Skeletal System
What is the skeletal system composed of?
-Bones
-Cartilage
-Ligaments
What are the functions of bone?
-Support
-Protection
-Movement
-Hemopoiesis
-Storage of minerals
-Storage of energy reserves
What are long bones? (Be able to describe them and give an example)
-Longer than they are wide
-Most common
-Elongated, cylindrical shaft
Examples: Arms, legs, fingers...
What are short/irregular bones? (Be able to describe them and give an example)
-They are as long as they are wide
Examples: Carpals, tarsals, and sesamoid
What are flat bones? (Be sure to describe then and give an example)
-Flat, thin surfaces that may be slightly curved
-They provide surface are for muscle
Diaphysis
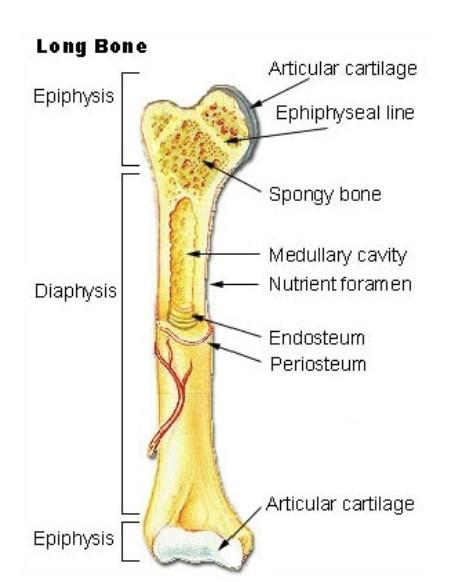
Elongated cylindrical shaft
Epiphysis
-End of the bone
-Proximal and distal
-Covered with articular cartilage (hyaline)
Medullary Cavity
The hollow cylindrical space within the diaphysis
Periosteum
A tough sheath that covers the outer surface of a bone
Outer layer is thick and tough
Inner layer is softer
Endosteum
Incomplete layers of cells that covers all internal surfaces of the bone (within the medullary cavity)
Blood supply
-Highly vascularized
-1 artery and 1 vein enter into the bone through the nutrient foramen
What are the two types of bone tissue?
Compact and Spongy
What is compact bone?
-Dense tissue
-Appears white, smooth, and solid
-Its structural unit is osteon
What are the parts of an osteon?
-Central canal
-Lamellae
-Lacuna
-Osteocyte
-Canaliculi
-Perforating Channels
What is the central canal (Haversian canal)?
-This is the central of the osteon that contains blood vessels and nerves
What is the Lamellae?
Concentric rings of bone matrix surrounding central canl
Circumferential lamellae
These are the rings immediately internal to the periosteum
Interstitial lamellae
These are between osteons that have been partially resorbed
What is lacuna?
Small space between lamellae where osteocytes live
What are osteocytes?
-Mature bone cells
-They help maintain the bone matrix and live in the lacuna
What are canaliculi?
These are small channels that connect the lacuna
What are perforating channels?
-Small channels that run through the lamella
-They contain blood vessels and nerves
What is spongy bone?
Location: Internal to the compact bone
Appearance: Porous
Erythrocytes are produced here
Trabeculae
-Open lattice of narrow rods and plates of bone
-space filled with marrow
Osteogenesis
The process of bone formation
This begins during weeks 8-12 of fetal development and starts off as mesenchyme tissue
Intermembranous ossification
this is the formation or developmental process of flat bones
(steps are in your power points)
Endochondral Ossification
This is the formation or development of long bones
(steps are in your power points)
Types of cells
-osteoprogenitor
-osteoblast
-osteocyte
-osteoclast
osteoprogenitor
stem cells
osteoblasts
immature bone cells
osteocyte
mature bone cells
osteoclast
specialized bone cells
Epiphyseal pate
-Zone 1: zone of resting cartilage
-Zone 2: zone of proliferating cartilage
-Zone 3: zone of hypertrophic cartilage
-Zone 4: zone of calcified cartilage
-Zone 5: zone of ossification
(go to power point for more information)
What are the two ways a facture can occur?
1.) An unusual stress on normal bone
2.) Normal stress on abnormal bone
How are fractures classified?
-Stress
-Pathologic
-Simple
-Compound
Stress
Thin break caused by increased, repetitive physical activity
Pathologic
bone that has been weakened by disease
Simple
does not pierce skin
Compound
pierces the skin
Hormones that increase bone tissue
-Growth hormones
-Thyroid hormones
-Calcitonin
-Sex hormones
Hormones that decrease bone tissue
-Parathyroid hormone
-Serotonin
-Sex hormones
-Glucocorticoids
Growth hormone
-stimulates liver to produce IGF (insulin-like growth factor)
-cause cartilage proliferation at epiphyseal plate
Thyroid hormone
stimulates the metabolic rate of osteoblasts
Calcitonin
promotes calcium deposition and inhibits osteoclasts
Sex Hormones (IBT and DBT)
stimulate osteoblast: promotes epiphyseal plate growth and closure
Parathyroid hormone
-increases blood calcium levels
-increases osteoclast activity
Serotonin
high levels of this hormone inhibits osteoprogenitor cells from differentiating into osteoblasts
Glucocorticoids
high levels increase bone loss