Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
2.2.2 - Shapes of molecules ✓
front 1 Linear | back 1 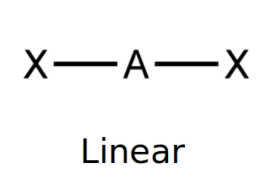 bond angle: 180o 2 electron pairs: 2 bonding, 0 lone. |
front 2 Trigonal planar | back 2 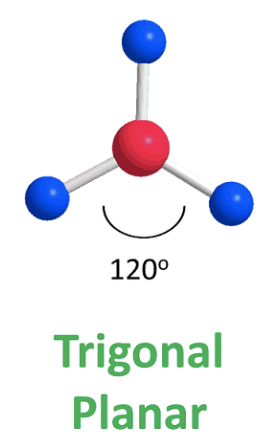 bond angle: 120o 3 electron pairs: 3 bonding, 0 lone |
front 3 non-linear (bent) (one lone pair) | back 3 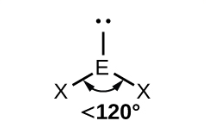 bond angle 118o 3 electron pairs: 2 bonding, 1 lone |
front 4 Tetrahedral | back 4 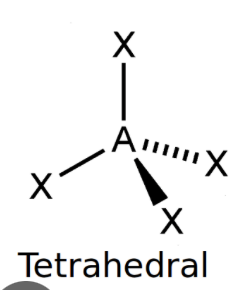 bond angle: 109.5o 4 electron pairs: 4 bonding, 0 lone |
front 5 Trigonal Pyramidal | back 5 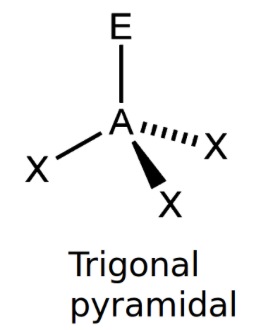 bond angle: 107o 4 electron pairs: 3 bonding, 1 lone |
front 6 Non linear (2 lone pairs) | back 6 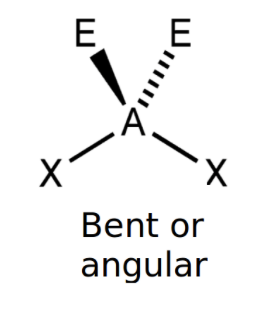 bond angle: 104.5o 4 electron pairs: 2 bonding, 2 lone |
front 7 Trigonal bipyramidal | back 7 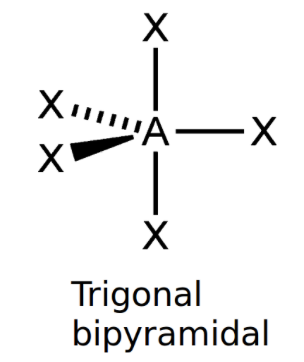 bond angle: 120o, 90o 5 electron pairs: 5 bonding, 0 lone |
front 8 trigonal pyramidal or see saw | back 8 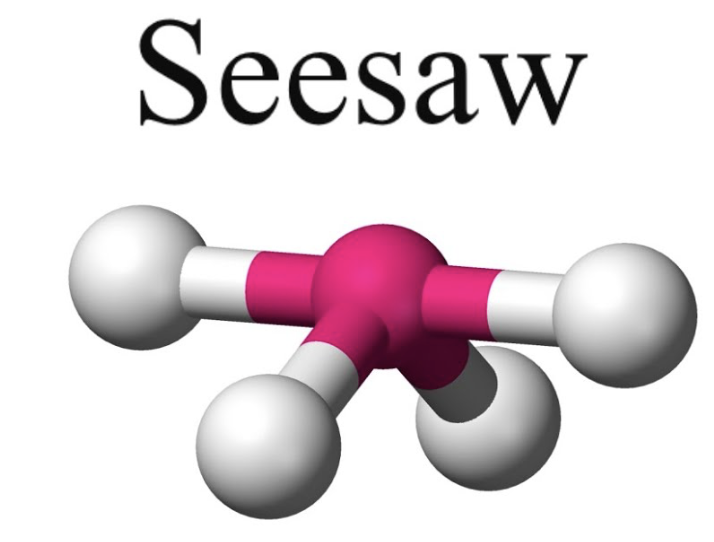 bond angle:119o, 89o 5 electron pairs: 4 bonding, 1 lone |
front 9 Trigonal planar or t shape | back 9 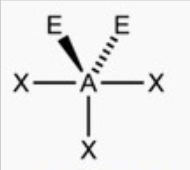 bond angle: 120o, 89o 5 electron pairs: 3 bonding, 2 lone |
front 10 octahedral | back 10 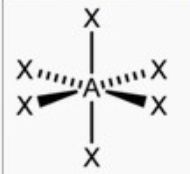 bond angle: 90o 6 electron pairs: 6 bonding, 0 lone |
front 11 square pyramid | back 11 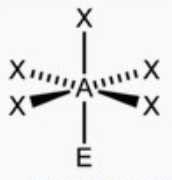 bond angle: 89o 6 electron pairs: 5 bonding, 1 lone |
front 12 square planar | back 12 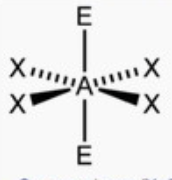 bond angle: 90o 6 electron pairs: 4 bonding, 2 lone |
front 13 What is the VSEPR theory | back 13 a model used in chemistry for explaining and predicting the shapes of molecules and polyatomic ions:
|