Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Climate and weather, clouds
front 1 What are the two ways water droplets form? Which never happens in nature? | back 1 Heterogenous and homogenous nucleation. Heterogenous nucleation only happens in labs. |
front 2 Hydrophilic aerosols are called what? | back 2 cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) |
front 3 ______________ nuclei dissolve in water. | back 3 Hygroscopic |
front 4 Is it easier or harder for water to evaporate from a solution? | back 4 Harder |
front 5 A droplet’s size is directly related to the relative | back 5 The curvature effect. The larger a droplet the harder it will be for it to evaporate. |
front 6 What are the three ways ice crystals form (with the help of ice nuclei). | back 6 • Directly from vapour if water vapour is deposited onto |
front 7 What condition does the presence of solutes change for forming water droplets? What is this effect called? | back 7 The relative humidity at which water droplets form which can be lower than 100%. The solute effect. |
front 8 In order for a droplet to increase in radius/diameter what must also increase to maintain the droplet/s existence? | back 8 The relative humidity |
front 9 What are the three favoured traits of an aerosol for condensation? | back 9 wettable (hydrophilic), large (so it's harder for the droplet to evaporate), and hygroscopic (dissolves in water) |
front 10 What condition does the presence of solutes change for forming water droplets? What is this effect called? | back 10 The relative humidity at which water droplets form which can be lower than 100%. The solute effect. |
front 11 Why is dust not a good CNN? | back 11 It doesn't dissolve |
front 12 When the water droplets in clouds start to precipitate their relative humidity's...? | back 12 Drop/decrease |
front 13 Why does the size of droplets tends to become uniform in a cloud? | back 13 Small droplets grow faster than big ones so all droplets get to be big and then kinda stop growing. |
front 14 Larger droplets freeze at slightly higher temperatures than their smaller counterparts, true or false? | back 14 True |
front 15 What temperature must it be in a cloud (in nature) for water droplets to freeze? | back 15 negative 40 degrees Celsius |
front 16 When the water droplets in clouds start to precipitate the cloud's relative humidity...? | back 16 Drops/decreases |
front 17 Favourable ice nuclei are _________ and ______________. Name two examples of ice nuclei. | back 17 large and insoluble,
|
front 18 What are the three ways ice crystals form (with the help of ice nuclei). | back 18 • Directly from vapour if water vapour is deposited onto |
front 19 What are the three ways to achieve saturation? | back 19 • Cooling the air to its dew-point temperature |
front 20 Clouds form due to...? | back 20 rising air |
front 21 What are the five basic mechanisms by which air rises to form clouds? | back 21 • Convection |
front 22 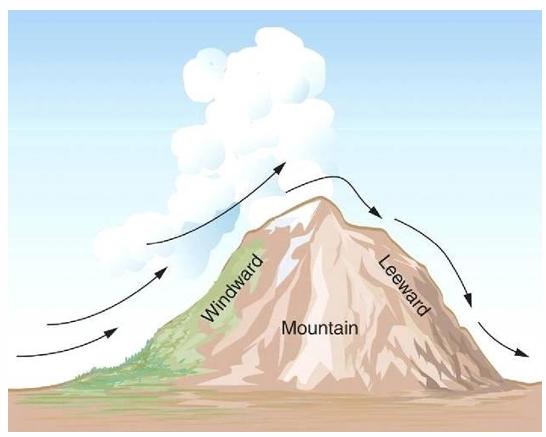 Which lifting mechanism is this? | back 22 Orographic lifting |
front 23 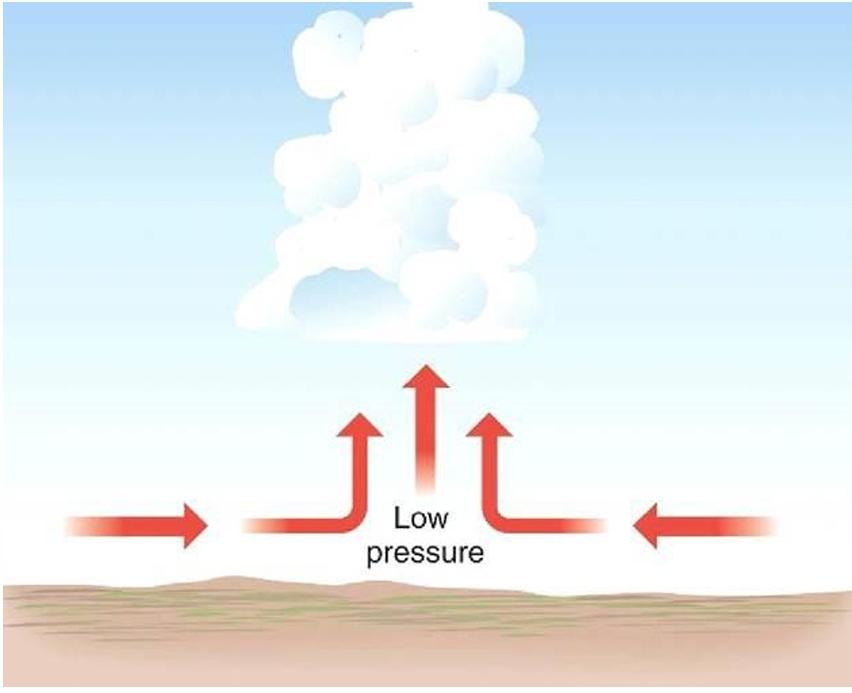 Which lifting mechanism is this? | back 23 Convergence |
front 24 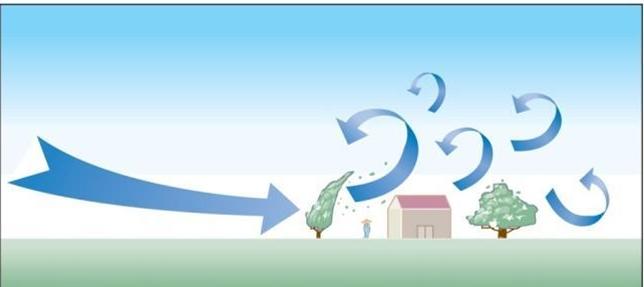 Which lifting mechanism is this? | back 24 Convection |
front 25 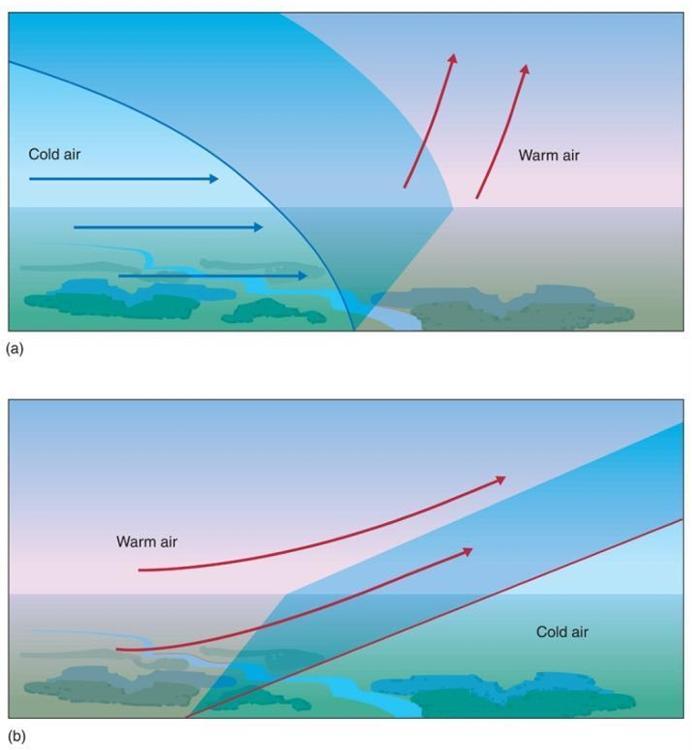 Which lifting mechanism is this? | back 25 Frontal lifting |
front 26 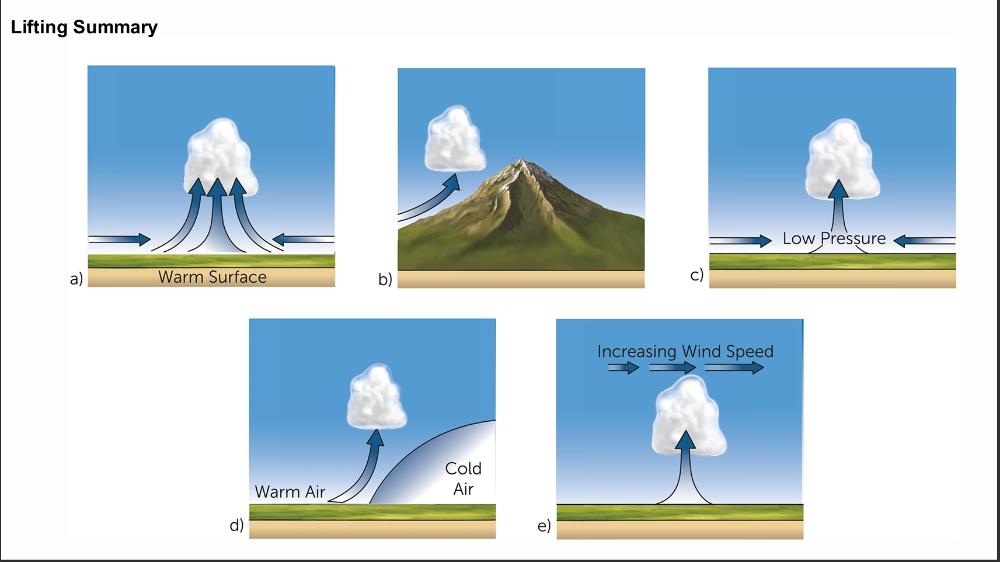 Name the lifting mechanism in b, c and d | back 26 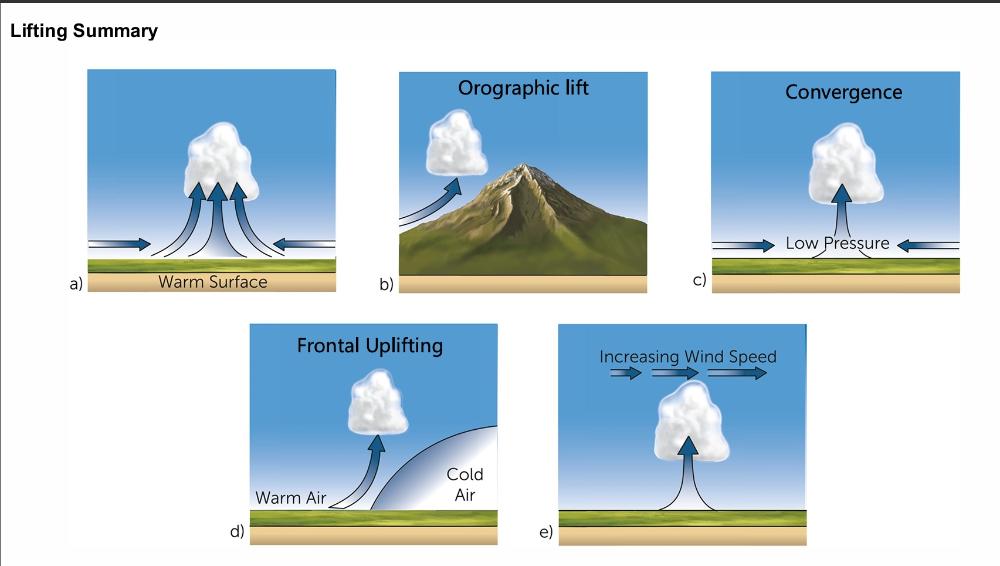 |
front 27 The classification of clouds is based on __________ and ___________. | back 27 shape and height |
front 28 Howard’s identification system uses Latin • Cumulus | back 28 • Cumulus (“heap”) |
front 29 ________ ____________ cause cirrus clouds to have ragged edges. | back 29 Ice crystals |
front 30 Of the classifications cirrus, cumulus and stratus which clouds are found only at high altitudes? | back 30 Cirrus |
front 31 Cumuliform Clouds (e.g., cumulus, stratocumulus, | back 31 unstable |
front 32 Cumulus humilis clouds are (small/large) and only last for a few minutes or hours. | back 32 small |
front 33 Fill in the blanks: Cumulus humilis -> time -> Cumulus _______________ -> rise until reaches a __________ ___________ -> ___________________ -> heavy precipitation | back 33 Cumulus humilis -> time -> Cumulus congestus -> rise until reaches a stable layer -> precipitation -> cumulonimbus -> heavy precipitation |
front 34 Stratiform Clouds (e.g., stratus, stratocumulus, | back 34 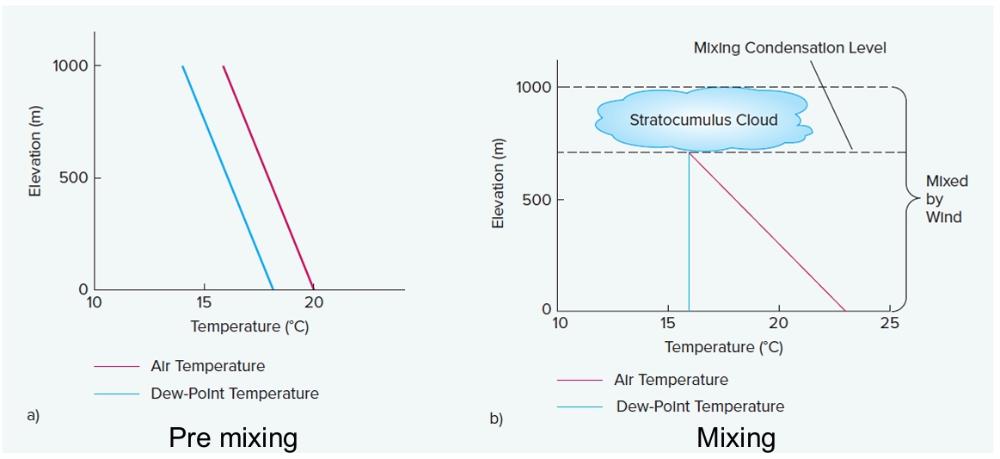 stable |
front 35 _______________ fog forms as air rising up a slope cools
adiabatically. Other fogs form by mixing or | back 35 Upslope, water vapour |
front 36 Radiation Fog forms when _____________ of radiation by the ___________ are mixed with water droplets through the mixed layer via ___________ __________. | back 36 emissions, surface, light wind |
front 37 Advection Fog forms due to conductive cooling as _________, ___________ air is advected over a cool surface | back 37 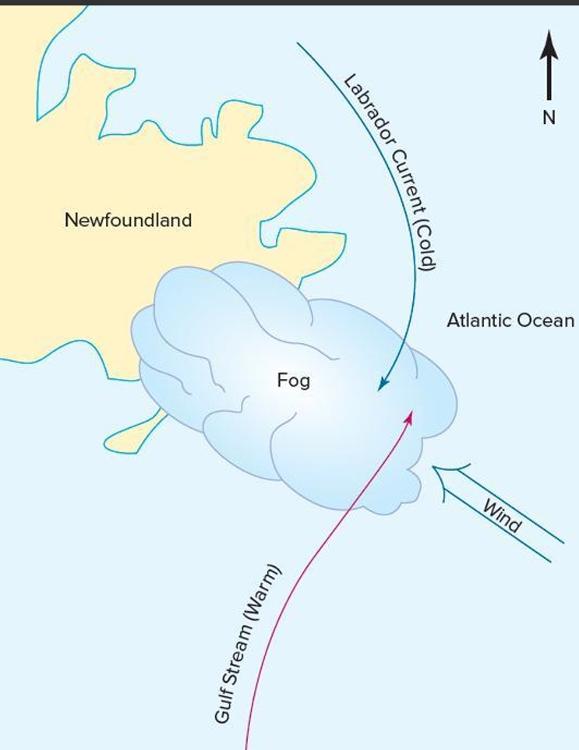 warm, moist |
front 38 What are the three ways to achieve saturation? | back 38 • Cooling the air to its dew-point temperature |
front 39 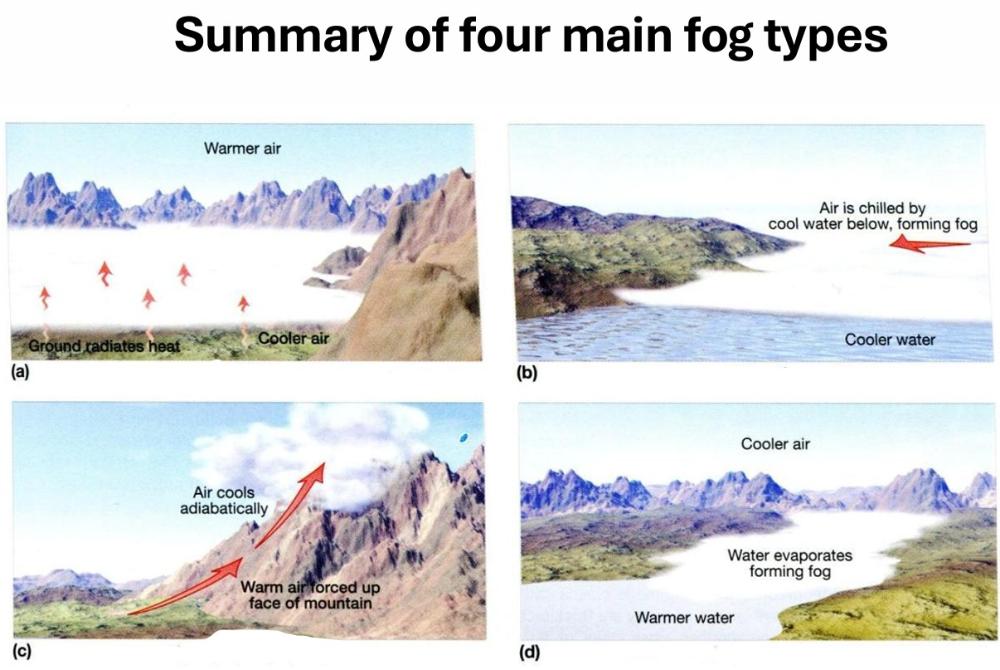 Name the four main fog types. | back 39 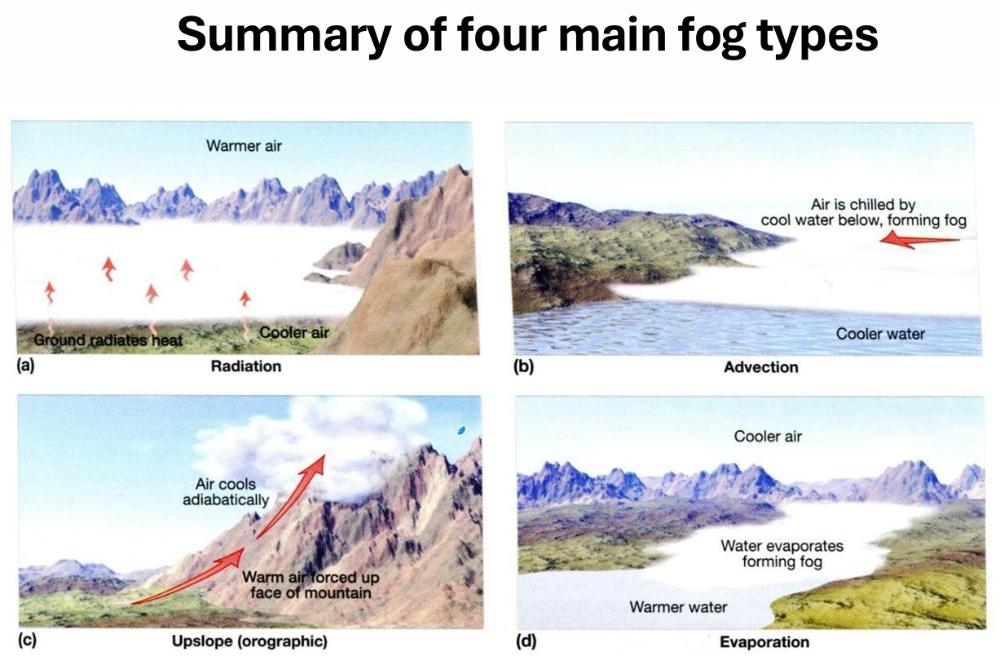 |