Microbiology Lecture- Chapter 5 (Microbial Metabolism)
The sum of all chemical reactions within a living organism is known as ______________.
Metabolism
_______ refers to chemical reactions that result in the breakdown of more complex organic molecules into simpler substances. ________ reactions release energy.
catabolism
catabolic
_________ refers to chemical reactions in which simpler substances are comined ro form more complex molecules. ___________ require more ____________.
Anabolism
anabolic
The energy of________ is used to drive ____________.
catabolic reactions is used to drive anabolic reactions
The energy for chemical reactions is stored in _____________.
ATP
_______ are proteins produced by living cells.
Enzymes
Enzymes function is to _____________________________________.
catalyze cheical reactionsby loering the activation energy
Enzymes are generally __________proteins with characterstic ____________ shape.
globular
3-D shape
Enzymes are efficient and can operate at relatively ________ temperatures and are subject to various cellular controls.
low
Enzyme names usually end in _________.
-ase
The 6 classes of enzymes are defined on the basis of the types of ________ they _____________.
reactions
catalyze
Most enzymes are _____________ consisting of a _________ and a _________.
protein portion- (apoenzyme)
non-protein porttion- (co-factor)
The cofactor can be a __________ (iron, cobalt, copper, magnesium, manganese, zinc and calcium) or a complex organic molecule known as ________________ (NAD+, NADP+, FMN, FAD, or coenzyme A).
metal ion
a coenzyme
True or false. When an enzyme and substrate combine the substrate is transformed and the enzyme is recovered.
true
Enzymes are characterized by ________________ which is characterized by their active sites.
specificity
At ____________ temperatures enzymes undergo ____________ and lose their catalytic properties.
high
denaturation
At __________ temperatures enzymes _________ rate _______________.
low
reaction rate
decreases
The pHat which enzymatic activity is maximal is known as the __________ pH.
optimum
Enzymatic activity increases as substrate concentration ___________ until the enzymes are _______________.
increases
saturated
________ inhibitors compete with normal substrate for the ________ site of the enzyme.
Competitive
active
_________ inhibitors act on other parts of the apoenzyme or on the cofactor and decrease the enzyme's ability to combine with normal substrate.
Non-competiitive
__________ ________ occurs when the end product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an enzyme's activity near the start of the pathway.
Feedback inhibition
________ are enzymatic RNA molecules that cut and splice RNA in eukaryotic cells.
Ribozymes
_______ it the removal of one or more electrons from a substrate. Protons (H+) are removed with the electrons.
Oxidation
Reduction of a substrate refers to its ______ of one or more ______________.
gain
electrons
True or false. Each time a substance is oxidized another is simultaneously reduced.
True
NAD+ is the reduced or oxidized form
oxidized
NADH is the _______form.
reduced
True or false. Glucose is a reduced molecule; energy is released during a cell's oxidation of glucose.
true
Energy released during certain metabolic reactions can be trapped to form _____ from ___________ and (P)-phosphate.
ATP
ADP
Adding a (P) to a molecule is called _______________.
Phosphorylation
During substrate-level phosphorylation a ______________ (P) from an intermediate in catabolism is added to ADP.
high energy
True or False. During oxidative phosphorylation energy is released as electrons are passed to a series of of electron acceptors (an electron transport chain) and finally to O2 or another inorganic compound,
true
Photophosphorylation only happens in ___________ organisms.
photosynthetic organisms
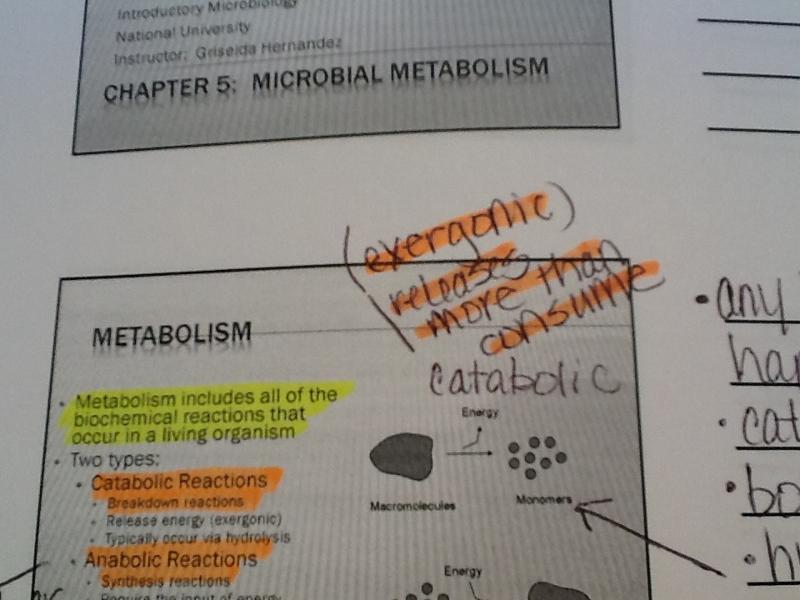
Catabolic reactions:
1.breakdown reactions
2. release energy (exergenic)
3. typically occur via hydrolysis
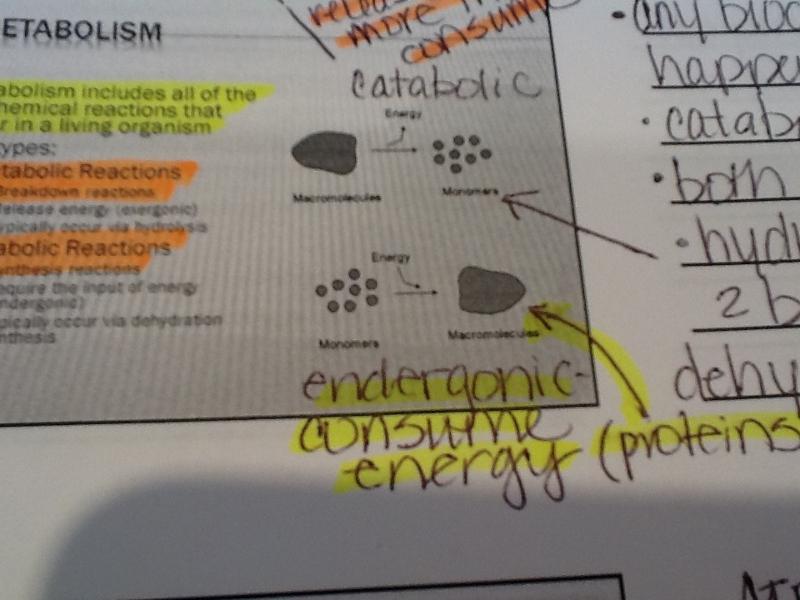
Anabolic reactions:
Synthesis reactions-put together -build
require the input of energy (endergonic)
typically occur via dehydration synthesis
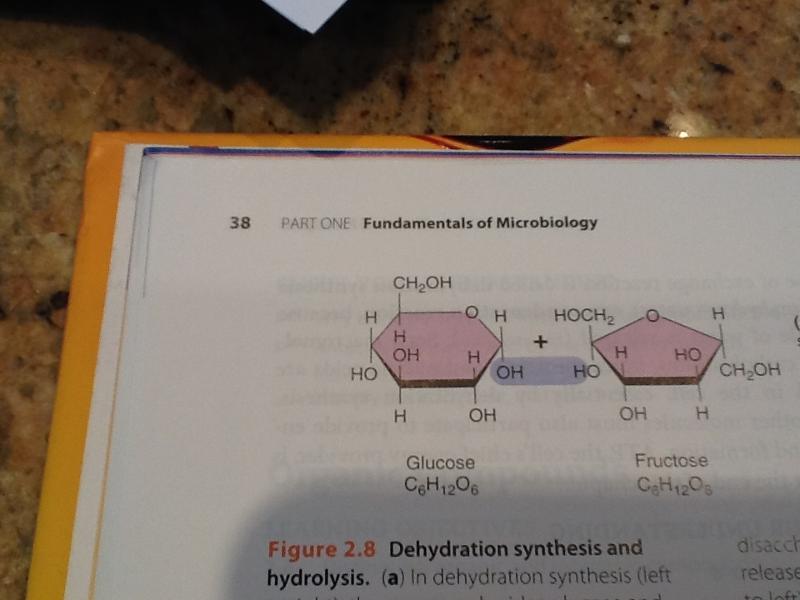
dehydration synthesis (left to right)
a chemical reaction in which a molecule of water is released in the reaction of the monosaccharides glucose and fructose combine to form a molecule of the disaccharide sucrose.
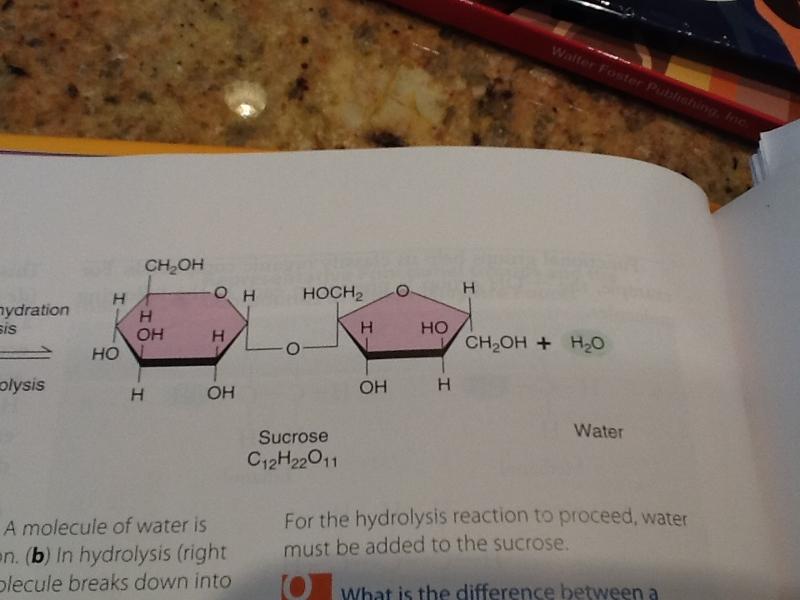
Hydrolysis (right to left)
in hydrolysis the sucrose molecule breaks down into the smaller molecules glucose and fructose. For the hydrolysis reaction to proceed, water must be added to the sucrose.
What is the most usable form of energy?
ATP
Catabolic ______ and _______ _________.
breakdown
and make ATP
Anabolic ________ and ______ _______.
build and use ATP
There are different types of energy
heat
light-plants
chemical energy
ATP is _____________ energy.
chemical
True or false. Heat is a useless energy it can't be reused.
true
Organic molecules contain energy stored in their bonds. More specifically energy is associated with _______ that form those bonds.
electrons
Most of a cell's energy is produced from the __________ of ________________.
oxidation of carbohydrates
What is the most commonly used carbohydrate?
glucose
The two major types of glucose catabolism are __________in which glucose is completely broken down and _________ is when it is partially broken down,
respiration
fermentation
What is the most common pathway for the oxidation of glucose?
glycolysis
What is the end product of glycolysis?
pyruvic acid
Two ATP and two NADH are produced rom one ________ ________.
glucose molecule
Cells extract energy and store it in ?
ATP
Oxidation reactions involves the oxidation of a molecule. A molecule loses energy-containing electrons. Reduction reactions involves the reduction of a molecule. A molecule gains energy containing electrons. What is a good way to remember this ?
LEO goes GER
Loss of electrons is oxidation; gain of electrons is reduction
or
OIL RIG
oxidation is loss and Reduction is gain
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) does what?
1. stores chemical energy released by catabolic reactions
2. provides energy for anabolic reactions
What is ATPs structure?
Adenosine unit (ribose and adenine) + 3 phosphate groups (3 like charges forced together =high energy bonds)
What are the three mechanisms of ATP?
1. substrate level phosphorylation - transfer of a high energy phosphate from a phosphorylated compound to ADP (sharing phosphate with ADP)
2. Oxidative phosphorylation- cellular respiration
-ETC creates proton motive force
-H+ channeled through ATP synthase along the concentration gradient
-energy from proton motive force used to phosphorylate ADP
3. Photophosphorylation-Photosynthetic organisms
-occurs only in photosynthetic organisms
-process similar to phosphorylation
During respiration _______ molecules are ________.
organic molecules
oxidized
During cellular respiration energy is generated from the ________________.
Electron transport chain (ETC)
In aerobic respiration what is the final electron acceptor?
O2 (oxygen)
In anaerobic respiration what is the final electron acceptor?
any other inorganic molecule other than O2
Decarboxylation of pyruvic acid produces one CO2 and one ________________ group.
acetyl
True or false. Pyruvic acid cannot enter the Krebs's cycle.
true
Collisions depend on?
molecular speed
molecular energy (only some will have enough)
molecular chemical configurations
Rate of reaction increases when ______________.
Amount of heat is increased
-molecular movement increases
-frequency of collision increases
-number of molecules that are at or above the activation energy level increases
Other ways to increase reaction rate:
-increase the pressure
-increase the number of reactants
True or false. Most enzymes are proteins.
true
Enzymes function as ______________.
catalysts
-speed up chemical reactions
-lower the activation energy of the chemical reaction
-not used up in a chemical reaction
- specific to the reaction that it catalyzes
-act on specific substrate (s)
Enzyme is like a puzzle. The pieces go in a specific way.
no answer just an analogy
A substrate is_____________.
A molecule your enzymes works on to make another product.
What site does the substrate bind to?
The active site-like a handshake a tightening fit
Cofactor is another piece but it is not a ______________.
protein
The cofactor and _________ make the whole piece that fits into the ________ site.
coenzyme
alosteric site
What factors affect enzymes?
1. temperature (optimal 35-37*C)
2. pH (7 optimal)
3. substrate concentration- goes high and plateaus
Enzyme inhibitors:
Competitive - competes directly for the active site
non-competitive- competes in directly for the alosteric site
-causes active site to change shape so the the correct substrate cant bind
(eg. DDT is an inhibitor)
Stop signal of enzyme always binds to ___________ .
Enzyme 1
Allosteric site does what?
causes active site to change shape halting substrate to fit
The stop signal is the?
end product itself
Cellular respiration is ______________________?
The process by which living organisms aerobically harvest energy from food
Cellular respiration involves 3 major steps:
1. Glycolysis-breaking down of glucose
2.Kreb's cycle-removal of all energy
3.Electron Transport chain-
Glycolysis is the _____________________.
Glucose breaking down -----> pyruvic acid
produces small amounts of ATP and NADH
occurs in cytoplasm
In the Krebs's cycle two carbon acetyl groups are __________.Electrons are picked up by NAD+ and FAD for the electron transport chain.
oxidized
From one molecule of glucose, oxidation produces __ molecules of NADH, two molecules of ________ and two molecules of ___________ .
6
FADH2
ATP
Decarboxylation produces six molecules of ______ .
CO2
Electrons are brought to the ETC by __________.
NADH
The ETC consists of _______ carriers.
three
Glycolysis means______________.
splitting of sugar
One glucose molecule produces two ____ and two_____.
ATP and NADH
The end product of glycolysis is ______________.
pyruvic acid
True or false. Two molecules of ATP are invested.
true
Step 1 of glycolysis:
glucose was phosphorylated and ATP was dephosphorylated.
Step 3 of glycolysis:
Fructose-6 phosphate was phosphorylated while ATP was dephosphorylated.
True or false pyruvic acid can't enter the Krebs's cycle.
true
___________ is decarboxylated (carbon removed)and is oxidized by_________. Acetyl group is attached via a high energy bond to coenzyme A (CoA)
pyruvic acid
NAD
Krebs's cycle steps:
acetyl enters the cycle
-CoA is reused to help another acetyl enter the Krebs's cycle
Acetyl is oxidized in a series of steps
CO2 is produced (all carbon that enters exists as CO2)
NADH and FADH are produced by redox reactions
Krebs's cycle is the complete oxidation of _______.
acetyl
- pull all the energy out from acetyl ----> oxidation remove electrons.
Oxygen is highly electronegative?
true
Examples of final electron acceptors
Nitrate-E. coli and pseudomonas
Fe3+ geobacter
Chemiosmosis is the generation of _____ using the ______.
ATP
ETC
ETC is embedded in __________________.
plasma membrane
Most of the cell's ATP is produced at this stage __________ .
chemiosmosis
H+ diffuse across the membrane through ______ channels containing an enzyme ______________.
protein
ATP synthase
know this summary
Fermentation is the metabolic process used to extract energy from a sugar or other _______ molecule.
organic
True or false. Fermentation does not require the Krebs's cycle or ETC
true
Does fermentation require oxygen?
no
In fermentation the final electron acceptor is _____________.
organic
It will either produce _______ or ______________.
alcohol
acid
Does fermentation yield any ATP?
yes but in small amounts only during glycolysis
Two types of fermentation:
1. lactic acid fermentation:
-pyruvic acid-----> lactic acid (streptococcus and lactobacillus are lactic acid bacteria)
homoplactic- can only produce lactic acid
2. alcohol fermentation:
-reduced
-heterolactic (variety of products due to fermentation)