igcse economics
Definition of PPC (Production Possibilities Curve)
A graphical representation that illustrates the maximum combination of two goods that can be produced by an economy with all the available resources.
Definition of demand curve
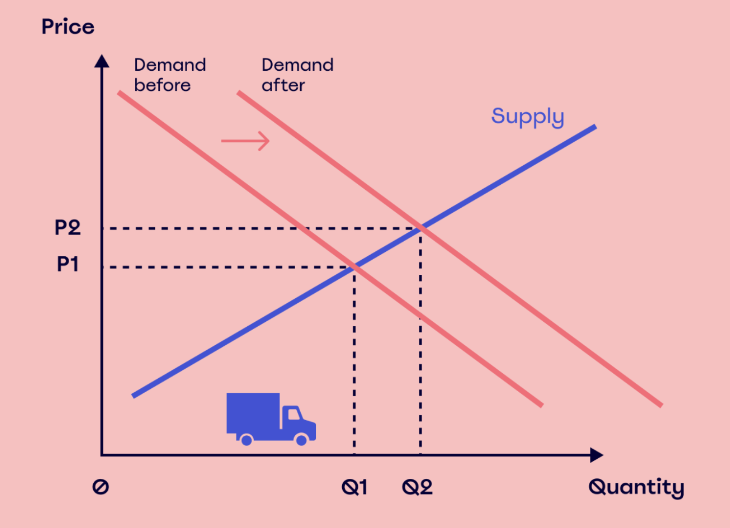
A demand curve is a graphical representation of the price and quantity demanded (QD) by consumers. Image shows increase
Definition of demand
Demand is the want and willingness of consumers to buy a good or services at a given price.
Resources
Resources are the inputs required for the production of goods and services.
The fundamental economic problem is...
The fundamental economic problem is that there is a scarcity of resources to satisfy all human wants and needs. There are finite resources and unlimited wants.
Scarcity
A lack of recourses. the basic economic problem where finite resources are available in relation to infinite human wants and needs.
Finite resources
Finite resources are those that exist in limited quantities and cannot be replaced at the rate they are being used.
Economic goods
Economic goods are those which are scarce in supply and so can only be produced with an economic cost and/or consumed with a price.
Free goods
Free goods are those which are abundant in supply, usually referring to natural sources such as air or sunlight.
the factors of production
The factors of production are the resources used to produce goods and services.
Land is defined
Land is defined as all natural resources used in the production of goods and services.
Labour refers to
Labour refers to the human effort, both physical and mental, that is used in the production of goods and services.
Capital is defined as
Any human-made resource used to produce goods and services.
Enterprise
The ability to take risks and bring together the various factors of production to produce goods or services.
Opportunity cost
The next best alternative that is sacrificed when a decision is made.
Points on PPC
If below the economy is inefficient, because it is producing less than what it can.
Outside the PPC, is unattainable because it is beyond the scope of the economy’s existing resources.
If shifts to left means economy shrinks, if to right means economy grows.
Economy
An area where people and firms produce, trade, and consume goods and services.
Microeconomics and decision makers
Microeconomics is the study of individual markets and sections of the economy, rather than the economy as a whole.
Microeconomic decision makers are producers and consumers.
Macroeconomics and decision makers
Macroeconomics is the study of an entire economy, as a whole.
Macroeconomic decisions are made by the government of the particular economy
Resource allocation and basic economics questions
The way in which economies decide what goods and services to provide, how to produce them and who to produce them for.
In bold are called ‘the basic economic questions’.
Market
Market is an arrangement that brings together all the producers and consumers of a good or service, so they may engage in exchange.
Market equilibrium
Market equilibrium refers to the point where the quantity of a good or service demanded by consumers equals the quantity supplied by producers, resulting in a stable market price.
Market disequilibrium
A situation where the quantity of a good or service demanded by consumers does not equal the quantity supplied by producers.
Results in too much demand or excess supply
How a market system works
A market system works to allocate scarce resources through the forces of demand and supply (the price mechanism)
price mechanism
The process where prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand in a free market.
Definition of effective demand
Effective demand is where the willingness to buy is backed by the ability to pay.
Quantity demanded.
The effective demand for a particular good or service.
Individual demand
Individual demand is the demand from one consumer.
market demand
The total (aggregate) demand for the product.
aggregate demand
The total demand for all goods and services in an economy at a given overall price level.
Supply curve drawing and definition of supply
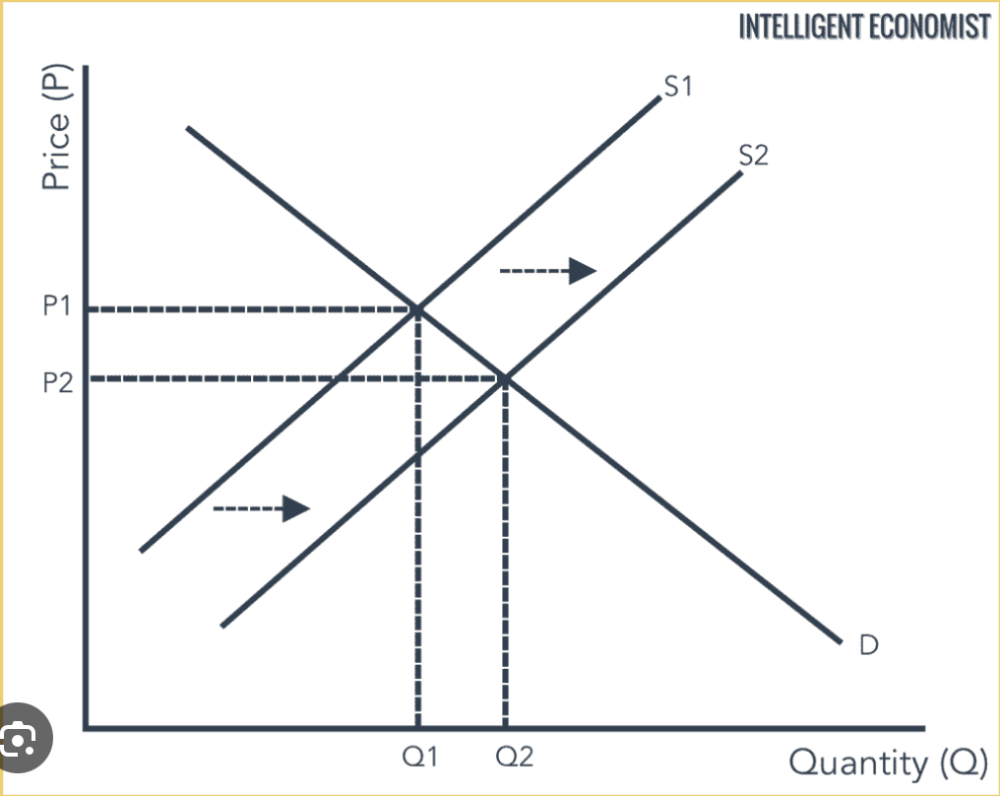
The amount of a good/service that a producer is willing and able to supply at a given price in a given time period. Image shows increase.
A shift to the left or right is caused by any factor other than change in price. A change in price causes a contraction or extension up or down the line.
Causes of supply curve shift
- Changes in the cost of production
- Changes in technology
- Government taxes and subsidies and regulation
- Change in climate (natural commodities such as coffee)
- Changes in the price of a substitute
- Changes in the numbers of competitors
Definition of PED (Price Elasticity Of Demand)
A numerical measure of the responsiveness of the quantity demanded to changes in its price.
PED (of a product) = % change in quantity demanded / % change in price.
Types of PED (Price Elasticity Of Demand)
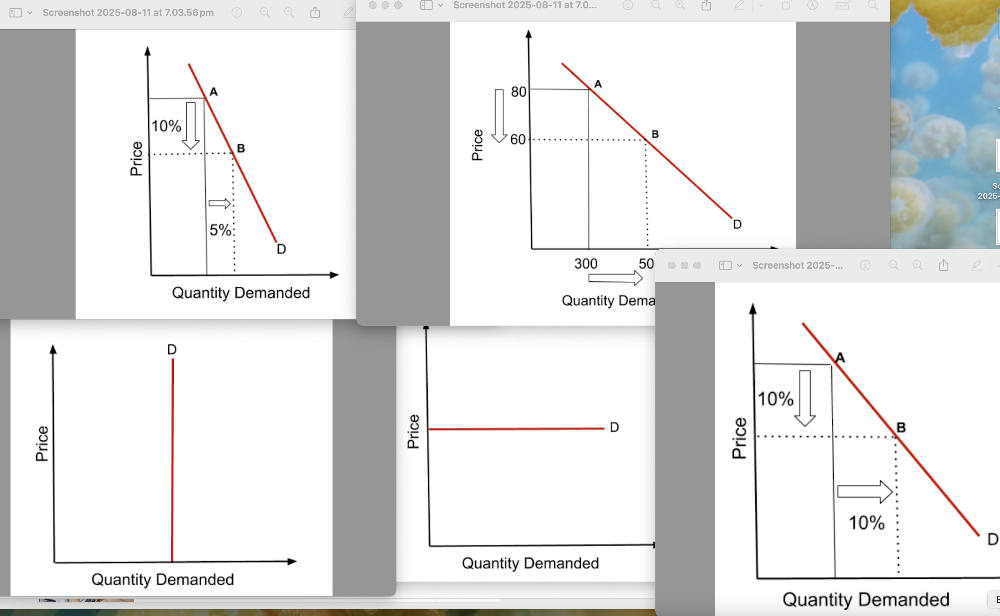
When the % change in quantity demanded is lesser than the % change in price, it is said to have a price inelastic demand. and vice versa.
When the % change in demand and price are equal, that is value is 1, it is called unitary price elastic demand.
When the price changes have no effect on demand whatsoever, it is said to have a perfect price inelastic demand. Their elasticity is 0.
When the quantity demanded changes without any changes in price itself, it is said to have an infinitely price elastic demand.
What effect PED and PES
PED: Number of substitutes, wether luxury or necessity, time it is increased for.
PES:
- Time of production: If the product can be quickly produced, it will have a price elastic supply as the product can be quickly supplied at any price,
- Mobility of the factors of production
- Availability of raw materials
- Ability to store goods
- Spare capacity if prices increase for a product and there is capacity to produce more in the factories that make those products, then supply will be elastic.
Definition of PES (Price Elasticity Of Supply)
A numerical measure of the responsiveness of its quantity supplied it to changes in its price.
PES of a product = %change in quantity supplied / % change in price.
Types of PES (Price Elasticity Of Supply)
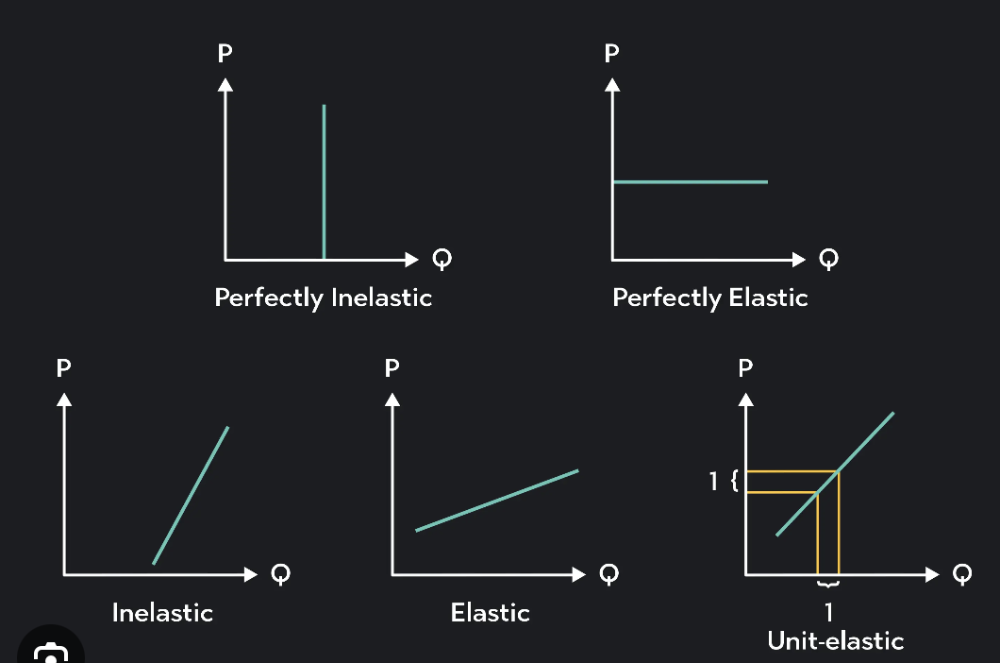
price elastic supply, price inelastic supply, perfectly price inelastic supply, infinitely price elastic supply and unitary price elastic supply.
Definition of market economic system
An economy that has no government intervention in the allocation of resources and distribution of goods/services.
The key terms associated with market failure: public good, merit good, demerit good, social benefits, external benefits, private benefits, social costs, external costs, private costs. definitions
- Public Good: Public goods are goods that are beneficial to society but which will not be provided by private firms.
- Merit Good: A good or service that is beneficial to society and would be under consumed in a free market because people do not fully recognise its benefits.
- Demerit Good:A good or service that is harmful to society and would be over consumed in a free market because consumers do not fully recognize its negative costs.
- Private Benefit:The direct benefit received by the individual or firm that produces or consumes the good or service.
- External Benefit:The benefit received by a third party who was not directly involved in the production or consumption of a good or service..
- Social Benefit:The total benefit to society, which is the sum of the private benefit and the external benefit
- Private Cost:The direct cost experienced by the individual or firm that produces or consumes the good or service.
- External Cost: The cost imposed on a third party who was not directly involved in the production or consumption of the good or service.
- Social Cost:The total cost to society, which is the sum of the private cost and the external cost.
Definition of the mixed economic system
A blend of a market economy and a planned economy, where the public and private sector all have a role in owning and allocating resources.
Characteristics of money
Durable, portable, recognisable, identical, and dividable.
Functions of money
-Medium of exchange (selling and buying)
-Store of value (when saved)
-Standard of deferred payments (allowing borrowing and spending)
-Unit of account (measure of value of goods)
Money definition and legal tender
Money - a universally accepted medium of exchange.
Legal tender - Any form of payment that must be accepted by law to settle a debt.
.
The role and importance of central banks and commercial banks for government, producers and consumers.
Central Banks
- For the Government: Banker, economic advisor, manages national debt, banker to commercial banks and lender of last resort (to banks if temporary shortage of cash), prints and destroys money.
- For Producers: monetary policy (sets interest rates and controls the money supply), financial system stability.
- For Consumers: price stability (manage inflation through monetary policy to protect the value of money and purchasing power), oversees commercial banks (protect consumers' savings and ensure fair banking practices)
Commercial Banks
- For the Government: facilitate Transactions
- For Producers: Business services (Offer loans to fund operations and expansion). Facilitate payments.
- For Consumers: Savings & Investments, Loans & Credit, Payment Systems, exchange foreign currency, look after valuables
factors affecting an individual’s choice of occupation
: Wage and non-wage factors.
wage factors - higher pay, overpay, bonuses, commision
Non wage - job satisfaction, type of work (manual, non-manual etc), work conditions, hours, holidays, pensions, fringe benefits, job security, prospect of promotion, size of firm, location
wage determination
Demand and supply of labour in jobs, trade unions, minimum wage, discrimination, skilled workers and esteem of job.
Advantages and disadvantages for workers, firms and the economy of specialisation
For Workers
-
Advantages:
- Skill acquisition: Workers can become highly skilled and efficient at a specific task.
- Higher wages: Due to increased productivity and specialization, skilled workers may command higher wages.
- Reduced training time: Less time is needed to train workers for specific tasks compared to comprehensive training.
-
Disadvantages:
- Monotony and boredom: Repetitive tasks can lead to decreased job satisfaction and motivation.
- Limited skill development: Workers may not gain a wide range of skills, making them less adaptable.
- Difficulty finding new work: Specialization in one task makes it difficult to find other types of employment if they lose their job.
For Firms
-
Advantages:
- Increased productivity and output: Workers become faster and more efficient at their specialized tasks.
- Higher quality products: Focusing on a single task often leads to improved quality.
- Lower costs: Reduced training costs, efficient use of tools, and higher productivity contribute to lower production costs.
- Economies of scale: Specialization allows for mass production, which can lower average costs.
-
Disadvantages:
- High staff turnover: Workers seeking more interesting opportunities may leave, increasing the firm's turnover rate.
- Boredom-related productivity drops: Reduced motivation from repetitive work can decrease output.
- Difficulty adapting to change: Firms may struggle to adapt to technological changes or new products if workers lack diverse skills.
For the Economy
-
Advantages:
- Economic growth: Increased overall productivity and output can lead to economic growth
definition of a trade union
Trade Union is a group of workers who join together to protect their interests and work for better wages and working conditions using collective bargaining.
the role of trade unions
Engaging in collective bargaining on wages, working hours and working conditions; protecting employment; and influencing government policy, take industrial action, provide training schemes.
things effecting the role of trade unions
-Strong economy means industries are doing well so can afford to treat workers well, they will also require workers and there will be low unemployment so they will want to retain workers and make it easier to recruit more.
-higher number of member, higher bargaining power, more funds and not many non-union member to replace union members with.
-if contains high skilled members as harder to replace
-consistent demand for product workers produce
-favorable gov legislation
The advantages and disadvantages of trade union activity for workers, firms and the government.
For Workers
-
Advantages:
- Collective Bargaining Power: Unions represent workers as a group, increasing their ability to negotiate for better pay, benefits, and working conditions than an individual could achieve.
- Improved Conditions: Unions advocate for safer, healthier, and fairer work environments.
- Job Security: Unions can provide support and representation to members facing dismissal or disputes with employers.
-
Disadvantages:
- Membership Fees: Workers often pay union dues, which are a direct financial cost.
- Risk of Industrial Action: Workers can be involved in strikes or other industrial actions, leading to lost wages.
- Limited Individual Autonomy: Union policies may sometimes conflict with individual worker priorities or preferences.
For Firms
-
Advantages:
- Improved Productivity: Better working conditions and job security can lead to a more motivated and productive workforce.
- Streamlined Communication: Unions can provide a single point of contact for workers, simplifying communication with a large workforce.
- Reduced Labour Turnover: Improved conditions can decrease employee turnover, saving firms on recruitment and training costs.
-
Disadvantages:
- Higher Labor Costs: Unions can negotiate for higher wages, increasing operating costs for firms.
- Disruption from Industrial Action: Strikes, overtime bans, and "work to rule" actions can significantly disrupt business operations.
- Reduced Flexibility: Unions may make it harder to dismiss unproductive workers or promote the most talented individuals based on merit.
For the Government
-
Advantages:
- Promo
internal and external economies and diseconomies of scale
-
Internal Economies of Scale:
- Technical Economies: Using more advanced technology or specialized machinery that is too expensive for small firms.
- Purchasing Economies: Buying materials in bulk to get a lower price per unit.
- Financial Economies: Accessing cheaper finance or loans due to being a large, established firm.
- Managerial Economies: Specializing management roles to improve efficiency and reduce waste.
-
External Economies of Scale are cost advantages
enjoyed by all firms in a particular industry or region as the
entire industry or region grows.
- Improved Infrastructure: Development of better roads, ports, or communication networks benefits all firms in the area.
- Skilled Labor Pool: A growing industry creates a pool of skilled workers available to all firms.
- Specialized Suppliers: The emergence of nearby specialized suppliers can reduce costs for multiple firms.
- Positive Externalities: A supportive business environment or reputation for the region can benefit all businesses there.
-
Internal Diseconomies of Scale are challenges
within the firm's own operations as it grows.
- Managerial Problems: Difficulty in managing a large workforce.
- Communication: Information becomes harder to distribute efficiently across a larger organisation.
-
External Diseconomies of Scale
- Increased Input Costs: A rapidly growing industry may lead to higher demand for raw materials, driving up their prices.
- Congestion: Increased activity in an area can lead to traffic congestion, making transportation and deliveries more difficult.
- Skilled Labor Scarcity: As the industry expand
The advantages and disadvantages of small firms, the challenges facing small firms and reasons for their existence.
Small firms thrive on close customer relationships, personalized services, and quick adaptability to market changes, offering unique products.
However, they face challenges like limited financial resources, difficulty attracting experienced staff, intense competition from larger firms, and vulnerability to economic downturns.
Small firms exist because of small market sizes, consumer preference for personalized services, owner preference for remaining small, lack of capital for expansion.
Definition, example, and advantages and disadvantages of the three types of mergers.
Horizontal Merger
- Definition:Two or more companies in the same industry, often direct competitors, merge.
- Example:The merger of HP and Compaq in 2011.
-
Advantages:
- Increased Market Share & Power, Economies of Scale.
- Expanded Reach: Access to new customer bases and markets.
-
Disadvantages:
- Reduced Flexibility: Larger size can lead to slower innovation and more bureaucratic processes.
- Potential for Monopolies, Integration Issues: Culture clashes and difficulties in combining operations can arise.
Vertical Merger
- Definition:A merger between companies operating at different stages of the same supply chain.
- Example:Disney acquiring Pixar.
-
Advantages:
- Supply Chain Control: Better control over the production of key inputs or the distribution of final products.
- Cost Reduction, Reduced Reliance on external suppliers or distributors.
-
Disadvantages:
- Loss of Flexibility: May restrict a company's options if it can't easily switch to other suppliers or distributors.
- Management Complexity: Integrating different stages of the supply chain can be difficult and expensive.
- Requires Expertise: Entering a new stage of production or distribution may require new skills and knowledge.
Conglomerate Merger
- Definition:A merger between two businesses that operate in completely unrelated industries.
- Example : General Electric:
- Advantages
- Spread risk, Business Expansion into new markets.
- Financial Benefits: Increased size can lead to better access to capital, and diversified revenue streams can make the company more appealing to investors, Economies of Scale.
- Cultural Clashes, harder to manage, Integration Complexity: Merging disparate operations, product lines, and corporate structures can be a difficult and complex process, Reduced Efficiency:
Factors that effect the demand for factors of production
Demand for the product, the price of different factors of production, their availability and their productivity.
\
Total cost (TC), average total cost (ATC), fixed cost FC), variable cost (VC), average fixed cost (AFC), average variable cost (AVC) definition and calculations and diagram
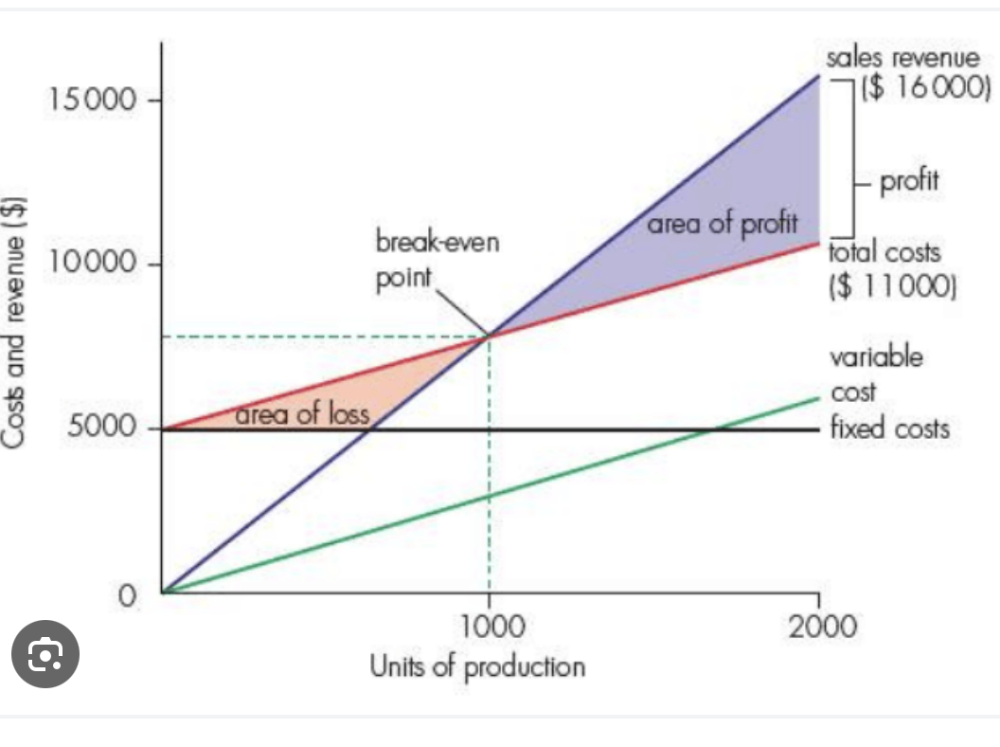
Fixed costs (FC) are costs that do not change with the level of output.
Variable costs (VC) are costs that change with output.
Total cost (TC) is the combination of FC and VC.
Average total cost (ATC) is TC divided by output, or total costs per unit of output.
Average fixed cost (AFC) is FC divided by output, or fixed costs per unit of output.
Average variable cost (AVC) is VC divided by output, or variable costs per unit of output.
Total revenue (TR) and average revenue (AR) definition and calculations
Total Revenue (TR) is the total income a firm receives from selling all its output, calculated as Price × Quantity.
Average Revenue (AR) is the revenue per unit sold, found by dividing Total Revenue by the quantity sold, meaning AR is equal to the price per unit.
objectives of firms 4
Survival, social welfare, profit maximisation and growth.
Characteristics, advantages and disadvantages of a monopoly.
- Single Seller:There is only one producer or firm in the market.
- High Barriers to Entry:It is difficult or impossible for other firms to enter the market, due to reasons like natural barriers (e.g., control of a resource) or artificial ones (e.g., patents).
- Price Maker:The monopolist controls the supply of the good or service, allowing it to set the market price.
Advantages include economies of scale, potentially invest in innovation but disadvantages include higher prices, reduced choice, potential for inefficiency (X-inefficiency), and no consumer sovereignty.
the role of government
Locally, nationally and internationally.
At a local level, governments manage services like local infrastructure, sanitation, and housing to meet community needs.
Nationally, they focus on macroeconomic goals such as controlling inflation, reducing unemployment, promoting economic growth, and ensuring social welfare through policies like taxes, subsidies, and infrastructure projects.
Internationally, governments engage in diplomacy, negotiate trade agreements, provide foreign aid, and manage international trade through restrictions or open markets to foster global relations and economic stability.
the macroeconomic aims of government.
Reasons behind the choice of aims and the criteria that governments set for each aim. Possible conflicts between aims.
1. Economic Growth
- Criteria:The primary criterion is a positive and sustainable annual increase in the Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- Goal:To raise the living standards of the population and improve overall prosperity.
2. Full Employment/Low Unemployment
- Criteria:A target unemployment rate that is low and stable, typically considered to be in the low single digits (e.g., 2-4%).
- Goal:To maximize the use of the nation's labor force, reduce poverty, and ensure that most people who want to work can find a job, max Govs revenue.
3. Stable Prices/Low Inflation
- Criteria:A low, stable, and predictable annual inflation rate, often around 2%.
- Goal:To prevent the erosion of purchasing power, maintain the confidence of consumers and businesses, and provide a stable environment for economic planning and investment.
4. Balance of Payments Stability
- Criteria:The government aims for a sustainable balance of payments, where export revenues generally equal or exceed spending on imports.
- Goal:To avoid excessive debt accumulation from running large, persistent import-led deficits and to ensure the country's international financial stability.
5. Redistribution of Income
- Criteria:A reduction in the gap between the rich and the poor through progressive taxation and social welfare programs, aiming for a fairer distribution of wealth.
- Goal:To reduce poverty, mitigate social problems arising from high inequality, and promote greater social cohesion.
Possible conflicts between aims:
-full employment versus stable prices (as when low unemployment higher demand for workers so businesses may have to raise wages leading to inflation.)
- economic growth versus balance of payments stability (Rapid economic growth can lead to increased imports and a trade deficit, as more demand and consumer disposable income.)
-full employment versus balance of payments stability as (Policies to achieve full employment might lead to increased wages and costs, making exports less competitive and potentially worsening the balance of payments.)
definition of the government budget
A financial plan outlining the government's expected revenue and planned expenditure for a specific period, usually one year.
main areas of government spending and the reasons for and effects of spending in these areas.
Main government spending areas include public goods and merit goods, welfare and social protection, infrastructure, and debt interest payments.
Reasons for spending are to correct market failures (like free riders and under-consumption), redistribute income, boost economic growth, and provide essential services. Spending effects include job creation, improved living standards, increased productivity, potential inflation, and changes in national debt.
reasons for levying taxation
- It is a source of government revenue.
- To redistribute income.
- To reduce consumption and production of demerit goods.
- To protect home industries: taxes are also levied on foreign goods entering the domestic market. Such a tax on foreign goods and services is called customs duty.
- To manage the economy: Lowering taxes increase aggregate demand and supply in the economy, thereby facilitating growth. Similarly, during high inflation, the government will increase taxes to reduce demand and thus bring down prices.
types of tax
- Progressive Tax
- Definition: Takes a larger percentage of income from high-income groups than from low-income groups.
- Example: UK Income Tax. People on higher incomes pay a higher percentage of their income in tax.
- Regressive Tax
- Definition: Takes a larger percentage of income from low-income groups than from high-income groups.
- Example: UK Fuel Duty. Everyone pays the same tax per litre, so a larger portion of a low-income earner's budget goes to this tax compared to a high-income earner.
- Proportional Tax
- Definition: Takes the same percentage of income from all income groups.
- Example: A flat Sales Tax at a fixed 5%. Everyone, regardless of income, pays 5% on their purchases. (can also be regressive)
- Direct
Tax
- Example: Income Tax or Corporation Tax. The individual or company on whom the tax is imposed is responsible for paying it directly to the government.
- Indirect Tax
- Definition: Levied on goods and services and can be passed on to the consumer through higher prices.
- Example: UK Value Added Tax (VAT) or Excise Duties. These taxes are included in the price of goods and services, and the consumer ultimately bears the burden.
The qualities of a good tax.
The impact of taxation on consumers, producers, government and economy as a whole.
- Fair, efficient (raises revenue with the least possible distortion to economic activity), economic (A good tax should generate more in revenue than it costs to administer and collect), predictable, flexible (adapt to changing economic conditions and government needs), Simple (easy for both taxpayers to understand and for the government to administer).
Consumers: Taxes raise prices, reduce disposable income, and influence buying behavior (e.g., discouraging harmful goods).
Producers: Taxes increase production costs, reduce supply, lower profits, and may cause inefficiencies in markets.
Government: Taxes provide revenue for public services, help stabilize the economy, redistribute income, and correct market failures.
Economy as a Whole: Taxes affect economic activity, can either reduce or improve efficiency, and support social welfare through public goods and inequality reduction.
definition of fiscal policy
Fiscal policy is a government policy which adjusts government spending and taxation to influence the economy.
Calculating a Budget Deficit or Surplus:
Budget Deficit = Government Spending - Government Revenue opposite for surplus
definition of money supply and monetary policy
The money supply is the amount of money in an economy at any given moment in time.
Monetary policy is adjusting monetary policy measures like interest in order to influence the total demand in an economy.
monetary policy measures and effects
Changes in interest rates, money supply and foreign exchange rates.
- Price Stability (Low Inflation)
- Measure: Raising interest rates, increasing the money supply.
- Mechanism: Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, reducing consumer and business spending, which reduces aggregate demand and curbs inflation.
- Economic Growth
- Measure: Lowering interest rates.
- Mechanism: Lower borrowing costs make it cheaper for businesses to invest and consumers to purchase durable goods, boosting demand and leading to higher economic growth. This also reduces unemployment.
Exchange Rate Stability
- Measure: change exchange rate
- Mechanism: A fall in exchange rate will make imports expensive and exports cheap. A rise in the exchange rate will make imports cheaper and exports expensive.
definition of supply-side policy
Supply side policies are microeconomic policies aimed at increasing supply in the economy,
supply-side policy measures and effects on government macroeconomic aims
Possible supply-side policy measures include:
education and training, labour market reforms, lower direct taxes, deregulation, improving incentives to work and invest, and privatisation.
2. Labour Market Reforms:
- How it works:Eases hiring and dismissal regulations, reduces the power of trade unions, and improves occupational mobility.
- Macroeconomic impact:Increases labour market flexibility, which makes it easier to hire workers, reduce structural unemployment, and boost overall economic efficiency and output.
3. Lower Direct Taxes:
- How it works:Reducing income and corporate taxes increases disposable income for workers and the profits available for businesses to reinvest.
- Macroeconomic impact:Provides stronger incentives for individuals to work and for firms to invest, boosting consumption, investment, and overall economic activity.
4. Deregulation:
- How it works:Reduces bureaucratic hurdles, barriers to entry, and restrictions on business activity.
- Macroeconomic impact:Encourages greater competition, innovation, and efficiency by lowering costs for firms and making markets more dynamic and responsive to consumer needs with lower prices.
6. Privatisation:
- How it works:Transfers ownership of state-run businesses to the private sector.
- Macroeconomic impact:Involves the profit motive, leading to increased efficiency, innovation, and a greater focus on providing goods and services that consumers desire.
definition of economic growth
The annual increase in the level of national output as measured by the gross domestic product (GDP).
measurement of economic growth 2 GDP ones
Real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the value of all goods and services produced in a country annually, adjusted for inflation.
Real GDP Growth Rate = Nominal GDP Growth Rate - Inflation Rate
GDP per capita, calculated by dividing Real GDP by the total population, showing the average output or income per person.
Meaning of recession
A recession occurs when an economy experiences two or more consecutive quarters of negative GDP growth
The costs and benefits of economic growth
Benefits of Economic Growth
- Greater economic activity creates more jobs, potentially reducing poverty and unemployment therefore living standards and boosting consumer spending.
- Increased Government Revenue
- Technological Advancement
Costs of Economic Growth
- increased pollution and resource depletion
- Inflationary Pressures:Rapid growth can outpace supply, leading to rising prices if demand grows faster than production.
- Income Inequality:The benefits of growth may not be distributed evenly, potentially widening the gap between the rich and the poor.
- Opportunity Costs:Resources diverted to economic growth may be unavailable for other objectives, such as environmental protection or leisure.
policies to promote economic growth
demand-side policies, which boost total spending through fiscal (government spending and taxation) and monetary (interest rates and money supply) measures.
supply-side policies, which improve the economy's productive capacity through education, training, deregulation, and investment incentives
definition of employment, unemployment and full employment
Employment: the economic use of labour as a factor of production ·
Full Employment is the situation where the entire labour force is employed. That is, all the people who are able and willing to work are employed.
A situation where people in the labour force who are able and willing to work are unemployed.
How unemployment is measured and the formula for the unemployment rate.
(Number of Unemployed / Total Labour Force) x 100.
Claimant Count : The number of people registered as officially unemployed and claiming unemployment benefits.
Labour Force Survey (LFS) : A regular survey of households that asks a series of questions to classify people as employed, unemployed, or economically inactive, based on ILO criteria.
causes/types of unemployment
Frictional Unemployment : (This is a natural, short-term form of unemployment) When people are temporarily between jobs or first entering the workforce.
Structural Unemployment is caused by a long-term mismatch between the skills workers possess and the skills demanded by employers (often caused by development, or a mismatch between the worker's location and job availability.)
Cyclical unemployment : Unemployment caused by a fall in the overall demand for goods and services, typically occurring during a recession or economic slowdown.
The consequences of unemployment for the individual, firms and the economy as a whole.
Unemployment has negative consequences for individuals (loss of income, health issues, damaged self-esteem), firms (reduced sales, lower output, loss of skills), and the overall economy (lower GDP, decreased tax revenue, increased government spending on benefits, economic stagnation).
definition of inflation and deflation
inflation is a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over time.
Deflation is a sustained decrease in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over time.
Measurement of inflation and deflation using the Consumer Prices Index (CPI).
Tracking the average change over time in the prices of a "basket" of consumer goods and services.
new CPI - old CPI / old CPI x 100.
A positive result indicates inflation, while a negative result signifies deflation.
Causes of inflation
Demand-Pull Inflation: Occurs when the total demand for goods and services in an economy exceeds the total supply.
Cost-Push Inflation: Occurs when the costs of producing goods and services rise.
Causes of deflation
Demand-Side Deflation: Results from a general decrease in aggregate demand in the economy.
Supply-Side Deflation: Occurs due to an increase in the overall supply of goods and services or a decrease in production costs.
The range of policies available to control inflation and deflation
- Monetary Policy:
- Inflation: Uses contractionary policies like raising interest rates to reduce borrowing and spending, slowing the economy.
- Deflation: Employs expansionary policies by lowering interest rates to encourage borrowing and spending, boosting aggregate demand.
- Fiscal Policy:
- Inflation: Uses contractionary policies like increasing taxes or cutting government spending to reduce aggregate demand.
- Deflation: Uses expansionary policies like increasing government spending or reducing taxes to increase aggregate demand.
- Supply-Side Policies:
- Inflation: lowering costs of production and reducing inflationary pressure, but doesn't address demand-side inflation.
The consequences of inflation and deflation for consumers, workers, savers, lenders, firms and the economy as a whole.
Inflation (rising prices)
- Consumers:Experience a fall in real purchasing power as more money is needed to buy the same goods and services.
- Workers:Real wages (wages adjusted for inflation) may fall unless they receive sufficient pay increases, leading to a reduction in living standards.
- Savers:The real value of their savings decreases, as the money they get back later will buy less than when it was saved.
- Lenders:Benefit from inflation as they are repaid with money that has a lower real value, which is favorable for those with fixed-rate loans.
- Firms:May see reduced demand as consumers' purchasing power falls. Some firms may benefit if they can raise prices more than costs, while others face challenges from increased input costs.
- Economy as a whole:Excessive inflation creates economic instability and can lead to a loss of confidence.
deflation
- Lower prices will discourage production, resulting in unemployment.
- As demand and prices fall, investors will be discouraged to invest, lowering the output/GDP.
- Deflation can cause recession as demand and prices continue to fall and firms are forced to close down as enough profits are not being made.
- Tax revenue of the government will fall.
- Borrowers will lose during a deflation because now the value of the debt they owe is higher than when they borrowed the money.
- Deflation will increase the real debt burden of the governmentas the value of debt money increases.
Real GDP per head and the Human Development Index (HDI), pros and cons
The Human Development Index (HDI) combines income, life expectancy, and education into a single score.
- Advantages: Broader
- Disadvantages: Complex so harder to understand, Income Component: Still includes income as a component, meaning it can be limited by the same issues as GDP per head, May Oversimplify: A single HDI score can oversimplify the complex realities of human development.
Real GDP per Head : The total value of goods and services produced in an economy, adjusted for inflation, and divided by the total population.
- Advantages: Allows for comparisons, Adjusted for inflation
- Disadvantages: Ignores Well-being factors, Doesn't Reflect Distribution: A high average GDP per head can hide significant income inequality.
Reasons for differences in living standards and income distribution within and between countries.
Factors Within Countries,: Education and skills, different employment opportunities, government policies, Inheritance and wealth, Discrimination, Rural vs. Urban Divide due to varying access to services and economic opportunities.
Factors Between Countries, Economic Structure: Countries with economies heavily reliant on the primary sector (agriculture) and a large proportion of the workforce in informal, low-wage jobs often have lower living standards. Economic Development & Technology, Natural Resources, Conflict, Crime, and Natural Disasters, Geographic Factors impact its ability to engage in trade, access markets, and experience economic growth.
definition of absolute and relative poverty, how measured
Absolute poverty: the inability to afford basic necessities needed to live. It's measured by the number of people living below the poverty line.
Relative Poverty is a situation where a person lacks the resources to maintain the average standard of living within their society. It's measured by a percentage of the national median income (e.g., less than 60% of the median).
causes of poverty : including unemployment, low wages, illness and age.
Policies include: promoting economic growth, improved education, more generous state benefits, progressive taxation, and national minimum wage.
advantages and disadvantages of specialisation and reasons
- A country specializes in goods and services where it has an advantage, meaning it can produce them at a lower opportunity cost relative to other countries. May have: Abundant resources, Skilled labor, Advanced technology, advantageous Climate and geographical conditions.
-
Advantages of specialization:
- Increased efficiency and productivity from economies of scale.
- Lower prices for consumers and g reater variety of goods: Through trade, countries can access a wider range of goods and services than they could produce on their own.
- Improved international competitiveness.
- Innovation and technological advancement: Focusing on a specific industry can stimulate innovation and investment in new technologies within that sector.
-
Disadvantages of specialization:
- Overdependence on a single industry and can become vulnerable to changes in global demand or supply for those products.
- Structural unemployment: When a country shifts production away from less efficient industries to more efficient ones, workers in the declining industries may face unemployment and need to retrain for new jobs.
- Loss of economic diversity: Excessive specialization can lead to a narrowing of the country's economic base, making it less resilient to external shocks.
- Potential for negative externalities: can lead to environmental issues if production processes are not properly regulated, or if there are negative social impacts associated with certain industries.
definition of globalisation
Globalisation is the increased economic interconnectedness of countries through increasing cross-border movement of people, goods/services, technology and finance.
multinational corporation definition
a business that has production facilities in two or more countries
MNCs and the costs and benefits to home and host countries.
Impact on home country:
Advantages:
- Remittances to home.
- Larger market as new abroad market.
- MNCs can produce goods more cheaply abroad and offer lower prices at home.
- (Risk Reduction) If sales fall in one place, they can rely on others.
Disadvantages :
- MNCs might pressure home governments for favourable rules.
- MNCs may be criticised at home for allowing bad working conditions and pollution abroad.
- Home country loses job opportunities and brain drain as MNC's take jobs with them.
Impact on host country
Advantages:
- Host countries get more product choices and access to new technologies.
- Job creation and economic growth and increase tax revenue.
- MNCs may invest in local infrastructure.
Disadvantages:
- Host countries may become too dependent on MNCs for jobs. If an MNC leaves, many people could lose their jobs.
- MNCs might influence politics and gain too much control.
- Host countries might suffer from environmental damage, labour and recourse exploitation.
- Competition for local businesses.
the benefits of free trade or consumers, producers and the economy
Consumers: Lower prices, Greater variety, Higher quality.
Producers: Expanded markets, Economies of scale, Lower costs: Producers can access cheaper raw materials and other production resources cheeper from other countries. Increased efficiency and innovation: Competition from foreign firms incentivises domestic companies to innovate.
For the economy: Economic growth, Efficient resource allocation: Countries can specialise in producing goods where they have a comparative advantage, leading to more efficient use of global resources. Increased competition so higher efficiency and Higher incomes and living standards, Spread of technology and ideas. Stronger international relations.
methods and reasons of protection
Tariffs are taxes on imported goods.
Quotas limit the quantity of imports.
Subsidies are government payments to domestic producers.
Embargoes are complete bans on trade.
To protect infant and declining industries, Strategic industries (industries that are considered crucial for a country's long-term economic growth or national security), and avoidance of dumping (when a company exports a product to another country at a price lower than its domestic market price or even below the cost of production leading to unfair competition).
*improving a country's trade balance in the short term by making imports more expensive and less competitive. However, it often leads to higher consumer prices, reduced choice, and can provoke retaliatory measures from trading partners, potentially harming export competitiveness and increasing global trade friction.
definition of foreign exchange rate
and two systems
the price of one country's currency in terms of another country's currency
Floating exchange rates are determined by market forces without government intervention, while fixed exchange rates are pegged to another currency by the government or central bank.
Floating exchange rate Advantages
- central bank can focus on other things
- Automatic adjustment: The exchange rate automatically adjusts to external shocks, helping the economy adapt without significant government intervention.
- No need for large reserves: Less foreign currency is needed compared to a fixed system.
Disadvantages
- Volatility and uncertainty: Exchange rates can fluctuate significantly, making it difficult for businesses to plan.
- Potential for inflation: If the currency depreciates, imports become more expensive, which can increase domestic inflation.
- Risk for investors: Investors face exchange rate risk, as the value of their investments can change due to currency fluctuations.
Fixed exchange rate: Stability and predictability which promotes trade and investment. But Loss of monetary policy independence: The central bank must focus on maintaining the fixed rate, limiting its ability to use interest rates for other domestic economic goals. Requires large foreign reserves: The central bank needs to hold large reserves to intervene and defend the peg if necessary. Vulnerability to speculative attacks: If speculators believe a fixed rate is unsustainable, they can attack the currency, potentially causing a currency crisis. Difficult to adjust: It can be hard to adjust to external shocks, sometimes requiring difficult and painful economic restructuring or devaluation.
causes of foreign exchange rate fluctuations
Changes in the demand for exports and imports
- Exports: An increase in the demand for a country's exports boosts demand for its currency on the foreign exchange market, potentially causing it to appreciate.
- Imports: A rise in demand for imports means people are buying more foreign goods, increasing the supply of the domestic currency on the foreign exchange market and causing it to depreciate.
Changes in the rate of interest
- Higher interest rates: A higher interest rate can attract foreign investment as investors seek better returns. This increases the demand for the domestic currency, leading to an appreciation.
- Lower interest rates: Lower interest rates may lead to a decrease in foreign investment, a fall in demand for the domestic currency, and a potential depreciation.
Speculation
- Speculation involves traders buying or selling a currency based on their expectations of future exchange rate movements.
the entry or departure of MNCs.
How change rate fluctuation impacts price of exports and imports.
A currency appreciation makes exports more expensive for foreign buyers and imports cheaper for domestic consumers, while a depreciation does the opposite.
The total effect of these changes on the volume of spending depends on the price elasticity of demand (PED)
Current account of balance of payments structure and calculation
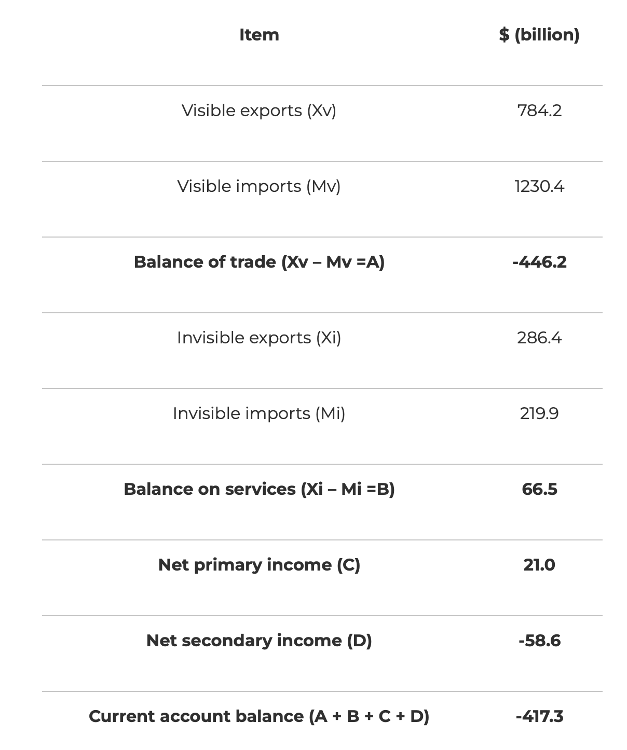
Trade in goods and services
-
Net primary income : net income received or made in
payment for the use of factors of
production.
- income debits (outflows) include wages paid to non-residents working in the country, interests, profits and dividends paid out to overseas shareholders.
- income credits (inflows) include wages paid to residents working overseas, interests, profits and dividends earned by UK residents and firms on investments they have in other countries
-
Net current transfers,(also called net
secondary income) which include payments between
governments for international co-operation and other transactions
that involve payments for non-productive
activities:
- debits (outflows) will include financial aid, donations, pension payments etc. paid to overseas residents and foreign governments, and tax and excise duties paid by UK residents on foreign purchases
- credits (inflows) will include financial aid, donations, grants, pension payments etc. received from overseas residents and foreign governments, and tax and excise duties paid by overseas residents on UK purchases.
- Add balance of goods and services, with net primary and secondary income to calculate current account balance.
Reasons for current account deficit and consequences
Causes of a current account deficit
- High exchange rate: A strong currency makes exports expensive for foreigners and imports cheap for domestic consumers, increasing imports and decreasing exports.
- High inflation: Higher domestic prices make a country's exports less competitive internationally, while cheaper foreign goods become more attractive to domestic consumers.
- Rapid economic growth: When the economy grows quickly, consumers have more disposable income and tend to increase their spending on all goods, including imports.
- Low productivity: If a country's firms are less efficient and have higher production costs, their exports will be more expensive and less competitive.
- Non-price factors: Poor quality, design, or marketing of a country's products can reduce their competitiveness and demand from foreign buyers.
Consequences of a current account deficit
- GDP: Can lead to slower economic growth or even a recession if export demand falls significantly.
- Employment: High unemployment can result as lower demand for domestic goods and services leads to lower output and fewer workers are needed.
- Inflation: Can contribute to cost-push inflation. As the currency depreciates, imports become more expensive, raising costs for businesses and consumers.
- Exchange Rate: The national currency tends to depreciate (weaken). This makes imports more expensive and exports cheaper, which can help correct the deficit over time, but adds to inflationary pressure.
Policies to achieve balance of payments stability
Policies to achieve balance of payments stability include exchange rate policies (A government can choose (devaluation) to devalue its currency to make exports cheaper and imports more expensive, thus improving the balance of payments or let it happen naturally from a current account deficit (Floating Exchange Rate)
Fiscal and monetary policies to reduce national income and demand, This decreases spending on imports, which helps to improve the balance of payments deficit.
Supply-side policies (to improve international competitiveness).