Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Molecular Toxicology Exam 1 Prep (Exam Review Based)
front 1 Define toxicology | back 1 Study of the adverse affects of xenobiotics |
front 2 Why is toxicology important and what did it form the basics of | back 2
|
front 3 Who is Paracelsus | back 3
|
front 4 What is thalidomide | back 4
|
front 5 Who is Francis Kelsey? | back 5 Discovered placenta-crossing |
front 6 What is the FDC Act? | back 6
|
front 7 What is the FIFRA Act | back 7
|
front 8 What was the importance of sulfanimide in toxicology history? | back 8
|
front 9 What was Agent Orange | back 9
|
front 10 What did prohibition lead to? | back 10
|
front 11 Toxicokinetics vs toxicodynamics | back 11
|
front 12 Define toxic response and the three different types | back 12 the phenotypic outcomes of the toxicity of a chemical
|
front 13 What is the adaptation toxic response? | back 13
|
front 14 What is the stress response toxic response? | back 14
|
front 15 What is hormesis? What is the hormetic region? | back 15
|
front 16 How are toxicants delivered into the body? | back 16
|
front 17 What is an uptake barrier and give examples | back 17
|
front 18 What factors affect the distribution of a toxicant | back 18
- lipophilicity, movement through ion channels, active or passive transport 2. Characteristics of the epithelium - mainly epithelial thickness 3. Toxin concentration - more concentration=faster delivery 4. Structure of capillary beds - how much vasculature (fenestrated (extremely porous) or no) 5. Does it bind reversibly |
front 19 What factors oppose distribution? | back 19
|
front 20 What is lipophilicity? | back 20 How hydrophobic or fat soluble is the compound |
front 21 What is the big difference between organic compounds and their inorganic form? | back 21 Their degree of lipophilicity is different |
front 22 What is the molecular importance of compounds like MeHG---Cystine | back 22 This is a specific example of a compound that partakes in molecular mimicry
|
front 23 What was an important example of reversible binding from the lecture? | back 23 Cadmium
|
front 24 What are the four mechanisms of transmembrane transport? | back 24
|
front 25 Briefly explain diffusion | back 25
|
front 26 Briefly explain facilitated diffusion | back 26
|
front 27 Briefly explain active transport | back 27
|
front 28 What are xenobiotic transport pumps | back 28
|
front 29 What are p-glycoproteins? | back 29
|
front 30 What is endocytosis? Explain and draw | back 30
Drawing: should include macrophage removing stuck molecule in lipid bilayer, dissolution of the molecule, and repair of the bilayer |
front 31 What is frustrated phagocytosis? Explain and draw examples (2). | back 31 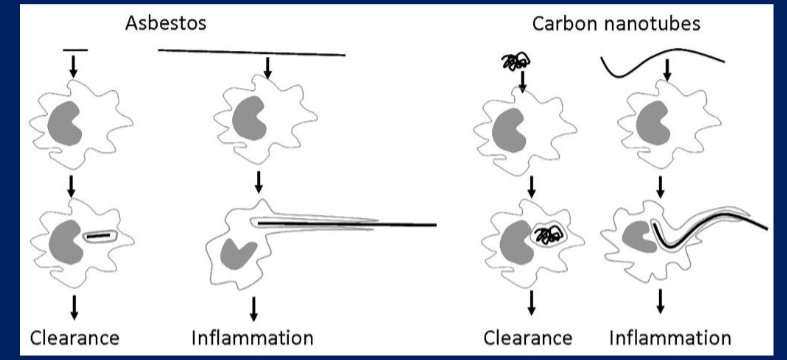
|
front 32 What leads to cell specific toxicity and give an example | back 32
MPTP (heroin)
|
front 33 What are the basics of phase 1 metabolism | back 33
|
front 34 What are the basics of phase 2 metabolism | back 34
|
front 35 What phase is the enzyme GST in and what does it do? | back 35
|
front 36 What phase is the enzyme EH in and what does it do? | back 36
|
front 37 What phase is UDP-GTS (or UGT) in and what does it do? | back 37
|
front 38 What phase is ST in and what does it do? | back 38
|
front 39 What is tamoxifen and what is it an example of? | back 39
|
front 40 What was the in class example of biotransformation with UGT enzyme? | back 40
|
front 41 What was the in class example of bioactivation with UGT enzyme? | back 41
|
front 42 What is biotransformation? | back 42
|
front 43 What is bioactivation? | back 43
|
front 44 What was the lecture example when discussing bioactivation? | back 44
|
front 45 Break down the components of the liver in 4 drawings stopping at the portal triad, make sure to label (slide 4 of metabolism ppt). | back 45 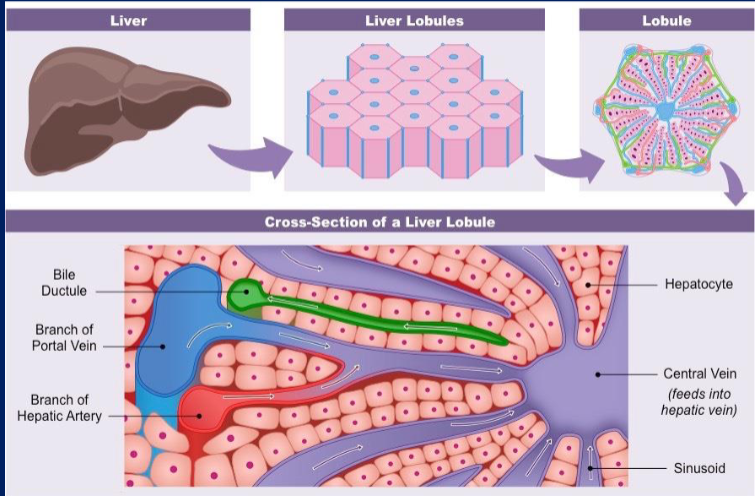 |
front 46 Draw and label the interior of the sinusoids | back 46 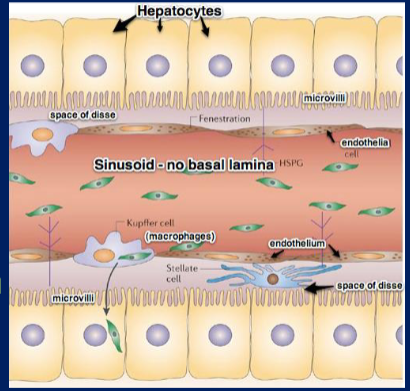 |