Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
B2, S2 - Thermal Energy Transfer
front 1  Conduction | back 1 Transfer of thermal energy that occurs in solids, liquids, and gases when two substances of different temperatures touch |
front 2  Conductor | back 2 A substance that allows the flow of electrical charge or transfers thermal energy through matter. |
front 3 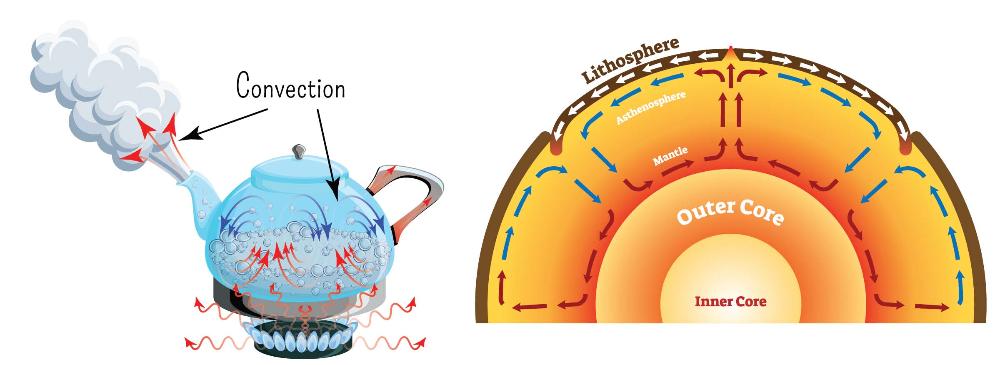 Convection | back 3 Heat transfer caused by the rising of hotter, less dense fluids and the falling of cooler, denser fluids. |
front 4 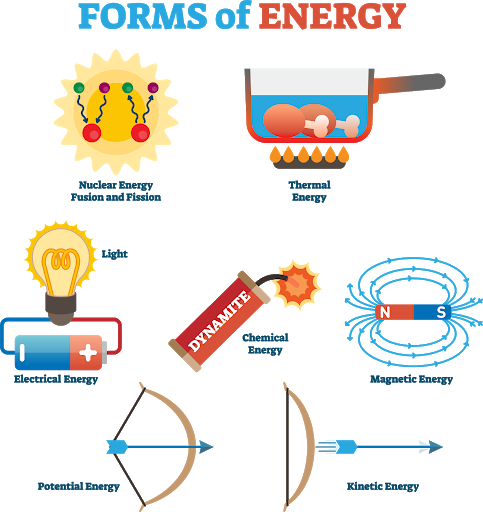 Energy | back 4 The ability of a system to do work; required for changes to happen within a system. |
front 5 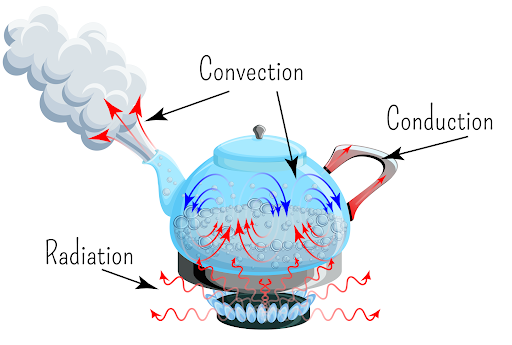 Heat Transfer | back 5 The thermal energy exchange between two objects of different temperatures; energy moves in a predictable pattern from warmer sites to cooler sites until all sites have reached the same temperature. |
front 6 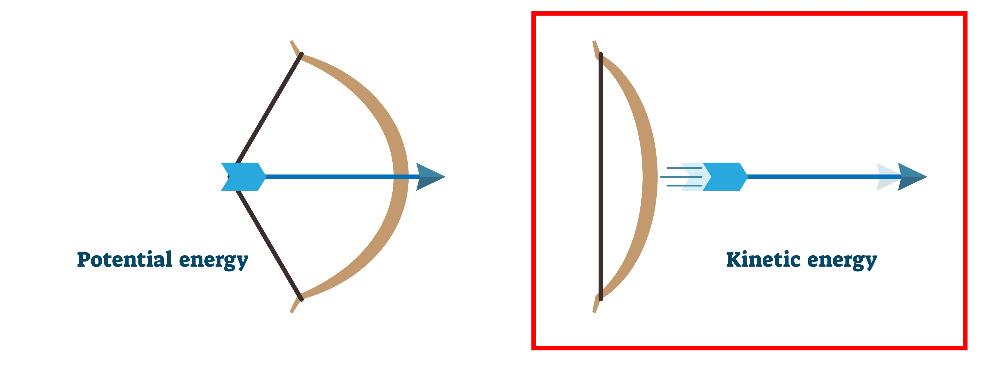 Kinetic Energy | back 6 Energy of motion. |
front 7 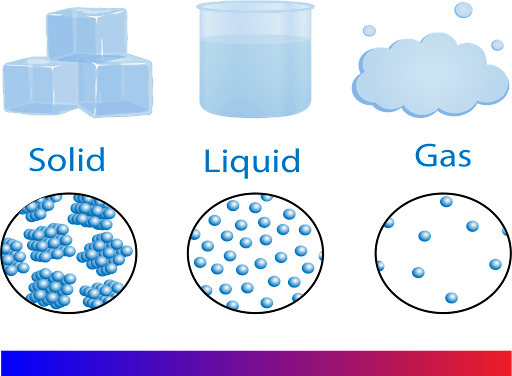 Matter | back 7 Anything that has volume and mass |
front 8 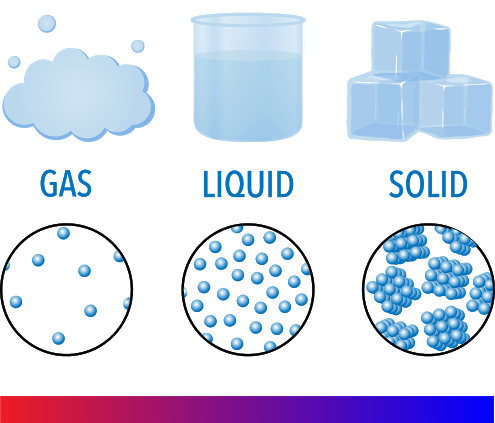 States of Matter | back 8 Distinct forms of matter known in everyday experience; solid, liquid, and gas; also referred to as phases. |
front 9 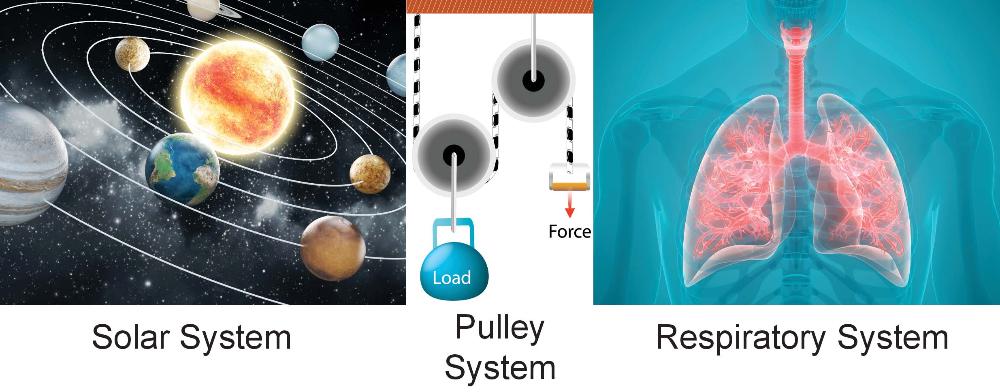 System | back 9 A group of interacting, interrelated, or interdependent elements forming a complex whole. |
front 10  Temperature | back 10 Average kinetic energy of all the particles in a material; measured by a thermometer in degrees (usually degrees Celsius or degrees Fahrenheit) |
front 11 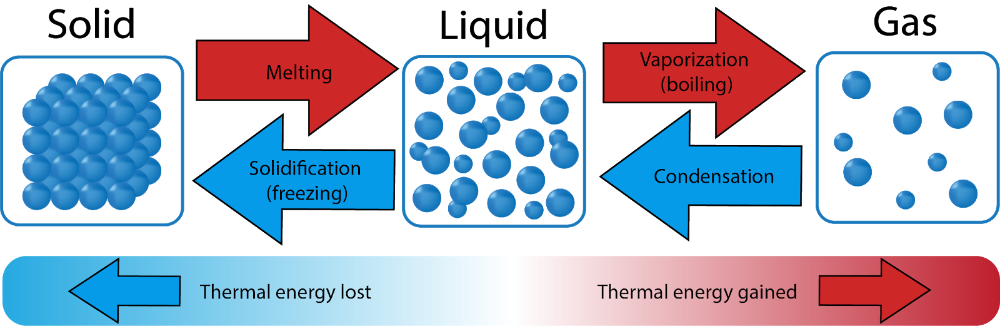 Thermal Energy | back 11 The total kinetic (motion) energy of the tiny particles that make up matter; the faster the particles move, the warmer the matter becomes. |
front 12  Radiation | back 12 The transfer of energy by the movement of electromagnetic waves or subatomic particles. |