A&P II Lab Practical #4

A
adrenal gland

B
renal artery

C
renal vein

D
kidney

E
ureter

F
uterus

G
urinary bladder

H
urethra

A
renal pyramids

B
renal cortex

C
minor calyx

D
ureter

E
renal pelvis

F
renal papilla

G
minor calyx

H
interlobar vessels

I
arcuate vessels

A
renal sinus

B
renal pelvis

C
hilum

D
renal papilla

E
ureter

F
renal cortex

G
renal medulla

H
renal pyramid

I
minor calyx

J
major calyx

K
kidney lobe

L
renal columns

M
fibrous capsule

A
renal cortex

B
renal medulla

C
major calyx

D
papilla of pyramid

E
minor calyx

F
renal pyramid in renal medulla

G
renal column

H
fibrous capsule

I
cortical radiate vein

J
cortical radiate artery

K
arcuate vein

L
arcuate artery

M
interlobar vein

N
interlobar artery

O
segmental arteries

P
renal vein

Q
renal artery

R
renal pelvis

S
ureter
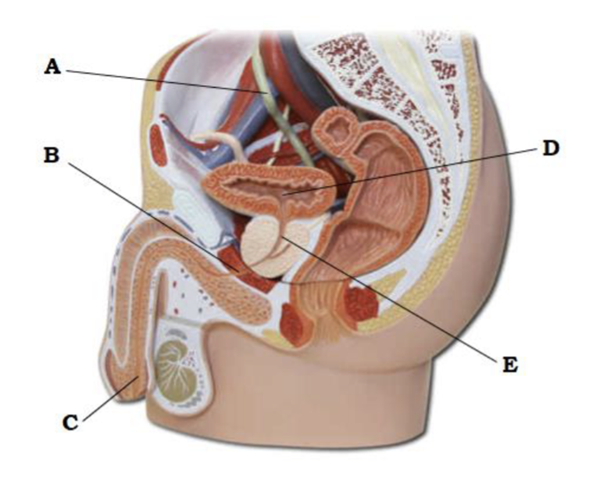
A
ureter

B
membranous urethra

C
spongy urethra

D
urinary bladder

E
prostatic urethra
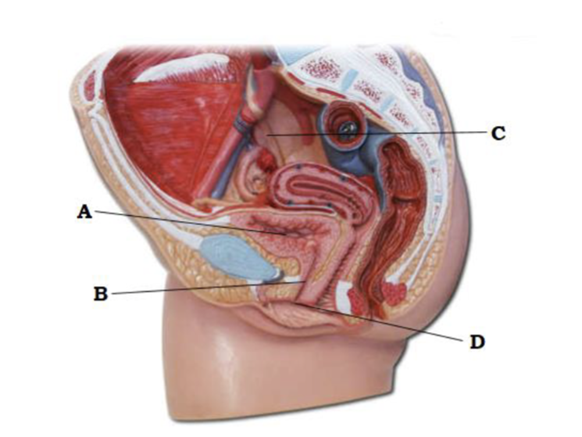
A
urinary bladder

B
urethra

C
ureter

D
external urethral orifice
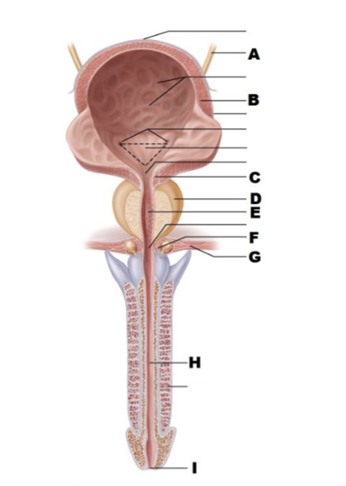
A
ureter

B
detrusor

C
internal urethral sphincter

D
prostate

E
prostatic urethra

F
external urethral sphincter

G
urogenital diaphragm

H
spongy urethra

I
external urethral orifice
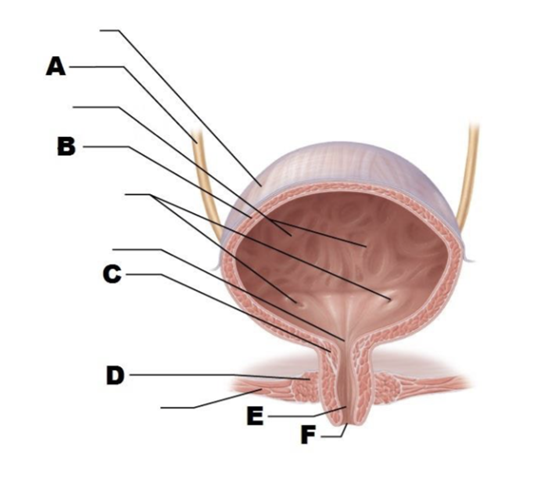
A
ureter

B
detrusor

C
internal urethral sphincter

D
external urethral sphincter

E
urethra

F
external urethral orifice
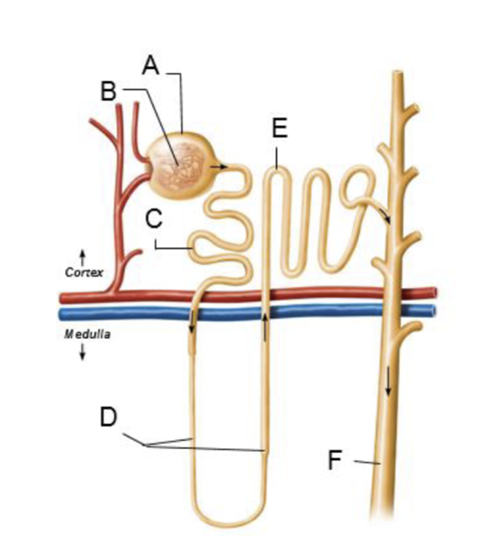
A
glomerular capsule

B
glomerulus

C
proximal convoluted tubule

D
nephron loop

E
distal convoluted tubule

F
collecting duct

A
cortical nephron

B
juxtamedullary nephron

C
glomerulus

D
glomerular capsule

E
proximal convoluted tubule

F
peritubular capillaries

G
ascending limb of nephron loop

H
nephron loop

I
descending limb of nephron loop

J
collecting duct

K
distal convoluted tubule

L
vasa recta

A
cortical radiate vessels

B
arcuate vessels

C
descending limb of loop of Henle

D
interlobar vessels

E
collecting duct

F
ascending limb of loop of Henle

G
distal convoluted tubule

H
efferent arterioles

I
proximal convoluted tubule

J
afferent arterioles

K
renal corpuscles
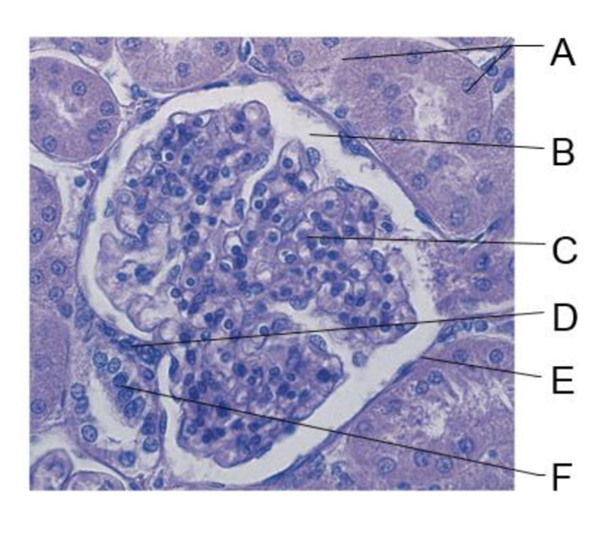
A
cuboidal epithelium of renal tubule

B
glomerular capsular space

C
glomerulus

D
granular cells

E
parietal layer of glomerular capsule

F
macula densa
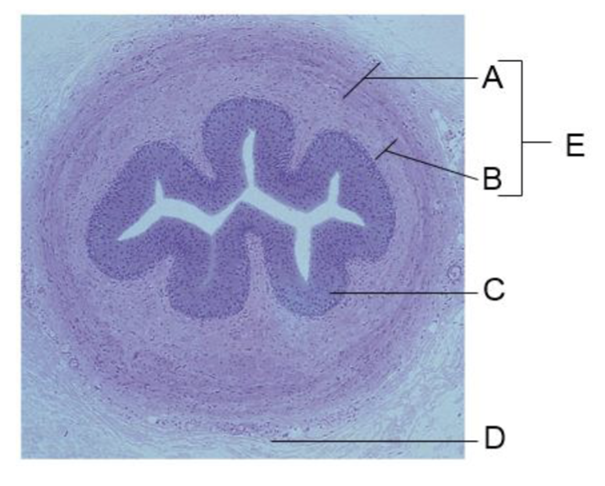
A
circular layer

B
longitudinal layer

C
transitional epithelium

D
adventitia

E
smooth muscle
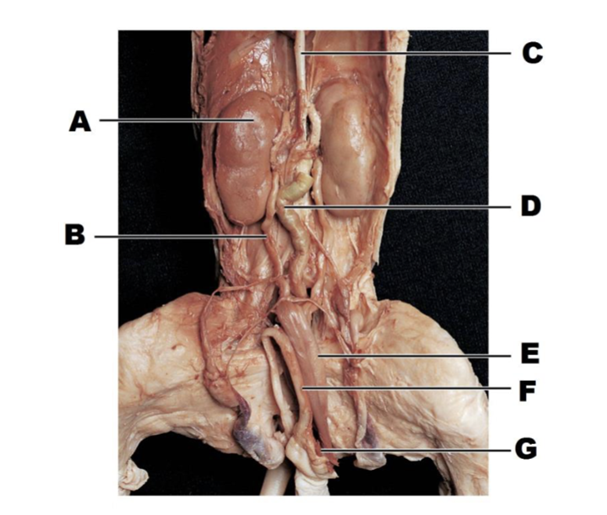
A
kidney

B
ureter

C
inferior vena cava

D
descending portion of colon

E
urinary bladder

F
penis

G
umbilical vein

A
inferior vena cava

B
ureter

C
urinary bladder

D
ureter (cut)

E
urethra

F
kidney

G
descending portion of colon

H
uterine horns

I
uterus

J
urogenital sinus
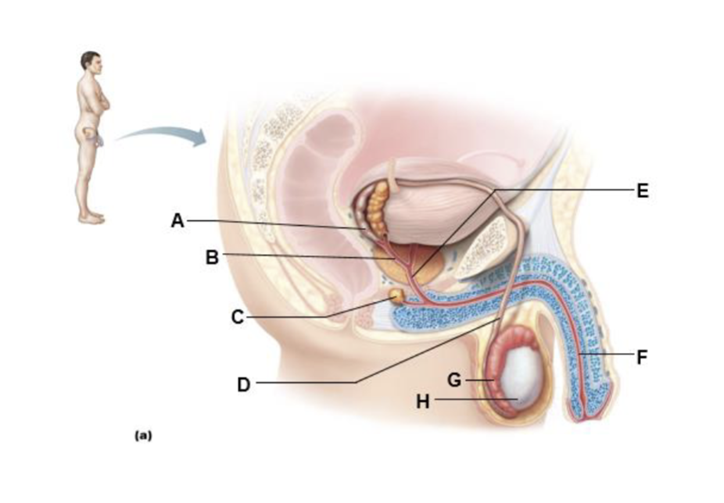
A
ampulla of ductus deferens

B
ejaculatory duct

C
bulbo-urethral gland

D
ductus (vas) deferens

E
prostatic urethra

F
spongy urethra

G
epididymis

H
testis

A
urinary bladder

B
prostate

C
prostatic urethra

D
intermediate part of urethra

E
root of penis

F
body (shaft) of penis

G
glans penis

H
external urethral orifice

I
prepuce (foreskin)

J
spongy urethra

K
testis

L
corpus spongiosum

M
epididymis

N
corpora cavernosa

O
ductus deferens

P
crus of penis

Q
bulb of penis

R
urogenital diaphragm

S
bulbo-urethral gland and duct

T
ejaculatory gland

U
seminal gland

V
ampulla of ductus deferens

W
ureter
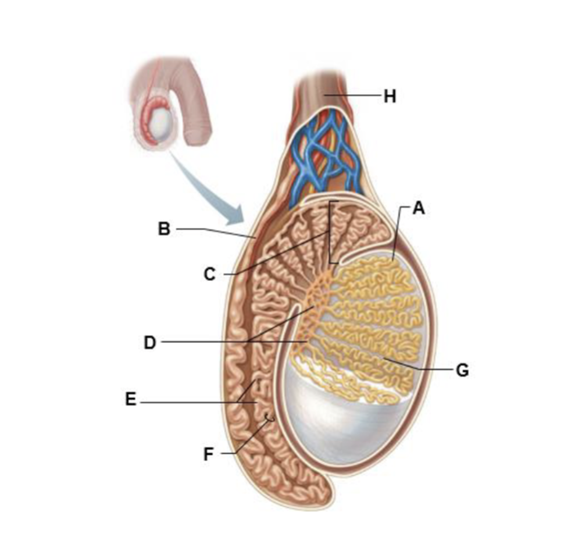
A
seminiferous tubule

B
ductus (vas) deferens

C
head of epididymis

D
rete testis

E
body of epididymis

F
duct of epididymis

G
septum

H
spermatic cord
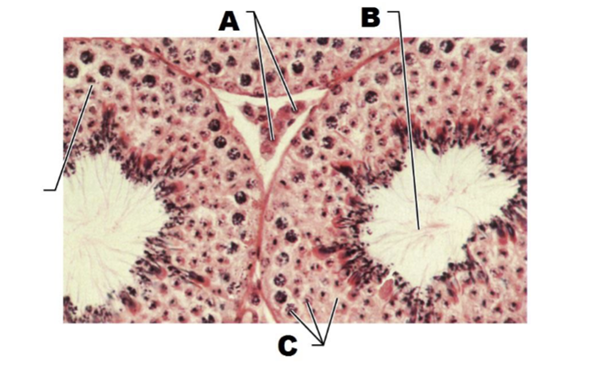
A
interstitial endocrine cells

B
immature sperm

C
spermatogenic cells
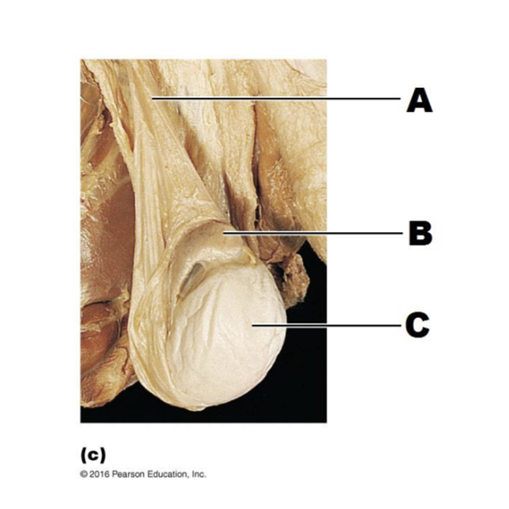
A
spermatic cord

B
epididymis

C
testis
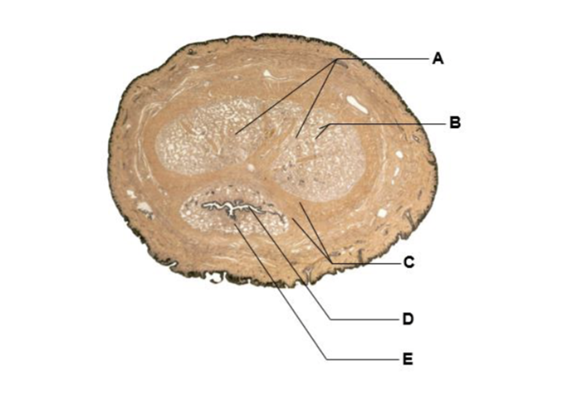
A
corpore cavernosa

B
venous cavities

C
tunic albuginea

D
lumen of spongy urethra

E
corpus spongiosum
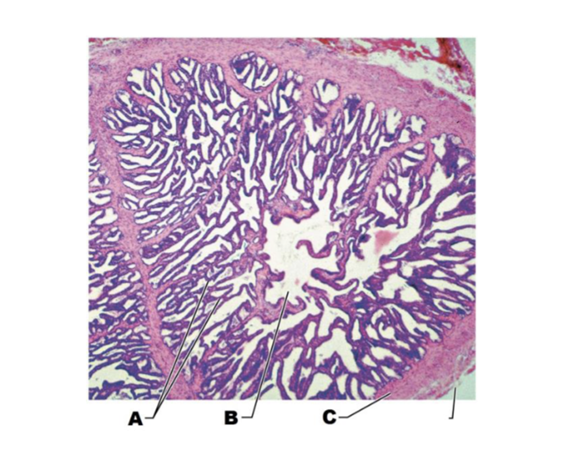
A
mucosal folds

B
lumen of seminal tubule

C
muscular wall
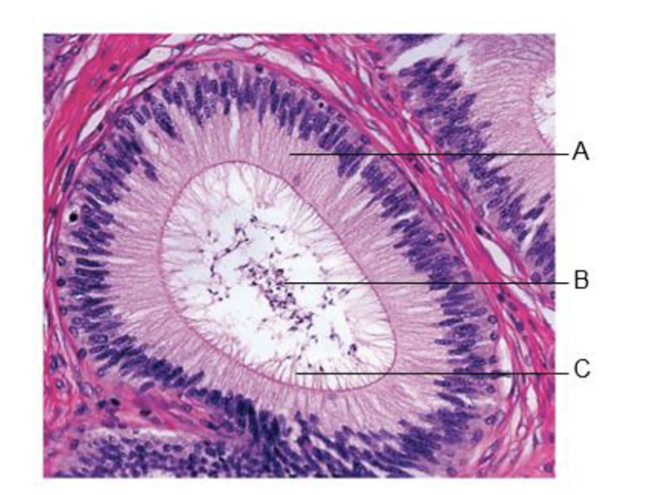
A
pseudostratified columnar epithelium

B
sperm in lumen

C
stereocilia
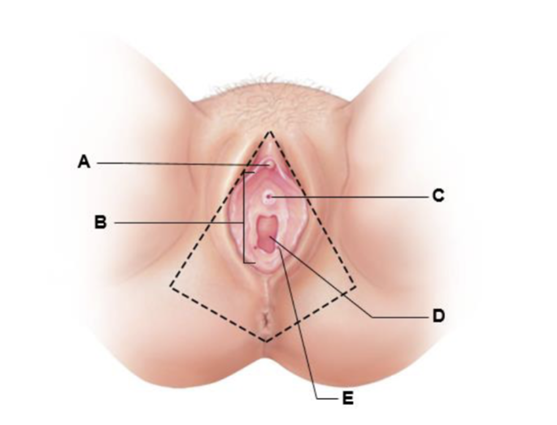
A
clitoris gland

B
vestibule

C
external urethral orifice

D
vaginal orifice

E
opening of the duct of the greater vestibular gland
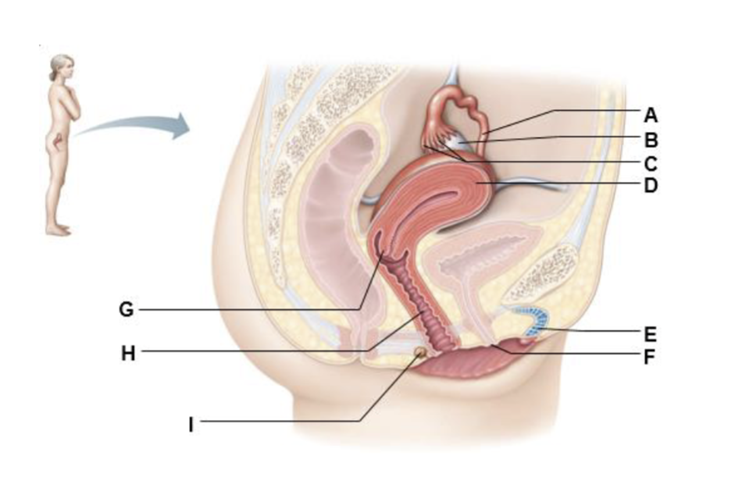
A
uterine tube

B
ovary

C
fimbrae

D
uterus

E
clitoris

F
external urethral orifice

G
cervix

H
vagina

I
greater vestibular gland

A
broad ligament

B
body of uterus

C
cervix

D
ovary

E
uterine (fallopian tube)

F
fimbriae

G
infundibulum

H
isthmus

I
ampulla

J
endometrium

K
vagina
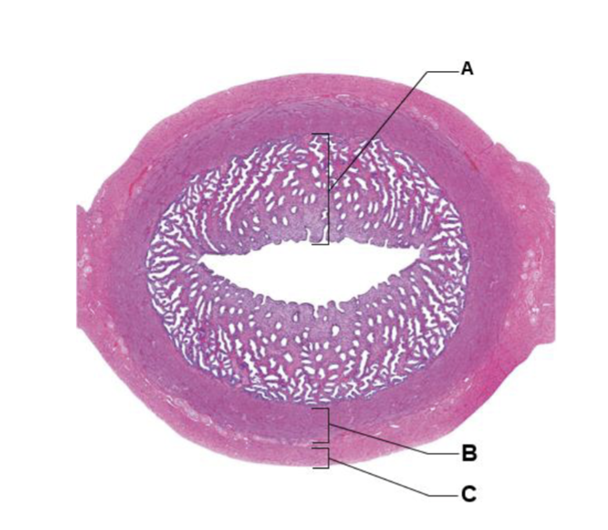
A
endometrium

B
myometrium

C
serosa

A
serosa

B
smooth muscle

C
highly folded mucosa

D
lumen
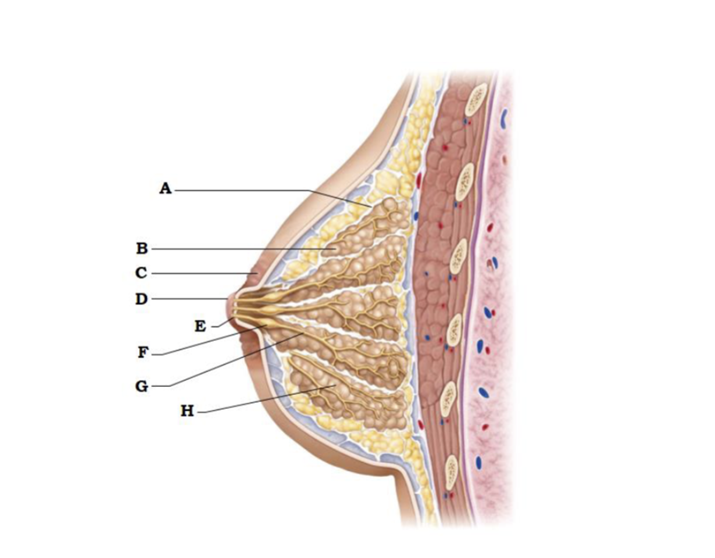
A
suspensory ligament

B
lobe

C
areola

D
nipple

E
opening of lactiferous duct

F
lactiferous sinus

G
lactiferous duct

H
lobule containing alveoli
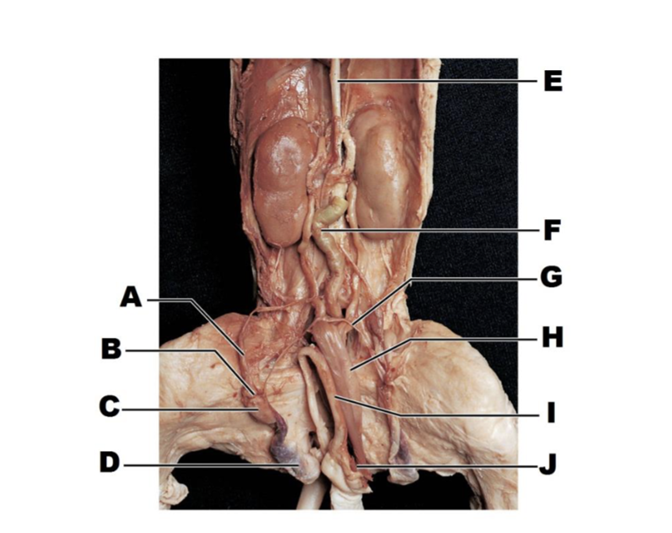
A
spermatic cord

B
epididymis (head)

C
testis

D
scrotal sac

E
inferior vena cava

F
colo

G
ductus deferens

H
urinary bladder

I
penis

J
umbilical vein
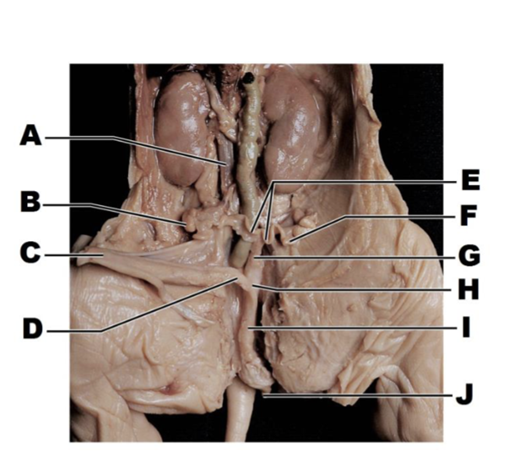
A
inferior vena cava

B
ovary

C
urinary bladder

D
urethra

E
uterine horns

F
uterine tube

G
body of uterus

H
vagina

I
urogenital sinus

J
genital papilla
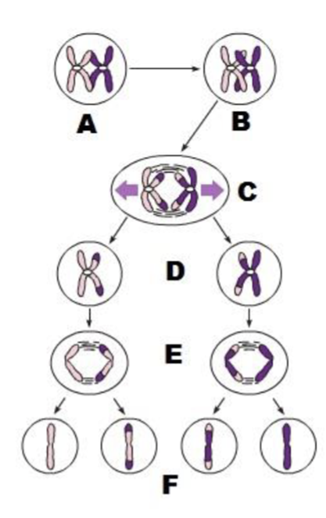
A
prophase I
tetrads form by synapis of homologous

B
crossover form

C
anaphase I
homologous separate

D
daughter cells of Meiosis I

E
anaphase II
sister chromatids separate

F
daughter cells of meosis II
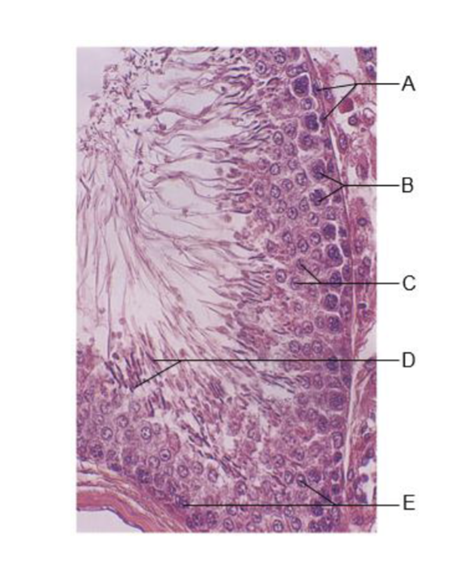
A
spermatogonia

B
primary spermatocytes

C
spermatids

D
immature sperm in lumen

E
sustentocytes (of testis)
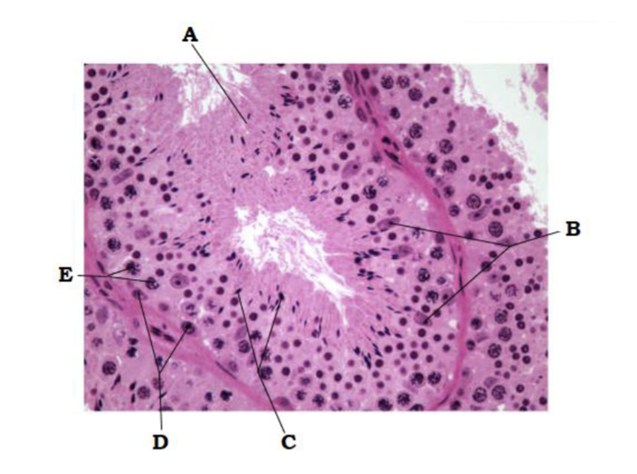
A
seminiferous tubule

B
sustentacular cell nuclei

C
spermatids

D
spermatogonia

E
primary spermatocytes
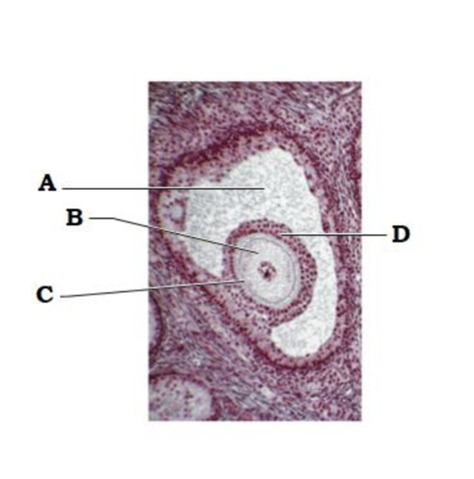
A
antrum

B
secondary oocyte

C
zona pellucida

D
corona radiata
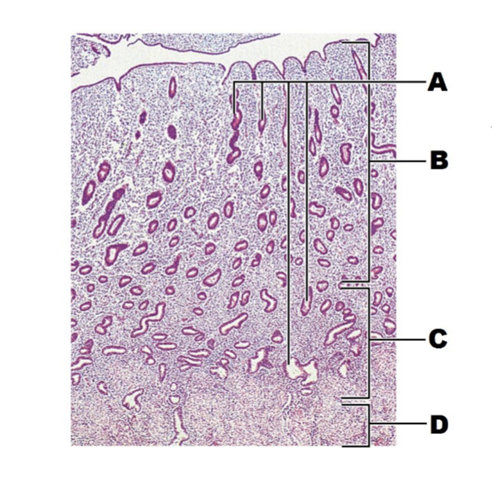
A
glands

B
functional layer

C
basal layer

D
myometrium

A
myometrium

B
endometrium

C
elaborated glands

A
medulla

B
corpus luteum

C
developing corpus luteum

D
corona radiata

E
ovulated secondary oocyte

F
zona pellucida

G
secondary oocyte

H
antrum

I
vesicular (antral) follicle

J
late secondary follicle

K
granulosa cells

L
secondary follicle

M
cortex

N
degenerating corpus luteum (corpus albicans)

O
primary follicles
describe the process of synapsis
the homologous chromosomes become closely aligned along their entire length
how does crossover introduce variability in the daughter cells?
where crossover occur, chromosome breakage occurs, and parts are exchanged. This results in chromosomes with different parental contributions
define homologous chromosome
chromosomes that carry genes for the same traits (one+ parental chromosome; the other = maternal chromosome
What are the hormones produced by the corpus luteum
Progesterone and estrogen
secondary spermatocyte
haploid, product of meiosis I
spermatogonium
primitive stem cell
sustentocyte
provides nutrients to developing sperm
spermatid
haploid, product of meiosis II
sperm
haploid, product of spermiogenesis
What uterine tissue undergoes dramatic changes during the menstrual cycle?
endometrium
primary oocyte
forming part of the primary follicle in the ovary
secondary oocyte
in the uterine tube before fertilization
in the vesicular follicle of the ovary
ovum
in the uterine tube shortly after fertilization
when during the female menstrual cycle would fertilization be unlikely? Explain why?
any time but the three-day interval (days 14-16) around ovulation (twenty-eight-day cycle is assumed)
amount of LH in the blood during menstruation IS LESS THAN
amount of LH in the blood at ovulation
amount of FSH in the blood on day 6 of the cycle GREATER THAN
amount of FSH in the blood on day 20 of the cycle
amount of estrogen in the blood during menstruation LESS THAN
amount of estrogen in the blood at ovulation
amount of progesterone in the blood on day 14 LESS THAN
amount of progesterone in the blood on day 23
amount of estrogen in the blood on day 10 GREATER THAN
amount of progesterone in the blood on dy 10
Menstruation
Days 1-5. Endometrium is sloughing off
primary follicle begins to grow
Proliferative
Days 6-14. Endometrium repaired, glands and blood vessels proliferate. Endometrium thickens
Follicular growth continues and vesicular follicle(s) produced. Estrogen secreted and peaks at day 14. Ovulation occurs on the 14th day.
Secretory
Days 15-28. Vascular supply increases and glands begin secretory activity.
Ruptured follicle is converted to a corpus luteum, which begins to produce progesterone (and some estrogen). Peaks at day 23 and then begins to decline.