Geology
Which of the following correctly describes the Atlantic and Pacific continental margins?
The Atlantic is a passive margin, and the Pacific is an active margin
Choose the true statement regarding the continental shelf.
The shelf represents the flooded portions of continents.
Turbidity currents travel from the shelf through __________, creating deep sea fans.
canyons
Relationship of volcanism and seismicity to plate tectonics:
Volcanism is primarily found at divergent and convergent plate boundaries. Most seismicity occurs along plate boundaries of all three types.
If the subduction angle is steep, the overriding plate may undergo __________.
subduction erosion
Which of the following is true regarding shallow subduction angles?
Sediment and seamounts are scraped from the downgoing plate to produce an accretionary wedge.
What happens as plates diverge at an oceanic ridge?
New oceanic crust and lithospheric mantle are generated by the cooling of molten rock upwelling from the mantle
What two layers of the ophiolite sequence are compositionally similar, but formed in different areas with respect to the crust?
Layer 2: Basalt pillow lavas and Layer 4: gabbro
Which of the following contains the entire ophiolite suite, in order from the mantle to the seafloor?
mantle peridotite
gabbro
sheeted dike complex
Basaltic pillow lavas
deep-sea sediments
What are the features associated with a divergent boundary that is spreading quickly?
a relatively smooth swell with gentle slopes
Which of the following accurately compares the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and East Pacific Rise?
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is spreading at a much slower rate than the East Pacific Rise.
Name the correct order of rifting events.
crustal upwarp
rift valley
linear sea
ocean
The Gulf of Aden represents which part of the rifting sequence?
linear sea
The timing of __________ and continental breakup strongly correlate.
flood basalt formation
What feature connects the South American Paraná and African Entedeka flood basalts?
seamount chains
What sequence of rocks would you expect rift valley evolution to produce, from oldest to youngest?
volcanic rocks
classic sedimentary rocks
deep sea
sedimentary rocks
Which of the following is a true statement regarding the Farallon Plate
It was an oceanic plate that used to exist between the Pacific and North American Plates.
The plate boundary in the U.S. Pacific Northwest is _____, while most of the California coast is characterized by a _____ plate boundary.
convergent; transform
Which statement regarding Baja Mexico and the city of Los Angeles is correct?
Both are located on the Pacific Plate
Strike-slip faulting of the Queen Charlotte and San Andreas fault systems shows __________.
a right lateral sense of motion
What happened to the Farallon Plate approximately 20 million years ago?
The San Andreas and Queen Charlotte Faults were established where it was subducted beneath the North American plate
Which of the following scenarios could result in the development of a compressional mountain belt?
two landmasses collide
Which geologic features would be present in compressional mountain belts? (Note: There may be more than one answer.)
folds
intrusive igneous rocks
thrust faults
Which of the following rocks are characteristic of compressional mountain building?
schist
Using the map provided in Figure 1, in which province would the Rocky Mountains of the United States be located?
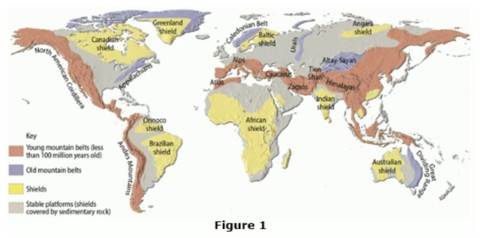
young mountain belts
Which of the following orogenies helped to create the Appalachian Mountains?
Taconic, Acadian, and Alleghanian
Which event marked the creation of the supercontinent Pangaea?
The Iapetus Ocean closed during the Alleghanian Orogeny.
Which of the Appalachian Mountain Belt Provinces are visible in the circled area of Figure 1?
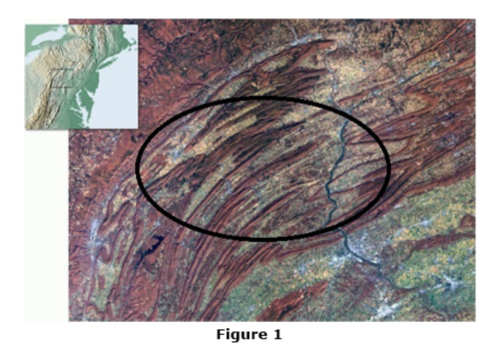
Valley and Ridge
Which of the following geographic provinces is the newest addition to the North American continent?
Coastal Plain
Which mountain range marks the boundary between the Indian and Eurasian Plates?
Himalayas
What kind of tectonic boundary is currently responsible for creating the Himalayas?
Continent-Continent Convergent Boundary
What geologic features were created in the Eurasian Plate when India underthrust beneath it?
thrust faults
thicker continental crust
As India moves northward, China and Southeast Asia are being relocated to the east and southeast because of "escape tectonics." What feature is allowing them to "escape"?
strike-slip faults
When the Indian Plate collided with Eurasian Plate, why didn't it subduct?
The Indian Plate is too buoyant.
The Indian Plate is too thick.
A terrane is __________.
a mass of rock that formed elsewhere and was added to a continent
Which tectonic boundary is associated with the addition of terranes to a continent?
convergent boundary
What is the name of the process by which terranes are added to continents?
accretion
Using the map in Figure 1, determine which of the named terranes accreted earliest to North America.
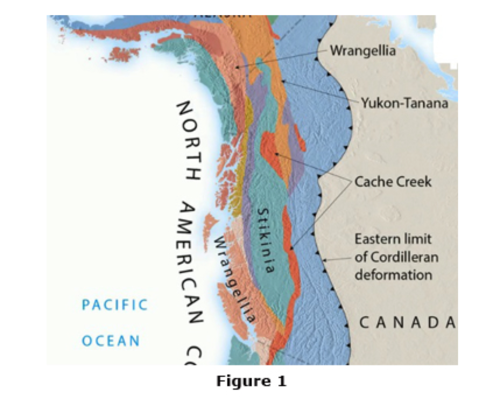
Yukon-Tanana
The map in Figure 2 is a cross-section of the North American continent 600 million years ago and after the break-up of Pangaea approximately 200 million years ago. Which material(s) had been accreted to North America as terranes?
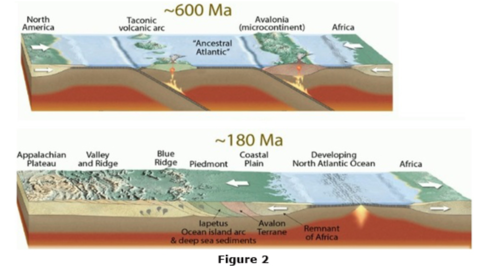
Iapetus Ocean Island Arc and sediments
the Avalon Terrane
and a remnant of Africa