B2, S2 - Thermal Energy Transfer

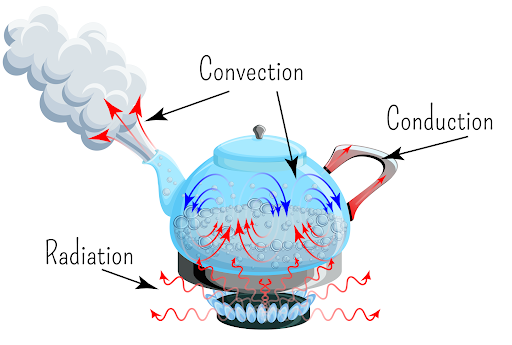
Conduction
Transfer of thermal energy that occurs in solids, liquids, and gases when two substances of different temperatures touch
Conductor
A substance that allows the flow of electrical charge or transfers thermal energy through matter.
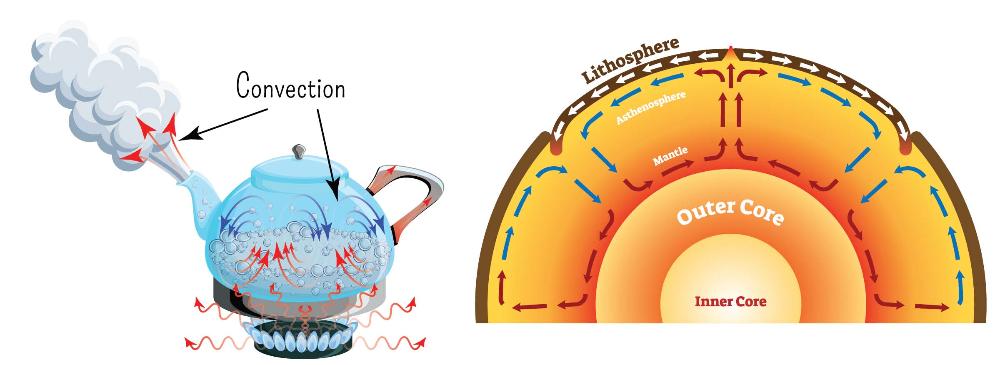
Convection
Heat transfer caused by the rising of hotter, less dense fluids and the falling of cooler, denser fluids.
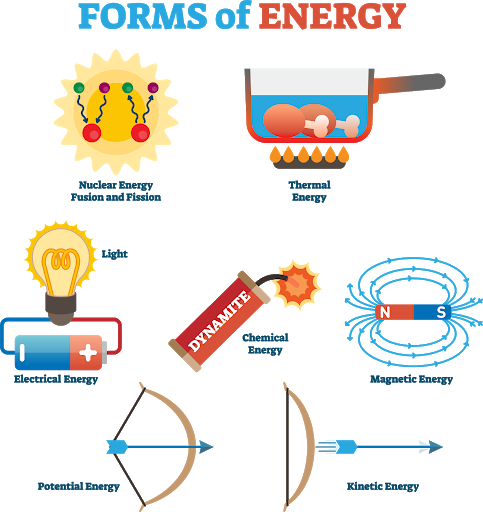
Energy
The ability of a system to do work; required for changes to happen within a system.
Heat Transfer
The thermal energy exchange between two objects of different temperatures; energy moves in a predictable pattern from warmer sites to cooler sites until all sites have reached the same temperature.
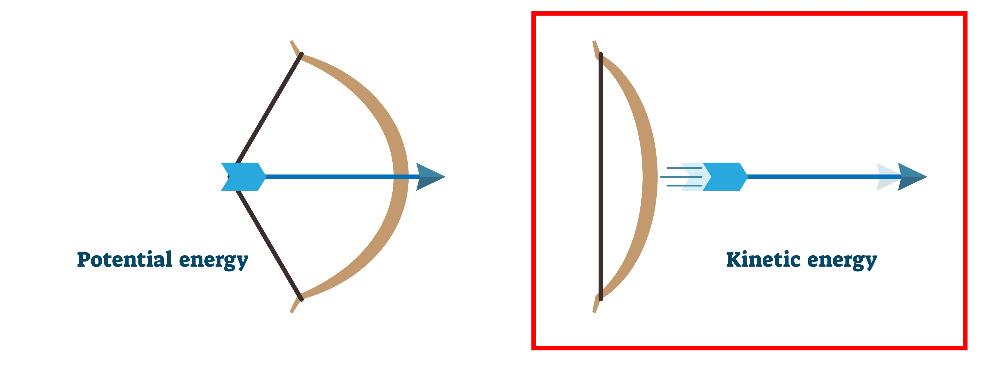
Kinetic Energy
Energy of motion.
Matter
Anything that has volume and mass
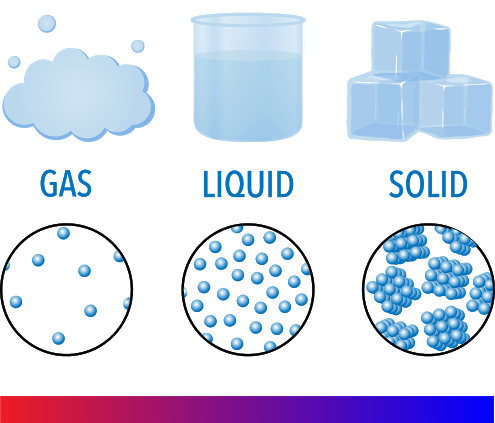
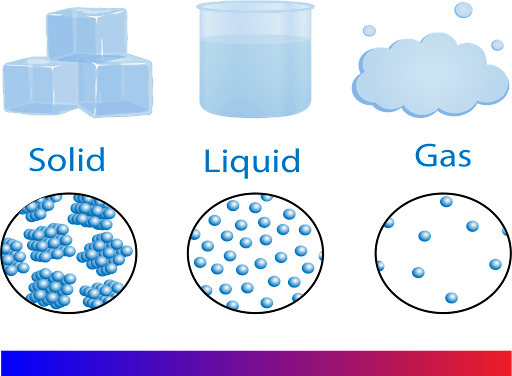
States of Matter
Distinct forms of matter known in everyday experience; solid, liquid, and gas; also referred to as phases.
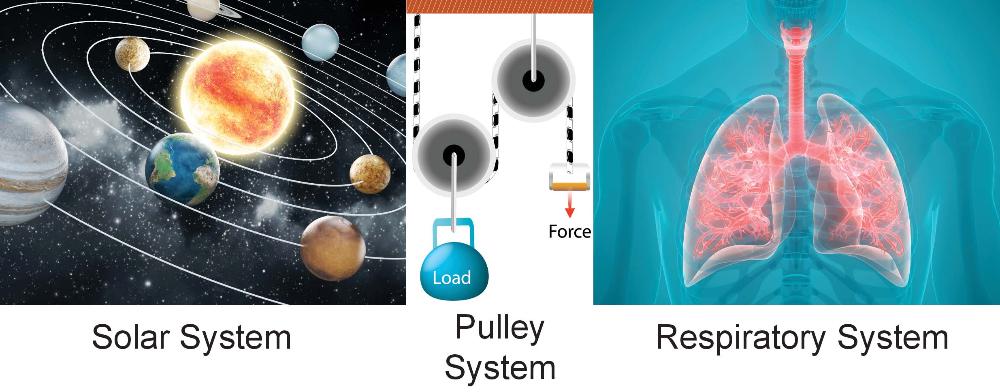
System
A group of interacting, interrelated, or interdependent elements forming a complex whole.
Temperature
Average kinetic energy of all the particles in a material; measured by a thermometer in degrees (usually degrees Celsius or degrees Fahrenheit)
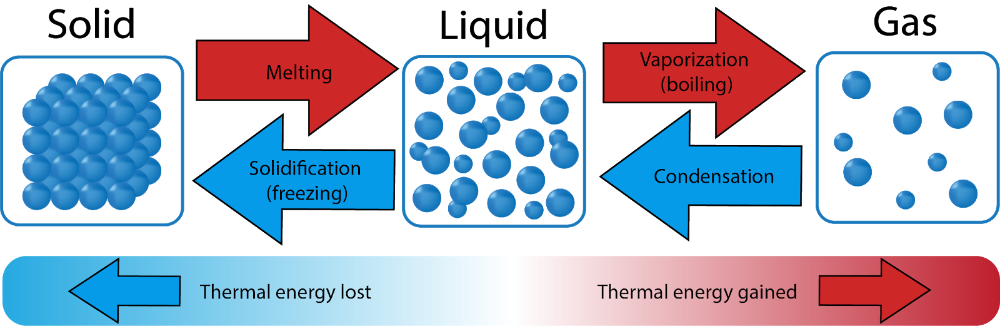
Thermal Energy
The total kinetic (motion) energy of the tiny particles that make up matter; the faster the particles move, the warmer the matter becomes.

Radiation
The transfer of energy by the movement of electromagnetic waves or subatomic particles.