front 1 ADD/ADHD cause and symptoms | back 1 - Causes distraction and impulsivity
- Caused by
insufficient inhibition of the DRD4 gene which uses dopamine as an
inhibitory NT
|
| back 2 - Dopamine receptor D4 gene
- D4 is the receptor
subtype
|
front 3 What is the PFC and what's so important about it regarding ADD/ADHD | back 3 - Pre frontal cortex
- Center of executive function
- Dopamine receptors are concentrated here
- Used as an
inhibitory signal when dopamine is binded
- Suppresses
impulsive behavior
|
front 4 Explain the DRD4-7R mutation | back 4 - In a normal population, people have about 2-11 repeats
- at exactly 7 repeats, this mutation causes ADD/ADHD
- Which causes D4 receptor binding with dopamine insensitivity
|
front 5 Define ADD and ADHD and what the difference and similarities are | back 5 - Attention deficit disorder and attention deficit hyperactivity
disorder
- The big difference is ADD does not include
hyperactivity as a Behavorial side effect
- Main similar
deficits are inability to suppress impulses due to insufficient
inhibition, attention switching, focused attention, and selective
attention
|
front 6 What is selective attention? | back 6 - Brain only pays attention to selective stimuli
|
front 7 Is ADD/ADHD a behavioral disorder or a neurological disorder | back 7 - Neurological due to broken brain circuitry (insufficient
inhibition)
|
front 8 What are the differences between fear and anxiety (list them) | back 8 - Fear
- short term, acute, suddenly or unexpectedly, can
potentially cause bodily harm, evoke a fearful response, FFF
response, highly energizing, energy expensive
- Anxiety
- Long term, chronic, ongoing and expected, may
cause bodily harm, physiological response, shut down body and
brain, CRF release in brain, suppress NGF/suppress
neuro-development
|
| back 9 - flight, fright, or fight response
|
| back 10 - Corticotropic releasing factor
- The hormone that causes
stress
|
| back 11 - Nerve growth factor
- which leads neuro-development
|
front 12 Importance and info about the amygdala | back 12 - Fear processing center
- Releases GABA NT to suppress
fear
- If not enough GABA is released, fear will persist,
leading to anxiety disorder
|
front 13 What experiment was done to test the cause and effect of anxiety disorders | back 13 - Rats were stressed out for a prolonged period of time
- The prolonged stress led to anxiety disorders
- The rats
offspring had anxiety disorders as well, without any exposure to
external stressors
|
| back 14 - Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
- Neuro-endocrine
system that functions with neurohormones
- Uses feedback
system to regulate
- If dysregulated, mental disorders
and affective disorders can occur
|
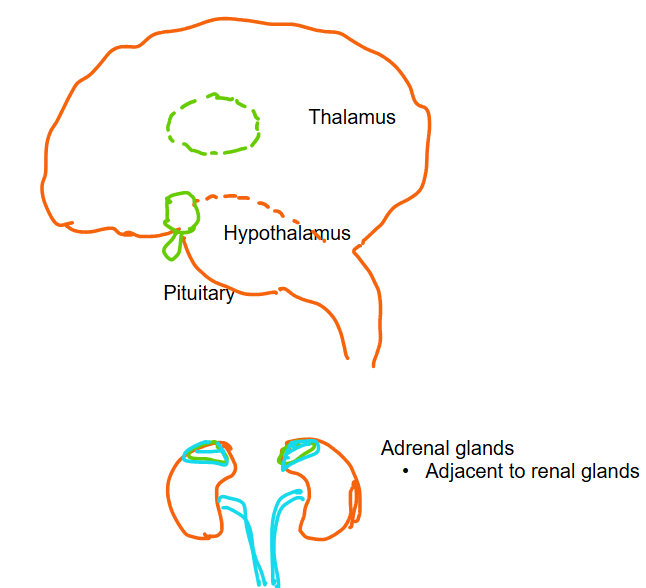
front 15 Draw and label the brains thalamus, hypothalamus, and pituitary as
well as the relative direction/position of the adrenal glands to the brain | |
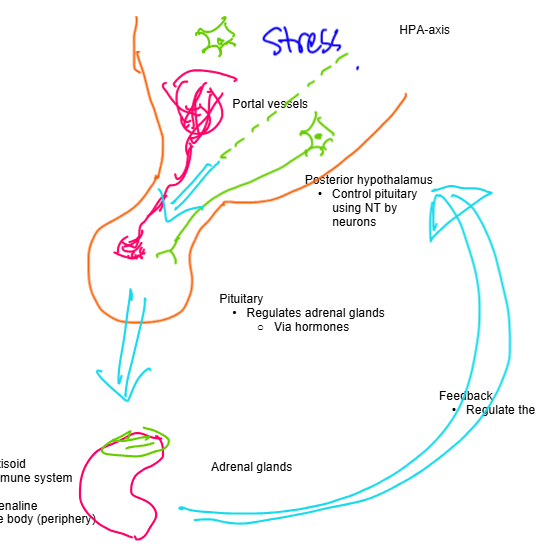
front 16 What is the anterior hypothalamus and what does it do | back 16 - Controls pituitary using hormones
- For acute stress
- For chronic
stress
- releases CRF and suppresses NRF
|
front 17 What is the posterior hypothalamus and what does it do? | back 17 - Controls pituitary by using neurotransmitters
|
front 18 What does the pituitary do? | back 18 - Regulates adrenal glands via hormones
|
front 19 What is the adrenal cortex and what does it do? What about the
adrenal medulla? | back 19 - Adrenal cortex: releases cortosoid to suppress the immune
system
- Adrenal medulla: Releases adrenaline to stimulate the
body
|
front 20 Draw and explain the HPA axis with labels and arrows depicting function | |
front 21 What does feedback from the adrenal glands do | back 21 - works to regulate the hypothalamus
|
front 22 List the differences between acute stress and chronic stress | back 22 - Acute stress
- Released hormone is epinephrine
(adrenaline)
- FFF response
- Pupils dilate
- Increased sweating, breathing rate, and very energy
expensive
- Heightened awareness (vigilance, focused
attention on specific stimuli)
- Chronic
stress
- Hormone released is CRF which will suppress NGF
- stress response
- CNS begin to shut down at CRF
release
- suppress immune system and become prone to
sickness and infection
|
front 23 Does sex have any effect on CRF? if so, what are they? | back 23 - Sensitivity of CRF hormone depends on sex
- Women are
10x more sensitive to CRF
- Men require higher level of
signals to respond
|
front 24 Explain the importance of estrogen | back 24 - Estrogen is a class of hormones
- E2 is estradiol which
is most potent and released during ovarian cycle
- Estrogen regulates the sensitivity of the 5-HT receptor
- Makes the receptor more sensitive
- Becomes
insensitive without estrogen leading to depressive states and
PMS
|
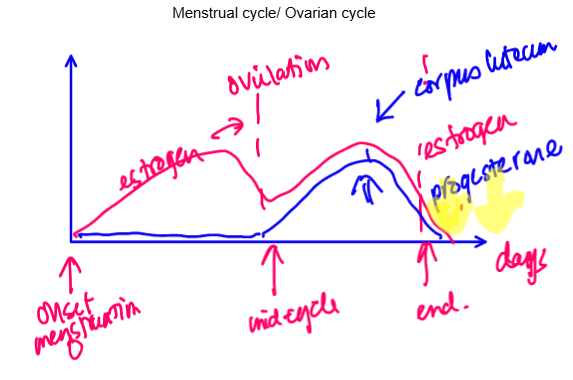
front 25 Draw menstrual cycle graph | |
front 26 What does progesterone do during womens cycle | back 26 - Progesterone binds with GABA receptor neurosteroid binding site
to suppress fear
- Without progesterone, no suppression of
amygdala or fear, leads to anxiety symptoms
|
front 27 When does estrogen peak on menstrual cycle | back 27 Luteal phase
most sensitive to estrogen and progesterone peaks as well |
front 28 What happens at the end of the menstrual cycle | back 28 Progesterone and estrogen levels drop and anxiety and depressive
symptoms may occur |
| back 29 - Regulates physiological drives such as hunger, thirst, and sex
drives
- Regulates energy needs to keep body homeostasis
|
front 30 Hypothalamic nucleus importance | back 30 - Intracellular conc of estrogen
- Orient animal toward
male mating partner
- In female brain
- Similar
in gay men’s brain
- In male brain
|
front 31 What is the motivational system | back 31 - Motivates behavior into action by sending signals to the motor
initiation system
- Helps to prepare for future similar
behavior to satisfy a goal
- Establishes learning
- need->action->goal->repeated, expected behavior to
achieve same outcome as before
- From external cues
- Increases chance of survival
|
front 32 What is the behavioral avoidance system? | back 32 - Drives animal to avoid something
- fear (ie. predation:
fear leads to fearful outcome of FFF response; fight the
predator, avoid the predator, or become petrified of
predator)
|