Pregnancy and Human development
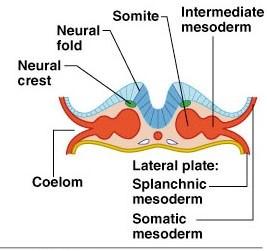
somite
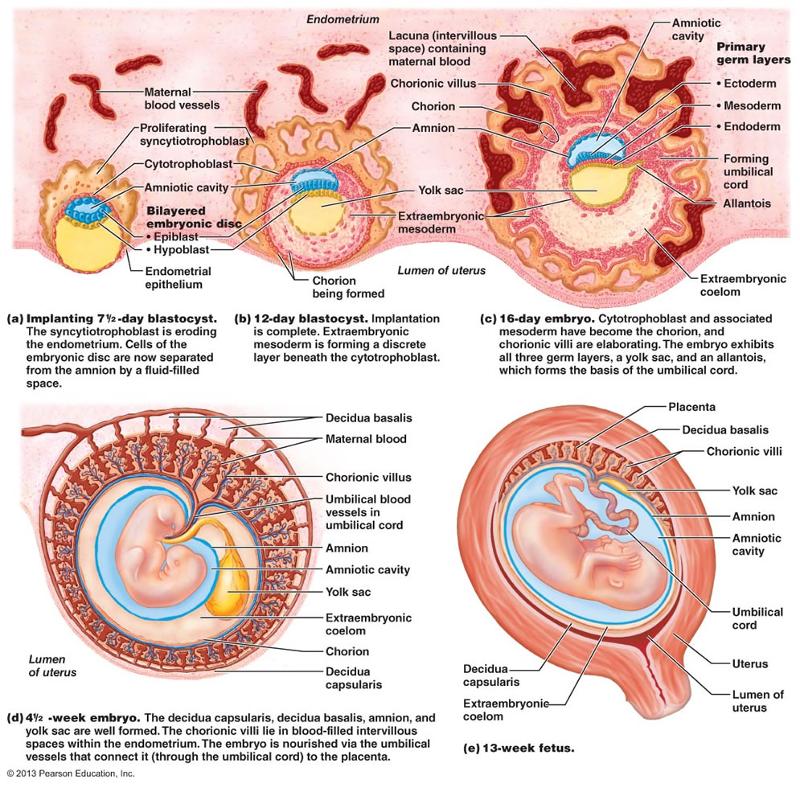
implantation is usually completed after
the blastocyst is entirely surrounded by endometrium
the chorionic membrane forms by which of the following layers in a developing embryo?
cytotrophoblast and syncitiotrophoblast
both B and C
which structure represents the remnant of the right to left atrial fetal shunt
fossa ovalis
which structure below is formed from endodermal tissue
esophagus
which structure below is formed from ectodermal tissues
brain
raised edged dorsal groove on early embryonic disc that establishes the longitudinal axis of the embryo is
primitive streak
which of the following is not a function of the placenta
urine formation
embryonic period from 2 to ___ weeks
8 weeks
the process which transforms the embryo into a three-layered stage is called
gastrulation
rod of mesodermal cells that serves as axial support is
notocord
abortion
expulsion of fetus before 20 weeks of gestation
hypoblast cells that form a sac on the ventral surface of the embryo called
yolk sac
the function of the ductus arteriosus is to
bypass the pulmonary circuit
following fertilization the zygote goes through a rapid period of cell division called
cleavage
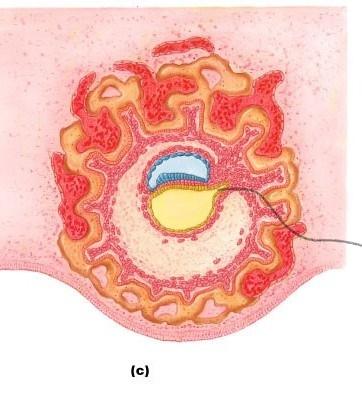
allantois
Which trimester is for weight gain
3rd trimester
Secondary oocyte completes the first meiotic division
at the time of ovulation
The second polar body forms from the secondary oocyte
after fertilization by sperm cell
the 16 or more cell stage (72 hours old)
morula
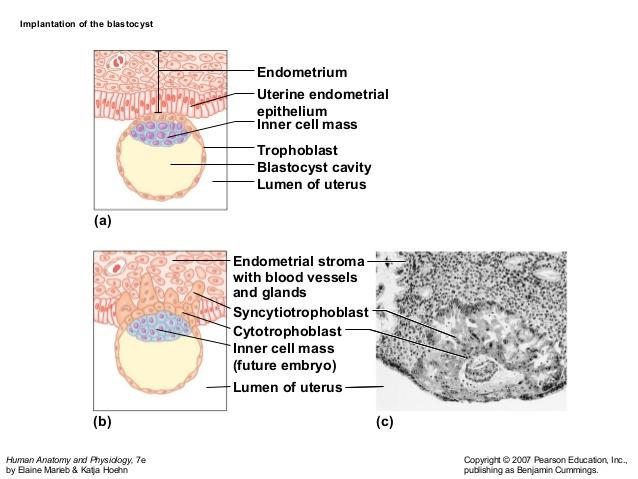
the cell layer which looses their plasma membranes and invade the endometrium is
syncitiotrophoblast
placenta forms from
embryonic trophoblasts and maternal endometrium
both A and B
Teratogenic (leading to structural deformity in newborn) drug such as thalidomide or phenothiazine mostly affect which stage of pregnancy and development
1st trimester
implantation is usually completed after
the blastocyst is entirely surrounded by endometrium
the outermost embryonic membrane is the
chorion
the process which transforms the embryo into a three-layered stage is called
gastrulation
How many weeks does the embryonic period last
8 weeks
epiblast cells on the dorsal surface of embryonic disc form a transparent membrane filled with fluid called
amnion
a small outpocketing at the caudal end of the yolk sac
allantois
organogenesis occurs during
1st trimester
raised edged dorsal groove on early embryonic disc that establishes the longitudinal axis of the embryo is
primitive streak
by the fourth or fifth day the pre-embryo consists of 100 cells called ____ stage
blastocyst
implantation is completed by the ___ day after ovulation
5th
allantois provides structural base for the ____
umbilical cord
there are ___ pairs of somites
40
somites have three functional parts
sclerotome, dermatome, myotome
Embryonic development of the digestive system (3rd week)
endoderm has folded and foregut and hindgut have formed
the midgut is open and continuous with the yolk sac
mouth and anal openings are nearly formed
8th week
accessory organs are budding from endoderm
rooting reflex
helps infants find the nipple
suckling reflex
aids in swallowing
morula
the 16 or more cells stage (72 hours old). By the fourth or fifth day the pre embryo consists of 100 or so cells
ectoderm
forms structures of the nervous system and skin epidermis
endoderm
forms epithelial linings of the digestive, respiratory and urogenital systems
mesoderm
forms all the other tissues
sclerotome
produce the vertebrae and ribs
dermatome
help form the dermis of the skin on the dorsal part of the body
myotome
form the skeletal muscles of the neck, trunk, and limbs
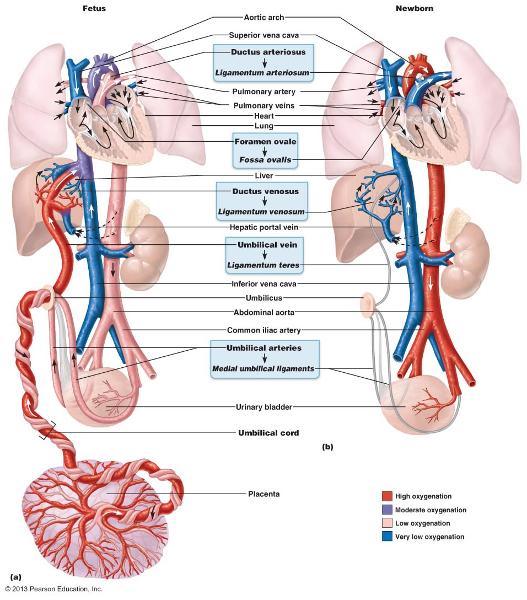
ductus venosus
venous shunt that by passes the liver
foramen ovale
opening in the interatrial septa to bypass pulmonary circulation
the chorionic membrane is formed by which of the following layers in a developing embryo?
cytotrophoblast and syncitiotrophoblast
both B and C
the umbilica cords becomes
ligamentum teres
ductus venosus becomes
ligamentum venosum
umbilical arteries becomes
medial umbilical ligaments
the foramen ovale becomes
fossa ovalis
ductus arteriosus becomes
ligamentum arteriosum
vasectomy
cutting and ligating the ducdtus deferens
ejaculation
propulsion of semen from the male duct system
suspensory
anchors the ovary laterally to the pelvic wall
mesovarium
suspends the ovary in between
broad ligament
contains the suspensory ligament and mesovarium
mittelschmerz
a twinge of pain sometimes felt at ovulation
Days 1-5
menstrual phase. uterus sheds all but the deepest part of the endometrium
days 6-14
proliferative (preovulatory) phase. endometrium rebuilds itself
Days 15-28
secretory (postovulatory) phase. endometrium prepares for implantation of the embryo
implantation of a blastocyst
inner cell mass
trophoblast
blastocyst activity
syncytiotrophoblast
cytotrophoblast
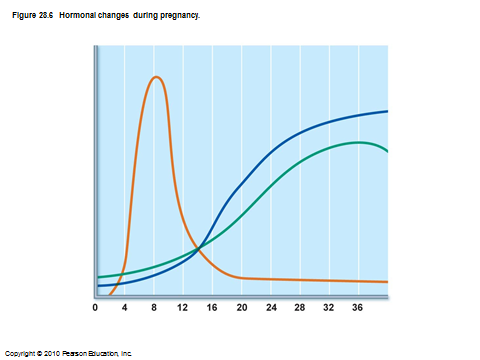
hormonal changes during pregnancy
hCG
estrogen
pregesterone
events of placentation
circulation in fetus and newborn
chadwick's signs
the female reproductive organs become increasingly vascular and engorged with blood, and the vagina develops a purplish hue
relaxin
causes pelvic ligaments and pubic symphysis to relax, widen, and becomes more flexible
stages of labor
dilation stage
expulsion stage
placental stage
dilation stage
time from labor's onset until the cervix is fully dilated by the baby's head ( about 10cm in diameter). last about 6-12 hours or more.
expulsion stage
lasts from full dilation to delivery of the infant or actual birth
placental stage
delivery of the placenta
engagement
occurs when the infant's head enters the true pelvis
crowning
occurs when the largest dimension of the baby's head distends the vulva