Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
A&P Lab Exam 1 Some PIctures
front 1 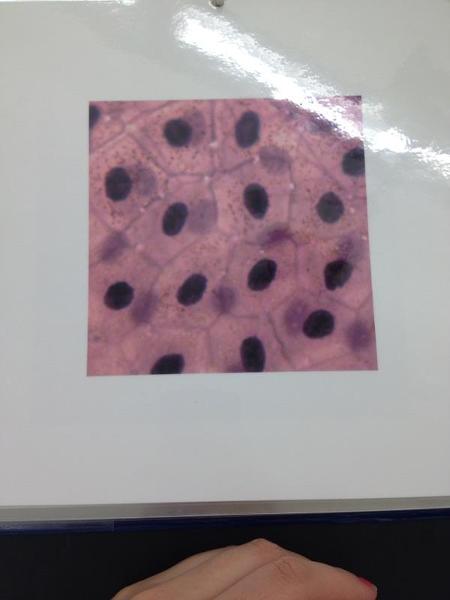 | back 1 Simple Squamous epithelium |
front 2 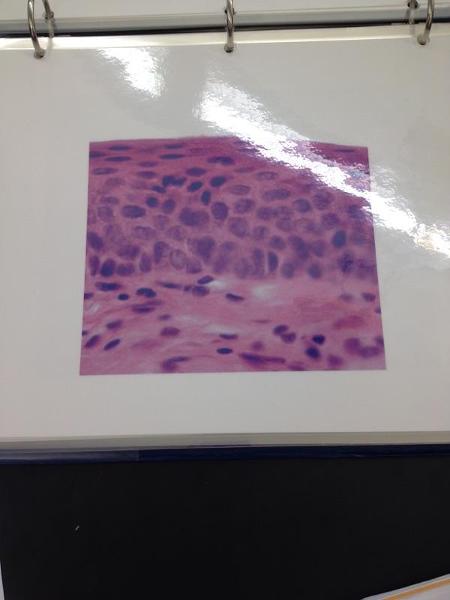 | back 2 Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium |
front 3 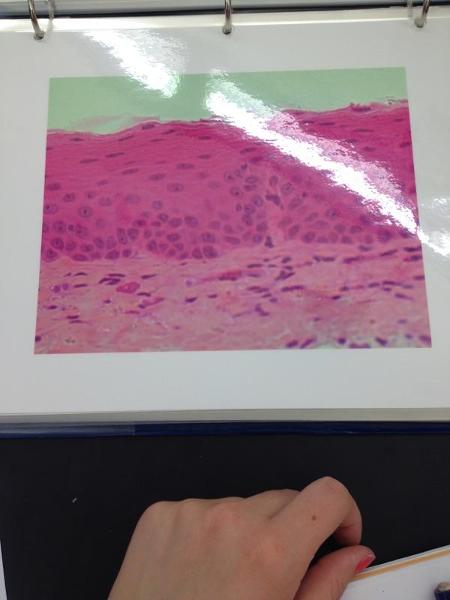 | back 3 Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium |
front 4 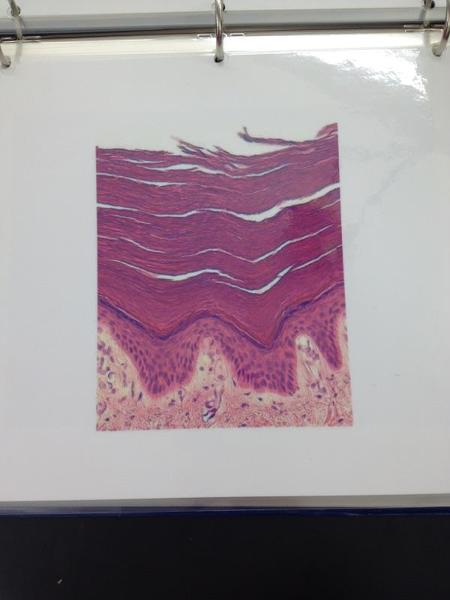 | back 4 Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium |
front 5  | back 5 Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium |
front 6 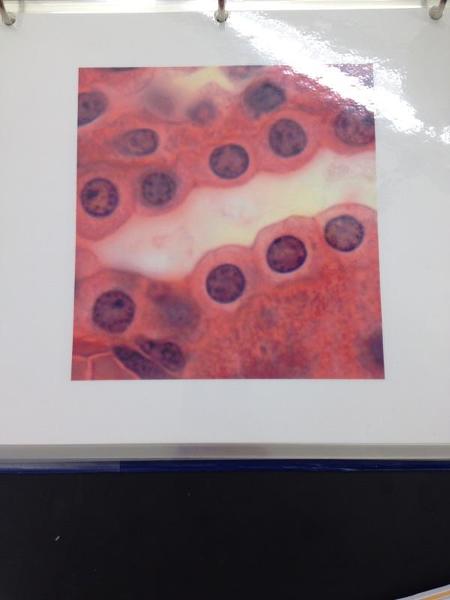 | back 6 Simple cuboidal epithelium |
front 7 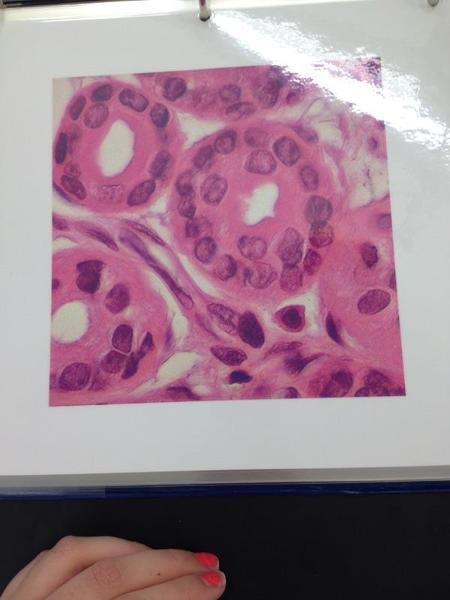 | back 7 Stratified cuboidal epithelium |
front 8 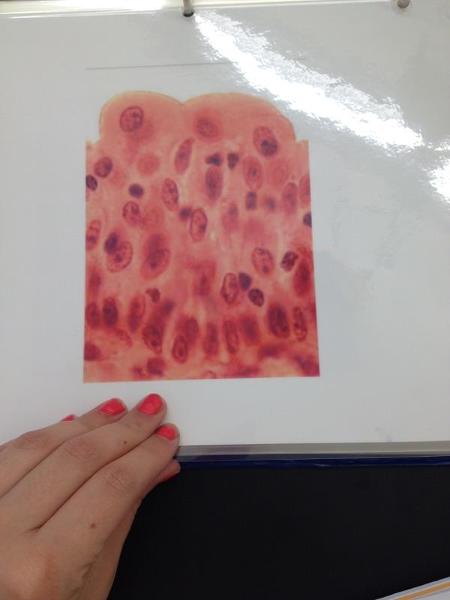 | back 8 Transitional epithelium |
front 9 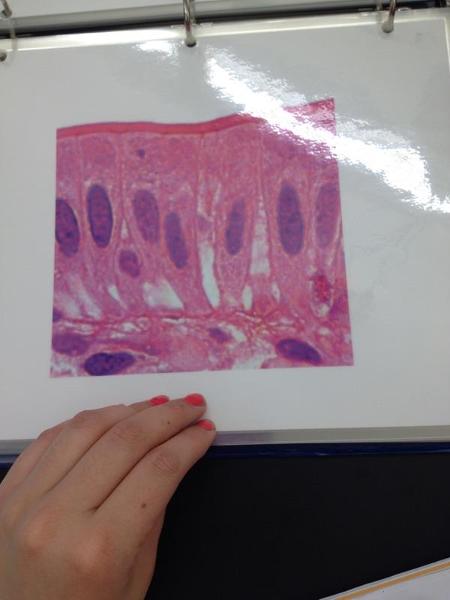 | back 9 Simple columnar epithelium |
front 10 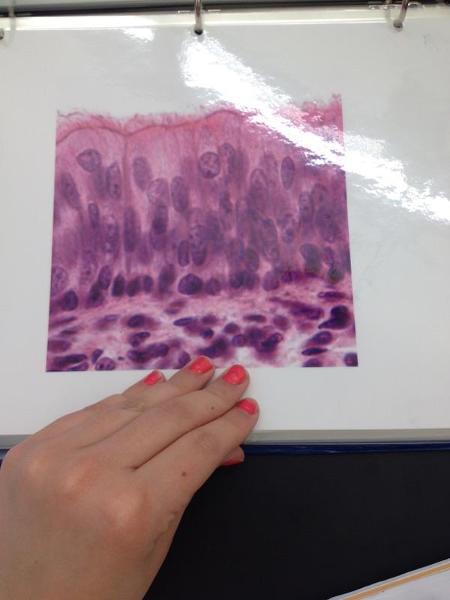 | back 10 Pseudostratified columnar epithelium |
front 11 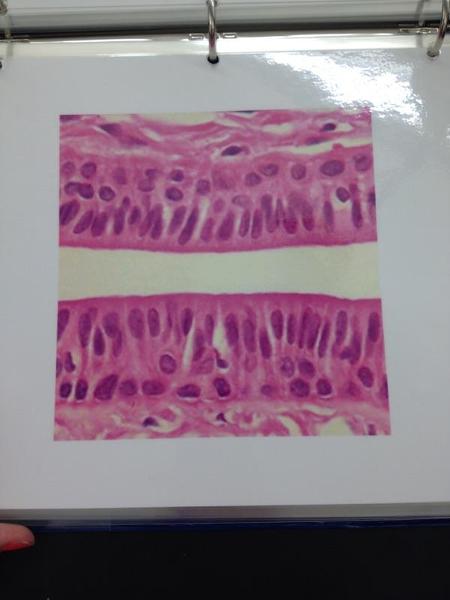 | back 11 Stratified columnar epithelium |
front 12  | back 12 Areolar connective tissue |
front 13 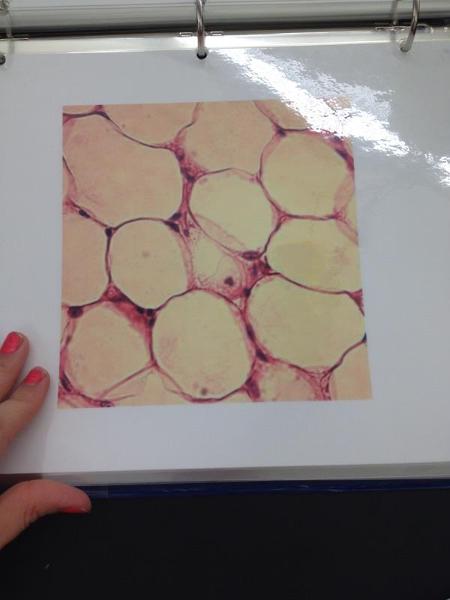 | back 13 Adipose connective tissue |
front 14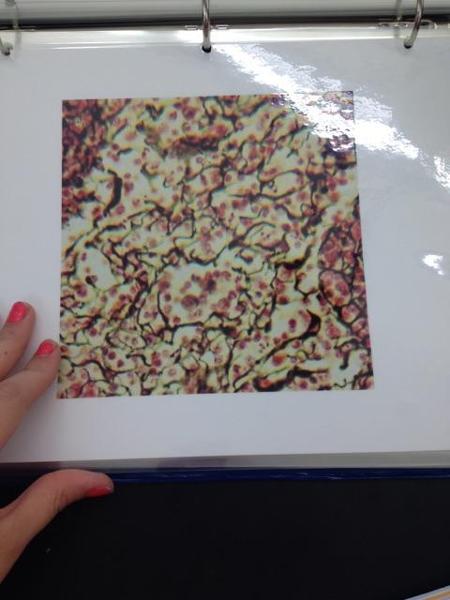  | back 14 Reticular connective tissue |
front 15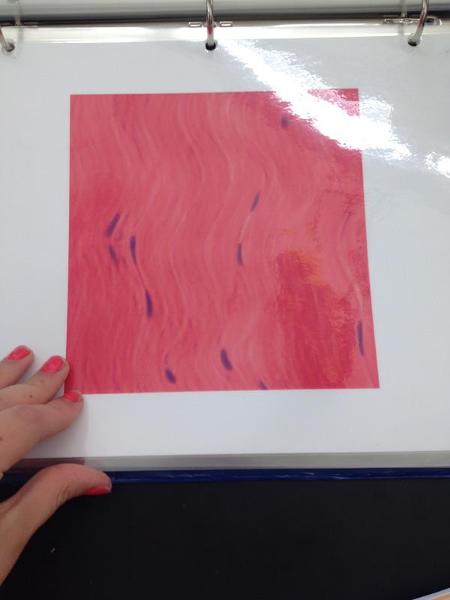  | back 15 Dense regular tissue |
front 16 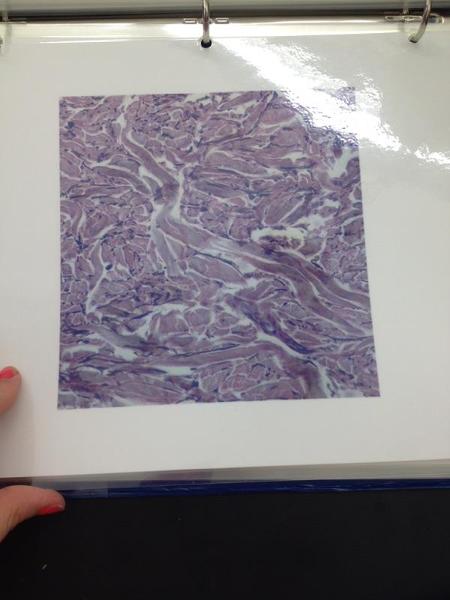 | back 16 Dense irregular connective tissue |
front 17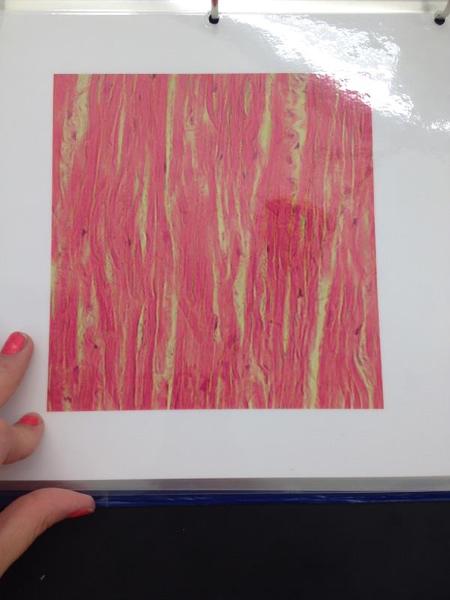  | back 17 Elastic connective tissue |
front 18 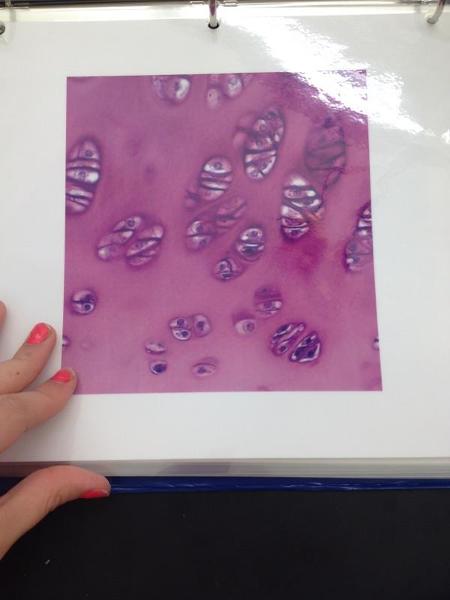 | back 18 Hyaline cartilage |
front 19 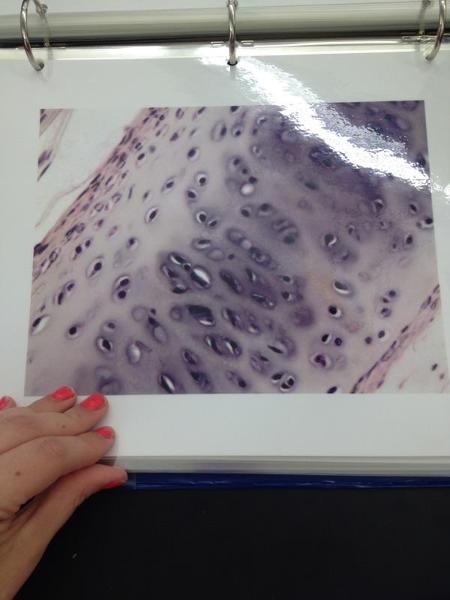 | back 19 Hyaline cartilage |
front 20 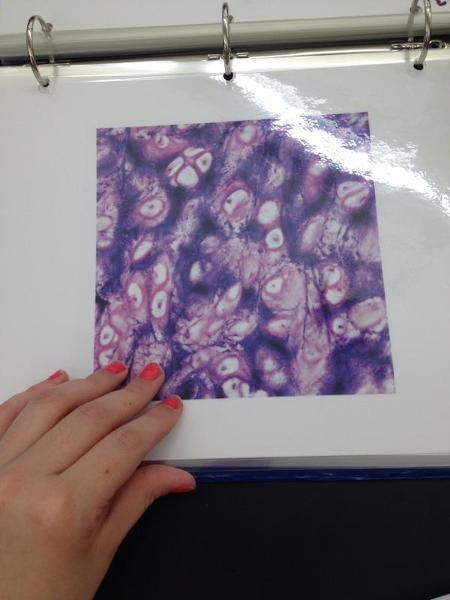 | back 20 Elastic cartilage |
front 21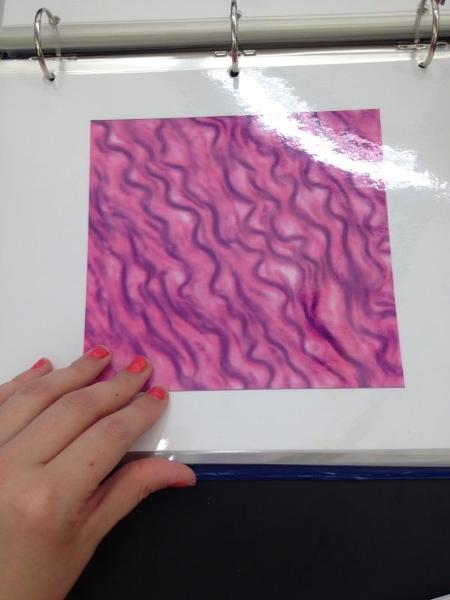  | back 21 Fibrocartilage |
front 22 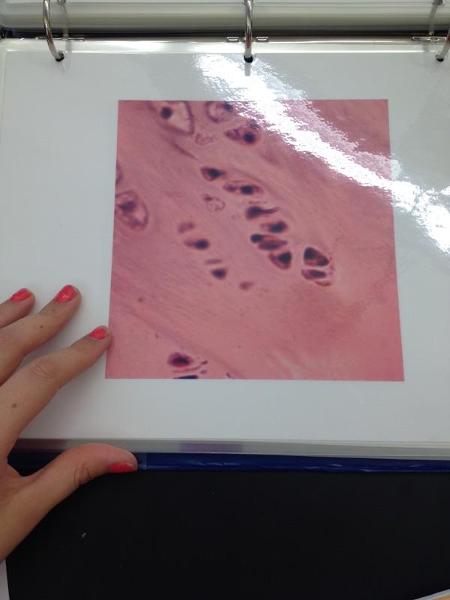 | back 22 Fibrocartilage |
front 23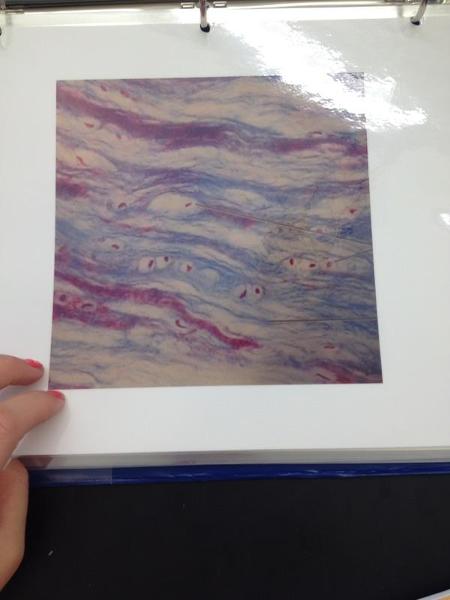  | back 23 Fibrocartilage |
front 24 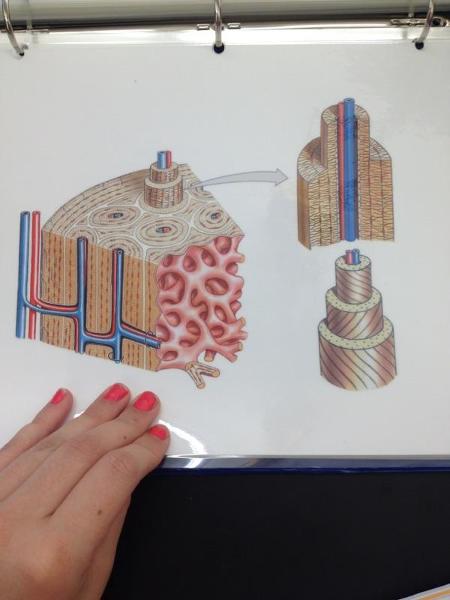 | back 24 Osseous tissue |
front 25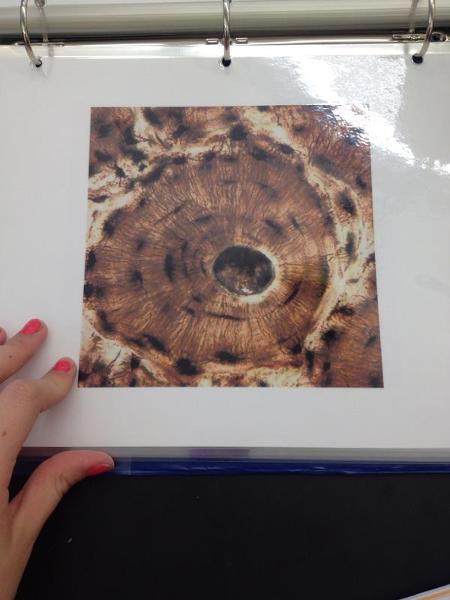  | back 25 Osteon |
front 26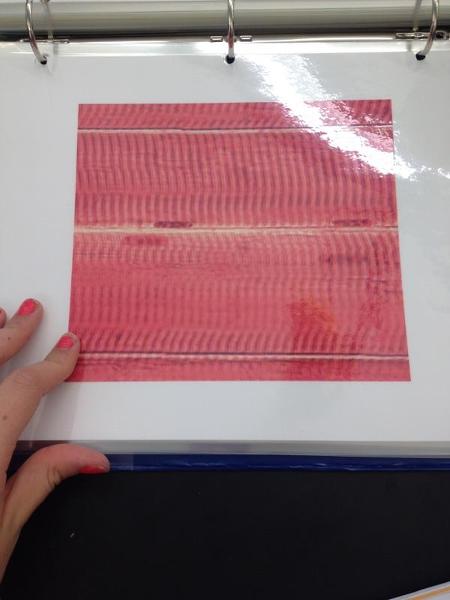  | back 26 Skeletal muscle |
front 27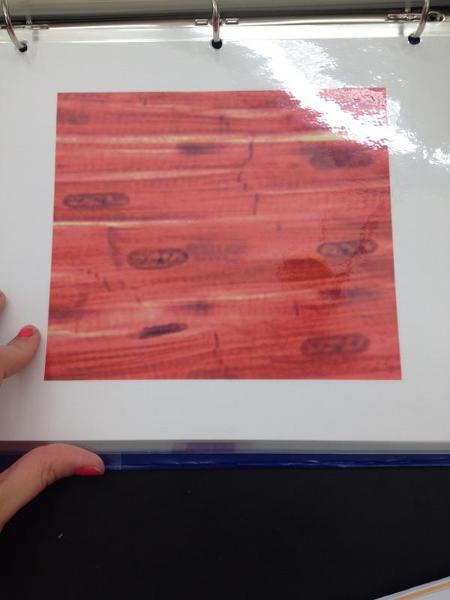  | back 27 Cardiac muscle |
front 28 Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium Locations and Functions | back 28 Locations: Lining of the nasal cavity, trachea, and bronchi; portions of male reproductive tract Functions: Protection, Secretion, moves mucous with cilia |
front 29 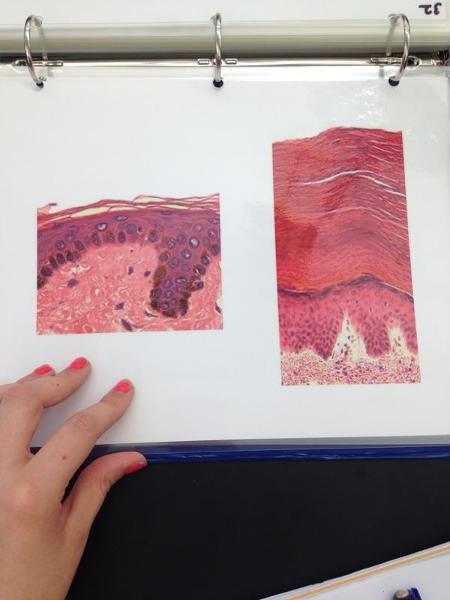 | back 29 Thin/thick skin |
front 30 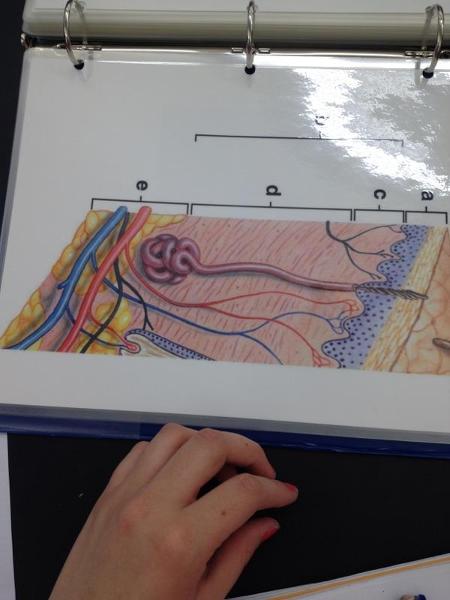 | back 30 Integument |
front 31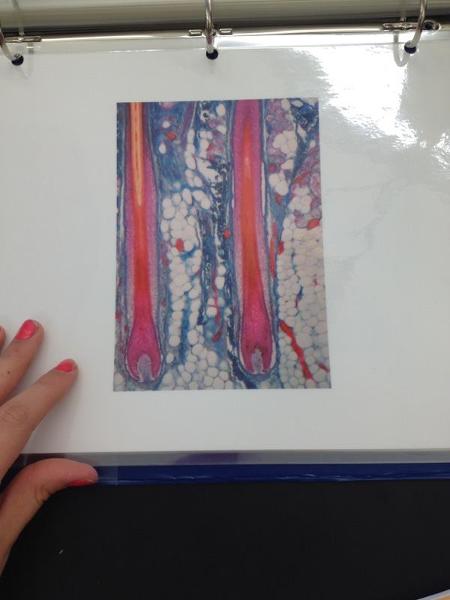  | back 31 Hair follicle |
front 32 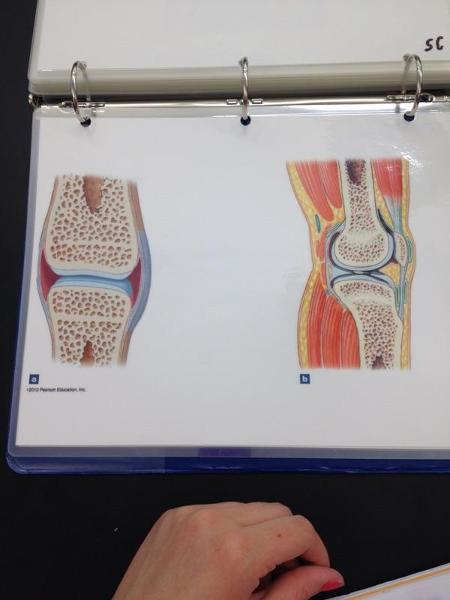 | back 32 Synovial joint |
front 33 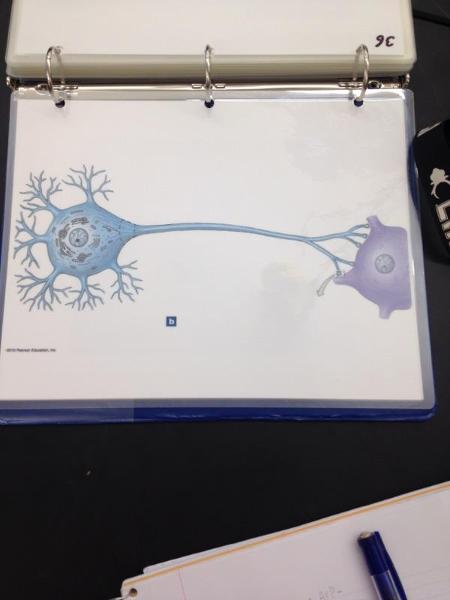 | back 33 Neuron |
front 34 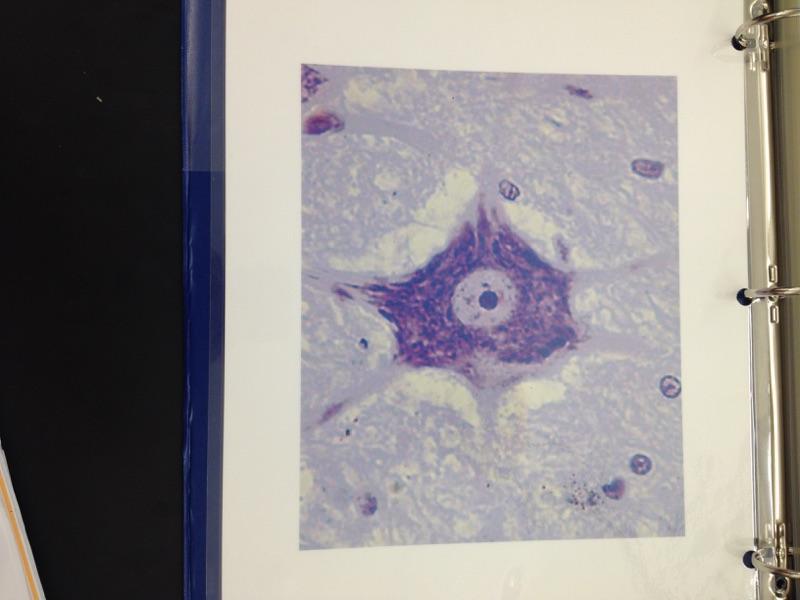 | back 34 Neuron |
front 35 Anterior | back 35 Same as VENTRAL- Front |
front 36 Posterior | back 36 Same as DORSAL- back |
front 37 Parietal LINNINGS | back 37 Superficial (outermost layer) |
front 38 Visceral LINNINGS | back 38 Inner layer |
front 39 Parietal Pluera (lungs) | back 39 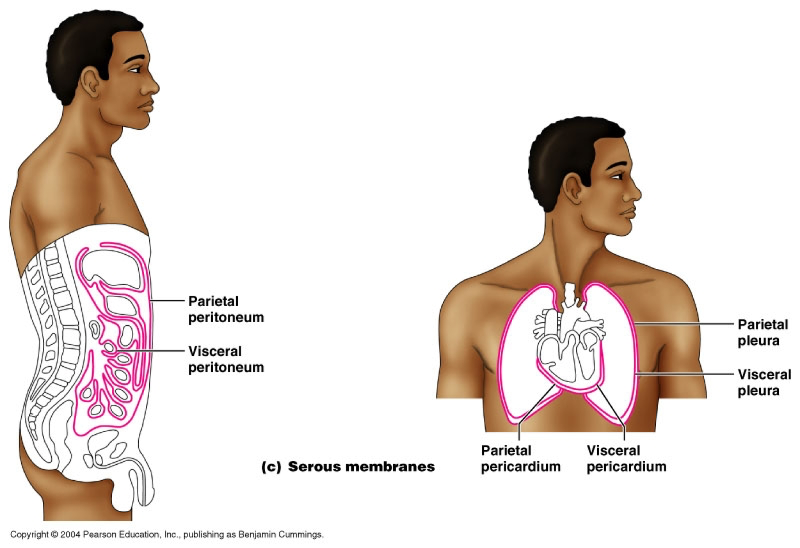 Outer layer of the lining of the lungs |
front 40 Visceral Pluera (lungs) | back 40 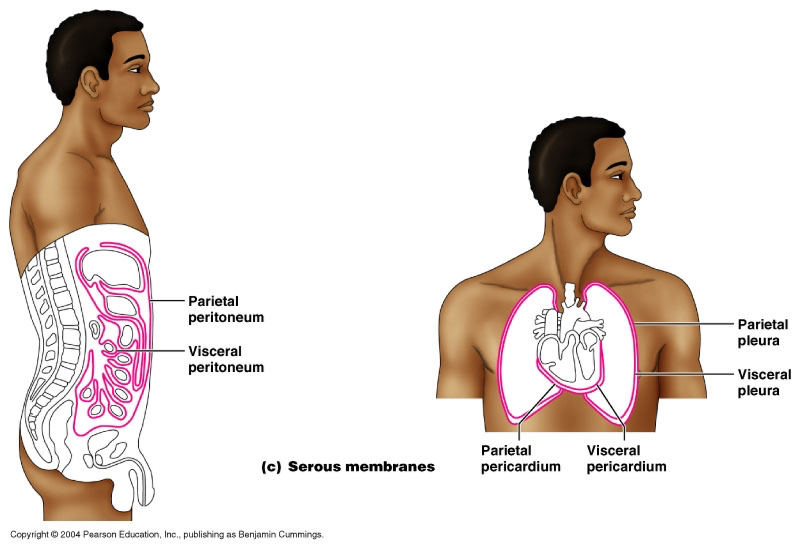 Inner layer of the lining of of the lungs |
front 41 Parietal Pericardium | back 41 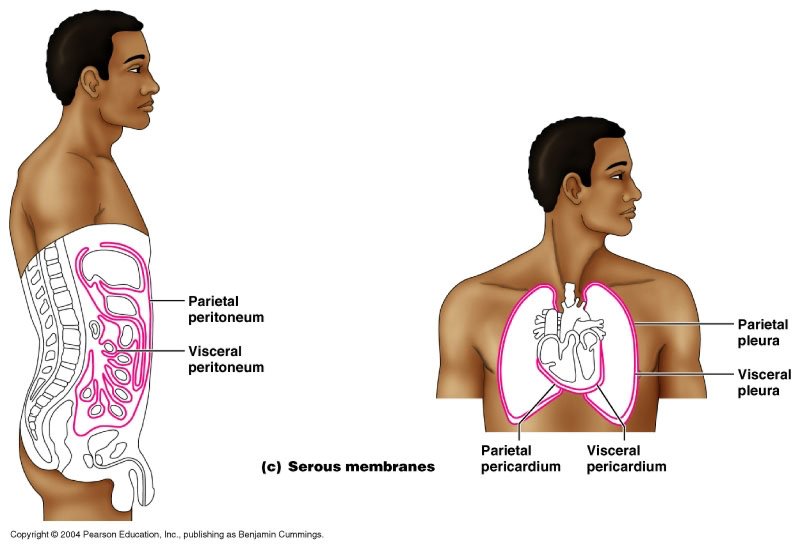 Outer layer of lining of heart |
front 42 Viseral Pericardium | back 42 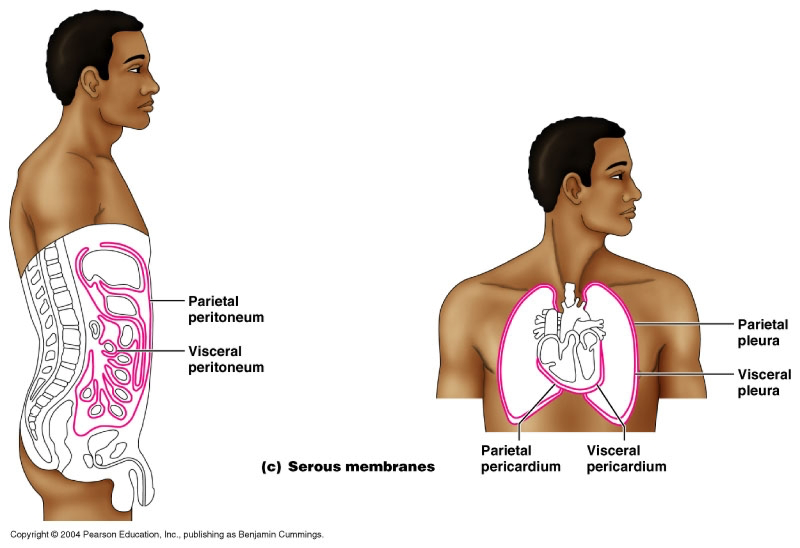 Inner layer of the lining of the heart |
front 43 Mediastinum | back 43 Contains the trachea, esophagus, and major vessels |
front 44 Parietal Peritoneum | back 44 lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities |
front 45 Visceral Peritoneum | back 45 covers the external surfaces of most abdominal organs, including the intestinal tract. |
front 46 Pelvic Cavity | back 46 Contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, last portion of the digestive tracts. |
front 47 Study Abdominal Pelvic Regions | back 47 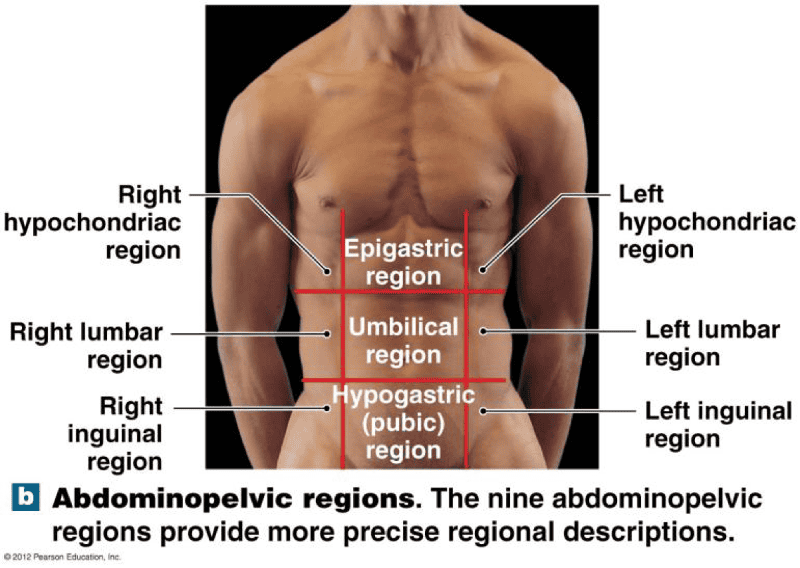 |
front 48 RUQ | back 48 Liver |
front 49 RLQ | back 49 Appendix |
front 50 LUQ | back 50 Spleen |
front 51 LLQ | back 51 Colon |
front 52 Epithelium | back 52 lines, protects and secretes |
front 53 Exocrine | back 53 secrete through ducts. Products go to places “outside” (surface of) the body Has Ducts Examples of Exocrine Glands- Sweat Glands, salivary, mammary, and liver |
front 54 Muscle tissue | back 54 excitable, contractile tissue for movement |
front 55 Nervous tissue | back 55 excitable tissue used to send short term signals throughout the body |
front 56 Simple Squamous Epithelium Locations and Functions | back 56 Locations: endothelia lining of the HEART and blood vessels, portions of the KIDNEY tubule, inner lining of the cornea, alveoli of the lungs Functions: Lines, protects and secretes. Reduces friction, controls vessel permeability; performs absorption and secretion |
front 57 Stratified Squamous Epithelium Locations and Functions | back 57 Locations: Surface of SKIN,lining of the mouth, throat, esophagus, rectum, anus and vagina. Functions: Provides physical protection against abrasion, pathogens, and chemical attack |
front 58 Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Locations and Functions | back 58 Locations: Glands, ducts; portion of kidney tubules; thyroid gland Function: Limited protection, secretion, and absorption. |
front 59 Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium Locations and Functions | back 59 Location: Lining of some ducts Functions: Protects, sectretion, absorption |
front 60 Simple Columnar Epithelium Locations and Functions | back 60 Locations: Lining of stomach, intestine, gallbladder, uterine tubes, and collecting ducts of kidneys Function: protection, secretion, absorption |
front 61 Stratified Columnar Epithelium Locations and Functions | back 61 Locations: Small area of pharynx, Epiglottis, annus, mammary glands, salivary glands ducts, and urethra FUNCTION: PROTECTION |
front 62 Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium Locations and Functions | back 62 Locations: Lining of the nasal cavity, trachea, and bronchi; portions of male reproductive tract |
front 63 Endocrine | back 63 secretes into. No ducts Examples of Endocrine Glands- Pineal gland, Parathyroid, Hypothalamus, Thyroid, thymus, kidney, Adrenal, Pancreas, testis, ovary |
front 64 Exocrine | back 64 secrete through ducts. Products go to places “outside” (surface of) the body Has Ducts Examples of Exocrine Glands- Sweat Glands, salivary, mammar, and liver |
front 65 3 Types of Exocrine secretion Glands | back 65 Merocrine Secretion Apocrine Secretion Holocrine Secretion |
front 66 Merocrine Secretion EXOCRINE GLAND | back 66 Secretes from Secretory vesicle |
front 67 Aprocrine Secretion | back 67 Cell pinches off. So the pinched off portion of cell is the secretion |
front 68 Holocrine | back 68 Cell dies. Mature cell dies and becomes secretory product |
front 69 Branching type of Glands | back 69 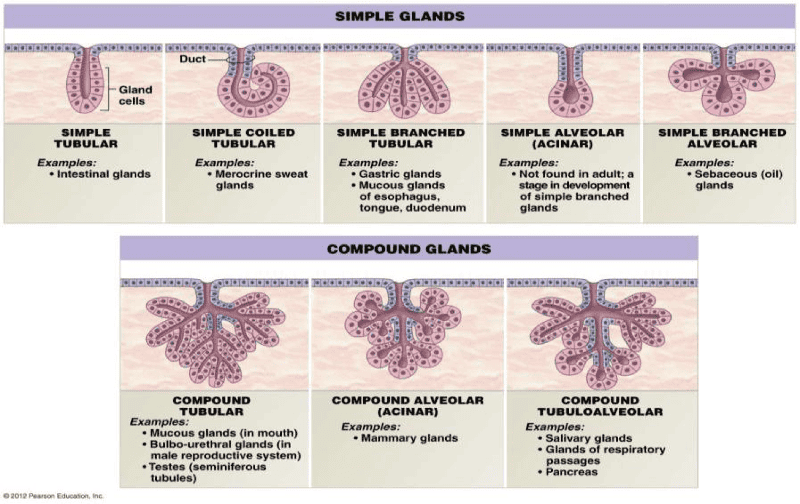 Example Question: Where would you find simple tubular gland? Intestinal Glands |
front 70 Study Areolar, Adipose and Reticular Tissue | back 70 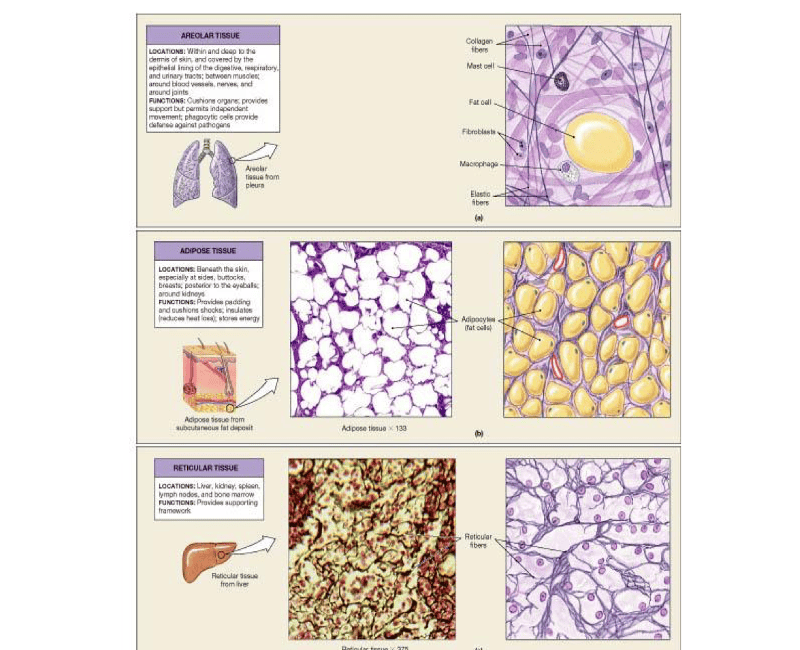 |
front 71 Study Connective Tissue | back 71 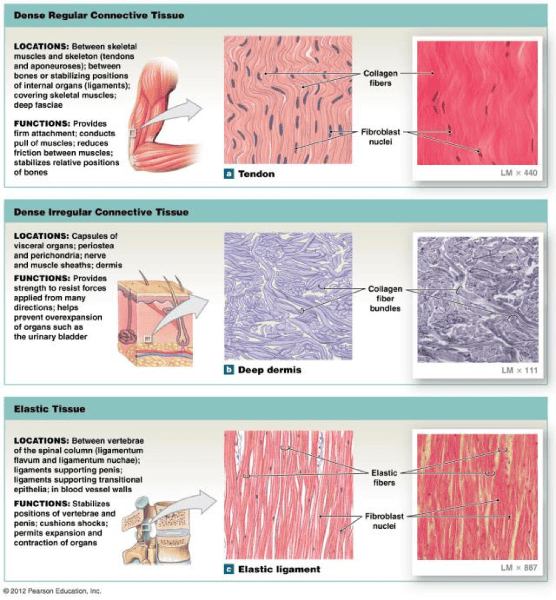 |
front 72 Hyaline Cartilage | back 72 Ground Substance |
front 73 Fibrous Cartilage | back 73 Ground substance with non-elastic collagen fibers |
front 74 Elastic Cartilage | back 74 Ground Substance with yellow elastic Fibers |
front 75 Study Cartilage | back 75 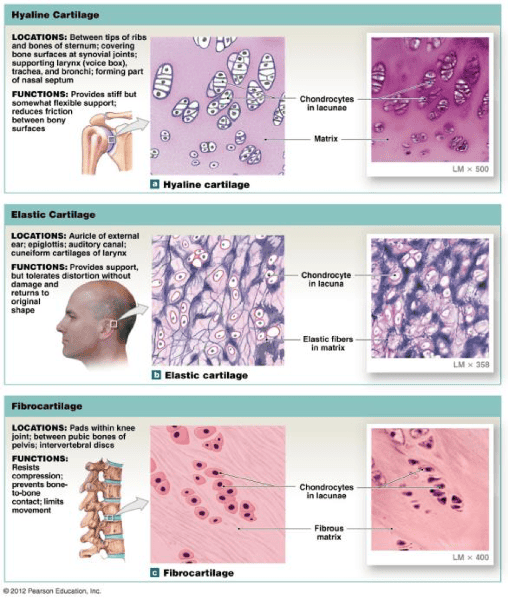 |
front 76 Study | back 76 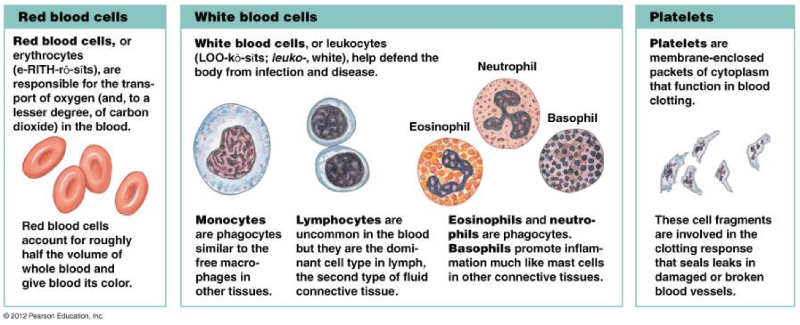 |
front 77 Granulocyte (with granules) | back 77 Neutrophil Basophil- Allergies Eosinophil- High means paracite |
front 78 Agranulocyte (without granules) | back 78 Monocytes Lymphocytes |
front 79 Study Osmosis and Hydrostatic pressure | back 79 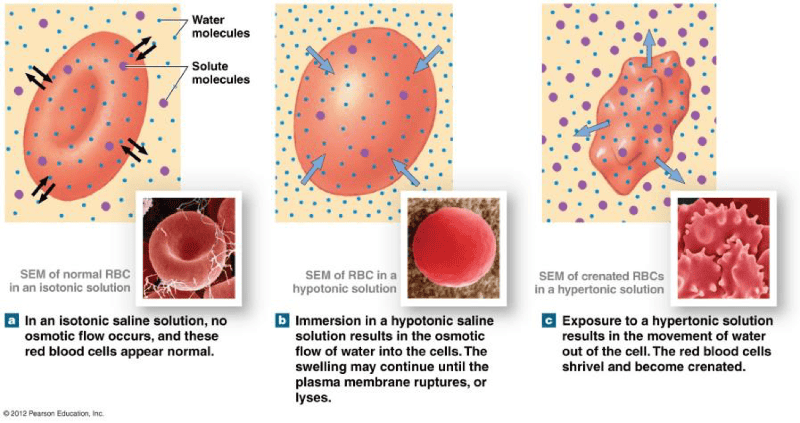 |
front 80 Levels of Organization | back 80 Chemical Level Cellular level Tissue Organ Organ system Organism |
front 81 Study | back 81 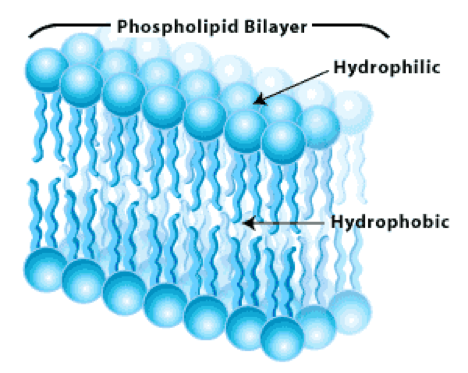 |
front 82 Plasma Membrane | back 82 Serves as the boundary for a cell |
front 83 Rough ER | back 83 Ribosomes attach to rough ER synthesize proteins that leaves cells via the Golgi apparatus |
front 84 Smooth ER | back 84 synthesizes lipids and removes and stores Ca+ from the cells interior |
front 85 Golgi apparatus | back 85 Synthesizes carbohydrates, combines it with protein, and PACKAGES the product |
front 86 Lysosomes | back 86 breaks down, digestive system |
front 87 Nucleus- | back 87 Houses the genetic code, which in turn dictates protein synthesis |
front 88 Ribosomes | back 88 Protein synthesis "Protein factory" |
front 89 Study Receptor | back 89 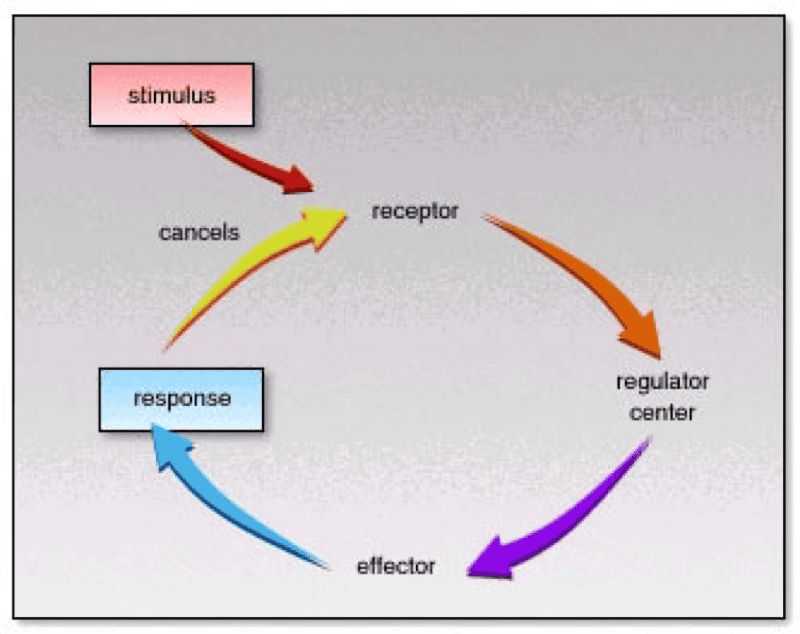 |
front 90 Study Too Little Water Pic | back 90 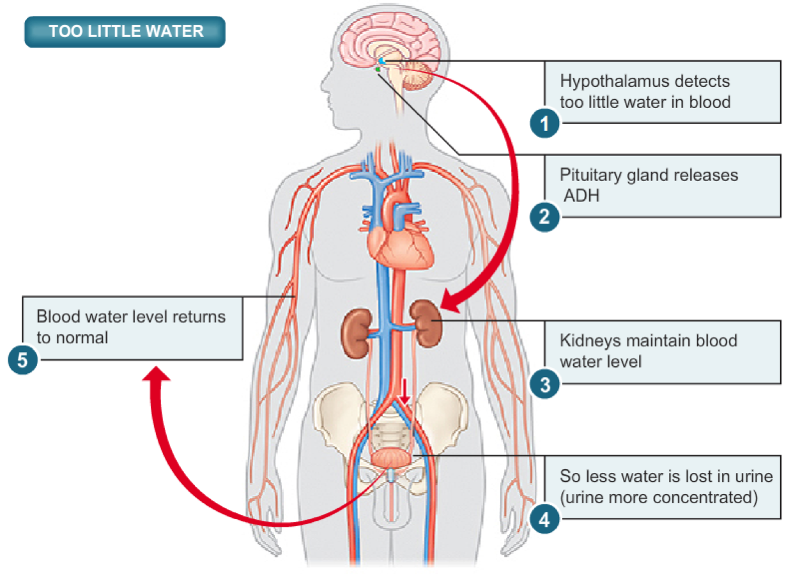 |