2.2.2 - Shapes of molecules ✓
Linear
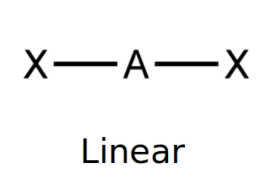
bond angle: 180o
2 electron pairs: 2 bonding, 0 lone.
Trigonal planar
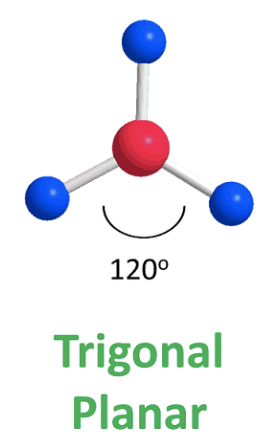
bond angle: 120o
3 electron pairs: 3 bonding, 0 lone
non-linear (bent) (one lone pair)
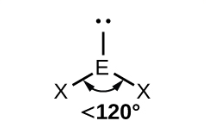
bond angle 118o
3 electron pairs: 2 bonding, 1 lone
Tetrahedral
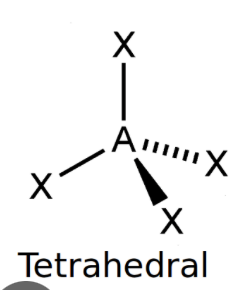
bond angle: 109.5o
4 electron pairs: 4 bonding, 0 lone
Trigonal Pyramidal
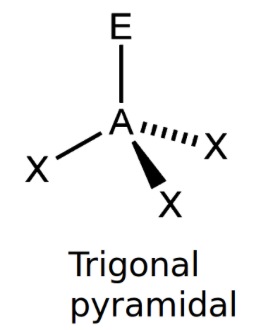
bond angle: 107o
4 electron pairs: 3 bonding, 1 lone
Non linear (2 lone pairs)
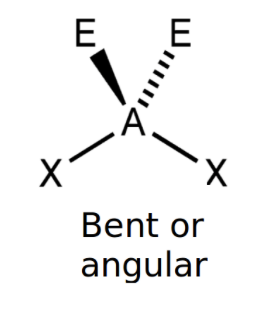
bond angle: 104.5o
4 electron pairs: 2 bonding, 2 lone
Trigonal bipyramidal
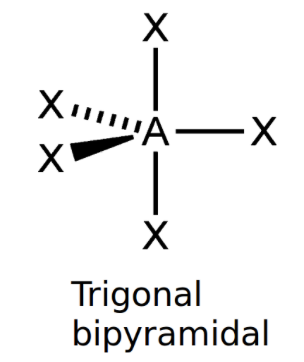
bond angle: 120o, 90o
5 electron pairs: 5 bonding, 0 lone
trigonal pyramidal or see saw
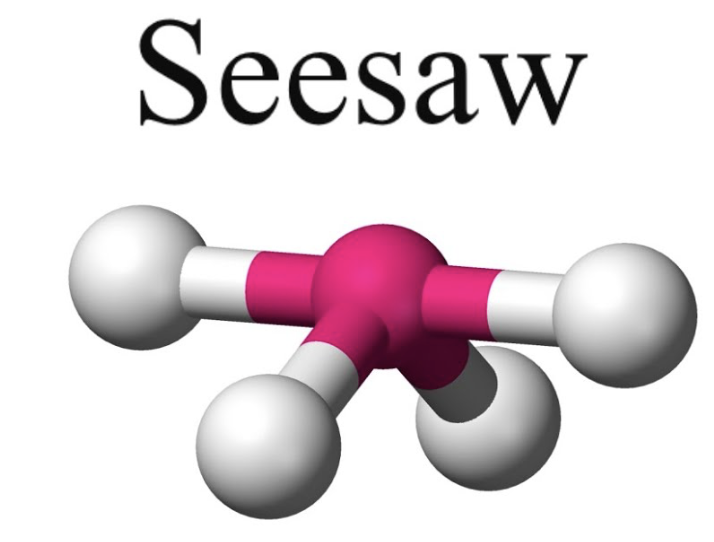
bond angle:119o, 89o
5 electron pairs: 4 bonding, 1 lone
Trigonal planar or t shape
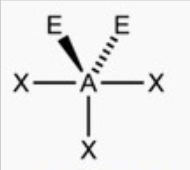
bond angle: 120o, 89o
5 electron pairs: 3 bonding, 2 lone
octahedral
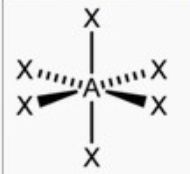
bond angle: 90o
6 electron pairs: 6 bonding, 0 lone
square pyramid
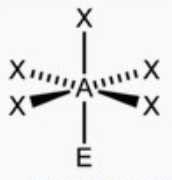
bond angle: 89o
6 electron pairs: 5 bonding, 1 lone
square planar
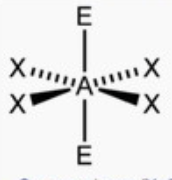
bond angle: 90o
6 electron pairs: 4 bonding, 2 lone
What is the VSEPR theory
a model used in chemistry for explaining and predicting the shapes of molecules and polyatomic ions:
- No. of electron pairs determine the shape
- Electron pairs repel each other to be as far apart as possible
- Arrangement of electrons minimise repulsion, holding the the bonded atoms in a definitive shape