Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Skeletal System
front 1 What is the skeletal system composed of? | back 1 -Bones -Cartilage -Ligaments |
front 2 What are the functions of bone? | back 2 -Support -Protection -Movement -Hemopoiesis -Storage of minerals -Storage of energy reserves |
front 3 What are long bones? (Be able to describe them and give an example) | back 3 -Longer than they are wide -Most common -Elongated, cylindrical shaft Examples: Arms, legs, fingers... |
front 4 What are short/irregular bones? (Be able to describe them and give an example) | back 4 -They are as long as they are wide Examples: Carpals, tarsals, and sesamoid |
front 5 What are flat bones? (Be sure to describe then and give an example) | back 5 -Flat, thin surfaces that may be slightly curved -They provide surface are for muscle |
front 6 Diaphysis | back 6 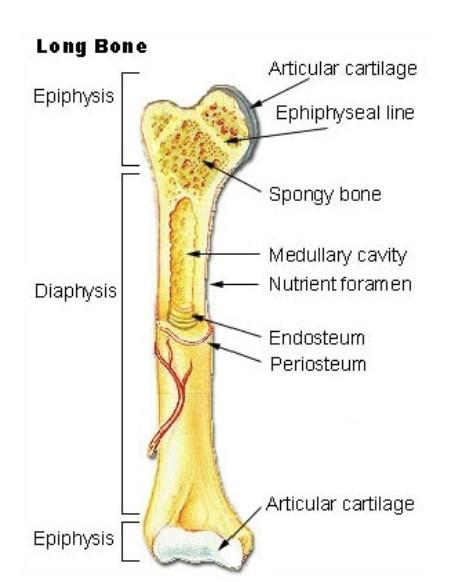 Elongated cylindrical shaft |
front 7 Epiphysis | back 7 -End of the bone -Proximal and distal -Covered with articular cartilage (hyaline) |
front 8 Medullary Cavity | back 8 The hollow cylindrical space within the diaphysis |
front 9 Periosteum | back 9 A tough sheath that covers the outer surface of a bone Outer layer is thick and tough Inner layer is softer |
front 10 Endosteum | back 10 Incomplete layers of cells that covers all internal surfaces of the bone (within the medullary cavity) |
front 11 Blood supply | back 11 -Highly vascularized -1 artery and 1 vein enter into the bone through the nutrient foramen |
front 12 What are the two types of bone tissue? | back 12 Compact and Spongy |
front 13 What is compact bone? | back 13 -Dense tissue -Appears white, smooth, and solid -Its structural unit is osteon |
front 14 What are the parts of an osteon? | back 14 -Central canal -Lamellae -Lacuna -Osteocyte -Canaliculi -Perforating Channels |
front 15 What is the central canal (Haversian canal)? | back 15 -This is the central of the osteon that contains blood vessels and nerves |
front 16 What is the Lamellae? | back 16 Concentric rings of bone matrix surrounding central canl |
front 17 Circumferential lamellae | back 17 These are the rings immediately internal to the periosteum |
front 18 Interstitial lamellae | back 18 These are between osteons that have been partially resorbed |
front 19 What is lacuna? | back 19 Small space between lamellae where osteocytes live |
front 20 What are osteocytes? | back 20 -Mature bone cells -They help maintain the bone matrix and live in the lacuna |
front 21 What are canaliculi? | back 21 These are small channels that connect the lacuna |
front 22 What are perforating channels? | back 22 -Small channels that run through the lamella -They contain blood vessels and nerves |
front 23 What is spongy bone? | back 23 Location: Internal to the compact bone Appearance: Porous Erythrocytes are produced here |
front 24 Trabeculae | back 24 -Open lattice of narrow rods and plates of bone -space filled with marrow |
front 25 Osteogenesis | back 25 The process of bone formation This begins during weeks 8-12 of fetal development and starts off as mesenchyme tissue |
front 26 Intermembranous ossification | back 26 this is the formation or developmental process of flat bones (steps are in your power points) |
front 27 Endochondral Ossification | back 27 This is the formation or development of long bones (steps are in your power points) |
front 28 Types of cells | back 28 -osteoprogenitor -osteoblast -osteocyte -osteoclast |
front 29 osteoprogenitor | back 29 stem cells |
front 30 osteoblasts | back 30 immature bone cells |
front 31 osteocyte | back 31 mature bone cells |
front 32 osteoclast | back 32 specialized bone cells |
front 33 Epiphyseal pate | back 33 -Zone 1: zone of resting cartilage -Zone 2: zone of proliferating cartilage -Zone 3: zone of hypertrophic cartilage -Zone 4: zone of calcified cartilage -Zone 5: zone of ossification (go to power point for more information) |
front 34 What are the two ways a facture can occur? | back 34 1.) An unusual stress on normal bone 2.) Normal stress on abnormal bone |
front 35 How are fractures classified? | back 35 -Stress -Pathologic -Simple -Compound |
front 36 Stress | back 36 Thin break caused by increased, repetitive physical activity |
front 37 Pathologic | back 37 bone that has been weakened by disease |
front 38 Simple | back 38 does not pierce skin |
front 39 Compound | back 39 pierces the skin |
front 40 Hormones that increase bone tissue | back 40 -Growth hormones -Thyroid hormones -Calcitonin -Sex hormones |
front 41 Hormones that decrease bone tissue | back 41 -Parathyroid hormone -Serotonin -Sex hormones -Glucocorticoids |
front 42 Growth hormone | back 42 -stimulates liver to produce IGF (insulin-like growth factor) -cause cartilage proliferation at epiphyseal plate |
front 43 Thyroid hormone | back 43 stimulates the metabolic rate of osteoblasts |
front 44 Calcitonin | back 44 promotes calcium deposition and inhibits osteoclasts |
front 45 Sex Hormones (IBT and DBT) | back 45 stimulate osteoblast: promotes epiphyseal plate growth and closure |
front 46 Parathyroid hormone | back 46 -increases blood calcium levels -increases osteoclast activity |
front 47 Serotonin | back 47 high levels of this hormone inhibits osteoprogenitor cells from differentiating into osteoblasts |
front 48 Glucocorticoids | back 48 high levels increase bone loss |