A&P Lab Exam 1 Some PIctures
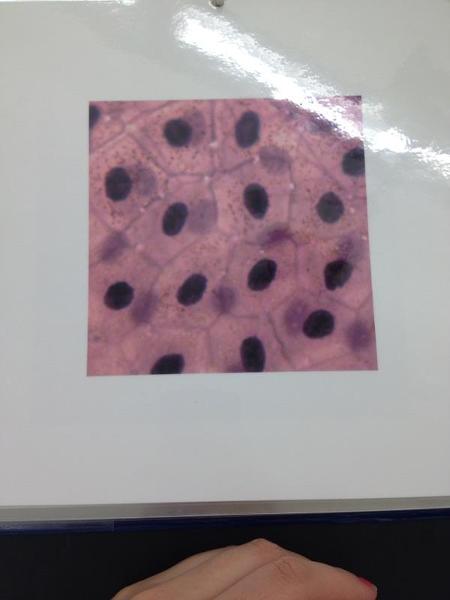
Simple Squamous epithelium
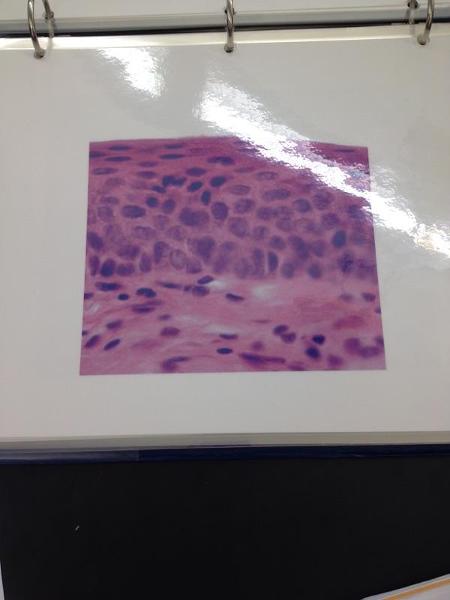
Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
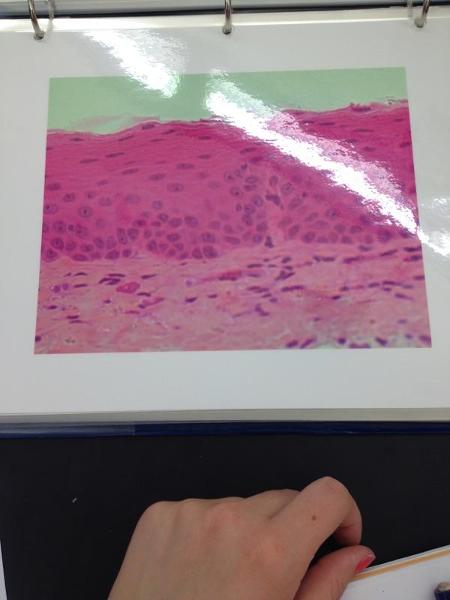
Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
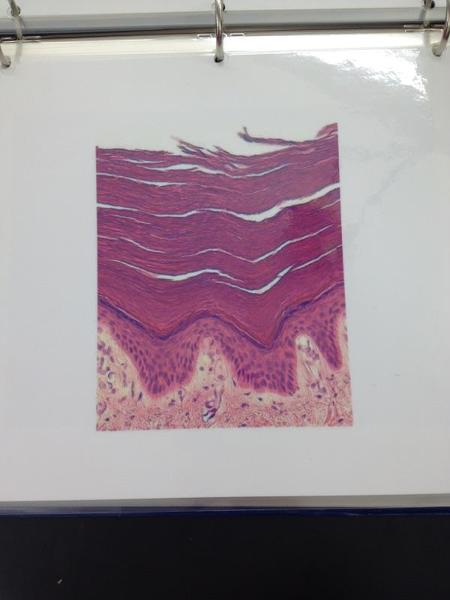
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium

Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
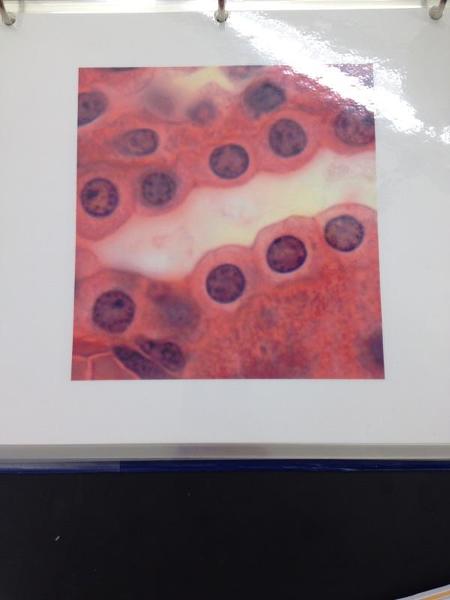
Simple cuboidal epithelium
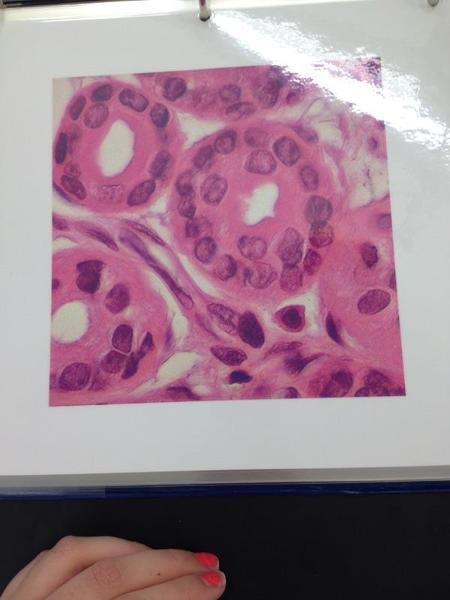
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
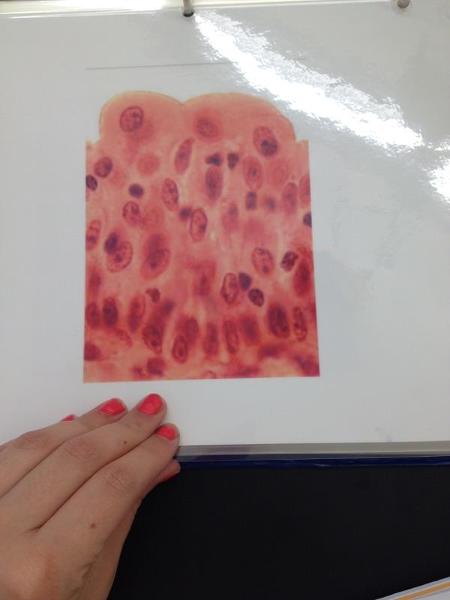
Transitional epithelium
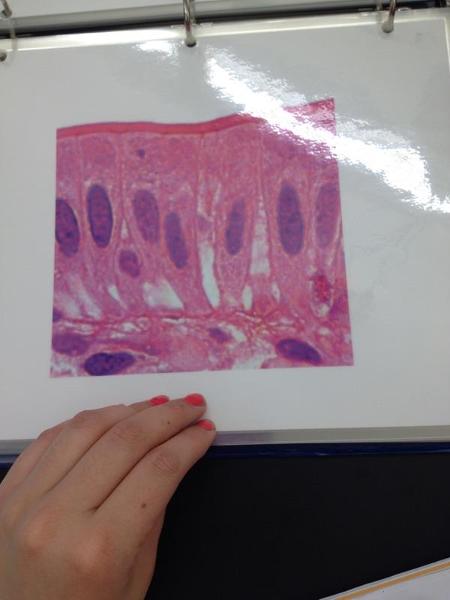
Simple columnar epithelium
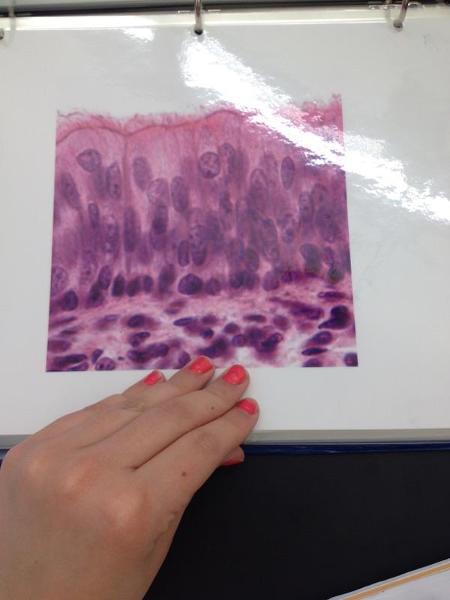
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
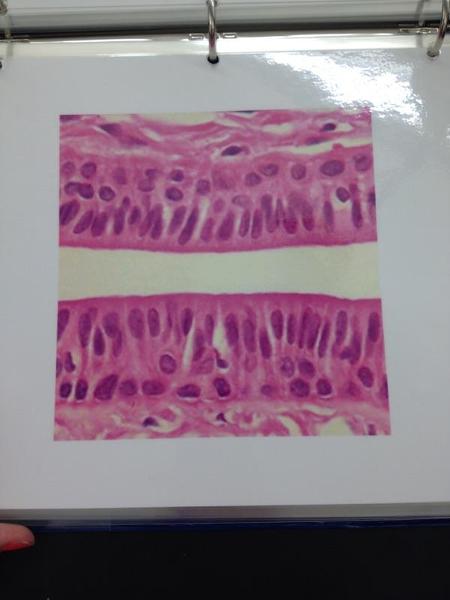
Stratified columnar epithelium

Areolar connective tissue
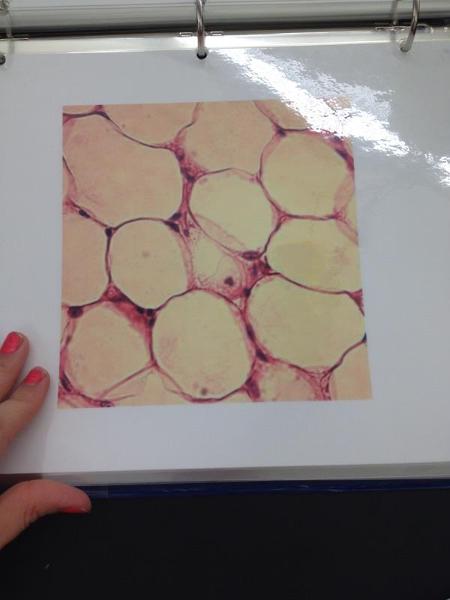
Adipose connective tissue
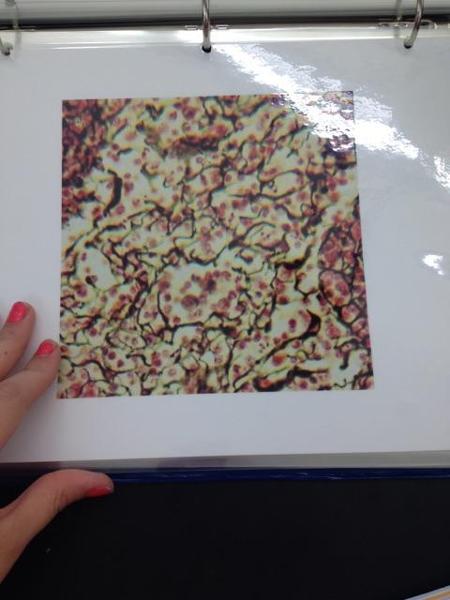

Reticular connective tissue
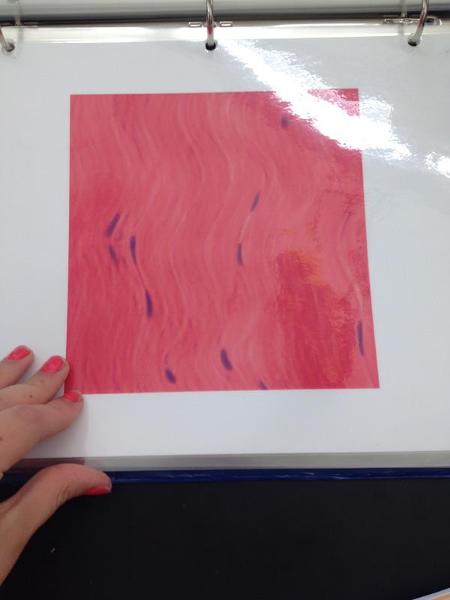

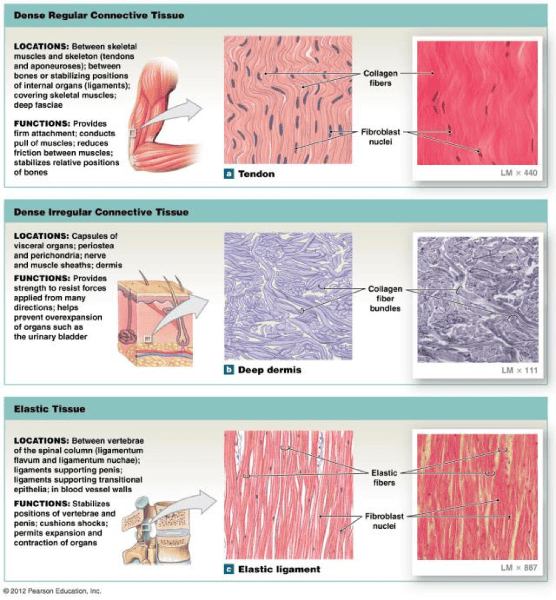
Dense regular tissue
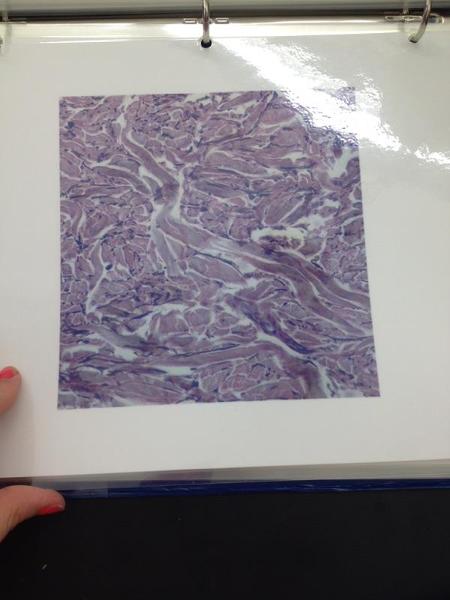
Dense irregular connective tissue
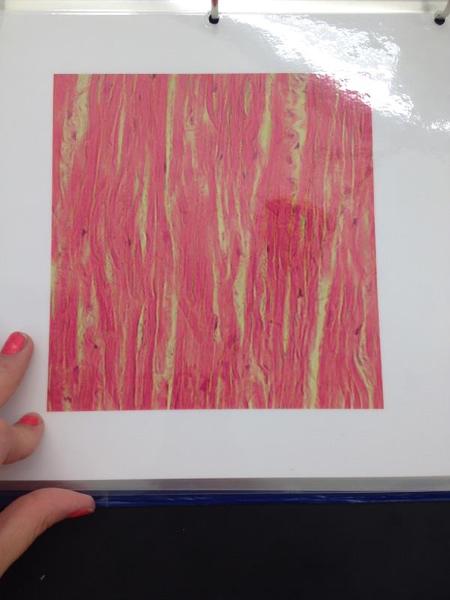

Elastic connective tissue
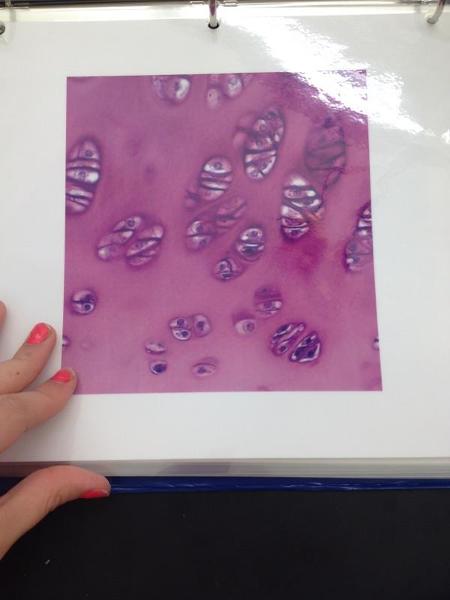
Hyaline cartilage
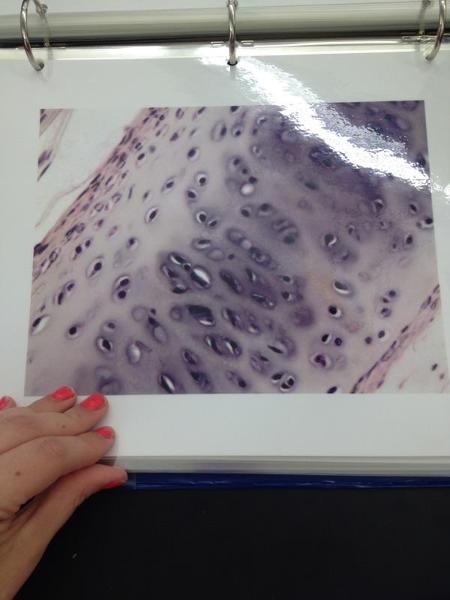
Hyaline cartilage
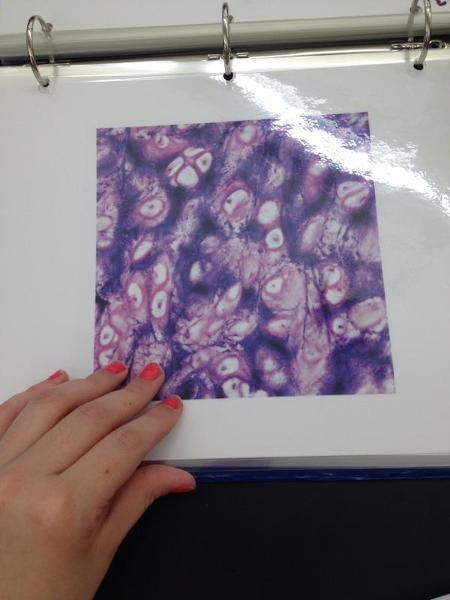
Elastic cartilage
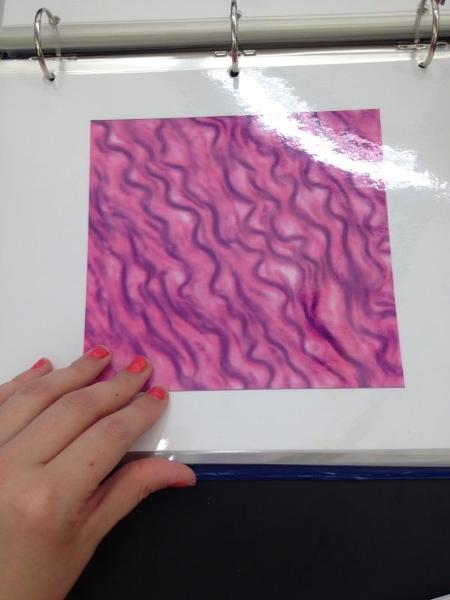

Fibrocartilage
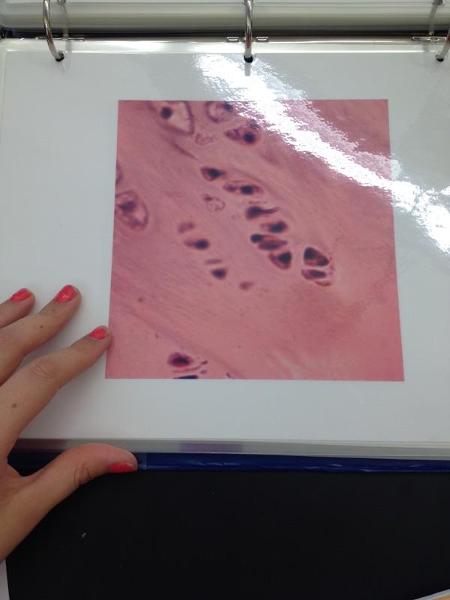
Fibrocartilage
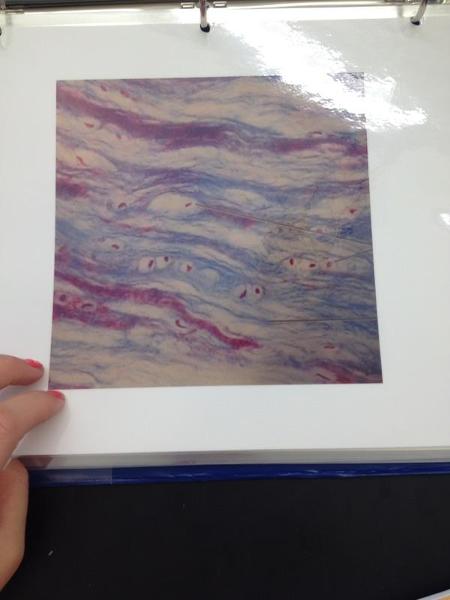

Fibrocartilage
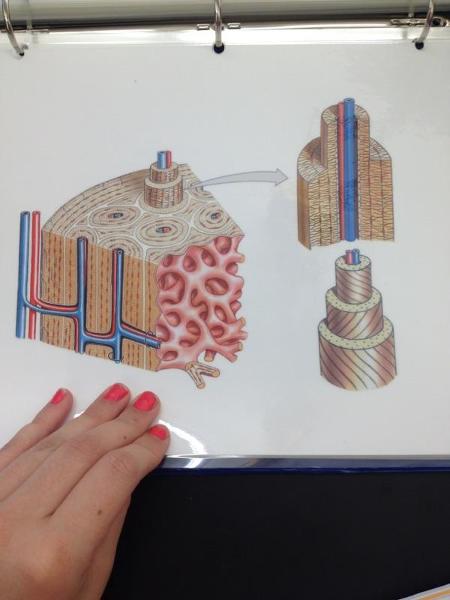
Osseous tissue
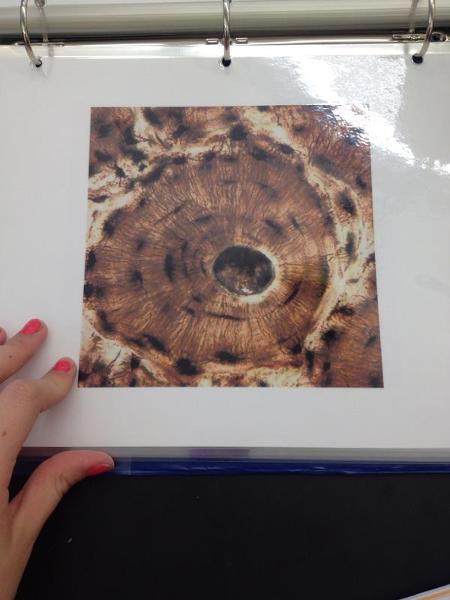

Osteon
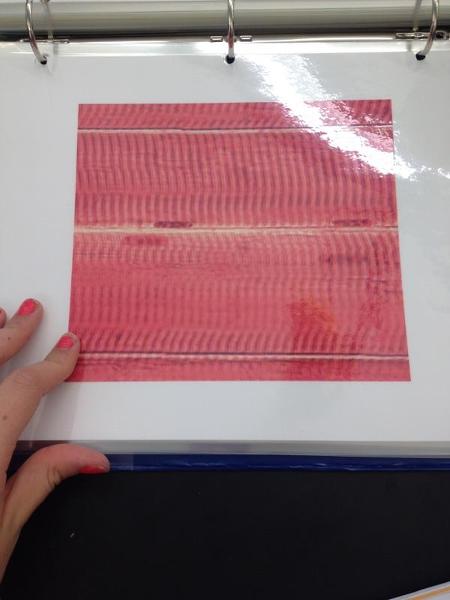

Skeletal muscle
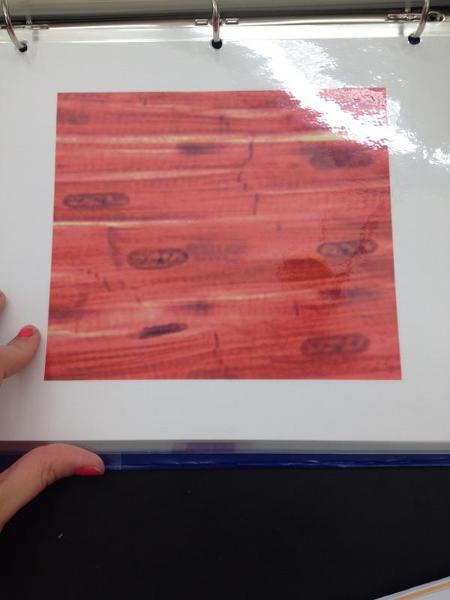

Cardiac muscle
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium Locations and Functions
Locations: Lining of the nasal cavity, trachea, and bronchi; portions of male reproductive tract
Functions: Protection, Secretion, moves mucous with cilia
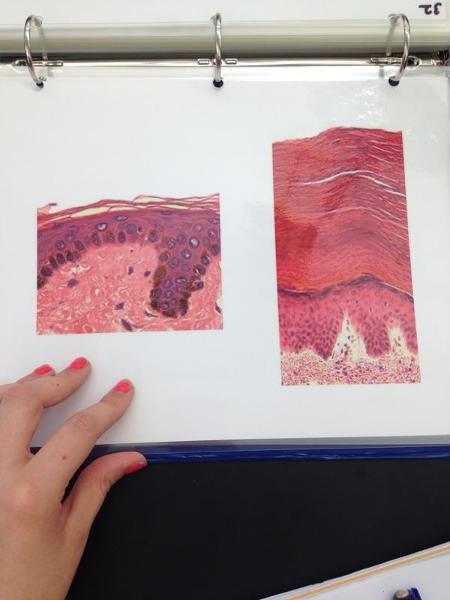
Thin/thick skin
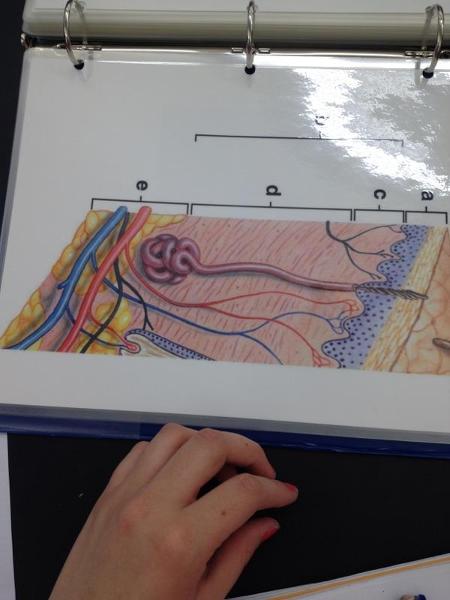
Integument
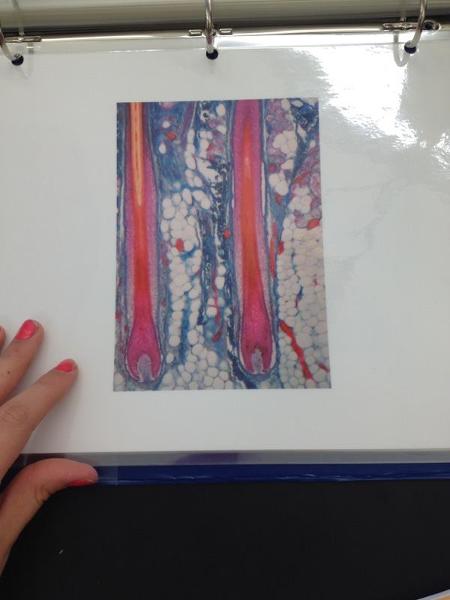

Hair follicle
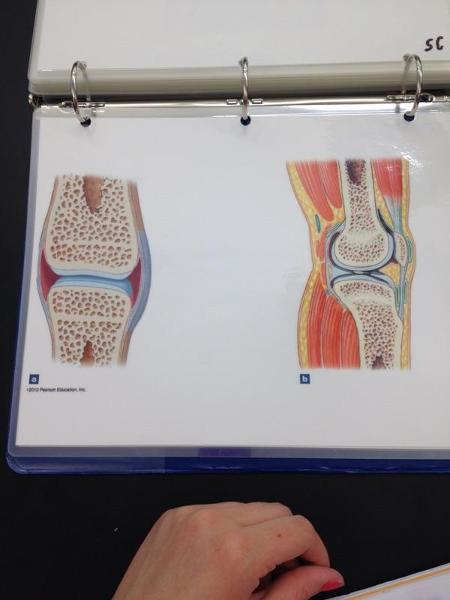
Synovial joint
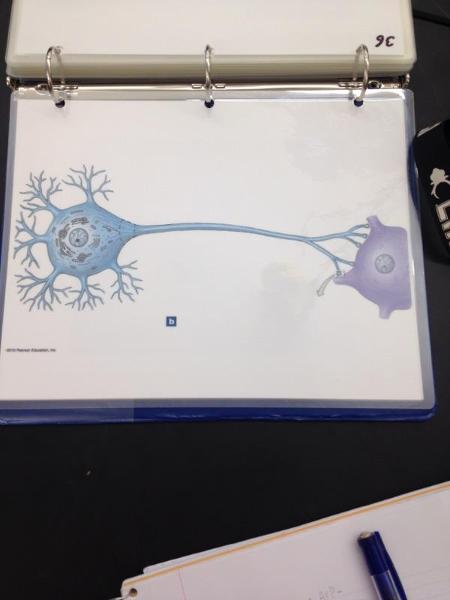
Neuron
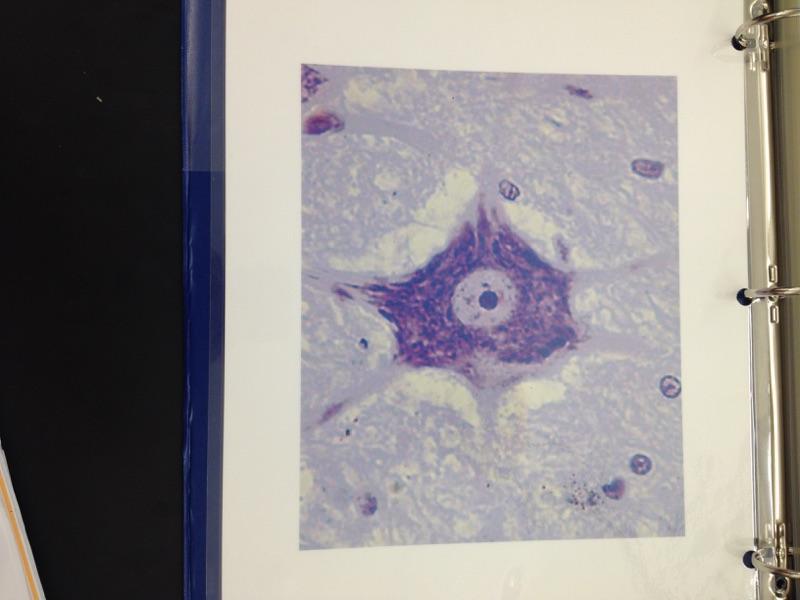
Neuron
Anterior
Same as VENTRAL- Front
Posterior
Same as DORSAL- back
Parietal LINNINGS
Superficial (outermost layer)
Visceral LINNINGS
Inner layer
Parietal Pluera (lungs)
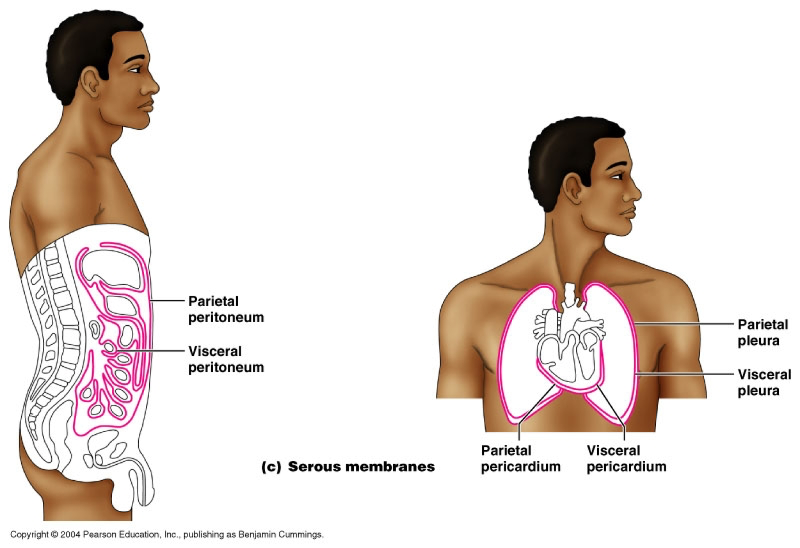
Outer layer of the lining of the lungs
Visceral Pluera (lungs)
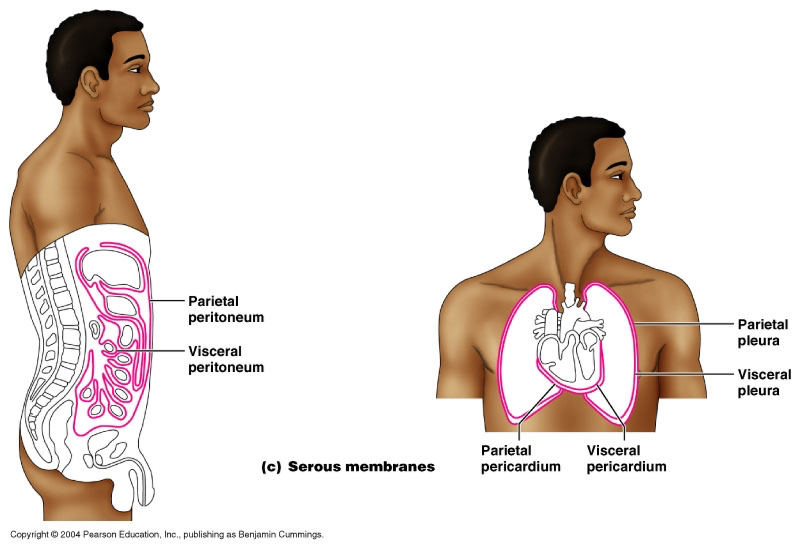
Inner layer of the lining of of the lungs
Parietal Pericardium
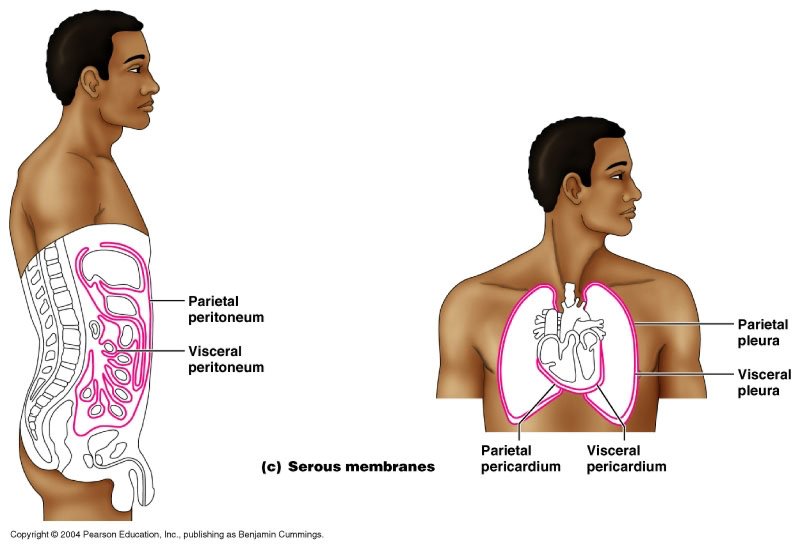
Outer layer of lining of heart
Viseral Pericardium
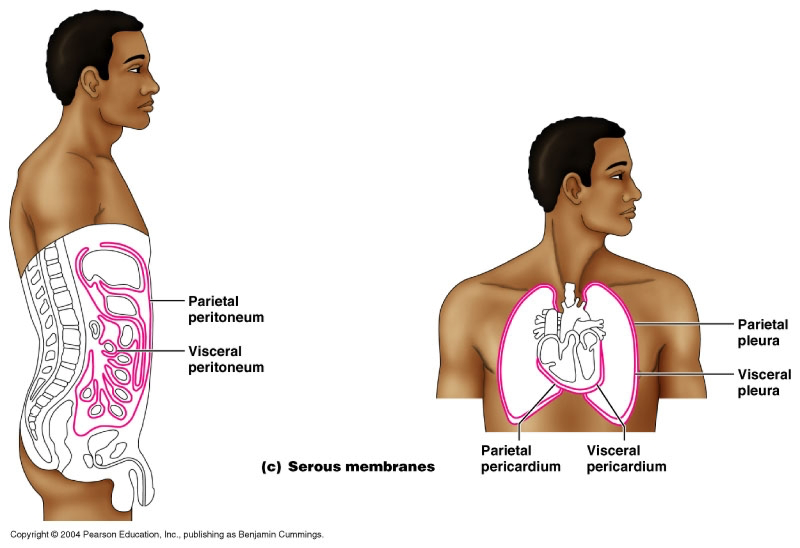
Inner layer of the lining of the heart
Mediastinum
Contains the trachea, esophagus, and major vessels
Parietal Peritoneum
lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities
Visceral Peritoneum
covers the external surfaces of most abdominal organs, including the intestinal tract.
Pelvic Cavity
Contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, last portion of the digestive tracts.
Study Abdominal Pelvic Regions
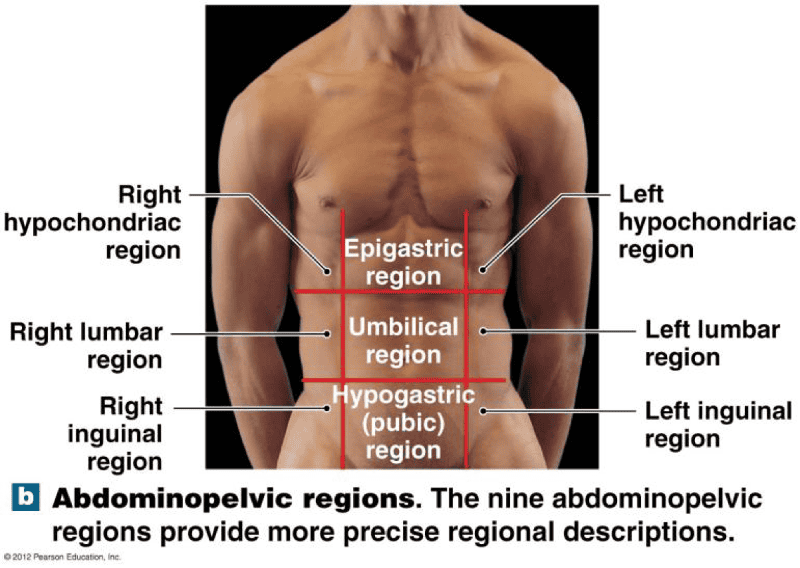
RUQ
Liver
RLQ
Appendix
LUQ
Spleen
LLQ
Colon
Epithelium
lines, protects and secretes
Exocrine
secrete through ducts. Products go to places “outside” (surface of) the body
Has Ducts
Examples of Exocrine Glands- Sweat Glands, salivary, mammary, and liver
Muscle tissue
excitable, contractile tissue for movement
Nervous tissue
excitable tissue used to send short term signals throughout the body
Simple Squamous Epithelium Locations and Functions
Locations: endothelia lining of the HEART and blood vessels, portions of the KIDNEY tubule, inner lining of the cornea, alveoli of the lungs
Functions: Lines, protects and secretes. Reduces friction, controls vessel permeability; performs absorption and secretion
Stratified Squamous Epithelium Locations and Functions
Locations: Surface of SKIN,lining of the mouth, throat, esophagus, rectum, anus and vagina.
Functions: Provides physical protection against abrasion, pathogens, and chemical attack
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Locations and Functions
Locations: Glands, ducts; portion of kidney tubules; thyroid gland
Function: Limited protection, secretion, and absorption.
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium Locations and Functions
Location: Lining of some ducts
Functions: Protects, sectretion, absorption
Simple Columnar Epithelium Locations and Functions
Locations: Lining of stomach, intestine, gallbladder, uterine tubes, and collecting ducts of kidneys
Function: protection, secretion, absorption
Stratified Columnar Epithelium Locations and Functions
Locations: Small area of pharynx, Epiglottis, annus, mammary glands, salivary glands ducts, and urethra
FUNCTION: PROTECTION
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium Locations and Functions
Locations: Lining of the nasal cavity, trachea, and bronchi; portions of male reproductive tract
Endocrine
secretes into. No ducts
Examples of Endocrine Glands- Pineal gland, Parathyroid, Hypothalamus, Thyroid, thymus, kidney, Adrenal, Pancreas, testis, ovary
Exocrine
secrete through ducts. Products go to places “outside” (surface of) the body
Has Ducts
Examples of Exocrine Glands- Sweat Glands, salivary, mammar, and liver
3 Types of Exocrine secretion Glands
Merocrine Secretion
Apocrine Secretion
Holocrine Secretion
Merocrine Secretion EXOCRINE GLAND
Secretes from Secretory vesicle
Aprocrine Secretion
Cell pinches off. So the pinched off portion of cell is the secretion
Holocrine
Cell dies. Mature cell dies and becomes secretory product
Branching type of Glands
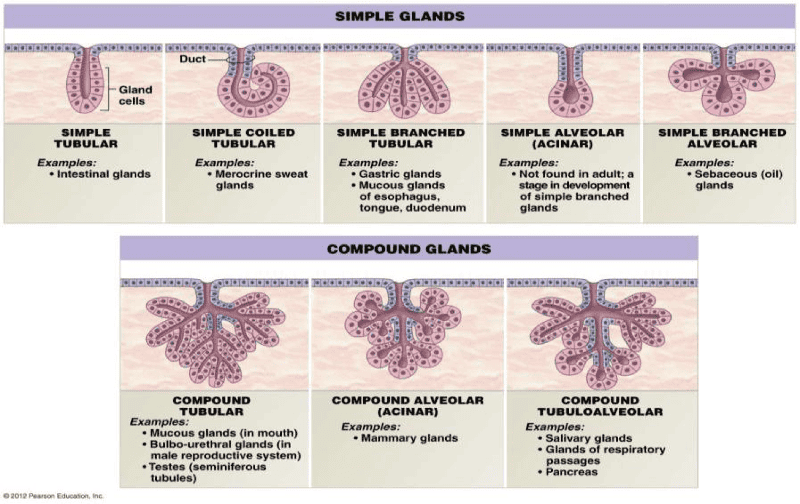
Example Question: Where would you find simple tubular gland?
Intestinal Glands
Study Areolar, Adipose and Reticular Tissue
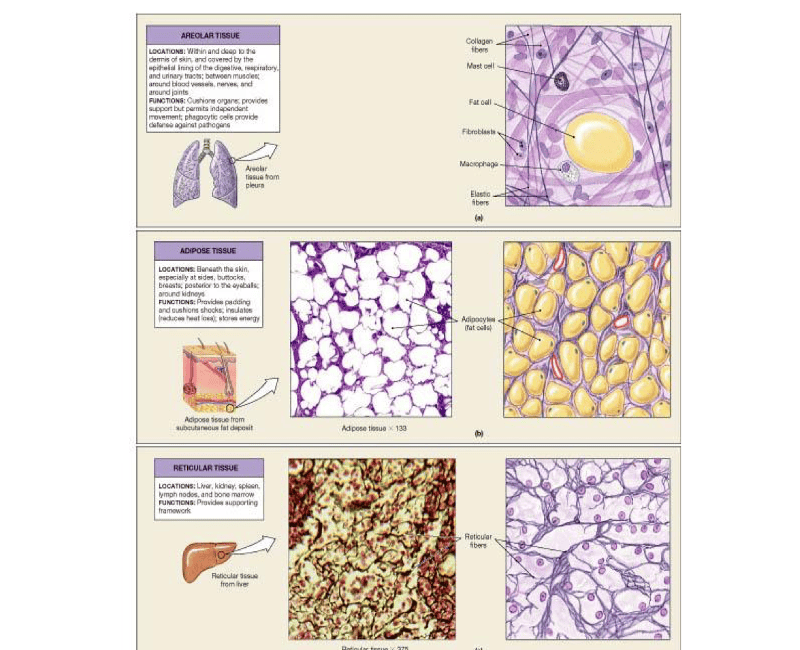
Study Connective Tissue
Hyaline Cartilage
Ground Substance
Fibrous Cartilage
Ground substance with non-elastic collagen fibers
Elastic Cartilage
Ground Substance with yellow elastic Fibers
Study Cartilage
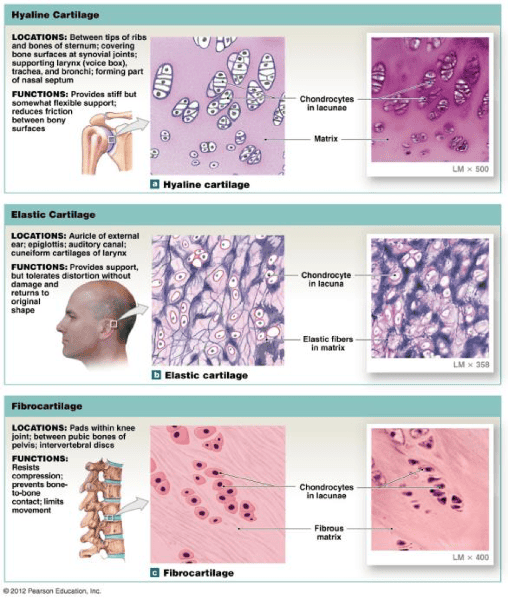
Study
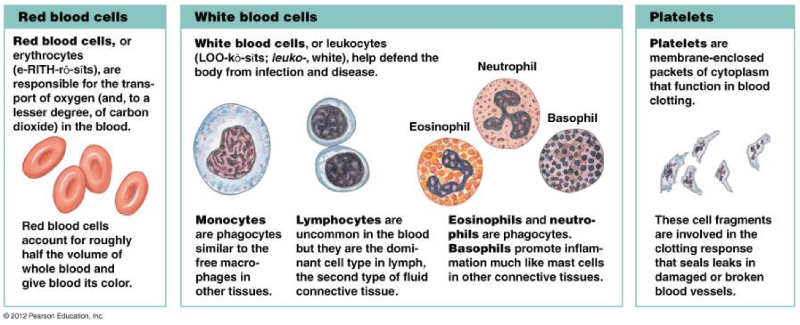
Granulocyte (with granules)
Neutrophil
Basophil- Allergies
Eosinophil- High means paracite
Agranulocyte (without granules)
Monocytes
Lymphocytes
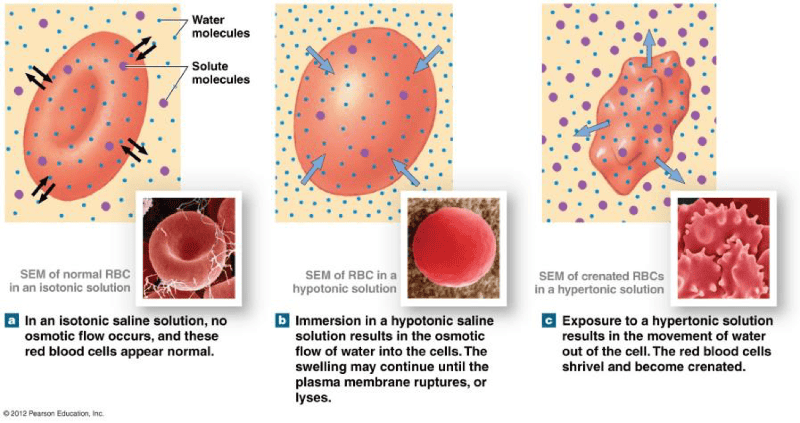
Study Osmosis and Hydrostatic pressure
Levels of Organization
Chemical Level
Cellular level
Tissue
Organ
Organ system
Organism
Study
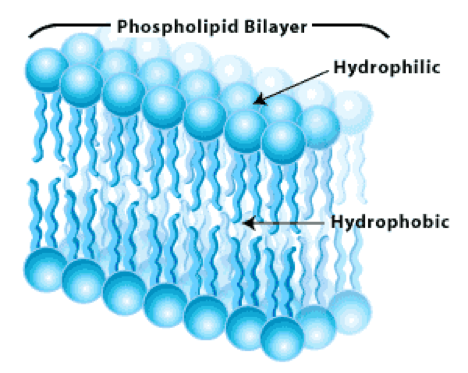
Plasma Membrane
Serves as the boundary for a cell
Rough ER
Ribosomes attach to rough ER synthesize proteins that leaves cells via the Golgi apparatus
Smooth ER
synthesizes lipids and removes and stores Ca+ from the cells interior
Golgi apparatus
Synthesizes carbohydrates, combines it with protein, and PACKAGES the product
Lysosomes
breaks down, digestive system
Nucleus-
Houses the genetic code, which in turn dictates protein synthesis
Ribosomes
Protein synthesis "Protein factory"
Study Receptor
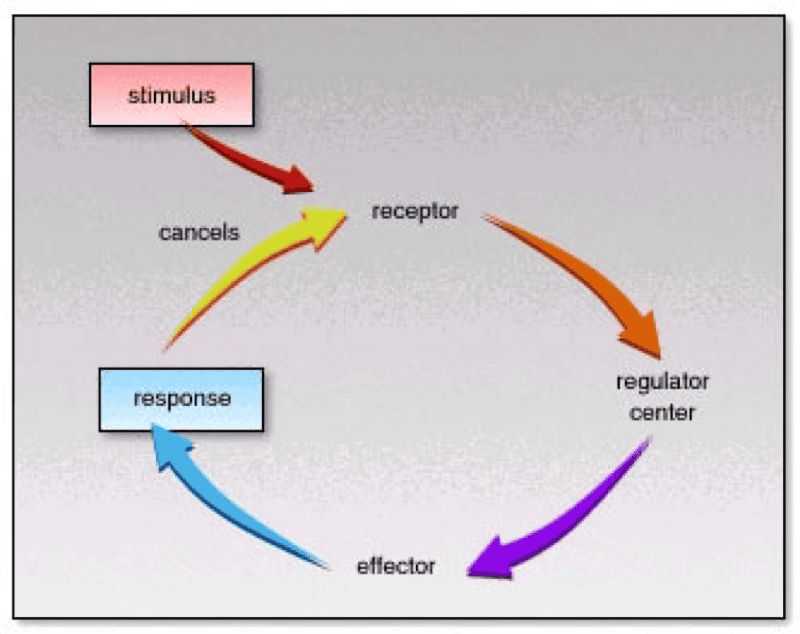
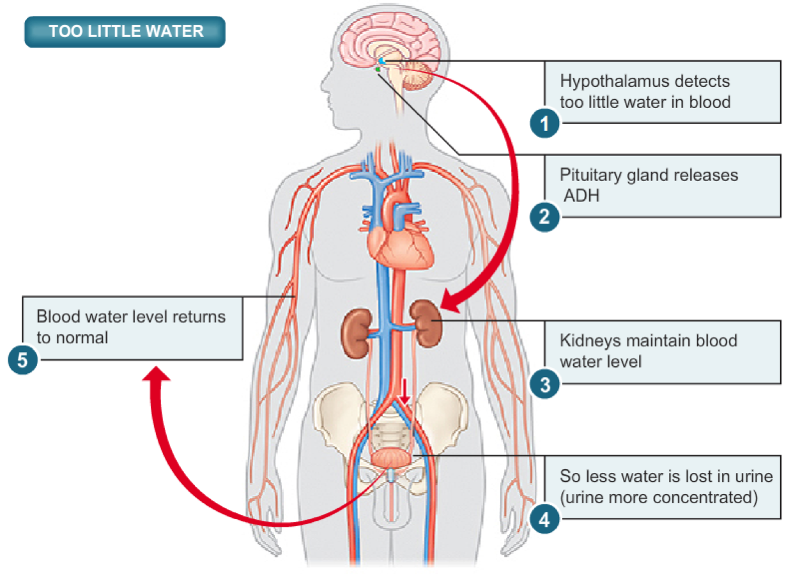
Study Too Little Water Pic