Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 11 Nervous System
front 1 Directacting | back 1 C) open ion channels to provoke rapid responses |
front 2 2) Which of the following is correct relative to Ohmʹs law? | back 2 B) Current is directly proportional to the voltage. |
front 3 3) Ciliated CNS neuroglia that play an active role in moving the
cerebrospinal fluid are | back 3 A) ependymal cells |
front 4 The sheath of Schwann is also called the ________. | back 4 C) neurilemma |
front 5 Bipolar neurons are commonly ________. | back 5 D) found in the retina of the eye |
front 6 An excitatory neurotransmitter secreted by motor neurons innervating
skeletal muscle is | back 6 C) acetylcholine |
front 7 A neural circuit in which a single impulse is transmitted over and over is a ________. | back 7 D) absolute refractory period |
front 8 A neuronal circuit that concentrates or directs a large number of
incoming impulses to a rather | back 8 C) converging circuit |
front 9 Which of the following is not a structural feature of a neuron? | back 9 A) synaptic cleft |
front 10 The part of a neuron that conducts impulses away from its cell body is called a(n) ________. | back 10 A) axon |
front 11 The chemically gated channel, NMDA, allows ________ ions entry into the nerve cell. | back 11 C) Ca2+ |
front 12 The point at which an impulse from one nerve cell is communicated to
another nerve cell is | back 12 B) synapse |
front 13 The role of acetylcholinesterase is to ________. | back 13 C) ganglia |
front 14 The term central nervous system refers to the ________. | back 14 C) brain and spinal cord |
front 15 The substance released at axon terminals to propagate a nervous
impulse is called a(n) | back 15 C) neurotransmitter |
front 16 A neuron that has as its primary function the job of connecting other
neurons is called a(n) | back 16 C) association neuron |
front 17 Saltatory conduction is made possible by ________. | back 17 A) the myelin sheath |
front 18 Which of these ions is actively transported through the cell membrane
to establish a resting | back 18 A) Na |
front 19 The part of the neuron that normally receives stimuli is called ________. | back 19 B) a dendrite |
front 20 Choose the statement that is most correct about membrane potential. | back 20 B) Voltage would be measured by placing one electrode inside the
membrane and another |
front 21 The sodiumpotassium | back 21 A) pumps three sodium ions outside the cell and two potassium ions inside |
front 22 An action potential ________. | back 22 A) is essential for impulse propagation |
front 23 Select the correct statement about synapses. | back 23 D) The synaptic cleft prevents an impulse from being transmitted
directly from one neuron |
front 24 Which of the following is a good example of a neuromodulator? | back 24 D) nitric oxide |
front 25 Which group of fibers spreads impulses at up to 1 meter per second? | back 25 C) group C fibers |
front 26 Ependymal cells ________. | back 26 D) help to circulate the cerebrospinal fluid |
front 27 Neuroglia that control the chemical environment around neurons by
buffering potassium | back 27 A) astrocytes |
front 28 Schwann cells are functionally similar to ________. | back 28 C) oligodendrocytes |
front 29 Immediately after an action potential has peaked, which cellular gates open? | back 29 D) potassium |
front 30 Nerve cell adhesion molecules (NCAMs) | back 30 D) are crucial for the development of neural connections |
front 31 An inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) is associated with ________. | back 31 B) hyperpolarization |
front 32 Which of the following will occur when an excitatory postsynaptic
potential (EPSP) is being | back 32 D) A single type of channel will open, permitting simultaneous flow
of sodium and |
front 33 When a sensory neuron is excited by some form of energy, the resulting graded potential is | back 33 D) generator potential |
front 34 All of the following are true of graded potentials except that they ________. | back 34 C) increase amplitude as they move away from the stimulus point |
front 35 Which of the following is true about the movement of ions across
excitable living | back 35 B) Some ions are prevented from moving down their concentration
gradients by |
front 36 ________ is an indolamine. | back 36 C) Serotonin |
front 37 A second nerve impulse cannot be generated until ________. | back 37 A) the membrane potential has been reestablished |
front 38 In what way does the interior surface of a cell membrane of a resting (nonconducting) | back 38 B) negatively charged and contains less sodium |
front 39 If a motor neuron in the body were stimulated by an electrode placed
about midpoint along | back 39 C) the impulse would spread bidirectionally |
front 40 Neurons may be classified according to several characteristics. Which
of the following is | back 40 C) Group C fibers are not capable of saltatory conduction. |
front 41 Select the correct statement about serial processing. | back 41 A) Spinal reflexes are an example of serial processing. |
front 42 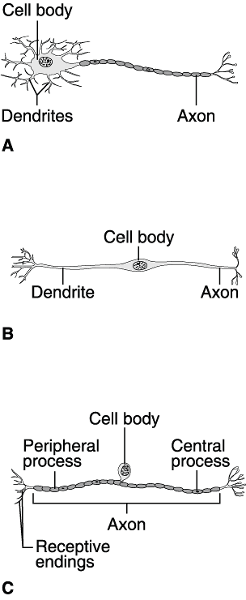 Using Figure 11.1, match the following: | back 42 1) Answer: A |
front 43 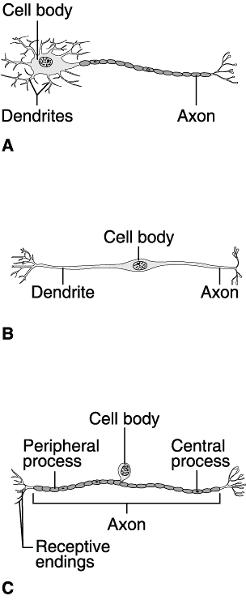 Using Figure 11.1, match the following: 5) Which neuron is rare? | back 43 5) Answer: B |
front 44 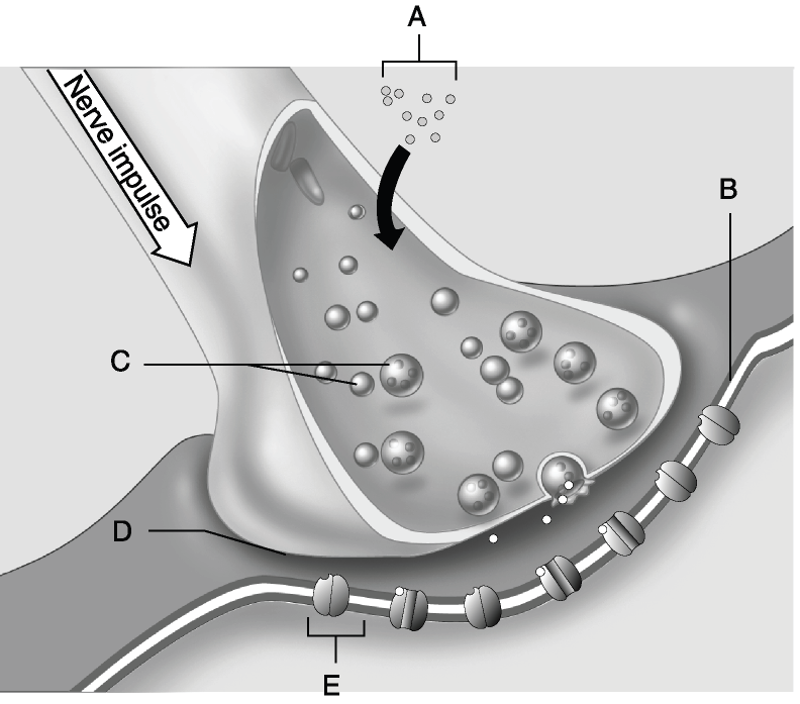 Using Figure 11.2, match the following: | back 44 9) Answer: E |
front 45 14) Neurotransmitters are | back 45 D) Axon terminal |
front 46 15) The rough ER of the cell. | back 46 A) Nissl bodies |
front 47 16) Receptive region of the | back 47 B) Dendrites |
front 48 17) Conducting region of the | back 48 C) Axon |
front 49 18) Period during which the | back 49 B) Absolute refractory period |
front 50 19) The interior of the cell becomes less negative due to an influx of sodium ions. | back 50 E) Depolarization |
front 51 20) The specific period during which potassium ions diffuse out of the neuron due to a change in membrane permeability | back 51 C) Repolarization |
front 52 21) Also called a nerve impulse | back 52 D) Action potential |
front 53 22) An exceptionally strong | back 53 A) Relative refractory period |
front 54 23) Numerous nerve impulses arriving at a synapse at closely timed intervals exert a cumulative effect. | back 54 A) Temporal summation |
front 55 24) Stimulation of a postsynaptic neuron by many terminals at the same time. | back 55 B) Spatial summation |
front 56 25) An insufficient stimulus. | back 56 D) Subthreshold stimulus |
front 57 26) Any stimulus below this intensity will result in no | back 57 C) Threshold stimulus |