A&P Cumulative Chapters 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9,11, 12, 13, 14, 15
Cartilage has a flexible matrix that can accommodate mitosis of chondrocytes.
True
Which of the following increases the surface area of certain epithelial tissues?
microvilli
__________ are collections of neuron cell bodies associated with nerves in the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Ganglia
Which ligament would one tap to generate the knee-jerk reflex?
patellar ligament
Articular cartilage found at the ends of the long bones serves to ________.
provide a smooth surface at the ends of synovial joints
Which brain nucleus is the body's "biological clock"?
suprachiasmatic nucleus
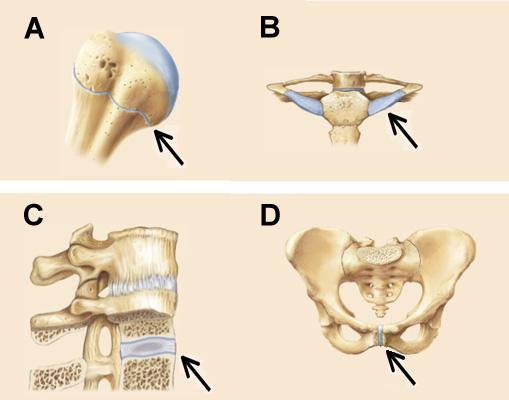
The joints indicated by the arrows in C and D are distinguished from those indicated in A and B by the presence of which of the following tissues?
fibro-cartilage
Information from balance (equilibrium) receptors goes directly to __________.
the brain stem
Connective tissues ________.
primarily consist of extracellular matrix
Which of the following is NOT a concept of the cell theory?
Cells are given life through a process known as spontaneous generation.
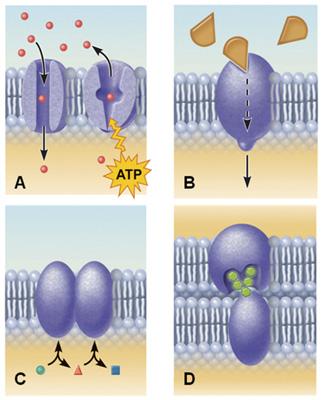
Which set of membrane proteins in the figure depicts the transport of solute molecules?
A
Schwann cells are functionally similar to ________.
oligodendrocytes
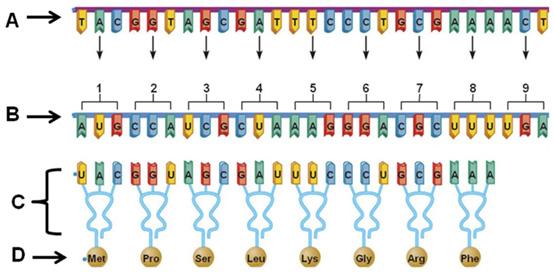
What process allows for the production of molecule B from a template consisting of molecule A?
transcription
A motor neuron and all the muscle cells that it stimulates are referred to as a motor end plate.
False
Motion sickness seems to ________.
result from mismatch between visual and vestibular inputs
Which of the following is NOT an autonomic nervous system (ANS) effector?
skeletal muscle
In adults, yellow marrow is located ________.
in the medullary cavity of long bones
The term diploë refers to the ________.
internal layer of spongy bone in flat bones
Which of the choices below describes the ANS?
motor fibers that conduct nerve impulses from the CNS to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands
Immediately after an action potential has peaked, which cellular gates open?
potassium
Arteries, veins, and lymphatics keep clots from sticking as long as their ________ is intact and healthy.
endothelium
The major role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum is to regulate ________.
intracellular levels of Ca2+
An osteon contains osteocytes, lamellae, and a central canal, and is found in compact bone only.
True
The force of a muscle contraction is NOT affected by __________.
the amount of ATP stored in the muscle cells
Which of the following is stored in bones?
phosphate
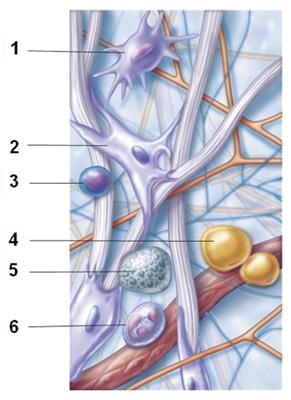
What activity does cell 1 undertake to contribute to the body's defense against injury and infection?
phagocytosis of foreign materials
Injured cartilage might heal more quickly if a treatment were discovered that would __________.
stimulate blood vessels to develop within cartilage
Functional classification of joints is based on ________.
the amount of movement allowed by the joint
Which part of the cerebral cortex is involved in intellect, cognition, recall, and personality?
prefrontal cortex
Phagocytosis is a form of exocytosis.
False
What are the two basic steps of polypeptide synthesis?
transcription and translation
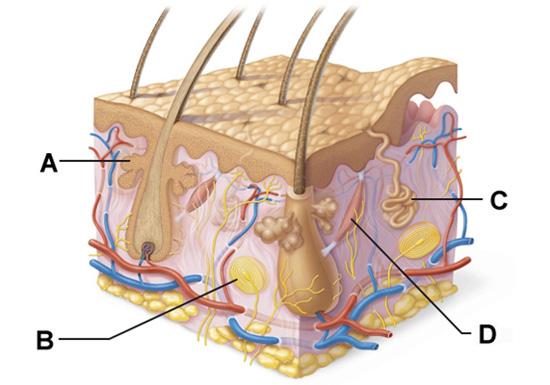
Which structure is a type of sudoriferous gland?
C
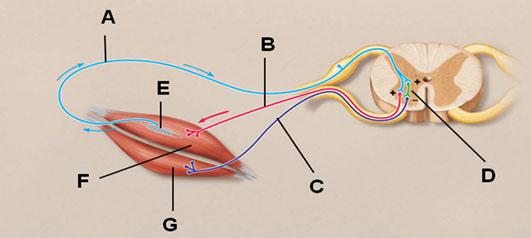
In the figure below, which letter points to an afferent neuron?
A
What is the primary function of the mitochondria?
They are the main sites of ATP production.
What cells line the ventricles of the brain?
ependymal cells
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT?
Tactile cells anchor the skin to the body.
The part of a neuron that conducts impulses away from its cell body is called a(n) ________.
axon
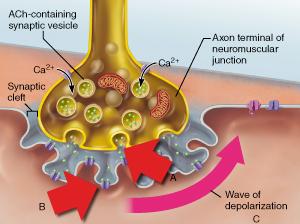
Which statement accurately describes the event indicated by B?
Binding of acetylcholine to a receptor triggers the opening of an ion channel.
Cholesterol helps to stabilize the cell membrane while decreasing the mobility of the phospholipids.
True
Which of the following is NOT a factor that contributes to joint stability?
amount of synovial fluid in the joint cavity
All epithelia have two surfaces, an apical surface and a basal surface, that differ in both structure and function.
True
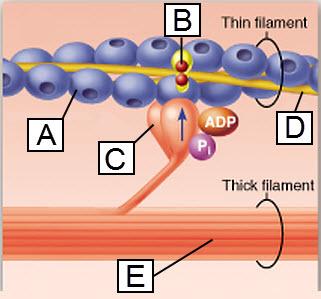
Which lettered protein functions as a motor protein?
C
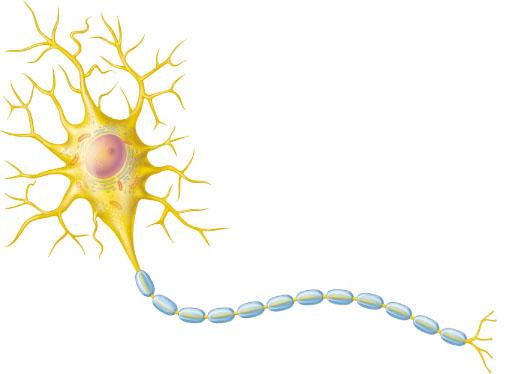
What structural classification describes this neuron?
multipolar
Which cell organelle provides the majority of the ATP needed by the cell to carry out its metabolic reactions?
mitochondrion
If cells are placed in a hypertonic solution containing a solute to which the membrane is impermeable, what could happen?
The cells will lose water and shrink.
Which of the following are cartilaginous joints?
Synchondroses
Bitter taste is elicited by ________.
alkaloids
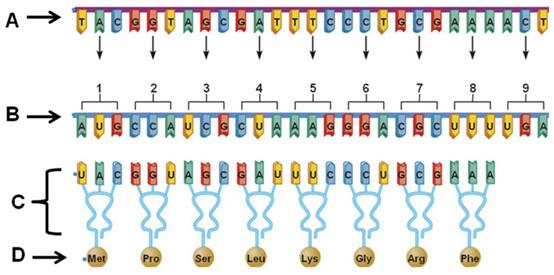
Which letter is pointing to an mRNA molecule?
B
Which neuroglia are the most abundant and versatile of the glial cells?
astrocytes
During interphase of the cell life cycle, the parent cell divides into two daughter cells.
False
Which of the following is the conducting region of the neuron?
axon
The electron microscope has revealed that one of the components within the cell consists of pinwheel array of 9 triplets of microtubules arranged to form a hollow tube. This structure is a ________.
centriole
Mitochondria ________.
contain some of the DNA and RNA code necessary for their own function
Use the figure to match the following descriptions.
Drag the
appropriate labels to their respective targets.
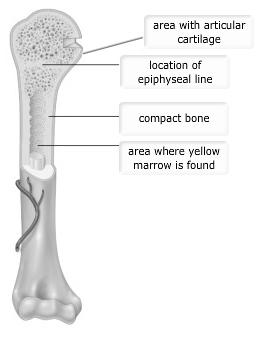
What kind of tissue is the forerunner of long bones in the embryo?
hyaline cartilage
What part of the nervous system performs information processing and integration?
central nervous system
Eye color is determined by the amount of brown pigment present in the iris.
True
The most dangerous type of skin cancer is ________.
melanoma
Which of the following is CORRECTLY paired?
multiaxial movement: movement in all three planes and around all three axes
Irritation of the phrenic nerve may cause diaphragm spasms called hiccups.
True
The RNA responsible for bringing the amino acids to the ribosome for protein formation is ________.
tRNA
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) includes the brain and spinal cord.
False
Peroxisomes ________.
are able to detoxify substances by enzymatic action
Which of the following is a function of a plasma membrane protein?
molecular transport through the membrane
Which of the following is not a step in tissue repair?
Formation of new stem cells
The main component of the cytosol is ________.
water
A fracture in the shaft of a bone would be a break in the ________.
diaphysis
Which of the following is CORRECTLY matched?
compound fracture: the fractured bone ends penetrate the skin
Axon diameter and degree of myelination determine nerve impulse conduction velocity.
True
After axonal injury, regeneration in peripheral nerves is guided by ________.
Schwann cells
Static equilibrium involves linear acceleration as well as changes in head rotation.
False
What indicates that a long bone has reached its adult length?
closure of the epiphyseal plate
Pressure, pain, and temperature receptors in the skin are ________.
exteroceptors
Creatine phosphate functions in the muscle cell by ________.
storing energy that will be transferred to ADP to resynthesize ATP
Cardiovascular effects of the sympathetic division include all except ________.
dilation of the blood vessels serving the skin and digestive viscera
All connective tissues arise from an embryonic tissue called mesenchyme.
True
Acetylcholine is the substance released by the axonal endings of the somatic efferent fibers and by the parasympathetic nerve fiber endings.
True
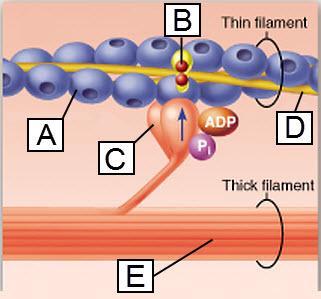
Which protein is indicated by E?
myosin
Cardiac muscle makes most of its ATP via anaerobic pathways.
False
Which of the following allows us to consciously control our skeletal muscles?
the somatic nervous system
Which of the following is CORRECTLY paired?
skeletal muscle: voluntary control
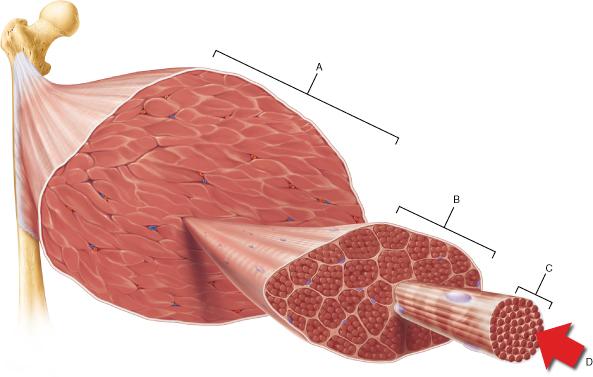
The connective tissue that covers structure A is continuous with which of the following?
tendon
Which of the following is the basic taste quality responsible for the "beef taste" of steak?
umami
The structure that allows equalization of the pressure in the middle ear with that outside the body is the external auditory meatus.
False
The trabeculae of spongy bone are oriented toward lines of stress.
True
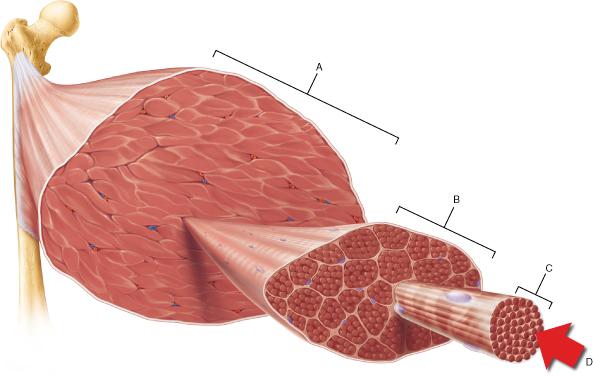
Which of the following is the smallest structural unit in which the distinctive striated bands characteristic of skeletal muscle are observed?
D
Which of the following is FALSE regarding the membrane potential?
The resting membrane potential is maintained solely by passive transport processes.
Which tissue type consists of a sheet of cells that covers a body surface or lines a body cavity?
epithelial tissue
When muscle cells break down glucose to generate ATP under oxygen deficient conditions, they will form ________.
lactic acid
All processing at the circuit level going up to the perceptual level must synapse in the ________.
thalamus
Broca's area ________.
is considered a motor speech area
The dense fibrous connective tissue portion of the skin is located in the reticular region of the dermis.
True
During isometric contraction, the energy used appears as movement.
False
If the ventral root of a spinal nerve were cut, what would be the result in the tissue or region that nerve supplies?
a complete loss of voluntary movement
What tissue forms the model for endochondral ossification?
cartilage
The autonomic nervous system may cause activation or inhibition, depending on the division that is active and the target that is affected.
True
In adults, hematopoietic tissue is NOT found in ________.
the medullary cavity of long bones
The skin consists of two main regions. From deep to superficial they are the ________.
dermis and epidermis
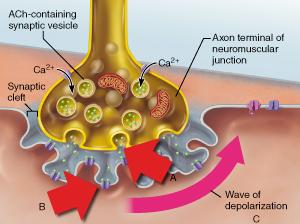
What specific neurotransmitter is released from the axonal terminus as shown in A?
acetylcholine
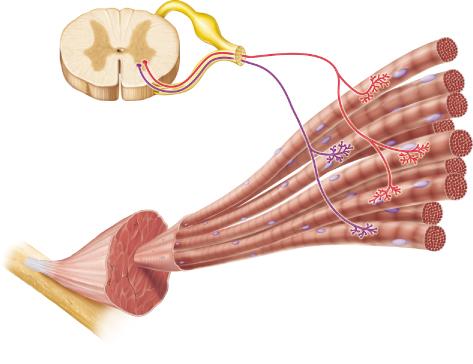
Which of the following describes the neurons shown in this figure?
somatic motor neurons