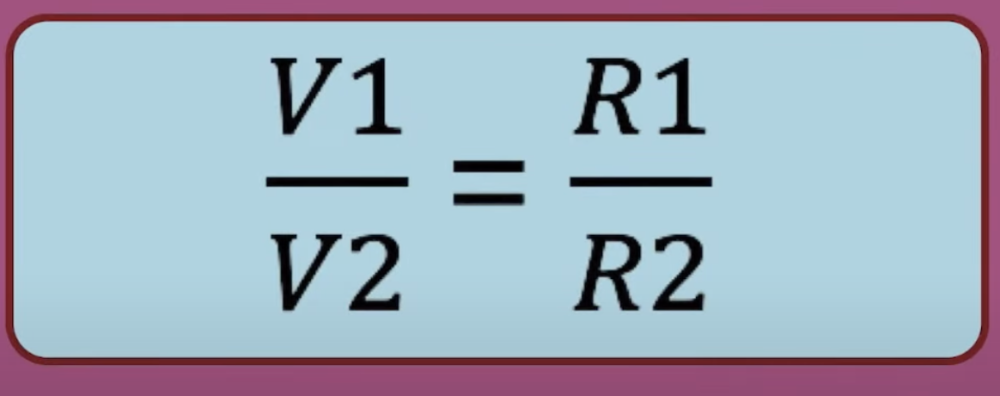physics igsce
Describe the life cycle of a star.
(a) a star is formed from interstellar clouds of
gas and dust that contain hydrogen
(b) a protostar is an interstellar cloud collapsing
and increasing in temperature as a result of
its internal gravitational attraction
(c) a protostar becomes a stable star when the
inward force of gravitational attraction is
balanced by an outward force due to the high
temperature in the centre of the star
(d) all stars eventually run out of hydrogen as
fuel for the nuclear reaction
(e) most stars expand to form red giants and
more massive stars expand to form red
supergiants when most of the hydrogen in
the centre of the star has been converted to
helium
(f) a red giant from a less massive star forms a
planetary nebula with a white dwarf star at
its centre
(g) a red supergiant explodes as a supernova,
forming a nebula containing hydrogen and
new heavier elements, leaving behind a
neutron star or a black hole at its centre
(h) the nebula from a supernova may form new
stars with orbiting planets
Length of one light year.
One light-year is equal to 9.5 × 10^15m
Define the Hubble constant
The ratio of the speed at which the galaxy is moving away from the Earth, to its distance from the Earth.
Equation and estimate of Hubbles constant.
H = v/d
Know that the current estimate for H is 2.2 × 10^–18 per second.
opposite of Hubbles constant to find age of universe. equation
Represents an estimate for the age of the Universe and that this is evidence for the idea that all the matter in the Universe was present at a single point.
1/H = d/v
The eight planets and their order from the Sun.
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
Contents of solar system:
(a) one star, the Sun
(b) the eight named planets
(c) minor planets that orbit the Sun, including
dwarf planets such as Pluto and asteroids in
the asteroid belt.
(d) moons
(e) smaller Solar System bodies, including
comets and natural satellites
Define average orbital speed of a planet with the equation
v = 2πr/T
where T is the orbital period
Describe how radioactive materials are moved, used, and stored in a safe way.
- Store the sources in lead-lined boxes and keep them at a distance from people
- Minimise the amount of time you handle sources and return them to their boxes as soon as you have finished using them
- During use, keep yourself (and others) as far from the sources as possible. When handling the sources do so at arm’s length, using a pair of tongs
- using shielding to absorb radiation
- Radioactive materials such as used nuclear fuel are transported in special containers called casks
- These casks can withstand extreme conditions such as fire, cold and being submerged in water.
Explain how the type of radiation emitted and the half-life of an isotope determine which isotope is used for household fire (smoke) alarms.
- Alpha particles are used in smoke detectors
- The alpha radiation ionises the air within the detector, creating a current
- The alpha emitter is blocked when smoke enters the detector
- The alarm is triggered by a microchip when the sensor no longer detects the alpha particles
- An isotope of alpha radiation with a long half-life is used for smoke detectors so they don't need replacing often
Explain how the type of radiation emitted and the half-life of an isotope determine which isotope is used for sterilisation of equipment using gamma rays
- Gamma is most suited to this because:
- It is the most penetrating out of all the types of radiation
- It is penetrating enough to irradiate all sides of the instruments
- Instruments can be sterilised without removing the packaging
- The source of gamma
radiation used for sterilisation has a half-life of around 5 years
- This means the sterilisation equipment does not need to be replaced often
Explain how the type of radiation emitted and the half-life of an isotope determine which isotope is used for measuring and controlling thicknesses of materials with the choice of radiations used linked to penetration and absorption.
- Beta radiation is most commonly used to measure the thickness
of materials because it will be partially absorbed by most materials
- Alpha particles are used for thinner materials because they have a lower penetrating power and are absorbed by a thin sheet of aluminium
- Gamma radiation can be used for very thick materials because they have a higher penetrating power and are mostly absorbed by thick pieces of lead.
- Radiation used to measure the thickness of materials has a half-life of many years (10-20 years) so that the count rate remains relatively constant each day
Explain how the type of radiation emitted and the half-life of an isotope determine which isotope is used for diagnosis and treatment of cancer.
Beams of gamma rays are directed at the cancerous tumour
- Gamma rays are used because they can penetrate the body, reaching the tumour
- Gamma radiation used in radiotherapy
has a half-life of around 5 years
- This means that it does not need to be replaced often within the machine that uses it.
Explain how the type of radiation emitted and the half-life of an isotope determine which isotope is used for irradiating food to kill bacteria.
- Food can be irradiated to kill any microorganisms that are present on it
- This makes the food last longer and reduces the risk of food-borne infections
- Gamma is most suited to
this because:
- It is the most penetrating out of all the types of radiation
- It is penetrating enough to irradiate all sides.
Variable resistor
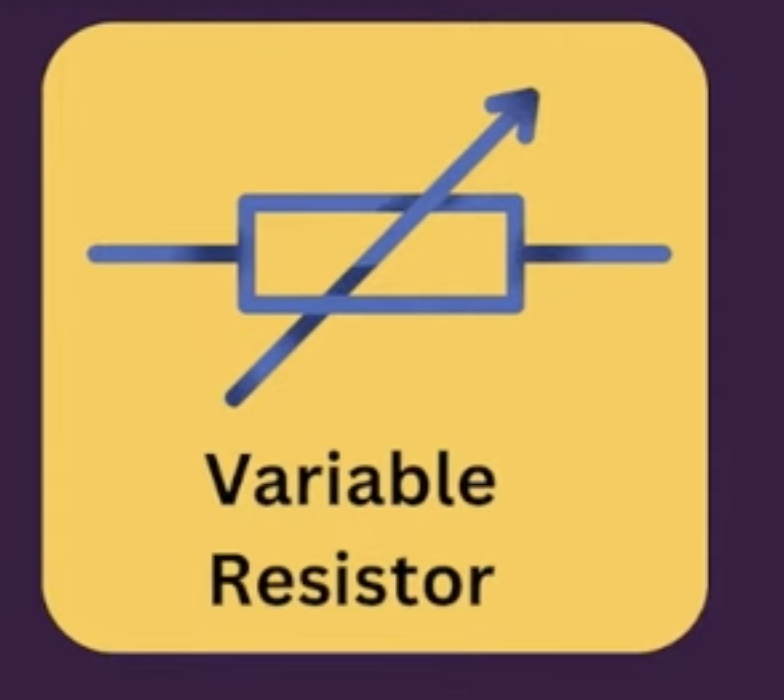
A resistor whose resistance can be changed, for example by turning a knob or a slider.
Light dependant resistor
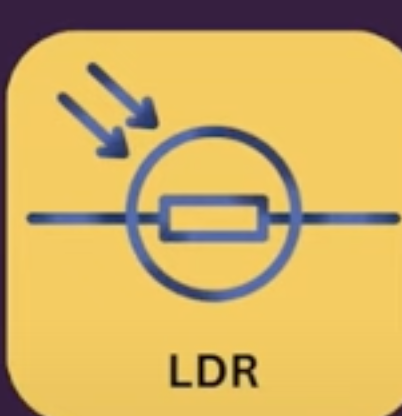
A resistor whose resistance is depending on the amount of light falling on it.
Thermistor

a type of resistor whose electrical resistance varies significantly with temperature
Diode

An electrical component that allows electricity to flow in one direction only.
which way current flows in a circuit and electrons.
Current from the positive terminal to the negative terminal, electrons from negative to positive.
Light emitting diode

Diode that emits light when current going through it.
Calculate resistance in parallel circuit
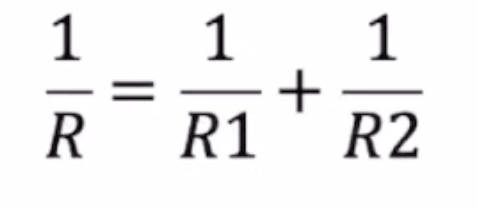
Calculating voltage formula
Voltage = current x resistance (V=IxR)
Potential divider
Two resistors connected in series to get a smaller voltage than supplied.
ratio