Chapter 11 Nervous System
Directacting
neurotransmitters ________.
C) open ion channels to provoke rapid responses
2) Which of the following is correct relative to Ohmʹs law?
B) Current is directly proportional to the voltage.
3) Ciliated CNS neuroglia that play an active role in moving the
cerebrospinal fluid are
called
________.
A) ependymal cells
The sheath of Schwann is also called the ________.
C) neurilemma
Bipolar neurons are commonly ________.
D) found in the retina of the eye
An excitatory neurotransmitter secreted by motor neurons innervating
skeletal muscle is
________.
C) acetylcholine
A neural circuit in which a single impulse is transmitted over and over is a ________.
D) absolute refractory period
A neuronal circuit that concentrates or directs a large number of
incoming impulses to a rather
small number of neurons is called
a(n) ________.
C) converging circuit
Which of the following is not a structural feature of a neuron?
A) synaptic cleft
The part of a neuron that conducts impulses away from its cell body is called a(n) ________.
A) axon
The chemically gated channel, NMDA, allows ________ ions entry into the nerve cell.
C) Ca2+
The point at which an impulse from one nerve cell is communicated to
another nerve cell is
the
________.
B) synapse
The role of acetylcholinesterase is to ________.
C) ganglia
The term central nervous system refers to the ________.
C) brain and spinal cord
The substance released at axon terminals to propagate a nervous
impulse is called a(n)
________.
C) neurotransmitter
A neuron that has as its primary function the job of connecting other
neurons is called a(n)
________.
C) association neuron
Saltatory conduction is made possible by ________.
A) the myelin sheath
Which of these ions is actively transported through the cell membrane
to establish a resting
potential?
A) Na
The part of the neuron that normally receives stimuli is called ________.
B) a dendrite
Choose the statement that is most correct about membrane potential.
B) Voltage would be measured by placing one electrode inside the
membrane and another
outside the membrane.
The sodiumpotassium
pump ________.
A) pumps three sodium ions outside the cell and two potassium ions inside
An action potential ________.
A) is essential for impulse propagation
Select the correct statement about synapses.
D) The synaptic cleft prevents an impulse from being transmitted
directly from one neuron
to another.
Which of the following is a good example of a neuromodulator?
D) nitric oxide
Which group of fibers spreads impulses at up to 1 meter per second?
C) group C fibers
Ependymal cells ________.
D) help to circulate the cerebrospinal fluid
Neuroglia that control the chemical environment around neurons by
buffering potassium
and recapturing neurotransmitters are ________.
A) astrocytes
Schwann cells are functionally similar to ________.
C) oligodendrocytes
Immediately after an action potential has peaked, which cellular gates open?
D) potassium
Nerve cell adhesion molecules (NCAMs)
________.
D) are crucial for the development of neural connections
An inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) is associated with ________.
B) hyperpolarization
Which of the following will occur when an excitatory postsynaptic
potential (EPSP) is being
generated on the dendritic membrane?
D) A single type of channel will open, permitting simultaneous flow
of sodium and
potassium.
When a sensory neuron is excited by some form of energy, the resulting graded potential is
D) generator potential
All of the following are true of graded potentials except that they ________.
C) increase amplitude as they move away from the stimulus point
Which of the following is true about the movement of ions across
excitable living
membranes?
B) Some ions are prevented from moving down their concentration
gradients by
ATP driven pumps.
________ is an indolamine.
C) Serotonin
A second nerve impulse cannot be generated until ________.
A) the membrane potential has been reestablished
In what way does the interior surface of a cell membrane of a resting (nonconducting)
B) negatively charged and contains less sodium
If a motor neuron in the body were stimulated by an electrode placed
about midpoint along
the length of the axon ________.
C) the impulse would spread bidirectionally
Neurons may be classified according to several characteristics. Which
of the following is
correct?
C) Group C fibers are not capable of saltatory conduction.
Select the correct statement about serial processing.
A) Spinal reflexes are an example of serial processing.
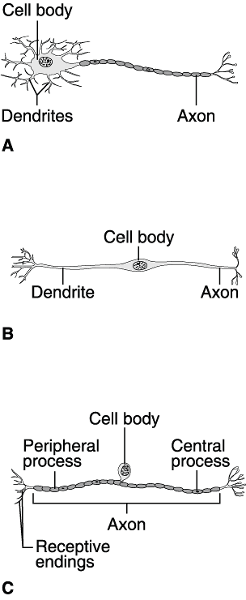
Using Figure 11.1, match the following:
1) Which neuron would
connect to a muscle?
2) Which neuron would be found in the retina
of the eye?
3) Which neuron is a sensory neuron found in a reflex
arc?
4) Which neuron is never myelinated?
1) Answer: A
2) Answer: B
3) Answer: C
4) Answer: B
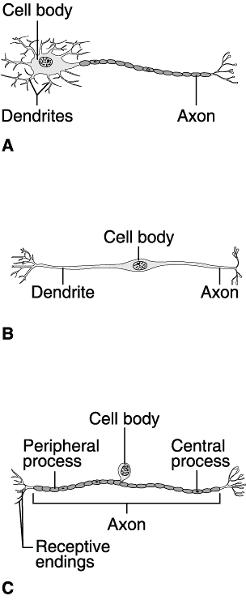
Using Figure 11.1, match the following:
5) Which neuron is rare?
6) In a reflex arc, which neuron has
its cell body inside the spinal cord?
7) Which neuron is common
only in dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord and
sensory
ganglia of
cranial nerves?
8) Which is by far
the most common neuron type?
5) Answer: B
6) Answer: A
7) Answer: C
8) Answer: A
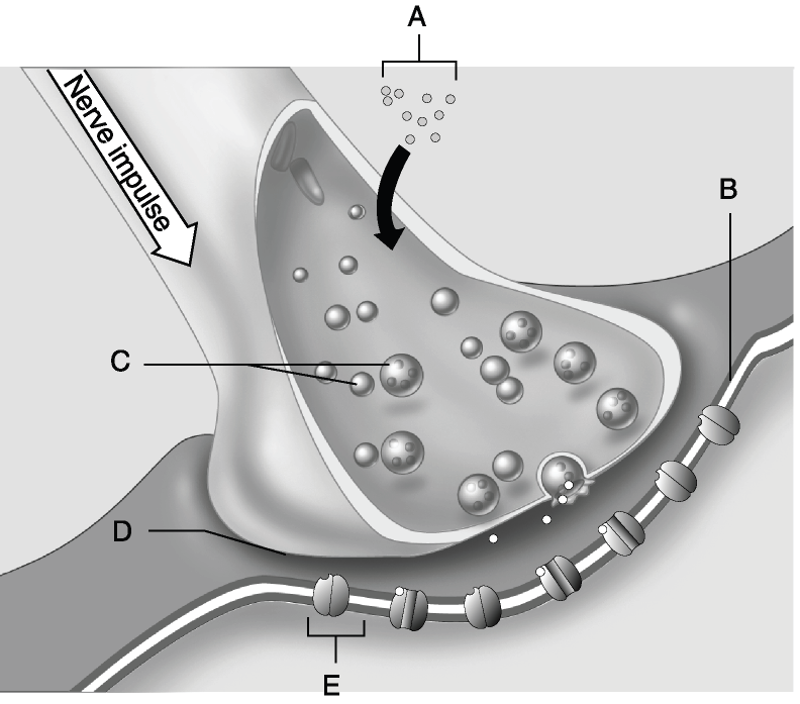
Using Figure 11.2, match the following:
9) Ion channel.
10)
Synaptic vesicles.
11) Calcium ions.
12) Postsynaptic
membrane.
13) Synaptic cleft.
9) Answer: E
10) Answer: C
11) Answer: A
12) Answer:
B
13) Answer: D
14) Neurotransmitters are
released at the ________.
D) Axon terminal
15) The rough ER of the cell.
A) Nissl bodies
16) Receptive region of the
neuron.
B) Dendrites
17) Conducting region of the
neuron.
C) Axon
18) Period during which the
neuron cannot respond to
a
second stimulus, no matter
how strong.
B) Absolute refractory period
19) The interior of the cell becomes less negative due to an influx of sodium ions.
E) Depolarization
20) The specific period during which potassium ions diffuse out of the neuron due to a change in membrane permeability
C) Repolarization
21) Also called a nerve impulse
transmitted by axons.
D) Action potential
22) An exceptionally strong
stimulus can trigger a
response.
A) Relative refractory period
23) Numerous nerve impulses arriving at a synapse at closely timed intervals exert a cumulative effect.
A) Temporal summation
24) Stimulation of a postsynaptic neuron by many terminals at the same time.
B) Spatial summation
25) An insufficient stimulus.
D) Subthreshold stimulus
26) Any stimulus below this intensity will result in no
response
in a neuron.
C) Threshold stimulus