Biology Exam ll (Chapter 6)
Bioenergetics
Energy in biological systems
Flow of Energy
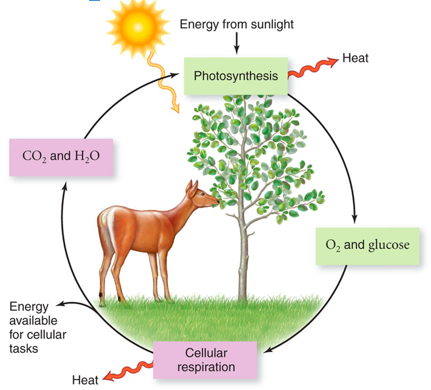
What is energy in the form of?
Energy is in the form of a photon.
Energy
The ability to do work which means to move matter against opposing forces such as gravity and friction
Carbon Cycle
Transforms carbon dioxide into glucose
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed
Potential Energy
ATP, an electrical/ion gradient, concentration gradient, NADH, Chemical Bonds
Water being held behind a dam
Stored energy
Due to structure or location
Pi + ADP ==> ATP
It has a change in free energy that is greater than 0. That means it has a delta G that is positive and therefore the reaction is endergonic.
Kinetic Energy
Movement
Na+ and K+ molecules moving through a transport protein
Noncompetitive Inhibitor
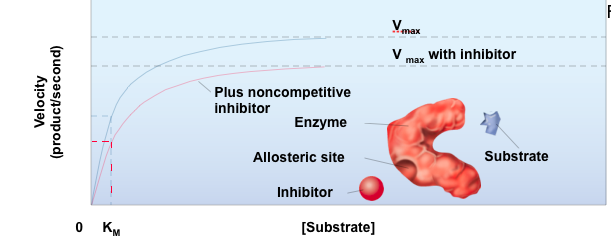
It lowers the Vmax and has no affect on the Km.
Fits into the Allosteric site to change the shape of the enzyme
Can cause a conformation change which will affect the enzyme's ability to bind to a substrate
Altering the three-dimensional structure of an enzyme might
Prevent the substrate from binding the enzyme's active site
Enzymes
Increase the rate of the reaction by reducing the activation energy.
They don't change the direction of the reactions
They do not change the amount of free energy available
It lowers the energy barrier needed for reactants to achieve the transition state or lowers the energy of activation of a reaction
Typical biological catalyst
Have a high affinity or high degree of specificity for a substrate
Can be recycled over and over
What are enzymes made of?
Mostly proteins but some are RNA molecules possess enzymatic functions called ribozymes
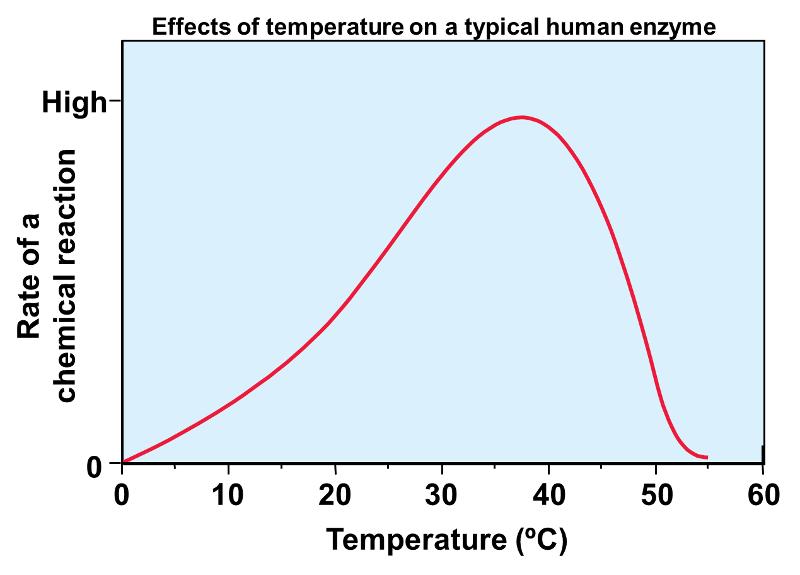
This enzyme's optimal function is at about 37 degrees C, the enzymatic activity of the enzymes slows down around 40 C
NAD+ + H+ --> NADH
What has happened to NAD+?
It has been reduced
Free energy
∆G
The amount of available energy that can be used to promote change do work
How do you overcome the effect of a competitive inhibitor on enzyme activity
Increase the amount of substrate (Km) for the enzyme
Positive ∆G
Favors formation of reactants
Negative ∆G
Favors formation of products
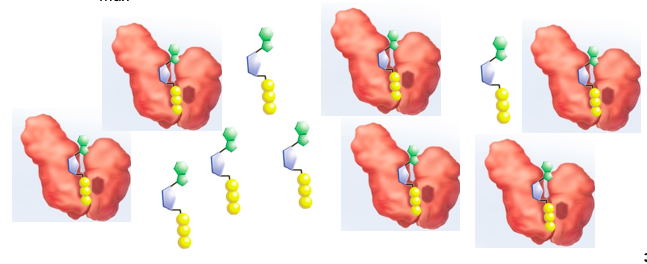
Steps of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction
1. substrates bind to enzyme; 2. enzyme and substrate reach transtition state; 3. substrates are converted to products; 4. products are released
Active Site of Enzyme
Where the chemical reaction takes place
Where a competitive inhibitor competes to bind to
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Every chemical reaction must increase the total entropy of the universe. Every chemical reaction represents a transfer of energy, which increases entropy
Energy must be spent to retain order - this spending of energy usually releases heat, which increases the entropy elsewhere
Competitive Inhibitor
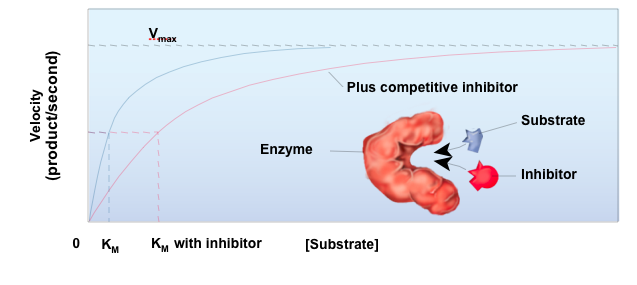
Only raises the Km
Tries to bind to the active site
Slows down the Vmax when it binds to the allosteric site
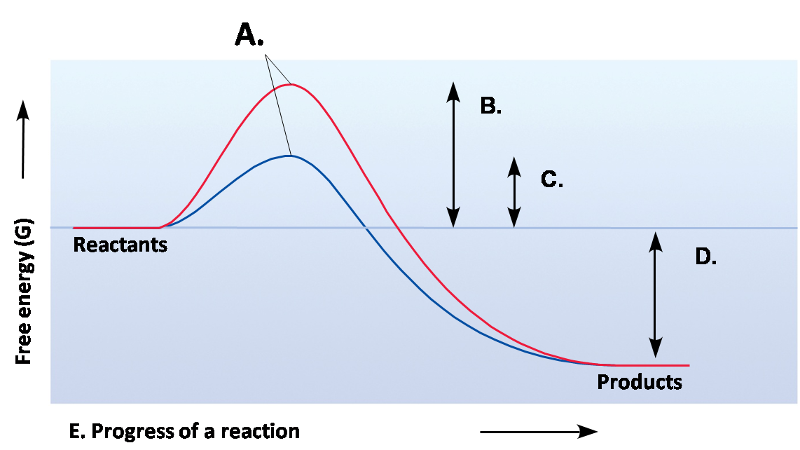
Exergonic
NADH is converted to NAD+ and H+. What has happened to NADH?
It has been oxidized.
Entropy
Measure of disorder
Exergonic Reaction
∆G is negative/less than zero
Spontaneous reaction (doesn't mean it will occur rapidly)
Favor making products (going from left to right)
Releases free energy
Endergonic Reaction
∆G is positive/greater than zero
Not spontaneous
Absorbs free energy
Favors making reactants
When you go from reaction to products, you have to add energy by coupling it with an exergonic reaction to make the overall ∆G negative
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
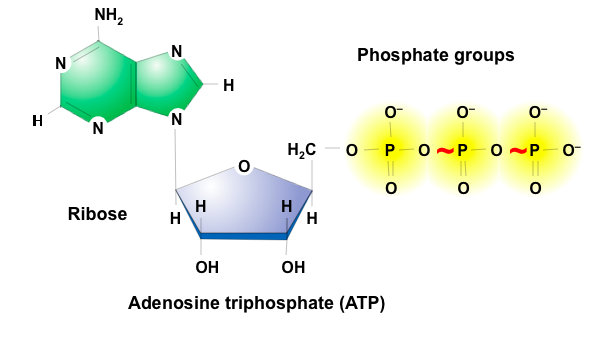
Universal energy molecule
Monomer of nucleic acids
Adenine, Ribose, and 3 phosphate groups connected to each other in a sequence
Energy intermediate
Is exergonic
Gets coupled with endergonic reactions (phosphorylation) -- Gives net negative free energy change
Source of energy for 20% of proteins
Undergoes 10,000 cycles of hydrolysis and re-synthesis every day
Likely underestimated because there may be other types of ATP-binding sites
A noncompetitive inhibitor for enzymes
The "energy currency" and how that we get work done
Change in free energy determines what?
The direction of chemical reactions
∆G =
∆H - T∆S
∆G
Free energy
∆H
Total energy
T
Absolute temperature
∆S
Entropy
Energy emitted through _______ is not usable.
Heat
Energy Systems
Are not efficient
Hydrolysis of ATP requires what to be exergonic?
Water and enzymes
The ∆G = -7.3 kcal/mole
Glucose + Phosphate --> glucose-phosphate + H2O
ΔG = +3.3 Kcal/mole and it is an endergonic reaction
Glucose + ATP → glucose-phosphate + ADP
Coupled Reaction
Phosphorylation
Direct transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to a substrate (an example being glucose)
It energizes the molecule
Spontaneous Reaction
Does not imply anything about its speed
Exergonic
Does not require inout of energy
Does require an enzyme
Catalyst
Speed up rate of reaction without being consumed
Names of enzymes usually end in ________ and typically describe what is going on.
-ASE
Activation Energy
Initial input of energy to start a reaction
Allows molecules to get close enough to cause bond rearrangement
Transition State
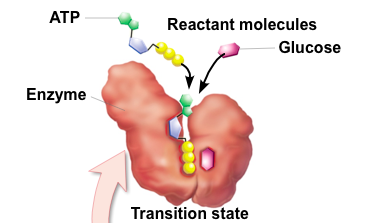
Bonds are stretched/strained
2 ways to overcome activation energy:
1. Large amounts of heat
2. Using enzymes to lower activation energy
How to measure enzyme activity:
Measure your substrates and your products
VMax
Velocity of reaction near maximum rate
Km
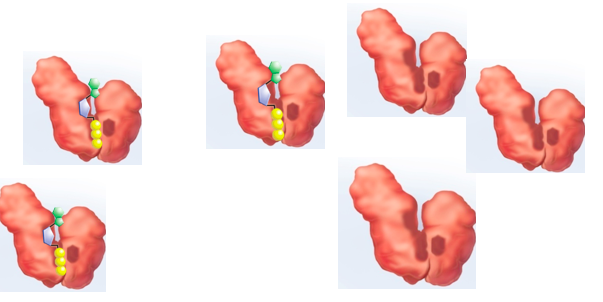
Substrate concentration at which VMax is at half of max rate
Shows how good your enzyme is
If Km is high, the enzyme needs ______. This means the enzyme has a low affinity for the substrate.
A lot of substrate
Saturation
Plateau where nearly all active sites are occupied by substrates
Why do cells use inhibitors?
To turn off or slow down an enzyme
Coenzyme
Enzyme "helper"
Organic molecule
Vitamins
Carry electrons
Tightly bounded to the active site or bounded loosely
Cofactor
Enzyme "helper"
Inorganic molecule
Carry electrons
Tightly bounded to the active site or bounded loosely
Enzyme helpers (coenzymes and cofactors) will _______.
Bind to the enzyme or participate in the reaction
Vitamin C
Functions in muscle formation (collagen)
Deficiency causes scurvy (loss of teeth, pale skin, and sunken eyes)
Vitamin B3
"Nicotine acid"
Functions in the coenzymes NAD and NADP
Deficiency causes pellagra (skin lesions)
Which structures do enzymes most heavily depend on?
Tertiary and quaternary
Denature
When structure is lost due to heat
Once a certain temperature is reached, bonds maintaining the 2o, 3o, and 4o structure of the protein collapse and the protein loses function
The shape of the enzyme is altered by _____?
1. pH - Measure of H+ (0-7 is acidic and 8-14 is basic)
2. Temperature (typically when temperature increases, rate of reaction will increase, but not always) (as temperature increases, the enzyme's active site may become unstable and function poorly)
3. Coenzymes/Cofactors
Metabolism
Each step is coordinated by a specific enzyme
2 types of metabolism
1. Catabolic Pathways (Reactions)
2. Anabolic Pathways (Reactions)
Catabolic Pathways (Reactions)
Breaks down reactants
Used for recycling macromolecules
Used to obtain energy for endergonic reactions
Metabolic pathway is complex
Lots of intermediates (ATP & NADH)
Lots of energy transfer steps
Spontaneous, but does not happen without correct enzyme
Anabolic Pathways (Reactions)
Promote synthesis (builds up, not breaks down)
Endergonic reactions
Must be coupled to an exergonic reaction
Protease
Turns proteins into amino acids (catabolic pathway)
Nuclease
Breaks down RNA into nucleotides (catabolic pathway)
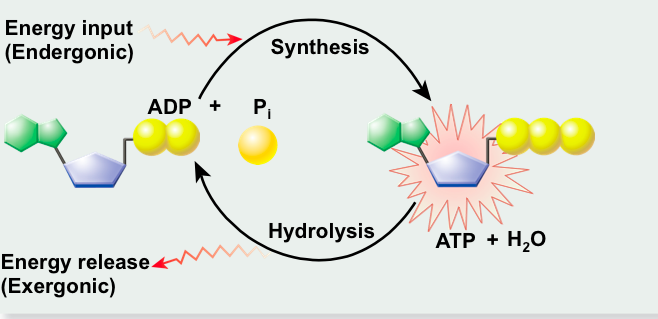
Hydrolysis of ATP ______ energy.
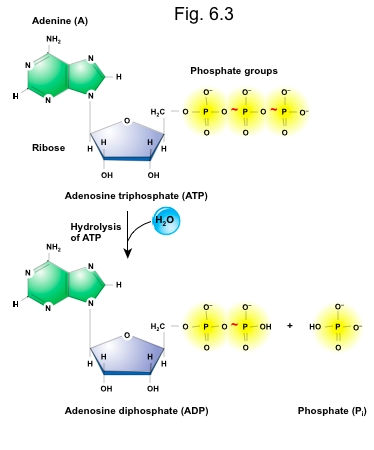
Releases
Is exergonic
The bonds are broken
When the terminal phosphate bond is broken, a molecule of inorganic phosphate (Pi) is formed which forms adenosine diphosphate, ADP + (Pi) which generates free energy
Synthesis of ATP _______ energy.
Requires
Is endergonic
Can be through substrate level phosphorylation or chemiosmosis
Phosphorylation (substrate level)
Finds a free floating Pi and takes it, which converts ADP to ATP
ATP Synthesis
Chemiosmosis
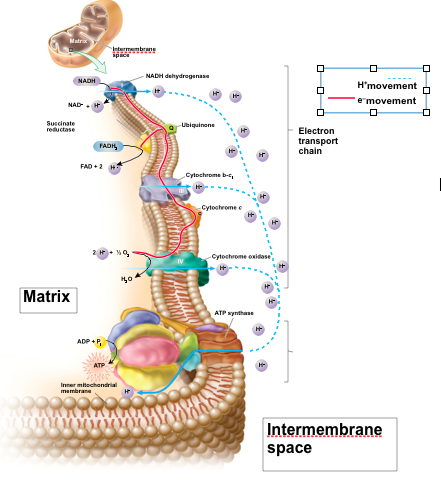
Deals with an electrochemical gradient
Intermediates
Compounds formed between initial reactants & products
Thermodynamics
Study of energy transformation
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
When an enzyme and a substrate come together
Held by hydrogen and/or ionic bonds
Enzyme action time is proportional to the concentration of the substrate:
The more substrate you have, the faster the reaction rate will be (until you reach saturation)
Enzyme Inhibitors
Chemicals that interfere with enzyme function
Are used to slow down/or stop an enzyme
Usually reversible in cells (when hydrogen or ionically bonded)
Allosteric site
Site on the enzyme that isn't the active site
Where noncompetitive inhibitors bind to
Energy Intermediates: Redox
Redox Reaction
Electron is removed from one molecule and added to another molecule
Oxidation (oil)
Removal of electrons
Reduction (Rig)
Addition of electrons
Ae- + B → A + Be-
A has been?
Oxidized (electron removed)
Ae- + B → A + Be-
B has been?
Reduced (electron added)
Energy Intermediates: NAD
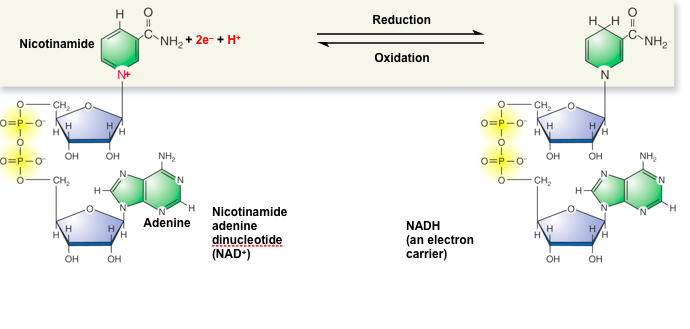
NAD is a type of nucleic acid
When NAD is reduced, NADH is formed
It's really easy to move electrons back and forth between NAD and NADH
Often coupled with reactions to give or remove energy
Electrons are synonymous with ______ in chemical reactions.
Energy
Where is energy found in molecules?
Bonds
Regulation of metabolic pathways
3 types:
1. Gene regulation
2. Cellular regulation
3. Biochemical regulation
Gene Regulation
Turn genes on or off
Cellular Regulation
Cell-signaling pathways like hormones
Biochemical Regulation
Feedback Inhibition- Product of pathway inhibits early steps to prevent over accumulation of product
Concentration Gradient
Refers to a differences of solutes (dissolved substances) in an adjacent area
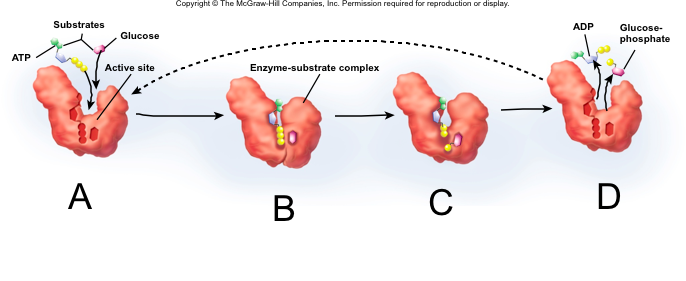
Enzyme-Catalyzed Reaction
A. Substrate binding
B. Transition State (induced-fit and Ea is lowered)
C. Substrate converted to product
D. Product is released