Molecular Toxicology Exam 1 Prep (Exam Review Based)
Define toxicology
Study of the adverse affects of xenobiotics
Why is toxicology important and what did it form the basics of
- formed basics of therapeutics, experimental medicine, environmental health, and fundamental science
- It's important in risk assessment for chemical compounds, medicines, food, etc
Who is Paracelsus
- father of modern toxicology (1493-1541)
- Chemical toxic and therapeutic properties are dependent on the dose
- Specifically studied water intoxication
What is thalidomide
- was a morning sickness medicine
- caused more than 10,000 children to be born with birth defects in Europe and Africa
- Led to discovery of placenta-crossing by Francis Kelsey
Who is Francis Kelsey?
Discovered placenta-crossing
What is the FDC Act?
- Federal food Drug Cosmetic Act (1938)
- Substances had to be tested for safety of human consumption
- Led to the founding of the FDA (food & drug administration)
What is the FIFRA Act
- Federal Insecticide, Rodenticide, and Fungicide Act (1947)
- States that a non-food/drug item must be effective and safe
What was the importance of sulfanimide in toxicology history?
- Antifreeze
- Was added to children's medicine to make it sweet before FDC Act
What was Agent Orange
- TCDD (dioxin)
- Carcinogen used during times of war as a jungle defoliant
What did prohibition lead to?
- Substances like methanol, lead, and triorthocresyl phosphate being added to alcohol to pass as medicine
- Triorthocresyl phosphate was added to rum to make Jamaican ginger
Toxicokinetics vs toxicodynamics
- Kinetics: concentration of compound in your body
- Very dependent on bioavailability as it has to be able to take up the toxin to have effect as well as uptake and transport
- Dynamics: determines the effect of the toxin
- Dependent on binding type and induction of toxic effects
Define toxic response and the three different types
the phenotypic outcomes of the toxicity of a chemical
- three types: Adaptation, stress response, and toxic response
What is the adaptation toxic response?
- physiological response to a "consistent" exposure
- Is possible within a given exposure/time range
- If exposure increases in time or concentration, it becomes toxic
What is the stress response toxic response?
- cellular stress
- Intended to limit the damage to the cell and tissue
- often non-specific
- Variety of conditions: oxidative stress, energy homeostasis, heat stress, and reactive metabolites
What is hormesis? What is the hormetic region?
- biological phenomenon where a toxic substance in low doses could be beneficial
- The hormetic region is the thin region between the substance being helpful and harmful to the receiving organism
How are toxicants delivered into the body?
- Main routes: skin, ingestion (GI tract), respiratory
- Lesser routes: injection, maternal transfer (placenta), bite, thorn, abrasion
What is an uptake barrier and give examples
- mechanism your body has to prevent drug uptake
- cell membrane, epithelial cells of GI tract, respiratory surface aka lung, and body surface
What factors affect the distribution of a toxicant
- How easy it moves across cell membranes
- lipophilicity, movement through ion channels, active or passive transport
2. Characteristics of the epithelium
- mainly epithelial thickness
3. Toxin concentration
- more concentration=faster delivery
4. Structure of capillary beds
- how much vasculature (fenestrated (extremely porous) or no)
5. Does it bind reversibly
What factors oppose distribution?
- Plasma proteins: bind to make toxin unavailable
- Barriers: (ie. BBB) keep toxins out
- Long term storage: (ie. fat cells) stores toxins to mitigate damage
- Binding proteins: (ie.metallothionine) to bind and attempt to make toxins useless
- Metabolism and elimination: break down toxin and excrete out of the body
What is lipophilicity?
How hydrophobic or fat soluble is the compound
What is the big difference between organic compounds and their inorganic form?
Their degree of lipophilicity is different
What is the molecular importance of compounds like MeHG---Cystine
This is a specific example of a compound that partakes in molecular mimicry
- in this specific one, MeHg----Cystine can mimic methionine and cross the BBB to cause neurological issues
What was an important example of reversible binding from the lecture?
Cadmium
- Compound induces production of metallothionine in the liver
- The Cd enters the liver and binds reversibly to the metallothionine
- It runs through your blood stream into your kidney
- Detaches from the metallothionine
- Causes tumor growth in your kidney
What are the four mechanisms of transmembrane transport?
- Diffusion
- Facilitated Diffusion
- Active transport
- Endocytosis
Briefly explain diffusion
- movement of small lipophilic compounds
- most toxins and compounds pass through this mechanism
Briefly explain facilitated diffusion
- High transport rate thanks to carrier proteins and ion channels (aka mediators)
- highly selective transport option and often temperature dependent
- The transport rate can be inactivated or inhibited (ie.metals)
Briefly explain active transport
- Requires ATP-pumps
- Na-K-ATPase
- often important in transport of material out of cells
What are xenobiotic transport pumps
- actively transport material out of cells
- extremely important from liver and kidneys
- Part of the ABC transporter family
What are p-glycoproteins?
- Form of active transport
- MDR protein
- Encoded by the MDR-1 gene
- Very little specificity; most lipophilic compounds can bind/be moved
- PGP/MDR pumps out chemo drugs from tumor cells which renders the drug ineffective
- Inhibitors are given to keep drug in the tumor cells
What is endocytosis? Explain and draw
- ATP expensive transport/dissolution of large molecule
Drawing: should include macrophage removing stuck molecule in lipid bilayer, dissolution of the molecule, and repair of the bilayer
What is frustrated phagocytosis? Explain and draw examples (2).
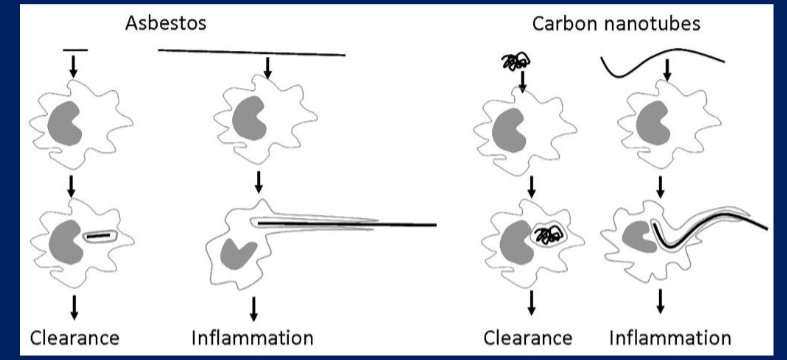
- Explanation should include more macrophages coming to attempt to digest large molecule and being unsuccessful and emitting reactive oxygen species (ROS)
What leads to cell specific toxicity and give an example
- differences in cellular transport as it determines how, what form, and where the toxicant enters the cell
- not all cells express specific transporter
MPTP (heroin)
- MPTP is the byproduct of heroin synthesis/metabolization
- leads to parkinsons like symptoms (loss of dopaminergic neurons)
- mimics dopamine enough to use dopamine transporters in brain
What are the basics of phase 1 metabolism
- Chemical modifications that introduce a functional group on a xenobiotic that provides sites for phase II metabolism
- "putting a handle on it"
- Takes place in smooth ER of a hepatocyte
- Major enzymes are cytochrome P450 (CYP) or mixed function oxygenase (MFO)
What are the basics of phase 2 metabolism
- Synthetic reaction of a xenobiotic with an endogenous substance that results in a product in which is more water soluble and will enhance excretion
- "Something grabs the handle"
- Neutralization of active metabolic intermediates
- Cytoplasm in hepatocyte is the area where reaction takes place
- Important enzymes: GST, EH, UDP-GTS, ST
What phase is the enzyme GST in and what does it do?
- GST is in phase II
- takes phase I metabolite and adds glutathionine (protein)
What phase is the enzyme EH in and what does it do?
- Phase II
- Detoxifies epoxides
What phase is UDP-GTS (or UGT) in and what does it do?
- Phase II
- adds glucuronic acid
What phase is ST in and what does it do?
- Phase II
- adds sulfer groups
What is tamoxifen and what is it an example of?
- Cancer drug
- Causes different types of cancer in rats
- ST enzyme example differences in rats and humans
What was the in class example of biotransformation with UGT enzyme?
- NSAID pain relievers (like ibuprofen)
What was the in class example of bioactivation with UGT enzyme?
- 2-napthylamine
- intermediate formed is more toxic
- Toxicity of the compound is determined by your bladder pH
- Acidic: connection w/acid is unstable which produces protonated compounds in the bladder which leads to bladder cancer
- basic: excreted normally
What is biotransformation?
- change in chemical structure through metabolism
- the parent compound structure is altered
What is bioactivation?
- change in the chemical structure through metabolism that makes the compound MORE reactive/toxic
- not all that are transformed are activated
- Does not occur in all tissues
- has different toxicokinetics and mechanisms
- May be species specific
What was the lecture example when discussing bioactivation?
- 4-ipomeanol
- fungal derived toxin that causes bronchiolar necrosis in most mammals but not humans
- Most mammals produce CYP4B1 enzymes in lungs which means the toxic response is in the lungs
- For humans CYP1A2 and CYP3A4 in liver so the toxic reaction for us is in our liver
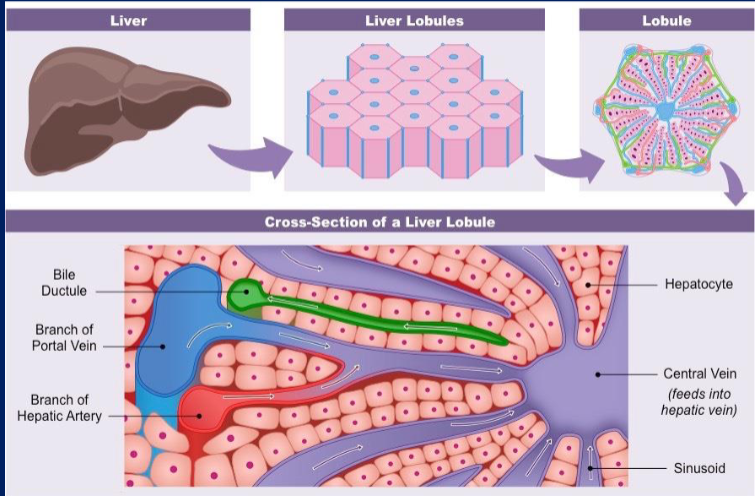
Break down the components of the liver in 4 drawings stopping at the portal triad, make sure to label (slide 4 of metabolism ppt).
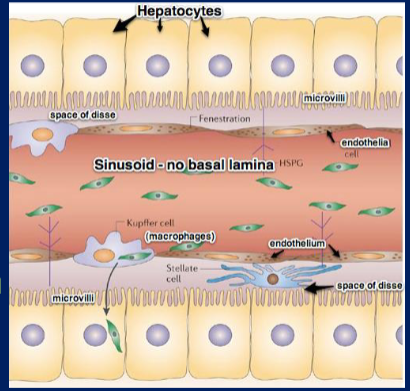
Draw and label the interior of the sinusoids