Ecology lab final
Define ecology
the study of the complex interactions
between organisms and
their environments
Define naturalists
individuals who dedicate their time and efforts to studying and
becoming experts on
plants and animals in the field
What is the difference between a null and alternative hypothesis?
Null= there is no difference or correlation between what you are testing.
Alternative hypothesis= The expected difference or correlation does exist
What information should be included in field note entries? (4 major components)
identification (to species when
possible), where observed (GPS
coordinates and local landmark reference), and natural history details
such as structure, size, body plan, life stage, behaviour, etc,
and an illustration
Our provided flowchart broke the scientific method into 5 major steps. What are they?
Information, question, hypothesis, prediction, test of hypothesis (observational study, experiment, modelling)
Define standard deviation
how far away from the mean the individual measurements tend to fall in a sample
Define quadrat
A plot that is laid down on the surface being studied to define a standard sampling area
List some important qualities for a naturalist to possess as they set about describing the natural history of an organism.
attention to detail, awareness pf surroundings, focus, an open mind, illustration skills
Based on the process of the scientific method, do observations of
natural history alone provide
evidence in support of hypotheses
about those observations? Why or why not?
No, hypotheses must go through the scientific method
Why are preserved animals important for study? (3)
They can be used to increase identification accuracy, to prepare a voucher collection, to keep repositories of genetic material for study and conservation purposes, etc
What are the three field sampling techniques?
Line transect, mark-recapture, quadrat
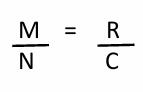
What are the variables in this equation?
M=marked upon first capture
N=population
R=Recaptured from the first round
C=total captured in second round
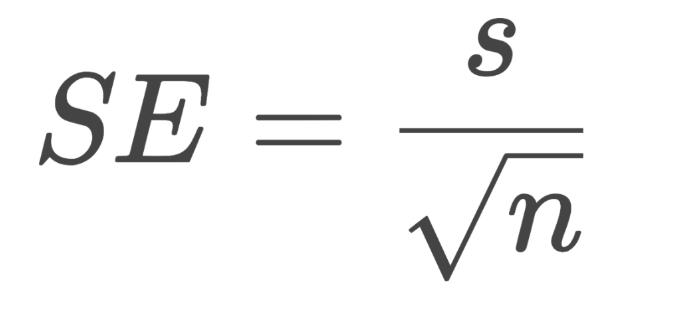
What are the variables in this equation?
SE=standard error
s=standard deviation
n=sample size
What is pseudo-replication?
When your sample size is artificially inflated because you took measurements that are not independent from each other (ex. measured the same cherry multiple times, measured cherries from only one tree).
How do you avoid bias in your measurements?
By taking randomized samples.
What are the two types of "error" in measurements?
Bias and random variation
What does standard error help you quantify?
How confident you should be in you estimate of the population mean.
What are the 4 categories of measurements/data?
Nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio
What is nominal data?
Values without quantitative (a measure number) value. Normally categories that are names.
What is ordinal data?
Categories that can be ranked according to some criteria.
ex. height, size, weight...
What are the three types of functional responses?
Type I - linear relationship, predator eats prey in direct proportion to abundance, no handling time
Type II - prey consumed initially rises with abundance but levels off with further increase
Type III - Type II but initially prey consumed does not quicky increase with abundance (an S ish shape)
What is ratio data?
Quantitative values where the scale has a true, physically meaningful, zero (ex. area, height, weight, Kelvin)
What is the difference between discrete and continuous data?
Discrete data has only certain possible values while continuous data can have any value.
What are the 4 ways we can evaluate distribution?
Geographical range, abundance, dispersal, survival and reproduction
What statistical analysis will you use if you are looking for...
a correlation that is parametric, where the X variable is independent of Y
Linear regression
What statistical analysis will you use if you are looking for...
a difference in variances
F-test
What statistical analysis will you use if you are looking for...
a difference in central tendencies that are parametric, where there are 2 treatments which are not paired
t-test
What statistical analysis will you use if you are looking for...
a difference in central tendencies that are parametric, where there are more than 2 treatments
ANOVA
What is a hypothesis?
An educated guess to answer a question which can be experimentally supported or not.
What is the difference between a null and alternative hypothesis?
Null= there is no difference is there is no difference or correlation between what you are testing.
Alternative hypothesis= The expected difference or correlation does exist
Why is the null and alternative hypothesis set up good for statistical analyses?
Because it allows us to find the probability that the null hypothesis is false, which supports our alternative hypothesis.
What are the 4 sources of phenotypic variation within a species?
Tolerance, acclimation, developmental responses, ecotypes.
What information should be included in field note entries? (4 major components)
identification (to species when
possible), where observed (GPS
coordinates and local landmark reference), and natural history details
such as structure, size, body plan, life stage, behaviour, etc,
conditions of the area/time, and an illustration
What is the meaning of a p-value?
The probability of getting the same results through random chance (which is why you want it to be small).
What are the 4 main elements of the introduction of a research paper?
Background information, research problem, thesis statement/research question, rational and significance
What are the two types of ecological study? Give a pro and a con for each.
Observational (natural)- pros: interacting variables, cheaper, more realistic, cons: less control over variables
Experiment (manipulative)- pros: more control over variables, manipulate the variables, cons: more expensive, less realistic,
Define controls.
A treatment in which the independent variable(s) is/are not being manipulated.
Define controlled variables.
Variables which you are manually manipulating in an experiment.
What is nominal data?
Values without quantitative (a measure number) value. Normally categories that are names.
What do rank abundance distributions show?
The relative abundance of species in a community in descending order (common to rare).
Define the predictions of a hypothesis.
The results that we would expect to see (in a particular experiment) if the hypothesis is true.
Define marginal value theorem/MTV (as it pertains to foraging).
An animal will stop foraging in a patch when the rate of energy gain drops below the average rate of energy gain in the habitat.
Define functional response.
The changes in prey consumption vs prey density
What are the three types of functional responses?
Type I - linear relationship, predator eats prey in direct proportion to abundance, no handling time
Type II - prey consumed initially rises with abundance but levels off with further increase
Type III - Type II but initially prey consumed does not quicky increase with abundance (an S ish shape)
What does Holling's disc equation describe?
Describes the realationship between search time, handling time, and consumption ate in type II functional responses
What are the variables in the Holling's disc equation? define them.
Pe - number of prey eaten
Th - handling time per prey item
Ts - total search time
Ttot - total time spent
a' - attack rate / search efficiency
N - prey density
Define competition.
When organisms both do worse when together than when apart.
Define interference competition.
When the mechanisms for competition are direct and physical (such as interfering with another organisms resource collection via hoarding).
Define exploitation competition.
When one organism completely makes a resource unavailable to another organism (one ant species blocking off entrances to another nest).
intraspecific competition, interspecific competition, which is between different species?
Interspecific competition
What does Holling's disc equation describe?
Describes the relationship between search time, handling time, and consumption rate in type II functional responses
What does Pielou's evenness index measure?
The evenness of a community.
What do rank abundance distributions show?
The relative abundance of species in a community in descending order (common to rare).
What do species accumulation curves show?
The cumulative number of species recorded (y-axis) verses the number of individuals sampled.
Define marginal value theorem/MTV (as it pertains to foraging).
An animal will stop foraging in a patch when the rate of energy gain drops below the average rate of energy gain in the habitat.
How do you transform your Shannon's diversity index value into a Pielou's evennesss index value?
You divide it by ln(S) or ln(species richness)
Note: species richness is number species in the community
Why are soil microorganisms important?
They help break down organic matter and make nutrients available to other organisms.
What are the 4 components of soil?
Minerals, decaying organic matter, air pockets and water
How do the feeding activities of macroinvertebrates accelerate the process of decomposition?
By physically breaking down organic material into smaller fragments which are more accessible to soil microbes.
How does macroinvertebrate burrowing allow microbes to penetrate deeper into the soil?
By creating channels.