Climate and weather, clouds
What are the two ways water droplets form? Which never happens in nature?
Heterogenous and homogenous nucleation. Heterogenous nucleation only happens in labs.
Hydrophilic aerosols are called what?
cloud condensation nuclei (CCN)
______________ nuclei dissolve in water.
Hygroscopic
Is it easier or harder for water to evaporate from a solution?
Harder
A droplet’s size is directly related to the relative
humidity
at which it will be in equilibrium (continue to exist). What is this
effect called and what does it mean in practice?
The curvature effect. The larger a droplet the harder it will be for it to evaporate.
What are the three ways ice crystals form (with the help of ice nuclei).
• Directly from vapour if water vapour is deposited onto
ice
nuclei
• When a supercooled water droplet
already contains an
ice nucleus and
temperatures get cold enough
• When
supercooled droplets (with a non ice nuclei)
collide with ice nuclei
What condition does the presence of solutes change for forming water droplets? What is this effect called?
The relative humidity at which water droplets form which can be lower than 100%. The solute effect.
In order for a droplet to increase in radius/diameter what must also increase to maintain the droplet/s existence?
The relative humidity
What are the three favoured traits of an aerosol for condensation?
wettable (hydrophilic), large (so it's harder for the droplet to evaporate), and hygroscopic (dissolves in water)
What condition does the presence of solutes change for forming water droplets? What is this effect called?
The relative humidity at which water droplets form which can be lower than 100%. The solute effect.
Why is dust not a good CNN?
It doesn't dissolve
When the water droplets in clouds start to precipitate their relative humidity's...?
Drop/decrease
Why does the size of droplets tends to become uniform in a cloud?
Small droplets grow faster than big ones so all droplets get to be big and then kinda stop growing.
Larger droplets freeze at slightly higher temperatures than their smaller counterparts, true or false?
True
What temperature must it be in a cloud (in nature) for water droplets to freeze?
negative 40 degrees Celsius
When the water droplets in clouds start to precipitate the cloud's relative humidity...?
Drops/decreases
Favourable ice nuclei are _________ and ______________.
Name two examples of ice nuclei.
large and insoluble,
- Clay minerals
- Combustion products
- Organic material
What are the three ways ice crystals form (with the help of ice nuclei).
• Directly from vapour if water vapour is deposited onto
ice
nuclei
• When a supercooled water droplet already contains an
ice nucleus and temperatures get cold enough
• When
supercooled droplets (with a non ice nuclei) collide with ice nuclei
What are the three ways to achieve saturation?
• Cooling the air to its dew-point temperature
• Adding water
vapour to the air
• Mixing air samples
Clouds form due to...?
rising air
What are the five basic mechanisms by which air rises to form clouds?
• Convection
• Orographic lifting
• Convergence of
surface winds
• Frontal lifting
• Divergence aloft
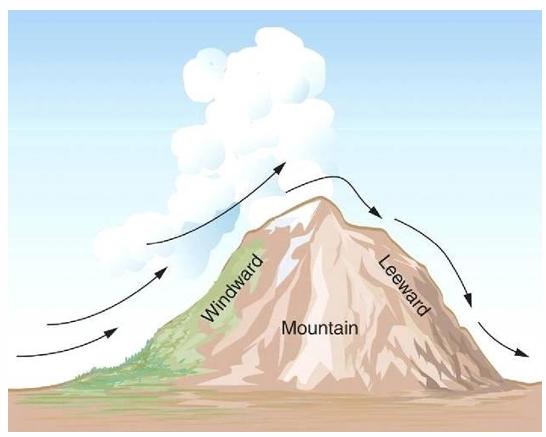
Which lifting mechanism is this?
Orographic lifting
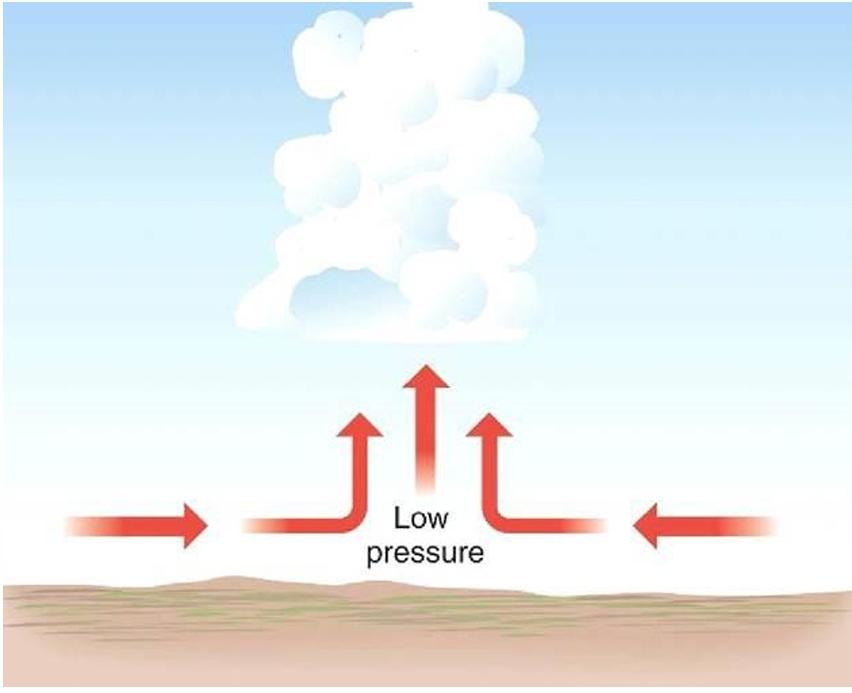
Which lifting mechanism is this?
Convergence
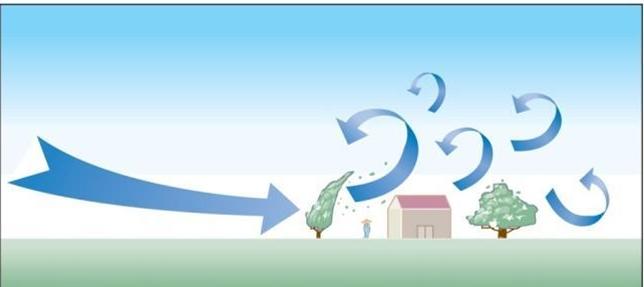
Which lifting mechanism is this?
Convection
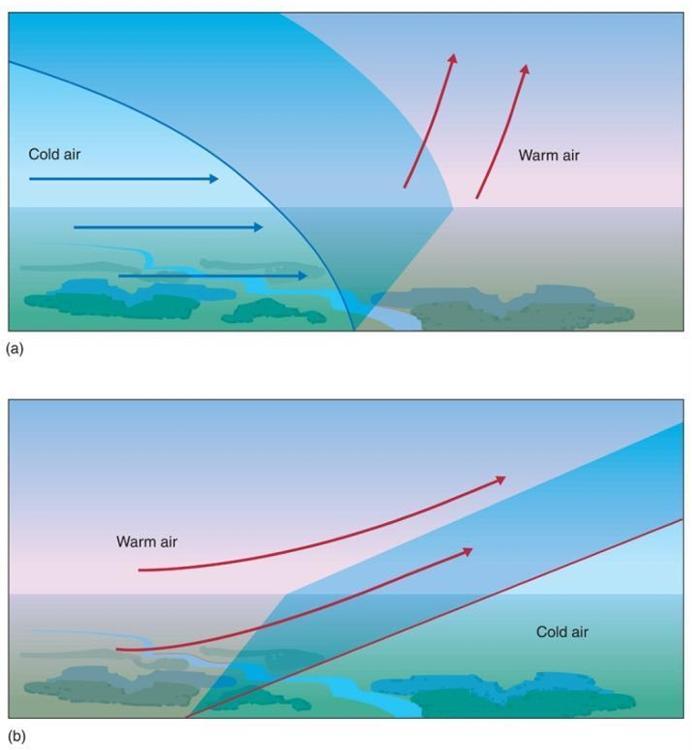
Which lifting mechanism is this?
Frontal lifting
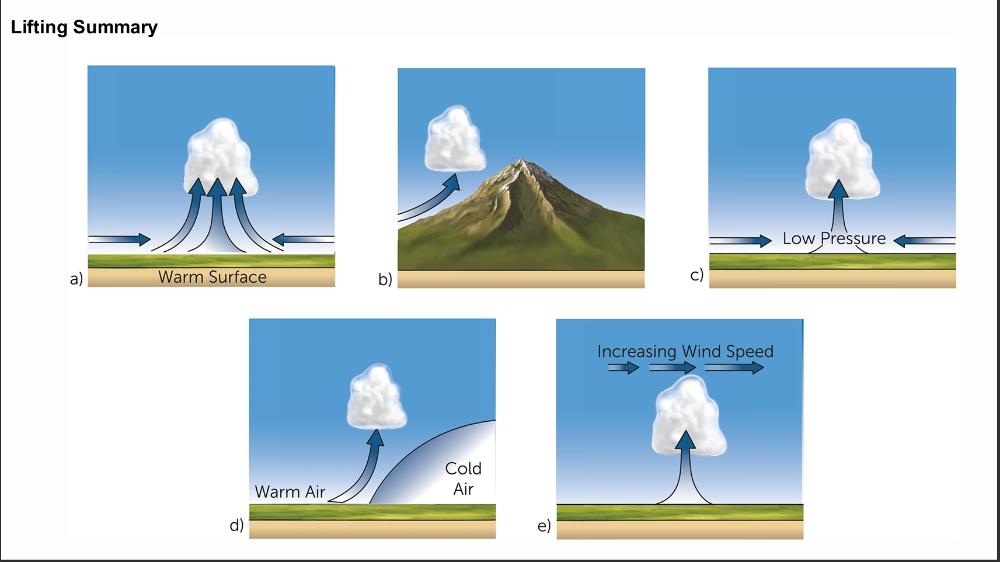
Name the lifting mechanism in b, c and d
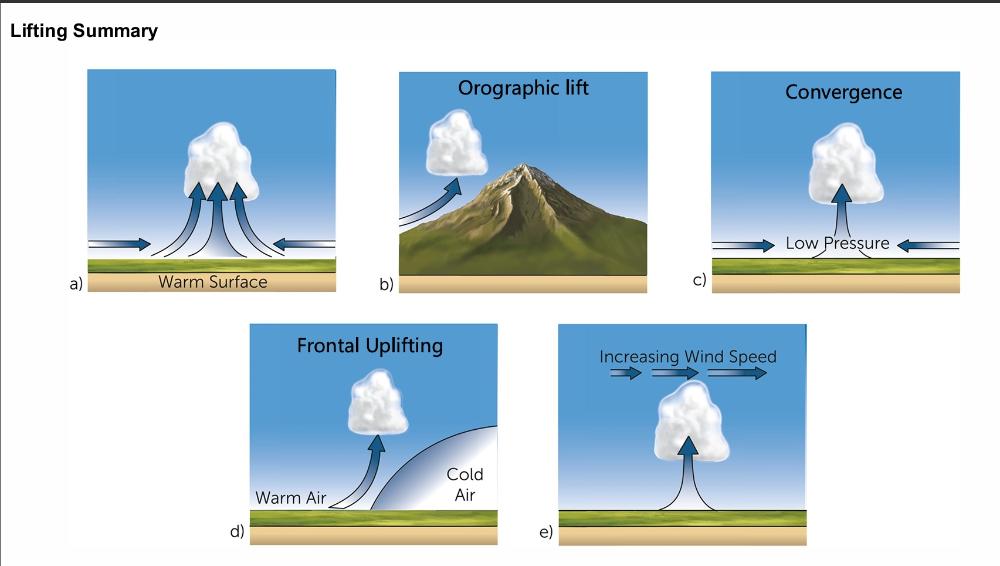
The classification of clouds is based on __________ and ___________.
shape and height
Howard’s identification system uses Latin
roots. What are these
words mean in English?
• Cumulus
• Stratus
• Cirrus
• Nimbus
• Cumulus (“heap”)
• Stratus (“layer”)
• Cirrus (“curl of
hair”)
• Nimbus (“rain”)
________ ____________ cause cirrus clouds to have ragged edges.
Ice crystals
Of the classifications cirrus, cumulus and stratus which clouds are found only at high altitudes?
Cirrus
Cumuliform Clouds (e.g., cumulus, stratocumulus,
cumulonimbus)
form in ______________ air.
unstable
Cumulus humilis clouds are (small/large) and only last for a few minutes or hours.
small
Fill in the blanks:
Cumulus humilis -> time -> Cumulus _______________ -> rise until reaches a __________ ___________ -> ___________________ -> heavy precipitation
Cumulus humilis -> time -> Cumulus congestus -> rise until reaches a stable layer -> precipitation -> cumulonimbus -> heavy precipitation
Stratiform Clouds (e.g., stratus, stratocumulus,
nimbostratus)
form in ____________ air as a result of forced lifting or as winds
cause turbulent mixing.
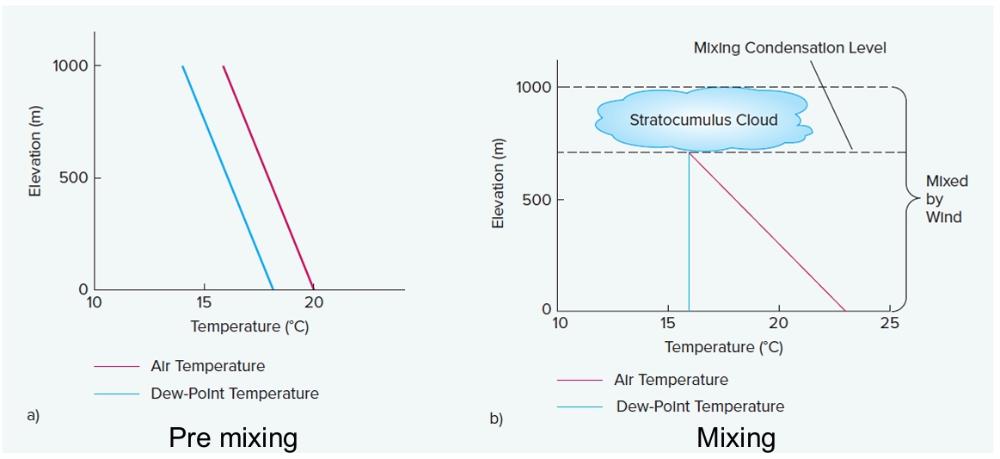
stable
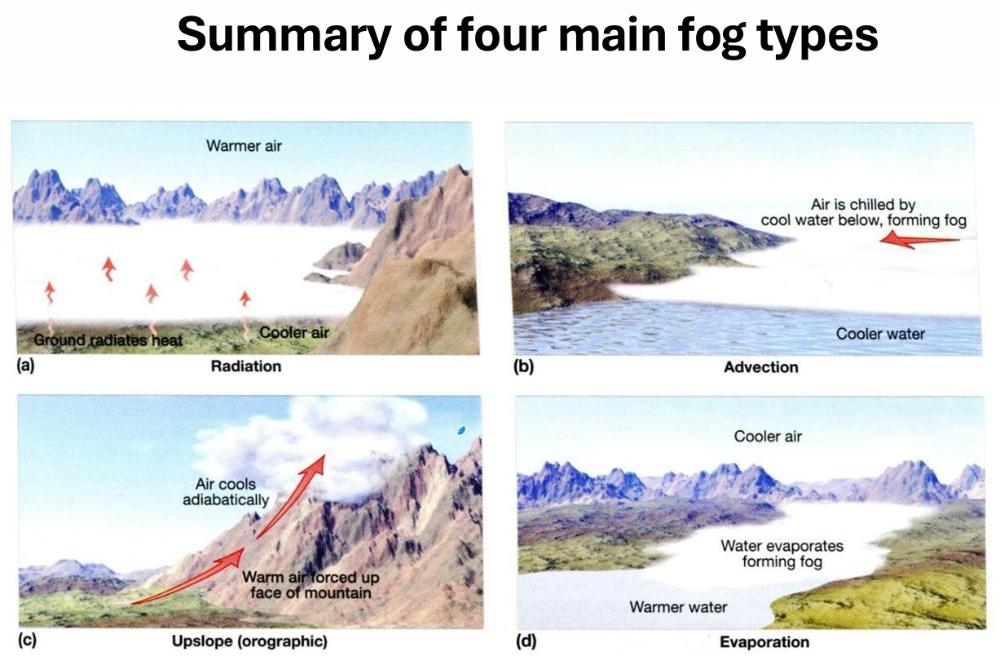
_______________ fog forms as air rising up a slope cools
adiabatically. Other fogs form by mixing or
adding ____________ _____________.
Upslope, water vapour
Radiation Fog forms when _____________ of radiation by the ___________ are mixed with water droplets through the mixed layer via ___________ __________.
emissions, surface, light wind
Advection Fog forms due to conductive cooling as _________, ___________ air is advected over a cool surface
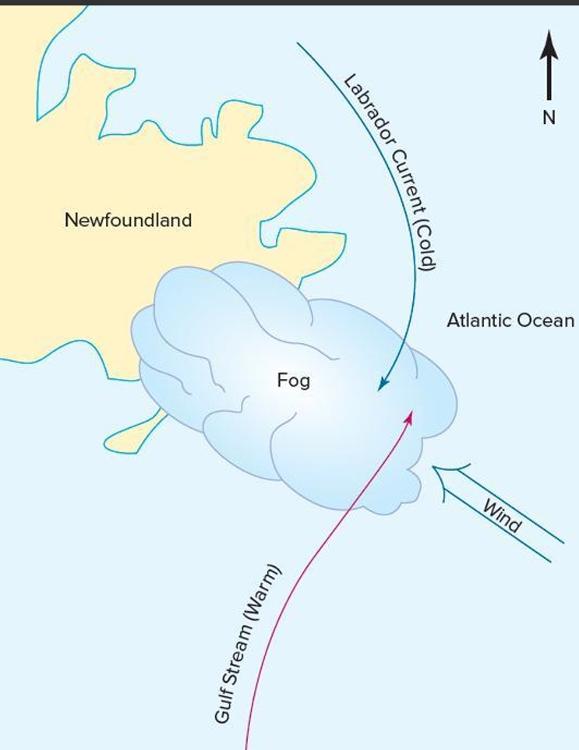
warm, moist
What are the three ways to achieve saturation?
• Cooling the air to its dew-point temperature
• Adding
water vapour to the air
• Mixing air samples
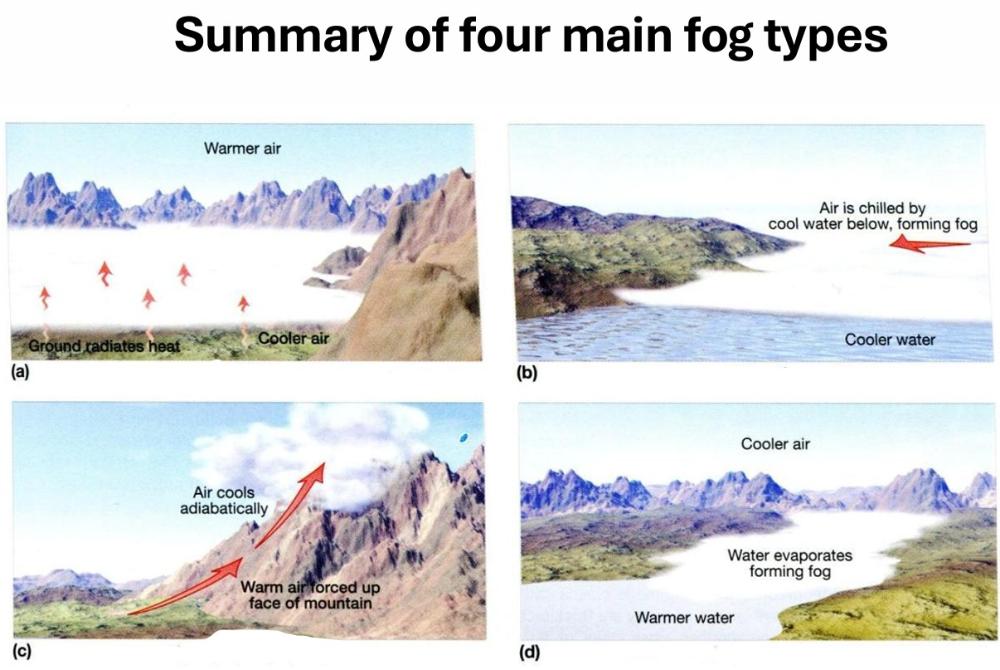
Name the four main fog types.