Anatomy & Physiology Lab 1: Overview of the Skeleton
Skeleton

-the body's framework, composed of cartilage & bone
-in embryos the skeleton is predominantly made up of hyaline cartilage, replaced by more rigid bone.
Functions of the skeleton.

-supports and protects the body
-responsible for body movement
-bones store lipid and minerals
-site of hematopoiesis
Axial Skeleton

-bones that lie around the body's center of gravity
Appendicular Skeleton

-bones of the limbs or appendages
Articular cartilage

-covers bone ends at movable joints
Costal cartilage

-connects ribs to sternum
Laryngeal Cartilage

-constructs the larynx (voice box)
Tracheal & Bronchial Cartilage

-reinforce passageways of the respiratory system
Nasal Cartilage

-supports the external nose
Invertebral Discs

-separates and cushions bones of the spine
Perichondrium

-dense connective tissue that surrounds cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage

-provides sturdy support with some resilience
-most skeletal cartilage is hyaline cartilage
Elastic Cartilage
-more flexible than hyaline cartilage
-located in the external ear and epiglottis
Fibrocartilage
-consists of rows of chondrocytes alternating with rows of thick collagen fibers
-great tensile strength, can withstand heavy compression
Compact Bone
-smooth and homogenous
Spongy Bone
-composed of small bars of bones and lots of open space
Long Bones
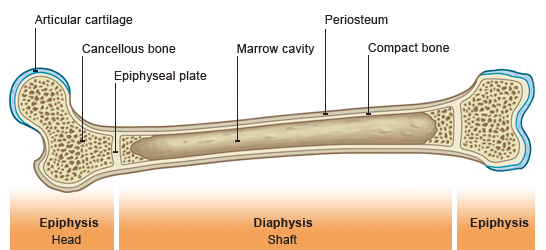
-much longer than they are wide
-generally consists of a shaft with heads at either end
-predominantly composed of compact bone
-examples: femur & phalanges
Short Bones

-typically cube shaped
-contains more spongy bone than compact bone
-example: tarsal and carpals
Flat Bones

-generally thin with 2 wafer-like layers of compact bone sandwiching a layer of spongy bone between them
-many flat bones are curved
Irregular Bones

-bones that do not fall into any of the categories
-ex: vertebrae
Sesamoid Bones

-special types of short bones formed in tendons
-Example: patellas
Sutural Bones

-tiny bones between cranial bones
Tuberosity

-large rounded projection
Crest
-narrow ridge of bone
Trochanter

-very large, blunt, irregulary shaped process
Line

-narrow ridge of bone; less prominent than a crest
Tubercle
- small rounded projection or process
Epicondyle

-raised area on or above a condyle
Spine

-sharp, slender, often pointed projection
Process
-any bony prominence
Head

-bony expansion carried on a narrow neck
Facet

-smooth, nearly flat articular surface
Condyle

-rounded articular projection
Ramus
-armlike bar of bone
Groove
-furrow
Fissure
-narrow, slitlike opening
Foramen

-round or oval opening through a bone
Notch

-indentation at the edge of a structure
Meatus
-canal like passageway
Sinus
-bone cavity, filled with air and lined with mucous membrane
Fossa
-shallow basin-like depression in a bone
Diaphysis

-the shaft of a bone
-composed of compact bone
-has a smooth surface
Periosteum

-fibrous membrane covering the bone
Perforating Fibers

-fibers of the periosteum that penetrates into the bone
Osteoblasts and osteoclasts are found on the inner, or osteogenic layer of the _____________.
Periosteum
Epiphysis
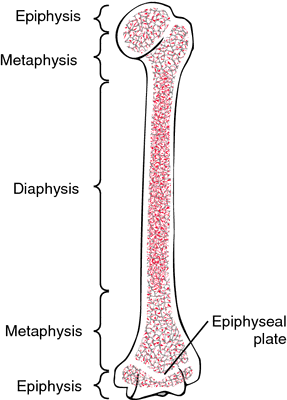
-end of the long bong
-composed of a thin layer of compact bone that encloses spongy bone
Epiphyseal Plate

-thin area of hyaline cartilage that provides for longitudinal growth of the bone during youth
Medullary Cavity

-storage region for adipose tissue, or yellow bone marrow
Epiphyseal Lines
barely, discernible remnants
Central (Haversian) Canal

-runs parallel to the long axis of the bone
-carries blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels through the bony matrix
Osteons

the central canal and all the concentric lamellae surrounding it
Canaliculi

-tiny canals radiating outward from a central canal to the lacunae of the first lamella and then lamella to lamella
-forms dense transportation networks through the hard bone matrix, connecting all the living cells of the osteon to the nutrient supply