Neuropsychopharmacology Exam 1 Review
ADD/ADHD cause and symptoms
- Causes distraction and impulsivity
- Caused by insufficient inhibition of the DRD4 gene which uses dopamine as an inhibitory NT
Define DRD4 gene
- Dopamine receptor D4 gene
- D4 is the receptor subtype
What is the PFC and what's so important about it regarding ADD/ADHD
- Pre frontal cortex
- Center of executive function
- Dopamine receptors are concentrated here
- Used as an inhibitory signal when dopamine is binded
- Suppresses impulsive behavior
Explain the DRD4-7R mutation
- In a normal population, people have about 2-11 repeats
- at exactly 7 repeats, this mutation causes ADD/ADHD
- Which causes D4 receptor binding with dopamine insensitivity
Define ADD and ADHD and what the difference and similarities are
- Attention deficit disorder and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
- The big difference is ADD does not include hyperactivity as a Behavorial side effect
- Main similar deficits are inability to suppress impulses due to insufficient inhibition, attention switching, focused attention, and selective attention
What is selective attention?
- Brain only pays attention to selective stimuli
Is ADD/ADHD a behavioral disorder or a neurological disorder
- Neurological due to broken brain circuitry (insufficient inhibition)
What are the differences between fear and anxiety (list them)
- Fear
- short term, acute, suddenly or unexpectedly, can potentially cause bodily harm, evoke a fearful response, FFF response, highly energizing, energy expensive
- Anxiety
- Long term, chronic, ongoing and expected, may cause bodily harm, physiological response, shut down body and brain, CRF release in brain, suppress NGF/suppress neuro-development
What is FFF
- flight, fright, or fight response
What is CRF
- Corticotropic releasing factor
- The hormone that causes stress
What is NGF
- Nerve growth factor
- which leads neuro-development
Importance and info about the amygdala
- Fear processing center
- Releases GABA NT to suppress fear
- If not enough GABA is released, fear will persist, leading to anxiety disorder
What experiment was done to test the cause and effect of anxiety disorders
- Rats were stressed out for a prolonged period of time
- The prolonged stress led to anxiety disorders
- The rats offspring had anxiety disorders as well, without any exposure to external stressors
Define HPA Axis
- Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
- Neuro-endocrine system that functions with neurohormones
- Uses feedback system to regulate
- If dysregulated, mental disorders and affective disorders can occur
Draw and label the brains thalamus, hypothalamus, and pituitary as well as the relative direction/position of the adrenal glands to the brain
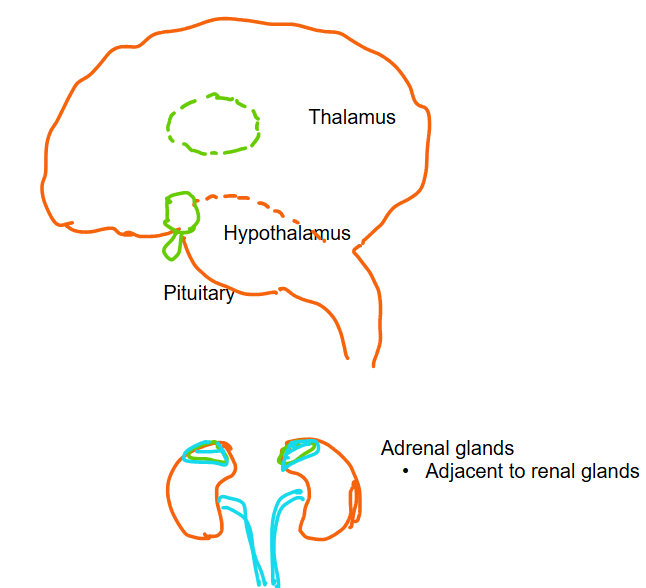
What is the anterior hypothalamus and what does it do
- Controls pituitary using hormones
- For acute stress
- releases adrenaline
- For chronic
stress
- releases CRF and suppresses NRF
What is the posterior hypothalamus and what does it do?
- Controls pituitary by using neurotransmitters
What does the pituitary do?
- Regulates adrenal glands via hormones
What is the adrenal cortex and what does it do? What about the adrenal medulla?
- Adrenal cortex: releases cortosoid to suppress the immune system
- Adrenal medulla: Releases adrenaline to stimulate the body
Draw and explain the HPA axis with labels and arrows depicting function
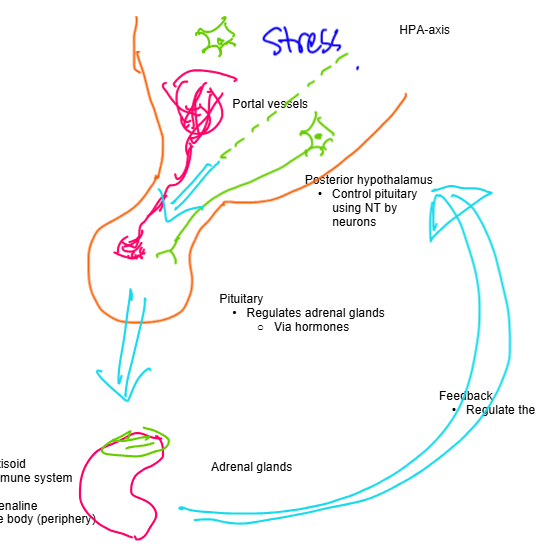
What does feedback from the adrenal glands do
- works to regulate the hypothalamus
List the differences between acute stress and chronic stress
- Acute stress
- Released hormone is epinephrine (adrenaline)
- FFF response
- Pupils dilate
- Increased sweating, breathing rate, and very energy expensive
- Heightened awareness (vigilance, focused attention on specific stimuli)
- Chronic
stress
- Hormone released is CRF which will suppress NGF
- stress response
- CNS begin to shut down at CRF release
- suppress immune system and become prone to sickness and infection
Does sex have any effect on CRF? if so, what are they?
- Sensitivity of CRF hormone depends on sex
- Women are 10x more sensitive to CRF
- Men require higher level of signals to respond
Explain the importance of estrogen
- Estrogen is a class of hormones
- E2 is estradiol which is most potent and released during ovarian cycle
- Estrogen regulates the sensitivity of the 5-HT receptor
- Makes the receptor more sensitive
- Becomes insensitive without estrogen leading to depressive states and PMS
Draw menstrual cycle graph
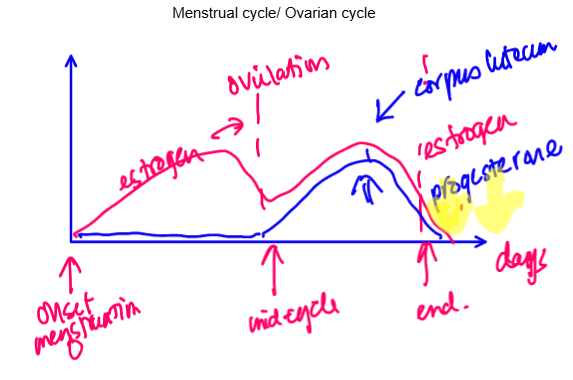
What does progesterone do during womens cycle
- Progesterone binds with GABA receptor neurosteroid binding site to suppress fear
- Without progesterone, no suppression of amygdala or fear, leads to anxiety symptoms
When does estrogen peak on menstrual cycle
Luteal phase
most sensitive to estrogen and progesterone peaks as well
What happens at the end of the menstrual cycle
Progesterone and estrogen levels drop and anxiety and depressive symptoms may occur
Hypothalamus function
- Regulates physiological drives such as hunger, thirst, and sex drives
- Regulates energy needs to keep body homeostasis
Hypothalamic nucleus importance
- Intracellular conc of estrogen
- Orient animal toward male mating partner
- In female brain
- Similar in gay men’s brain
- In male brain
- Lower estrogen conc
What is the motivational system
- Motivates behavior into action by sending signals to the motor initiation system
- Helps to prepare for future similar behavior to satisfy a goal
- Establishes learning
- need->action->goal->repeated, expected behavior to achieve same outcome as before
- From external cues
- Increases chance of survival
What is the behavioral avoidance system?
- Drives animal to avoid something
- fear (ie. predation: fear leads to fearful outcome of FFF response; fight the predator, avoid the predator, or become petrified of predator)