganism growing
should contain sufficient moisture, properly adjusted pH, and suitable level of O2
must be sterile
sterile
must contain no living microorganism
agar
solidifying agent
liquefies at 1000C and solidifies at ~ 400C
chemically defined media
one whose exact chemical composition is known
medium must provide an energy source
organism that require many growth factors are fastidious
complex media
made up of nutrients including extracts from yeast, meats, or plants
anaerobic growth media and methods
reducing media is used because anaerobes might be killed by exposure to oxygen. Medium contains sodium thioglycolate that chemically combine with dissolved oxygen and deplete oxygen in the culture medium.
capnophiles
microbes that can grow better at high CO2 concentrations
selective media
designed to suppress the growth of unwanted bacteria and encourage the growth of desire microbes
differential media
makes it easier to distinguish colonies of desired organisms from unnecessary ones
enrichment culture
designed to increase very small numbers of the desired type of organism to detectable levels
reducing media
takes away the oxygen
anaerobic bacteria grows in ot
gas gangreen
anaerobes produces to protect itself
anaerobic chamber
takes away O2 and creates CO2
generation time
time required for a cell to divide
generation number is the exponent
phases of growth