Biology 1A
What is the distinction between evolution in language
(example:
the evolution of galaxies) and evolution in
biology?
In biology, evolution involves heredity
What is the core theme of Biology?
Evolution
In Linnaeus' binomial nomenclature. The organisms
genus and species
What is the "Goal" of evolution?
There is no goal for evolution.
A common
question to ask is "Why is this the way it is?"
with
the expectation that some structure or other
feature
has a purpose behind it. There will not
always be a good reason.
For example, the
vagus /laryngeal nerve pathways that control
the
heart / larynx. The laryngeal nerve follows the
vagus
nerve down from the brain to the heart,
then loops around and
proceeds back up to the
larynx. This makes no sense from a functional
aspect.
What is energy?
the capacity to do work
What is metabolism?
The sum of all the chemical reactions in an
organism.
Organic Molecules contain: (MARK ALL THAT
APPLY)
a. Nitrogen
b. Phosphorous
c. Hydrogen
d. carbon
e. Oxygen
a. Nitrogen
b. Phosphorous
c. Hydrogen
d.
carbon
e. Oxygen
A control group:
does not receive a treatment.
Organic Molecules are molecule that come from
living organisms
and contain what elements? (Mark
all that apply)
a. S
b. C
c. O
d. H
e. N
a. S
b. C
Note,
this is note a strict definition,
some sources say a
CC bond is considered an
organic molecule
also.
c. O
d. H
e. N
A Hydrocarbon contains: (Mark all that apply)
a. N
b. O
c. H
d. S
e. C
a. N
b. O
c. H
d. S
e. C
Isomers are compounds with:
the same numbers of atoms of the same
elements but with
different structures
Which functional group (sidechain) can be
"cross
linked" in protein?
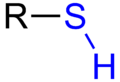
sulfhydryl
What is a polymer?
long molecule consisting of many similar
building blocks.
Hydrogen bonds are: (MARK ALL THAT APPLY)
a. between ions
b. covalent bonds
c. represented by dotted
lines
d. between a positive (partial) and negative
(partial) charge
a. between ions
b. covalent bonds
c. represented by
dotted lines
d. between a
positive (partial) and negative
(partial) charge
The hydrogen bonds water forms with other
molecules make it
sticky. This results in properties
such as: (MARK ALL THAT APPLY)
a. capillary action
b. cohesion
c. surface tension
d. adhesion
a. capillary
action
b. cohesion
c. surface
tension
d. adhesion
water sticks to and attracts anything with a charge (ionic or partial)
Molecules can have both polar and nonpolar
portions, what
happens to the nonpolar portions in
water.
They aggregate away from water.
What happens to solutes, such as ions, in a solution?
Water forms a hydration shell around it.
This means that water
is attracted to the solute
and must therefore also be in a higher
proportion
in solution.
The primary function of starch is:
Energy storage
What functional group is most common in a
monosaccharide?
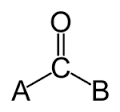
Carbonyl
Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates and may be subcategorized as aldoses or ketoses. The sugar is an aldose if it contains an aldehyde functional group. A ketose signifies that the sugar contains a ketone functional group.
Which of the following is NOT a monosaccharide?
a. Galactose
b. Fructose
c. Glucose
d. Maltose
e. riobse
d. Maltose
Monosaccharides
a. Galactose
b. Fructose
c. Glucose
e. riobse
Which form of a monosaccharide is more prevalent in
water?
ring
When 2 monosaccharides combine they form what kind
of bond?
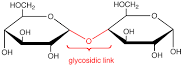
Glycosidic
A very long chain of monosaccharides is called a:
polysaccharide
Which of the following is composed of ONLY glucose
monomers?
(mark all that apply)
a. Cellulose
b. Starch
c. glycogen
d.
chitin
e. Maltose
a. Cellulose
b. Starch
c. glycogen
d. chitin
e. Maltose
All lipids are:
hydrophobic
Which of the following is NOT a lipid?
a. phospholipid
b. steroids
c. Triacylglycerol
d.
polypeptide
e. cholesterol
d. polypeptide
Lipids
a. phospholipid
b. steroids
c. Triacylglycerol
e. cholesterol
Which of the following is NOT a polymer?
a. proteins
b. DNA
c. starch
d.Fats
d.Fats
A fatty acid consist of: (Mark All That Apply)
a. glycerol
b. hydrocarbon chain
c. carboxyl
d.
triglyceride
e. amino
b.
hydrocarbon chain
c.
carboxyl
An amphipathic (or biphasic) molecule:
is hydrophobic on one side and hydrophilic on
the other.
How many rings are in cholesterol?
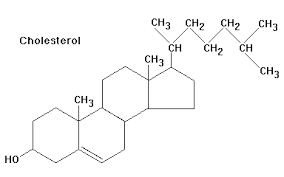
4
a triglyceride is composed of: (Mark All That Apply)
a. amino groups
b. cholesterol
c. fatty acids
d. glycerol
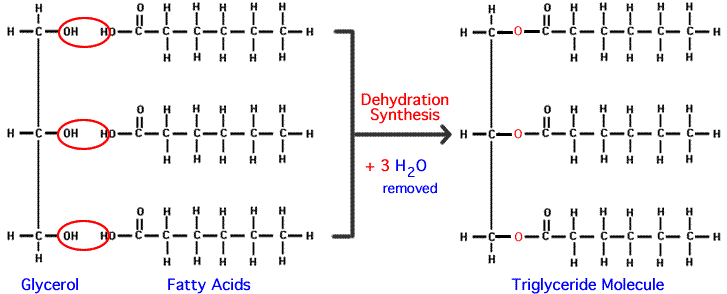
a. amino groups
b. cholesterol
c. fatty acids
d. glycerol
The building blocks of protein are:
amino acids
Which of the following are functional groups attached
to the
central alpha carbon of an amino acid? (Mark
All That Apply)
a. carboxyl group
b. ester
c. amino group
d.
hydrogen atom
e. side chain
f. phosphate
a. carboxyl
group
b. ester
c. amino group
d. hydrogen atom
e. side chain
f. phosphate
Which of the parts of an amino acid are always the
same? (Mark
All That Apply)
a. central alpha carbon with hydrogen
b. side chain
c.
carboxyl group
d. amino group
a. central
alpha carbon with hydrogen
b. side
chain
c. carboxyl group
d. amino group
These are called the amino acid backbone.
Amino acid backbone.
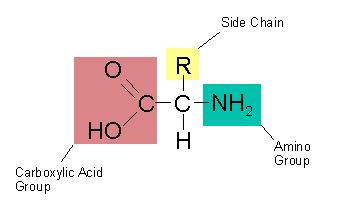
central alpha carbon with hydrogen
carboxyl group
amino group
Which part of an amino acid is unique to a particular
amino acid?
side chain
This is often referred to as the variable group or R
group.
Although R is also a generic way of saying
anything with a C (carbon).
Category for the side chains?
b. Hydrophobic / nonpolar
c. Hydrophillic negatively charged
d. Hydrophillic
positively charged
e. Hydrophillic / polar
When multiple amino acids link up together they form
a polymer
(long chain) called a:
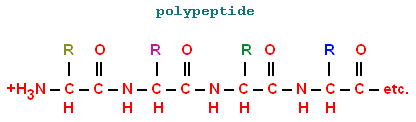
Polypeptide
How many levels of protein structure are there?
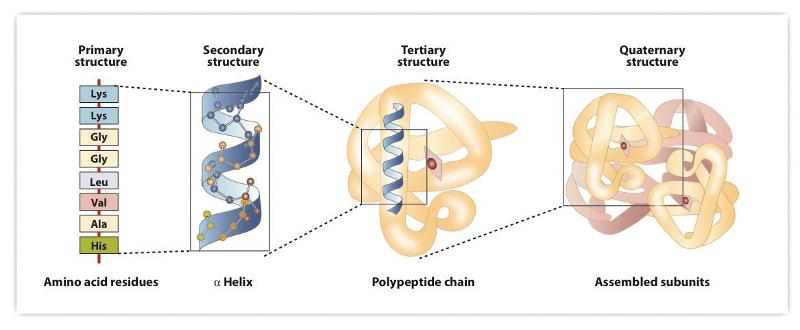
4
Primary level of protein structure
Sequence of amino acids
Secondary level of protein structure
segments of the chain forming coiled or folded
Tertiary level of protein structure
the main, 3dimensional shape.
description of the complex and irregular folding of the peptide chain in three dimensions
Quaternary level of protein structure
The 3dimensional shape of an aggregate
arrangement of more than one protein molecule in a multi-subunit complex.
What are the 2 most common secondary structures of a protein?
Alpha-helicies
Betapleated sheets
There were only 2 listed in your reading, these are
considered
the most common, however, there are
many other common secondary structures.
a betapleated sheet is an example of what level of
protein structure?
secondary
What is the best / most accurate (currently) method
for
determining a protein structure?
Xray crystallography
What is it called when the shape of a protein is
destroyed?
denaturation
degradative processes in metabolism are called:
catabolic pathways
for a reaction to be spontaneous it must have:
a negative change in G
A reaction that absorbs energy is:
endergonic
How do you get an endergonic reaction to happen?
couple it to an exergonic reaction
Which of the following is NOT true about enzymes?
a. The provide and alternate route for a chemical reaction
b.
They are used up in the reaction and are lost
c. They are
catalysts
d. They lower activation energy
a. The provide and alternate route for a chemical reaction
b. They are
used up in the reaction and are lost
c.
They are catalysts
d. They lower activation energy
The location on the enzyme that binds to substrates is called the:
active site
A noncompetitive inhibitor:
binds to an enzyme away from the active site
when a molecule affects enzyme's shape and function it is known as:
What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide?
nitrogenous base
(usually just referred to as
the "base" (base as in acid/base)
phosphate
pentose
(a monosaccharide, pentose (5) because
there are 5 carbons)
what is the variable part of a nucleotide?
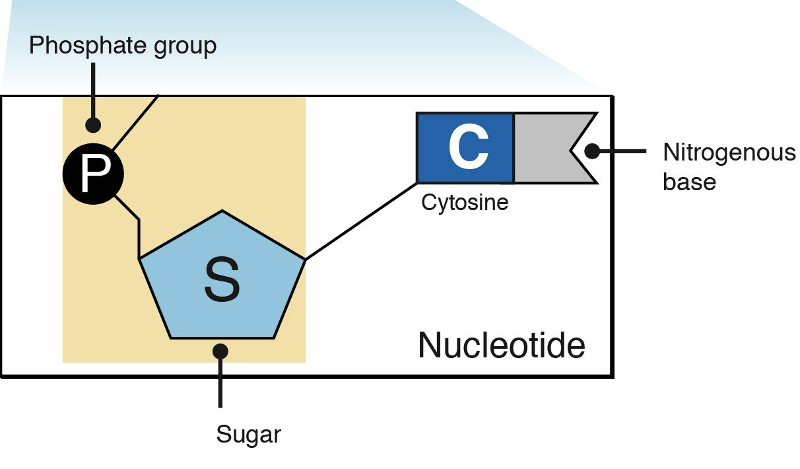
base
A nucleotide is one of the structural components, or building blocks, of DNA and RNA. A nucleotide consists of a base (one of four chemicals: adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine) plus a molecule of sugar and one of phosphoric acid.
What is the structure of phosphate?
PO4
What is the difference between Ribose and
deoxyribose?
deoxyribose has one few hydroxyl group (OH)
Which of the following is NOT in RNA?
a. Uracil
b. Cytosine
c. Adenine
d. Guanine
e. Thymine
a. Uracil
b. Cytosine
c. Adenine
d. Guanine
e. Thymine
How many rings does a purine have?
2
The 2 strands of DNA go in opposite directions, which is called:
antiparallel
What direction does DNA ALWAYS go in?
5' > 3'
What feature do all cells have?
plasma membrane
The liquid/jelly portion of a cell is called the:
Cytosol
The______ cell's size the _________ the surface
area to volume ratio.
smaller / larger
What type of organism lacks a nucleus
prokaryote
Which of the following is found only in plant cells and
NOT in
animal cells?
chloroplast
Function of Ribosome
carries out protein synthesis
Organells of cell Involved in the transport of proteins
b. golgi apparatus
c. Transport Vesicles
d. Endoplasmic reticulum
Organelle that would likely be able to break down bacteria?
lysosome
What is a protein that has a carbohydrate covalent
bonded to it called?
a. glycoprotein ?
b. lipoprotein ?
d. glycolipid ??
Which of the following is not a fiber of the
cyoskeleton
a. microfilaments
b. centriole
c. microtubule
d. keratins
a. microfilaments
b.
centriole
c. microtubule
d. keratins
How do ions pass through the lipid bilayer?
Transport Proteins
Which direction will molecules diffuse?
Down its concentration gradient
What is it called when substances use energy to cross a membrane?
active transport
the diffustion of water is called:
Osmosis
A cell that has more nonpenetrating solutes is:
hypertonic
The process by which molecules are taken into the cell by pinching in to form a new vesicle is called:
endocytosis
What is the most prevalent catabolic pathway?
aerobic respiration